Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) represents a transformative force in technology, reshaping how we live, work, and interact with the world. The advantages and disadvantages of AI are multifaceted, touching upon various aspects of society and industry. On one hand, AI offers unparalleled benefits such as enhanced efficiency, reduced human error, and innovative solutions across sectors. On the other hand, it poses challenges including ethical concerns, potential job displacement, and high implementation costs. This article aims to provide a comprehensive examination of these aspects, shedding light on the dual-edged nature of AI's impact on modern life and future prospects.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an expansive branch of computer science concerned with building smart machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. At its core, AI aims to create systems that can reason, learn, adapt, and execute tasks autonomously. This involves the integration of various disciplines, including computer science, cognitive science, and robotics, to mimic the decision-making processes and problem-solving capabilities of the human mind. The development of AI has led to the creation of algorithms and models that can process vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make informed decisions, thereby enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of various processes and applications.
The journey of AI has evolved from simple rule-based algorithms to complex neural networks and deep learning techniques, enabling machines to process and interpret complex data structures. This evolution underscores the dynamic nature of AI, which continuously expands its capabilities through machine learning and adaptive learning. The advantages and disadvantages of AI are evident in its wide-ranging applications, from automating routine tasks and analyzing big data to driving innovation in fields such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles. As AI technology advances, it promises to unlock new frontiers, raising both opportunities and challenges in its wake.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
The advantages of AI span across various dimensions, profoundly impacting the efficiency, innovation, and capabilities of numerous sectors. AI's ability to automate, enhance decision-making processes, and foster innovations presents a transformative potential for businesses, healthcare, and daily life. As we delve into the specific benefits, it's crucial to acknowledge the breadth of AI's influence, from mundane tasks to complex problem-solving scenarios, highlighting how it's becoming an indispensable tool in the modern world. Let's explore some of the key benefits that illustrate the positive impact of AI.
Reduction in Human Error
The reduction in human error stands out as a significant benefit of artificial intelligence, marking a pivotal shift in how tasks are executed across various fields. By leveraging AI, tasks that were traditionally prone to inaccuracies due to human oversight can now be performed with a higher degree of precision. AI systems are programmed to follow specific instructions and algorithms, which allows them to process information and make decisions based on factual data and predefined rules. This minimizes the chances of errors that can occur due to subjective judgment, fatigue, or other human limitations.
In sectors where the margin for error is minimal, such as in healthcare diagnostics, financial forecasting, and manufacturing, the role of AI becomes crucial. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze medical images with remarkable accuracy, reducing the likelihood of misdiagnoses. Similarly, in financial services, AI can execute complex calculations and predict market trends with a level of consistency far beyond human capabilities. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also boosts confidence in the outcomes produced, demonstrating the transformative potential of AI in reducing human error.
Zero Risks
The concept of zero risks is another compelling advantage of artificial intelligence, particularly in contexts where human safety and well-being are paramount. AI systems can be deployed in hazardous environments or situations where human involvement would pose significant risks, such as space exploration, deep-sea exploration, and handling of toxic substances. By utilizing robots or AI-driven machinery, tasks can be performed without jeopardizing human lives, ensuring that operations are conducted safely and effectively.
Moreover, the advantages and disadvantages of AI become apparent when considering scenarios like disaster response and diffusing explosives. In such high-stake situations, AI can provide real-time data analysis, make quick decisions, and execute actions with precision, all while operating in conditions that would be perilous or impossible for humans. This not only mitigates the risk to human life but also enhances the efficiency and outcome of such operations, showcasing the vital role AI plays in transforming high-risk tasks into safer, manageable endeavors.
24x7 Availability
ne of the standout advantages of artificial intelligence is its ability to remain operational 24x7, without the limitations faced by human workers such as the need for rest, breaks, or shifts. AI systems, unlike humans, do not suffer from fatigue, which allows them to perform continuous and consistent service around the clock. This aspect of AI is particularly beneficial in industries that require constant monitoring and operations, such as customer service, cybersecurity, and manufacturing.
The implementation of AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants in customer service is a prime example of AI's round-the-clock availability. These AI solutions can handle a vast number of queries simultaneously, at any time of the day, providing instant responses and support to users globally. Similarly, in the realm of cybersecurity, AI systems can continuously monitor networks for suspicious activities, providing an immediate response to potential threats. This 24x7 operational capability of AI not only enhances efficiency and productivity but also significantly improves user experience and security measures, illustrating the profound impact of AI's non-stop service in various sectors.
Digital Assistance
Digital assistance, facilitated by artificial intelligence, represents a significant leap in how individuals and businesses interact with technology, offering personalized and efficient support. AI-powered digital assistants, such as virtual assistants on smartphones or voice-activated devices in homes, have become integral in simplifying user interactions with technology. They process natural language, understand user requests, and provide relevant information or perform tasks ranging from setting reminders to controlling smart home devices, all through simple voice commands or text inputs.
In the corporate world, AI-driven digital assistants enhance productivity by automating routine tasks such as scheduling meetings, managing emails, and providing real-time information, allowing employees to focus on more complex and creative tasks. These assistants can adapt to individual preferences and learn from interactions, making them increasingly efficient over time. The deployment of digital assistants in customer service roles further exemplifies the advantages of AI, as they can handle numerous customer inquiries simultaneously, providing timely and personalized responses.
New Inventions
The role of artificial intelligence in fostering new inventions is one of its most transformative advantages, driving innovation across various domains. AI's ability to analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and generate insights has led to breakthroughs that were previously unimaginable. By leveraging complex algorithms and computational power, AI has become a crucial tool in research and development, facilitating the discovery of new materials, pharmaceuticals, and energy solutions.

In the realm of healthcare, AI algorithms are instrumental in decoding genetic sequences and understanding complex biological processes, paving the way for personalized medicine and novel treatments. Similarly, in environmental science, AI assists in climate modeling and predicting ecological changes, contributing to sustainable solutions and conservation efforts. The capacity of AI to process and analyze data far beyond human capabilities not only accelerates the pace of innovation but also opens up new avenues for exploration and discovery.
Unbiased Decisions
The capacity of artificial intelligence to make unbiased decisions stands out as a notable advantage, particularly in scenarios where human decision-making can be influenced by personal biases, emotions, or other subjective factors. AI systems operate based on algorithms and data analysis, making decisions that are rooted in logic, patterns, and statistical probabilities without the interference of personal prejudices or emotional responses.
This characteristic of AI is especially beneficial in areas like hiring processes, loan approvals, and legal judgments, where impartiality is crucial. By analyzing data and outcomes objectively, AI can help ensure fairness, equality, and efficiency in decision-making processes. For instance, in the recruitment sector, AI-driven tools can screen resumes and evaluate candidates based on skills and qualifications alone, reducing the likelihood of bias related to gender, ethnicity, or background.
Perform Repetitive Jobs
The ability of artificial intelligence to efficiently perform repetitive jobs is a substantial advantage, particularly in sectors where consistency and precision are crucial. AI excels in automating tasks that are monotonous for humans, such as data entry, transaction processing, and even intricate manufacturing operations. This automation not only accelerates processes but also allows human employees to engage in more complex and creative tasks, thereby boosting overall productivity and innovation.
In addition, AI's role in repetitive tasks goes beyond mere automation to include process optimization. For instance, in manufacturing, AI can manage assembly lines, ensuring smooth and efficient operations, and adapt parameters in real time for optimal performance. Similarly, in data management, AI can process and analyze large volumes of data, performing routine tasks with unmatched speed and accuracy. This capacity of AI to undertake and enhance repetitive jobs underscores its transformative impact, leading to higher quality results and improved efficiency across various industries.
Daily Applications
Artificial Intelligence has seamlessly integrated into daily life, enhancing convenience and efficiency through various applications. One of the most familiar instances is in personal smartphones, where AI powers virtual assistants like Siri and Google Assistant, helping users perform tasks such as setting reminders, making calls, and searching information through simple voice commands. Navigation apps like Google Maps use AI to analyze traffic data in real-time, offering the best routes and reducing travel times.

In the realm of entertainment, streaming services like Netflix and Spotify leverage AI to analyze viewing and listening habits, respectively, providing personalized recommendations that improve user experience. Similarly, smart home devices, including thermostats and lighting systems, use AI to learn user preferences, automating home environments for comfort and energy efficiency. These daily applications of AI not only make routine tasks more manageable but also enhance the quality of life by providing tailored services and information, showcasing the pervasive and beneficial impact of AI in everyday life.
AI in Risky Situations
Artificial Intelligence plays a crucial role in managing and mitigating risks in situations where human safety is at stake. In emergency response and disaster management, AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, including satellite imagery and sensors, to predict natural disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes with greater accuracy. This enables timely evacuations and more efficient resource allocation, potentially saving lives and reducing the impact of such events.
Moreover, AI is instrumental in hazardous work environments, such as nuclear reactors, deep-sea exploration, and space missions, where human exposure can be dangerous or even lethal. Robots and AI-controlled drones can perform tasks like monitoring radiation levels, conducting underwater repairs, or exploring other planets' surfaces, all without putting human lives at risk. These applications of AI in risky situations not only enhance safety but also extend the boundaries of human capabilities, allowing for exploration and work in environments that were previously inaccessible or too hazardous for direct human involvement.
Medical Applications
In the medical field, artificial intelligence has revolutionized diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care, offering profound benefits. AI algorithms are capable of analyzing complex medical data, such as imaging scans, at a speed and accuracy that surpass human capabilities. This has led to earlier and more precise diagnoses of diseases like cancer, where early detection can significantly impact treatment outcomes. Furthermore, AI systems assist in identifying patterns and correlations in vast datasets, contributing to the development of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual characteristics of each patient.
AI also enhances patient care through the implementation of virtual health assistants and chatbots, providing 24/7 support and basic healthcare guidance, thereby improving accessibility and efficiency in healthcare services. In surgical procedures, AI-driven robots assist surgeons, offering precision and control beyond human limitations, leading to less invasive procedures and faster recovery times. These medical applications of AI not only improve healthcare outcomes but also push the boundaries of medical science, enabling innovations that were once deemed impossible.
Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Despite the numerous advantages that artificial intelligence brings to the table, it's crucial to address the various disadvantages that accompany its widespread adoption. These drawbacks not only highlight the limitations of current AI technologies but also underscore the potential societal, ethical, and economic challenges that need careful consideration and management. From financial barriers to ethical concerns, understanding the disadvantages of AI is essential for developing balanced and responsible AI strategies. Let's delve into some of the key challenges posed by AI, which remind us of the technology's current limitations and the need for thoughtful integration into society.
High Costs
The high costs associated with artificial intelligence systems represent a significant disadvantage, impacting their accessibility and adoption across various sectors. Developing, deploying, and maintaining AI technologies require substantial investments in specialized hardware, sophisticated algorithms, and vast datasets for training purposes. Additionally, the expertise needed to create and manage AI systems is highly specialized, contributing to the overall expenses due to the high demand for skilled professionals in the field of AI and data science.
These financial barriers can deter small and medium-sized enterprises from leveraging AI solutions, potentially creating a divide between organizations that can afford to invest in AI and those that cannot. Moreover, the ongoing costs of updating AI models, ensuring data security, and complying with regulatory standards further escalate the financial burden. This aspect of AI emphasizes the need for cost-effective AI solutions and broader access to AI technologies to ensure that the benefits of artificial intelligence can be realized across all sectors of society, not just within well-resourced organizations.
No Creativity
One notable limitation of artificial intelligence is its inherent lack of creativity. AI systems operate based on algorithms and data patterns, which means they excel in tasks that involve analysis, pattern recognition, and logical reasoning. However, when it comes to generating original ideas, artistic expressions, or innovative solutions that require outside-the-box thinking, AI falls short. The creative process involves intuition, emotional depth, and subjective interpretation, qualities that are inherently human and difficult to replicate in machines.
This limitation becomes particularly evident in fields that highly value creativity, such as arts, literature, and certain aspects of research and development. While AI can assist in these areas by providing tools and enhancing certain processes, the spark of creativity—the ability to conceive something truly novel and impactful—remains a uniquely human trait. This distinction underlines the complementary nature of AI, serving as a tool that can augment human capabilities but not replace the creative essence that drives innovation and cultural expression.
Unemployment
The impact of artificial intelligence on employment is a significant concern, as the automation of tasks traditionally performed by humans could lead to job displacement in various sectors. AI-driven systems, capable of executing tasks ranging from routine administrative duties to complex analytical work, present a double-edged sword. On one hand, they enhance efficiency and productivity; on the other, they reduce the need for human labor in certain roles, potentially leading to unemployment.
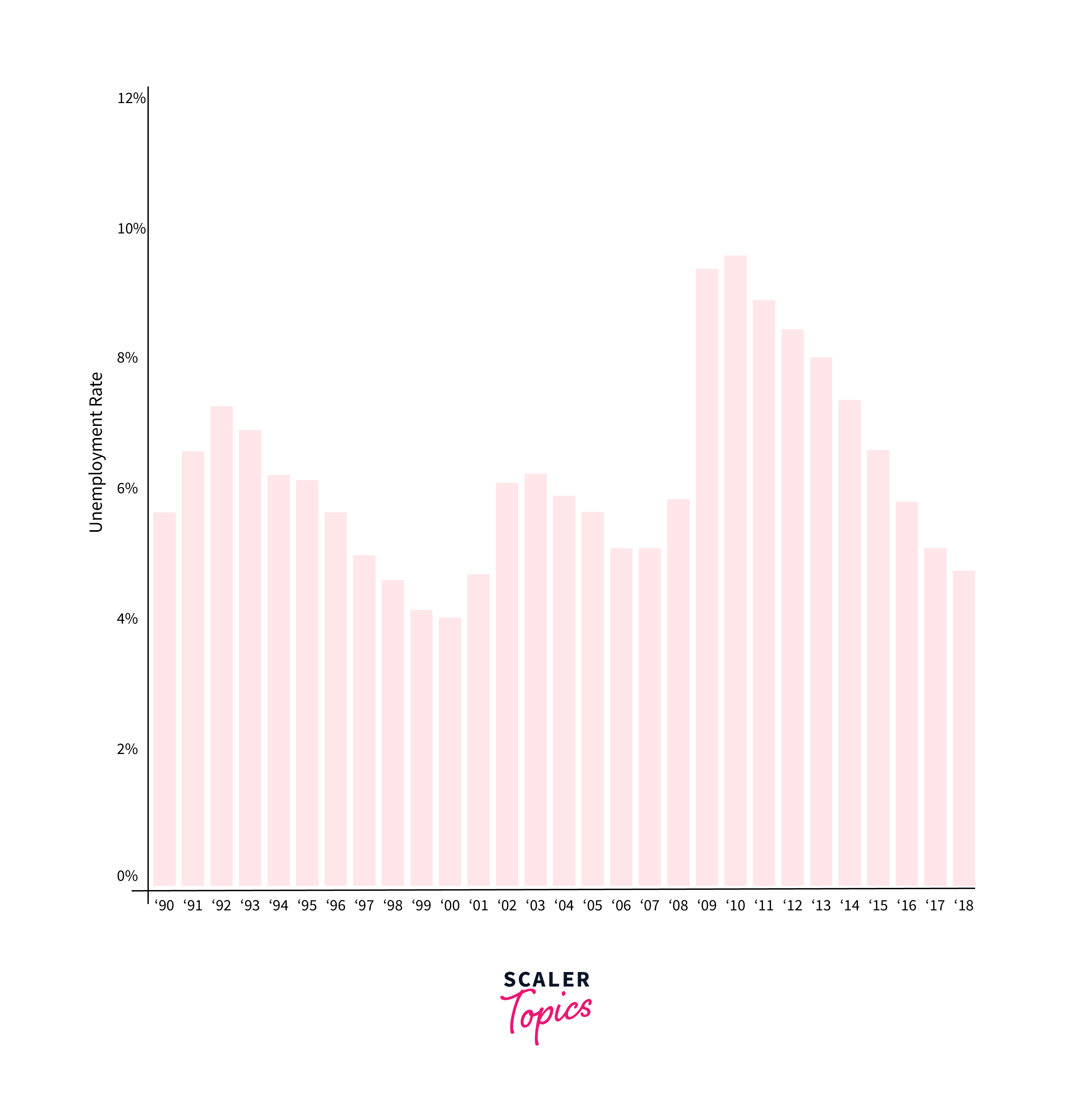 This shift in the job market necessitates a reevaluation of workforce skills and the development of strategies to mitigate the adverse effects of automation. While AI can create new job opportunities in tech-driven fields, the transition may be challenging for those whose skills are rendered obsolete by AI advancements. The situation calls for comprehensive policies and educational programs aimed at reskilling and upskilling workers, ensuring they can adapt to the evolving job landscape where human-AI collaboration becomes the norm.
This shift in the job market necessitates a reevaluation of workforce skills and the development of strategies to mitigate the adverse effects of automation. While AI can create new job opportunities in tech-driven fields, the transition may be challenging for those whose skills are rendered obsolete by AI advancements. The situation calls for comprehensive policies and educational programs aimed at reskilling and upskilling workers, ensuring they can adapt to the evolving job landscape where human-AI collaboration becomes the norm.
Make Humans Lazy
The convenience and efficiency brought by artificial intelligence can inadvertently lead to a dependency that may diminish human initiative and problem-solving skills. As AI systems take over more tasks, from personal assistants managing our schedules to smart home devices controlling our living environments, there's a growing concern that this reliance could make individuals less proactive or less inclined to engage in critical thinking. The ease with which information and services are delivered can reduce the necessity for individuals to develop or maintain certain skills, such as navigation skills in the age of GPS apps, or basic research skills with search engines providing instant answers.
This potential for increased dependency underscores the importance of maintaining a balance between leveraging AI for convenience and ensuring that individuals continue to develop and exercise their cognitive abilities. Encouraging education and activities that foster critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving can help counteract the tendency towards complacency, ensuring that AI serves as a tool for enhancement rather than a substitute for human engagement and effort.
No Ethics
Artificial intelligence, by its very nature, lacks the capacity for ethical reasoning and moral judgment, presenting a significant disadvantage in scenarios where ethical considerations are paramount. AI systems make decisions based on data and algorithms without the ability to discern right from wrong or consider the moral implications of their actions. This limitation raises concerns, especially in sensitive applications like autonomous vehicles, where decisions may have life-or-death consequences, or in data handling, where privacy and consent are crucial.
The challenge lies in embedding ethical principles into AI systems, a task that is inherently complex due to the subjective nature of ethics and the diversity of cultural and individual values. As AI becomes more integrated into daily life and critical decision-making processes, the development of ethical AI frameworks and guidelines becomes imperative. These measures are essential to ensure that AI systems operate in a manner that is not only efficient and effective but also aligned with human values and ethical standards.
Emotionless
The emotionless nature of artificial intelligence poses a significant disadvantage, particularly in fields where emotional intelligence and human empathy are crucial. AI systems, regardless of their sophistication in processing information and making decisions, lack the ability to understand or replicate the nuances of human emotions. This absence of emotional depth can lead to challenges in sectors like healthcare, customer service, and therapy, where empathy and emotional connection play a key role in the effectiveness of the service provided.
While AI can mimic certain aspects of emotional intelligence, such as recognizing facial expressions or interpreting speech patterns, the genuine understanding and empathy that comes from shared human experiences are beyond its capabilities.
No Improvement
A notable limitation of artificial intelligence is its inability to self-improve beyond the parameters set by its initial programming and training data. AI systems rely on algorithms and data to learn and make decisions, but they do not possess the intrinsic ability to reflect on past actions, learn from mistakes in a human-like manner, or innovate beyond their programming. This means that AI can continue making the same errors unless humans intervene to adjust the algorithms or provide new data for training.
This static nature of AI underscores the importance of continuous human oversight and periodic updates to ensure that AI systems remain effective and relevant. It also highlights the necessity for AI to be designed with adaptability in mind, allowing for updates and improvements based on new information and evolving requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AI in Different Sectors and Industries
Here's a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of AI in various sectors and industries:
| Sector/Industry | Advantages of AI | Disadvantages of AI |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Improved diagnostics, personalized treatment, automation in routine tasks | High costs, lack of empathy in patient care |
| Automotive | Enhanced safety with autonomous vehicles, efficient manufacturing processes | Job displacement in manufacturing, ethical concerns in decision-making |
| Finance | Fraud detection, personalized financial advice, automated trading | Risk of algorithmic biases, high initial implementation costs |
| Retail | Personalized shopping experiences, inventory management, customer service automation | Reduced human interaction, potential job losses in customer service |
| Education | Personalized learning, automation in grading and administrative tasks | Lack of emotional support, potential for widening educational inequalities |
| Manufacturing | Increased efficiency, predictive maintenance, optimized supply chains | Job displacement, high costs of AI integration |
| Entertainment | Content personalization, enhanced user experiences, creative content generation | Reduced creative jobs, over-reliance on algorithms for content recommendation |
| Security | Enhanced surveillance, threat detection, cybersecurity measures | Privacy concerns, ethical issues in surveillance |
| Environmental | Climate modeling, wildlife protection, efficient energy use | Dependence on large datasets, high operational costs |
FAQs
Q. What are the benefits of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
A. AI enhances efficiency, reduces human error, and enables data-driven decision-making, leading to innovations across various sectors.
Q. What are the disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
A. AI can lead to job displacement, lacks emotional understanding, and involves high initial costs and ethical concerns.
Q. How can businesses benefit from adopting AI?
A. Businesses can improve operational efficiency, personalize customer experiences, and gain insights from data analytics through AI.
Q. What are some AI applications in everyday life?
A. AI applications include virtual assistants, navigation apps, personalized content recommendations, and smart home devices.
Q. What are the advantages of AI in education?
A. AI offers personalized learning experiences, automates administrative tasks, and provides accessible educational tools.
Q. How does Artificial Intelligence reduce costs?
A. AI reduces costs by automating routine tasks, optimizing processes, and minimizing errors, leading to more efficient operations.
Q. Can AI replace human intelligence and creativity?
A. While AI can augment certain tasks, it cannot replicate the nuanced creativity and emotional intelligence inherent to humans.
Conclusion
- Artificial Intelligence significantly enhances efficiency and innovation across various sectors, offering solutions that were previously unattainable.
- Despite its potential, AI presents challenges such as ethical dilemmas, potential job displacement, and the need for substantial investment.
- The balance between leveraging AI's benefits and mitigating its disadvantages is crucial for sustainable and ethical AI integration.
- Ongoing advancements in AI technology necessitate continuous evaluation of its impact on society, emphasizing the importance of adaptability and ethical considerations.
- The future of AI promises further transformation of industries and daily life, underscoring the importance of human oversight and interdisciplinary collaboration to harness its full potential responsibly.
