Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a key component of modern IT infrastructure, There are many pros and cons of cloud computing. This thorough examination explores the pros and cons of cloud computing environment and reveals benefits like scalability, cost-effectiveness, and easy collaboration. It also tackles urgent issues like technological complexity, reliance on internet connectivity, and security flaws. Come along as we explore the benefits and disadvantages of cloud computing as we delve deeply into this complex world.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
-
Back-up and restore data:
The major advantage of Cloud Computing are cloud services. Cloud Services with their automated and effective solutions, are revolutionising data backup and recovery processes. Rather than depending on conventional backup techniques like tangible storage units or on-site servers, cloud-based backup systems use the internet and distant servers to safely store data off-site. -
Improved collaboration:
Regardless of a team member's location, cloud-based collaboration tools facilitate easy communication and teamwork. Because they enable smooth communication and collaboration across geographic boundaries, cloud-based collaboration tools have completely changed the way teams operate and considered a major advantage of Cloud Computing for an organization looking for a global scale. Teams can work together efficiently from any location in the world by utilizing these cloud computing-powered tools, which provide instantaneous access to shared documents, messaging apps, project management tools, and online meeting rooms. -
Excellent accessibility:
Remote access to cloud services eliminates traditional barriers to productivity associated with geographic constraints and office-based work environments. Employees no longer need to commute to a central office to access critical resources or collaborate with colleagues. Instead, they can seamlessly transition between workspaces and environments while maintaining uninterrupted access to essential tools and data.
- Low maintenance cost:
Low maintenance costs are a significant advantage of cloud computing solutions, offering businesses the opportunity to streamline their IT operations and allocate resources more efficiently. Traditional IT infrastructure often requires substantial upfront investments in hardware, software, and maintenance, along with ongoing expenses for upgrades, repairs, and system administration. In contrast, cloud computing shifts the burden of infrastructure management and maintenance to third-party cloud service providers, resulting in significant cost savings and operational efficiencies.

-
Mobility:
One major benefit of cloud services is mobility, which is transforming how people work, collaborate, and access information in today's world where mobile devices are used more and more. With cloud computing, users can work remotely and have more flexibility in their work schedules by having access to apps, data, and resources from any internet-connected device. -
Services in the pay-per-use model:
Unlike traditional on-premises infrastructure, which requires organisations to make significant upfront investments in hardware and software licences, One of the primary advantages of the pay-per-use model is its scalability and elasticity, enabling businesses to scale their resources up or down dynamically in response to changing demand or workload patterns. With cloud services, organizations can provision additional computing power, storage capacity, or network bandwidth instantly to accommodate sudden spikes in traffic, seasonal fluctuations, or business growth without incurring unnecessary costs or over-provisioning resources. -
Unlimited storage capacity:
Unlimited storage capacity enables businesses to consolidate their data storage infrastructure and centralize their data repositories in the cloud, simplifying data management and reducing operational overhead. Instead of managing multiple on-premises storage systems scattered across different locations, organizations can leverage cloud-based storage solutions to store all their data in a single, centralized repository, streamlining data access, backup, and disaster recovery processes. -
Data security:
One of the key aspects of data security in the cloud is encryption, which involves encoding data using cryptographic algorithms to render it unreadable to unauthorized users. Cloud providers leverage advanced encryption techniques, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), to encrypt data before storing it in the cloud, as well as during transmission over the internet. Additionally, cloud providers typically offer client-side encryption options, allowing businesses to encrypt data on their premises before uploading it to the cloud, further enhancing data security and control.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
-
Internet Connectivity:
The primary disadvantage of cloud computing is its reliance on dependable and steady internet connectivity. Because cloud services are internet-based, companies need a reliable, fast internet connection to access cloud resources, apps, and data that are kept on distant servers. Any loss of internet connectivity can cause latency problems, service interruptions, and performance degradation, which can impede business operations and productivity. -
Vendor lock-in:
One of the key concerns associated with vendor lock-in in cloud computing is the adoption of proprietary technologies and standards by cloud providers. Cloud vendors often develop their own proprietary software, tools, and APIs to differentiate their services and lock customers into their ecosystems. As a result, businesses may find it difficult to integrate their existing infrastructure, applications, and data with alternative cloud platforms or migrate between different cloud environments without facing compatibility issues and interoperability challenges. This could be a concerning disadvantage of cloud computing if an organization is trying to scale application and make it multi cloud.
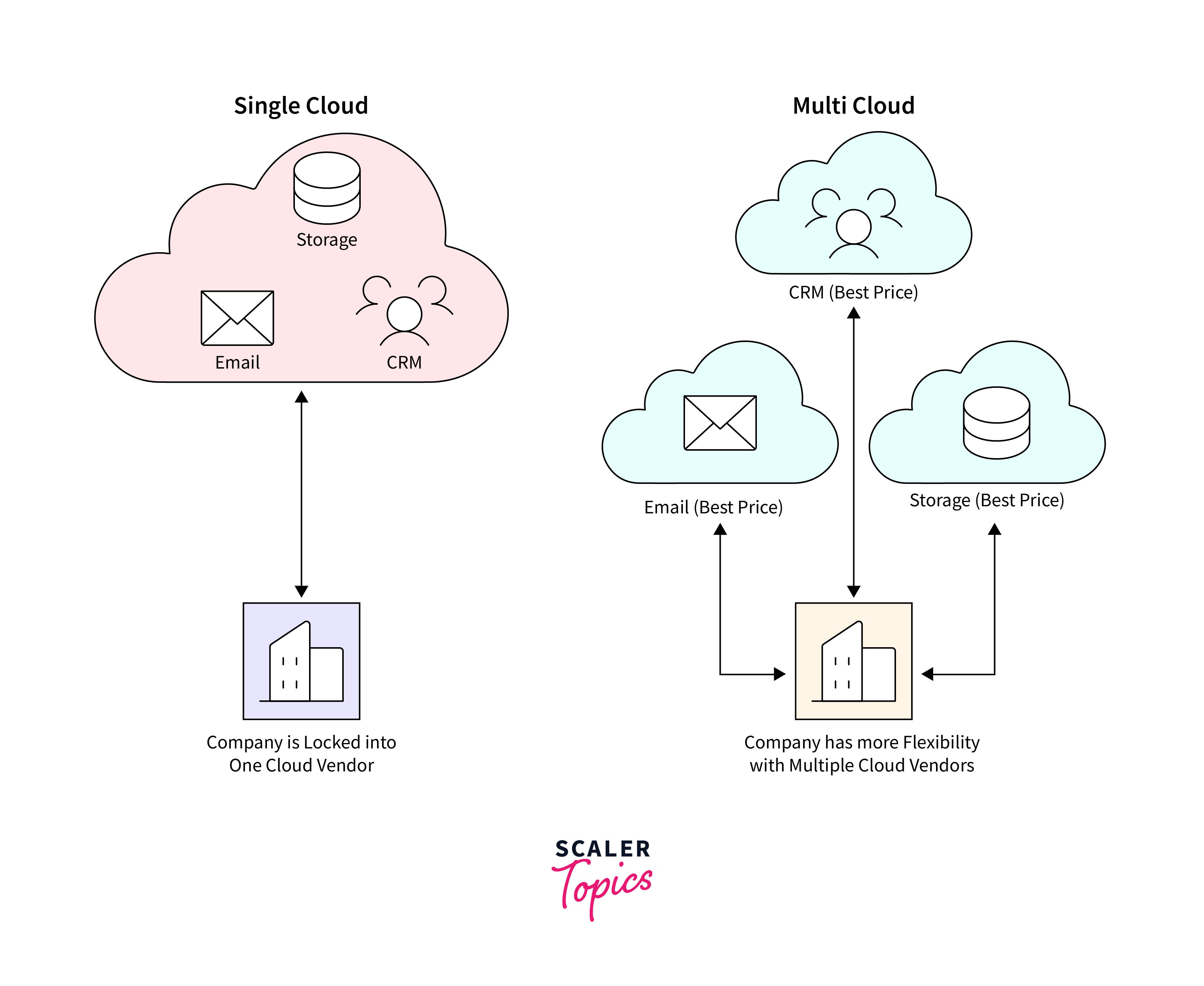
-
Limited Control:
Limited control is a significant concern for businesses when transitioning data and applications to the cloud, as it entails relinquishing a certain level of autonomy and oversight over the underlying infrastructure and management processes to the cloud service provider. While cloud computing offers scalability, agility, and cost-effectiveness, businesses may encounter challenges related to visibility, governance, and customization, which can impact security, compliance, and operational efficiency. -
Security:
One notable disadvantage of cloud computing is the potential for data breaches and unauthorized access. Despite the security measures put in place by cloud providers, data breaches can still occur due to various factors such as misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, or human errors. Hackers may exploit weaknesses in cloud infrastructure or gain unauthorized access to cloud accounts, compromising the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data. -
Performance Can Vary:
The performance of cloud services is subject to variability, influenced by several factors that can impact the speed, reliability, and responsiveness of applications and data hosted in the cloud. One of the primary factors affecting performance is network latency, which refers to the delay or lag in data transmission between client devices and cloud servers. High latency can occur due to network congestion, long distances between users and data centres, or suboptimal routing, resulting in delays in data transfer and communication. -
Technical Issues:
Technical issues are an inevitable aspect of cloud computing environments, stemming from various factors such as software bugs, hardware failures, network outages, and system maintenance activities. These issues can disrupt cloud services, compromise data integrity, and impact business continuity, posing significant challenges for organizations relying on cloud-based infrastructure and applications. -
Lower Bandwidth:
Lower bandwidth can pose significant challenges for businesses relying on cloud services, impacting data transfer speeds, application performance, and user experience. Despite advancements in internet connectivity and network infrastructure, bandwidth limitations can hinder the seamless transmission of data and the efficient delivery of cloud-based services, particularly for bandwidth-intensive workloads or real-time applications. -
Lacks of Support:
One of the primary disadvantage of cloud computing is lack of support, limited availability of support channels and options provided by cloud providers. While many cloud vendors offer self-service support portals, forums, and community resources for troubleshooting common issues and accessing documentation, businesses may require direct assistance from knowledgeable support personnel to address specific technical challenges or resolve critical issues affecting their cloud environments.
Conclusion
- There are numerous advantages of cloud computing, such as scalability, cost-efficiency, and accessibility, but it also presents challenges related to security, reliability, and control.
- Businesses must carefully evaluate the benefits and disadvantages of cloud computing before adopting cloud-based solutions to ensure alignment with their strategic objectives and operational requirements.
- Despite the security measures implemented by cloud providers, data breaches, compliance issues, and security incidents remain significant concerns for businesses storing sensitive information in the cloud.
- Variability in performance, network latency, and technical issues can impact the reliability and responsiveness of cloud services, affecting user experience and business operations.
- Vendor lock-in, limited control, and lack of support options can hinder businesses' ability to manage and customize their cloud environments effectively, leading to dependency on specific cloud providers and potential challenges in troubleshooting and resolving technical issues.
- There are many pros and cons of cloud computing but the right way to evaluate is to look, what problems you are trying to solve and select the solution which suits the need.
