Artificial Intelligence Ethics
Overview
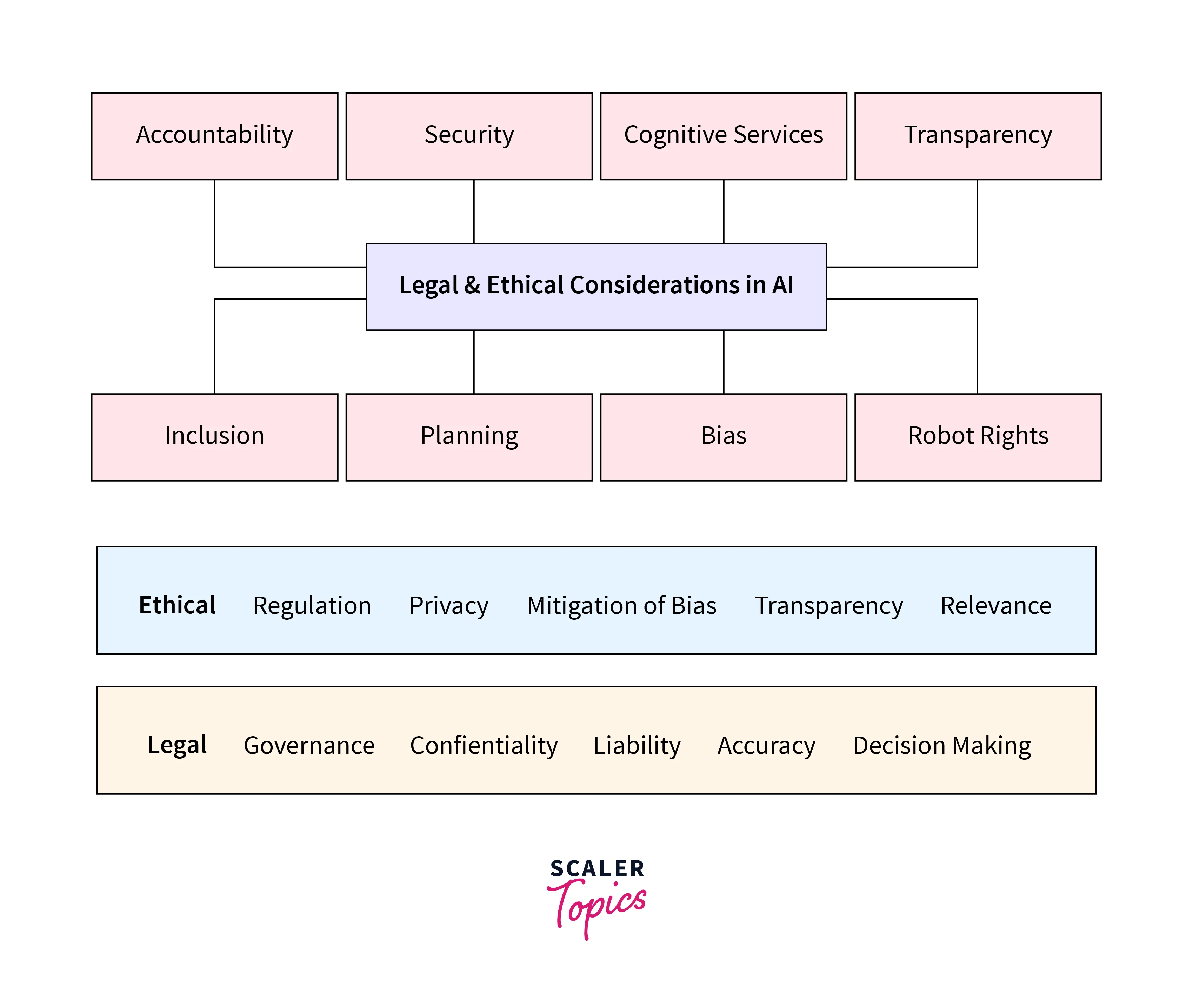
Artificial Intelligence Ethics (AI Ethics) focuses on the ethical considerations surrounding developing, deploying, and using AI systems. It addresses fairness, transparency, accountability, privacy, and bias concerns. As AI becomes increasingly prevalent in society, it is crucial to establish guidelines and principles that ensure responsible AI practices. The ethical dimensions of AI have gained significant attention, prompting the need for comprehensive understanding and the establishment of frameworks to govern the ethical implications of AI technologies.
Artificial Intelligence Ethics encompasses the ethical considerations and principles that govern the design, development, deployment, and use of AI systems. With the rapid advancement and increasing deployment of AI technologies across various industries, concerns about the ethical implications have come to the forefront. It is essential to ensure that AI systems are developed and utilized in a responsible and ethical manner, taking into account their potential impact on society, individuals, and fundamental human values.
AI Ethics addresses a wide range of concerns, including fairness, transparency, accountability, privacy, bias, and the potential socioeconomic impact of AI. These ethical considerations aim to address the challenges and risks associated with the use of AI while also maximizing the benefits and potential positive impact of this transformative technology.
What is Artificial Intelligence Ethics?
Artificial Intelligence Ethics refers to the ethical considerations and principles that guide the development, deployment, and use of AI systems. It involves addressing the societal, economic, and moral implications of AI technologies to ensure responsible and ethical practices.
AI Ethics encompasses a wide range of concerns that arise due to the unique characteristics and capabilities of AI systems. These concerns include:
-
Fairness:
Fairness in AI systems aims to prevent bias and discrimination. AI algorithms should be designed and trained to provide equal treatment and opportunities to individuals, regardless of their race, gender, age, or socioeconomic background. Fairness ensures that AI does not perpetuate or amplify existing societal biases.
-
Transparency:
Transparency refers to the openness and explainability of AI algorithms and decision-making processes. It is essential for users and stakeholders to understand how AI systems arrive at their conclusions or recommendations. Transparent AI enables accountability, facilitates trust, and allows for the identification and mitigation of potential biases or errors.
-
Accountability:
Accountability involves determining responsibility for the actions and decisions made by AI systems. When AI systems make mistakes or cause harm, it is important to identify who is responsible and ensure appropriate mechanisms for recourse and redress. Holding individuals, organizations, and developers accountable for the consequences of AI technologies helps establish trust and encourages responsible behavior.
-
Privacy:
The use of AI often involves collecting and analyzing large amounts of personal data. AI Ethics emphasizes the need to protect individual privacy rights and ensure the secure handling of sensitive information. Safeguarding privacy helps build trust between users and AI systems and prevents unauthorized access or misuse of personal data.
-
Bias and Discrimination:
AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in the data they are trained on. AI Ethics seeks to minimize and eliminate biases to ensure fair and equitable outcomes. It involves careful data selection, preprocessing, and algorithm design to mitigate bias and discrimination, especially in high-stakes applications such as hiring, lending, and law enforcement.
-
Human Agency and Autonomy:
AI Ethics also considers the impact of AI on human agency and autonomy. It explores how AI systems can enhance human decision-making rather than replace or undermine it. Balancing the capabilities of AI with human values, judgment, and control is crucial to preserving human dignity and decision-making power.
Establishing Principles for Artificial Intelligence Ethics
Establishing principles for Artificial Intelligence Ethics is crucial to guide the responsible development and deployment of AI systems. These principles provide a framework for addressing ethical considerations and ensuring that AI technologies align with societal values and respect fundamental rights.
Respect for Persons
Respect for Persons is a foundational principle in Artificial Intelligence Ethics. It emphasizes the inherent dignity, autonomy, and rights of individuals affected by AI systems. This principle recognizes that AI should be designed and used in a way that respects and upholds the moral and legal rights of all individuals, regardless of their race, gender, age, or socioeconomic status.
Respect for Persons entails several important considerations in AI Ethics. First, it emphasizes the need for informed consent when collecting and using personal data in AI systems. Users should have the right to know how their data is being collected, stored, and utilized, and they should have the ability to provide consent or withdraw consent when necessary.
Additionally, Respect for Persons requires that AI systems are designed to ensure user privacy and data protection. It involves implementing robust security measures to safeguard personal information from unauthorized access or misuse. Respecting the privacy of individuals not only maintains trust but also prevents potential harm or discrimination resulting from the mishandling of sensitive data.
Beneficence
Beneficence is another important principle in AI Ethics that focuses on maximizing the benefits and minimizing the potential harm caused by AI systems. It emphasizes the ethical obligation to use AI technology for the greater good, ensuring that it contributes positively to individuals, communities, and society as a whole.
Under the principle of Beneficence, AI developers and users are encouraged to consider the potential impacts of AI systems on various stakeholders. This involves conducting comprehensive risk assessments, anticipating possible unintended consequences, and taking proactive measures to mitigate harm.
AI systems should be designed to prioritize the well-being, safety, and quality of life of individuals. For example, in healthcare applications, AI systems should aim to enhance medical diagnosis and treatment, improving patient outcomes and reducing errors. In transportation, AI can contribute to safer roads and more efficient traffic management. By considering the potential benefits and carefully managing risks, the principle of Beneficence ensures that AI is used to enhance human lives and promote societal progress.
Justice
The principle of Justice in AI Ethics concerns the fair distribution of benefits, burdens, and opportunities associated with AI systems. It aims to address disparities, prevent discrimination, and promote equitable access to the advantages offered by AI technology.
-
Equal Share:
This aspect of justice advocates for equal distribution of benefits and burdens among individuals and communities. It calls for ensuring that AI systems do not disproportionately advantage or disadvantage specific groups based on factors like race, gender, or socioeconomic status. Equal share promotes fairness and social equity in AI applications.
-
Individual Need:
Justice based on individual needs suggests that AI systems should prioritize and allocate resources and services based on the specific needs of individuals. This ensures that those who require assistance or support the most receive adequate attention and resources from AI technologies.
-
Individual Effort:
Justice based on individual effort emphasizes that individuals should reap the rewards or benefits of their own efforts and contributions. In the context of AI, this principle suggests that AI systems should recognize and reward individual achievements, skills, and hard work, rather than solely relying on predetermined biases or systemic advantages.
-
Societal Contribution:
Justice based on societal contribution highlights the importance of recognizing and acknowledging the contributions individuals make to society. AI systems should consider the broader impact of an individual's actions or contributions, taking into account their positive contributions to the well-being of communities and society as a whole.
Primary Concerns of AI Today
Artificial Intelligence has brought forth transformative advancements, but it also raises significant concerns that demand attention in the realm of AI Ethics. The following subsections delve into the primary concerns associated with AI today:
Technological Singularity
Technological Singularity is a concept that raises profound ethical concerns within the field of Artificial Intelligence. It refers to a hypothetical point in the future where AI systems surpass human intelligence, leading to a potential shift in the dynamics of society, economy, and even human existence itself. The concern surrounding technological singularity stems from the uncertainty and unpredictability of AI systems once they reach a level of superintelligence.
Ethical considerations regarding technological singularity revolve around the need for AI to align with human values and ethical principles. As AI progresses toward superintelligence, there is a fear that it may exhibit behaviors or intentions that are beyond human comprehension or control. This raises questions about the ethical implications of creating AI systems that may have objectives or motivations that conflict with human values, potentially leading to unintended consequences or even existential risks.
To address these concerns, researchers and policymakers in the field of AI Ethics emphasize the importance of value alignment and the development of AI systems that prioritize human well-being and align with societal values. The concept of value alignment refers to the effort to ensure that AI systems understand and adhere to ethical principles and human preferences. This includes mechanisms for ensuring that AI systems operate within specified boundaries, respect human autonomy, and do not act in ways that are detrimental to humanity.
AI Impact on Jobs
The impact of Artificial Intelligence on jobs is a significant concern in today's rapidly evolving technological landscape. As AI technologies continue to advance, there is growing apprehension about the potential displacement of human labor across various industries. While AI has the potential to enhance productivity, efficiency, and innovation, it also raises ethical considerations regarding the impact on employment and the workforce.
One of the key concerns is the potential loss of jobs due to automation. AI systems can perform tasks that were traditionally carried out by humans, leading to fears of widespread job displacement. This raises questions about the ethical responsibility of organizations and policymakers to address the potential societal impact of job losses and to ensure a just transition for affected individuals.
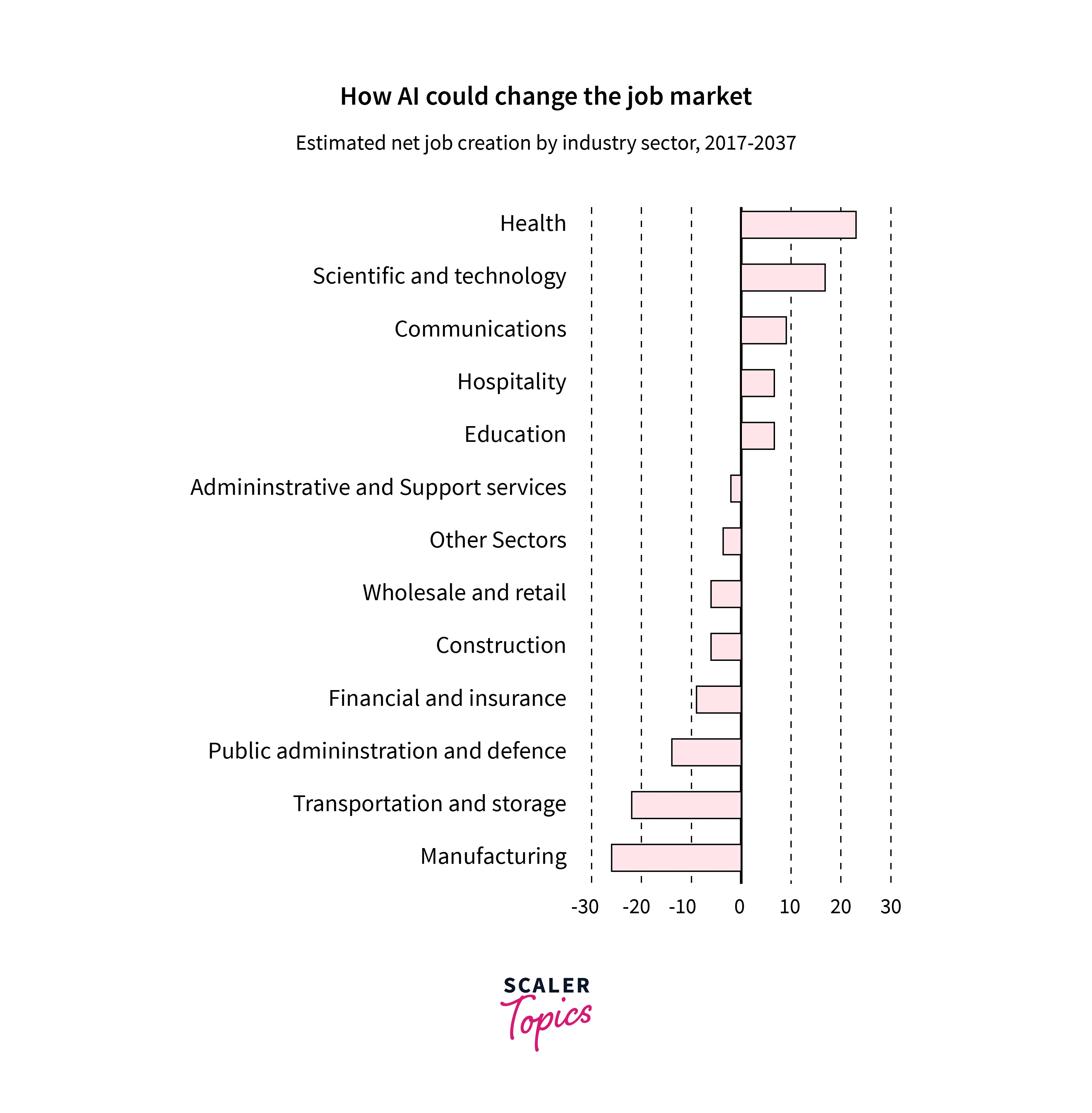
Ethical considerations surrounding AI's impact on jobs involve several aspects. First and foremost is the need to implement comprehensive reskilling and upskilling programs to equip individuals with the skills needed to adapt to the changing job market. This requires collaboration between governments, educational institutions, and businesses to provide accessible and inclusive training opportunities that enable workers to acquire new skills that are in demand.
Privacy
Privacy is a paramount concern in the context of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and raises significant ethical considerations. As AI systems rely on vast amounts of data for training and decision-making, the protection of individual's privacy rights becomes crucial to maintain trust and ensure ethical practices.
AI systems often process sensitive personal information, including but not limited to personal identifiers, biometric data, and behavioral patterns. The collection, storage, and utilization of such data raise ethical questions about informed consent, data ownership, and the potential for unauthorized access or misuse.
One key ethical consideration is the implementation of robust data protection measures. This includes adhering to privacy frameworks and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), that provide guidelines for the responsible handling of personal data. Organizations developing AI systems must ensure that data is collected and stored securely, with appropriate safeguards in place to prevent breaches or unauthorized access.
To promote privacy in AI, organizations should adopt a privacy-by-design approach, embedding privacy considerations into the entire AI development lifecycle. This involves conducting privacy impact assessments and anonymizing or de-identifying data where possible.
Bias and Discrimination
Addressing bias and discrimination in Artificial Intelligence systems is a critical ethical concern. AI systems learn from data, and if the training data is biased or reflects societal prejudices, the resulting algorithms can perpetuate and amplify such biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
Bias in AI can manifest in various ways. It may occur due to biased data collection, where the training datasets are not representative of the diverse population or contain inherent biases.
To mitigate bias and discrimination, AI Ethics emphasizes the need for fairness and inclusivity. One approach involves promoting diversity and inclusivity in AI development teams. By having diverse perspectives and expertise, teams can identify and mitigate biases more effectively, ensuring a broader understanding of the potential societal impacts of AI systems.
Another crucial step is to address bias throughout the AI development lifecycle. This includes careful data collection to ensure representativeness and avoid skewed datasets. Data preprocessing techniques can be employed to identify and mitigate biases in the training data.
Accountability
Ensuring accountability is a vital aspect of Artificial Intelligence Ethics. As AI systems become more autonomous and make decisions that impact individuals and society, it is crucial to establish mechanisms that hold both the developers and deployers of AI systems accountable for their actions.
Accountability in AI Ethics encompasses various dimensions. Firstly, developers and organizations must take responsibility for the design, development, and deployment of AI systems. They should adhere to ethical guidelines and standards, ensuring that AI systems operate within legal and ethical boundaries. This includes considering the potential societal impact, addressing biases, and mitigating risks associated with AI technologies.
Transparency plays a significant role in fostering accountability. Organizations should provide clear information about the capabilities, limitations, and potential biases of AI systems.
In cases where AI systems make decisions with significant consequences, such as in healthcare, criminal justice, or financial sectors, mechanisms for contestability and redress should be in place. This means individuals affected by AI decisions should have the right to challenge the outcomes, request explanations, and seek remedies in case of errors or unfair treatment. It is important to ensure that individuals have recourse when they believe AI systems have acted inappropriately or violated their rights.
How to Establish Artificial Intelligence Ethics
To establish Artificial Intelligence Ethics, it is essential to implement robust frameworks and mechanisms that promote responsible and ethical practices in the development and deployment of AI systems. This subsection explores two key aspects: governance and explainability.
Governance
Governance plays a crucial role in establishing AI Ethics. Effective governance frameworks provide guidelines, regulations, and oversight to ensure that AI systems operate within ethical boundaries and align with societal values. The following are some key considerations for governance:
-
Ethical Guidelines and Principles:
Developing comprehensive ethical guidelines and principles specific to AI is crucial. These guidelines should outline the ethical expectations, values, and principles that AI developers and deployers should adhere to. They should cover areas such as fairness, transparency, privacy, accountability, and non-discrimination.
-
Regulatory Frameworks:
Governments and regulatory bodies should establish clear and enforceable regulations to govern the development, deployment, and use of AI systems. These regulations should address issues such as data protection, algorithmic transparency, bias mitigation, and the ethical implications of AI technologies in various sectors.
-
Collaboration and Multistakeholder Engagement:
Establishing collaboration between governments, industry leaders, researchers, civil society organizations, and other stakeholders is vital for effective AI governance. Multistakeholder engagement ensures diverse perspectives are considered and decisions are made collectively to reflect societal values and interests.
-
Oversight and Auditing:
Implementing mechanisms for oversight and auditing of AI systems is essential to monitor compliance with ethical guidelines and regulations. Independent auditing bodies can evaluate AI algorithms, assess their fairness and transparency, and ensure that they operate within legal and ethical boundaries.
-
International Cooperation:
Given the global nature of AI and its potential impact, international cooperation and collaboration are crucial. Countries should work together to establish common ethical standards, share best practices, and address cross-border challenges associated with AI technologies.
Explainability
Explainability refers to the ability to understand and explain the decisions and behaviors of AI systems. Explainability is important for ensuring transparency, accountability, and trust in AI technologies. The following factors contribute to achieving explainability:
-
Interpretability of AI Algorithms:
AI algorithms should be designed to be interpretable, allowing humans to understand how they arrive at their decisions. This can involve using simpler and more transparent models or developing techniques that provide insights into the decision-making process of complex models.
-
Explanations for AI Decisions:
AI systems should be able to provide meaningful explanations for their decisions. Users and stakeholders should have access to information about the factors considered, the data used, and any potential biases or limitations in the decision-making process.
-
Algorithmic Auditing:
Conducting audits of AI algorithms to evaluate their fairness, bias, and ethical implications is essential. These audits can help identify potential issues and biases, providing an opportunity to rectify and improve the algorithms.
-
User Empowerment:
Empowering users with the ability to interact with and influence AI systems can contribute to explainability. Providing users with control over their data, decision-making preferences, and the ability to request explanations for AI decisions fosters a sense of trust and allows users to verify the fairness and reliability of AI systems.
Ethical AI organizations
Several organizations are actively working towards advancing Artificial Intelligence Ethics and promoting responsible AI practices. Here are brief descriptions of five notable organizations in this field:
-
AlgorithmWatch:
It is an independent research and advocacy organization that focuses on algorithmic accountability and transparency. They investigate and analyze the societal impact of AI algorithms, advocate for algorithmic transparency, and promote ethical practices in algorithmic decision-making. AlgorithmWatch conducts research, publishes reports, and engages in public policy discussions to address the ethical implications of AI technologies.

-
AI Now Institute:
The AI Now Institute is an interdisciplinary research institute based at New York University. Their mission is to examine the social implications of AI and advocate for the responsible and ethical development and deployment of AI systems. They conduct research, publish reports, and provide policy recommendations to address issues such as bias, accountability, labor impacts, and the social implications of AI technologies.
-
DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency):
DARPA is an agency of the United States Department of Defense that focuses on technological advancements and innovation. While not solely dedicated to AI Ethics, DARPA invests in research and development to ensure the ethical and responsible use of AI technologies in defense applications. They prioritize transparency, accountability, and the development of AI systems that align with ethical and legal standards.
-
CHAI (Center for Human-Compatible AI):
It is based at the University of California, Berkeley, and aims to develop AI systems aligned with human values and goals. They research AI safety, value alignment, and human-AI collaboration. CHAI focuses on addressing potential risks and ethical concerns associated with AI technologies and aims to ensure that AI systems are beneficial and compatible with human well-being.
-
NASCAI (National Artificial Intelligence Safety and Certification Agency):
It is an organization dedicated to ensuring the safety, reliability, and ethical use of AI systems. They focus on certifying AI systems to meet rigorous safety and ethical standards. NASCAI establishes guidelines and certification processes to assess the performance, robustness, and adherence to ethical principles of AI technologies. They aim to build trust and confidence in AI systems by ensuring their responsible development and deployment.
Conclusion
- Artificial Intelligence Ethics is a critical field that addresses the ethical considerations and implications of AI technologies in various domains.
- Establishing principles for AI Ethics, such as respect for persons, beneficence, and justice, ensures that AI systems operate in a fair, transparent, and responsible manner.
- The primary concerns of AI today include technological singularity, AI's impact on jobs, privacy issues, bias and discrimination in AI systems, and the need for accountability.
- To establish AI Ethics, governance frameworks should be implemented, encompassing ethical guidelines, regulatory frameworks, multistakeholder engagement, oversight mechanisms, and international cooperation.
- Explainability is crucial for AI Ethics, as it promotes transparency, accountability, and user trust in AI systems by enabling individuals to understand and assess AI decisions.
- Several organizations, such as AlgorithmWatch, AI Now Institute, DARPA, CHAI, and NASCAI, are actively working towards advancing AI Ethics through research, advocacy, policy recommendations, and certification processes.
