Applications of Information Technology
Information Technology (IT) applications encompass diverse fields, from business and healthcare to education and entertainment. IT facilitates efficient data management, communication, automation, and innovation, enhancing productivity and connectivity in various industries globally.
Evolution of IT
The evolution of information technology (IT) can be traced through several distinct stages, each marked by significant advancements in technology and computing capabilities.
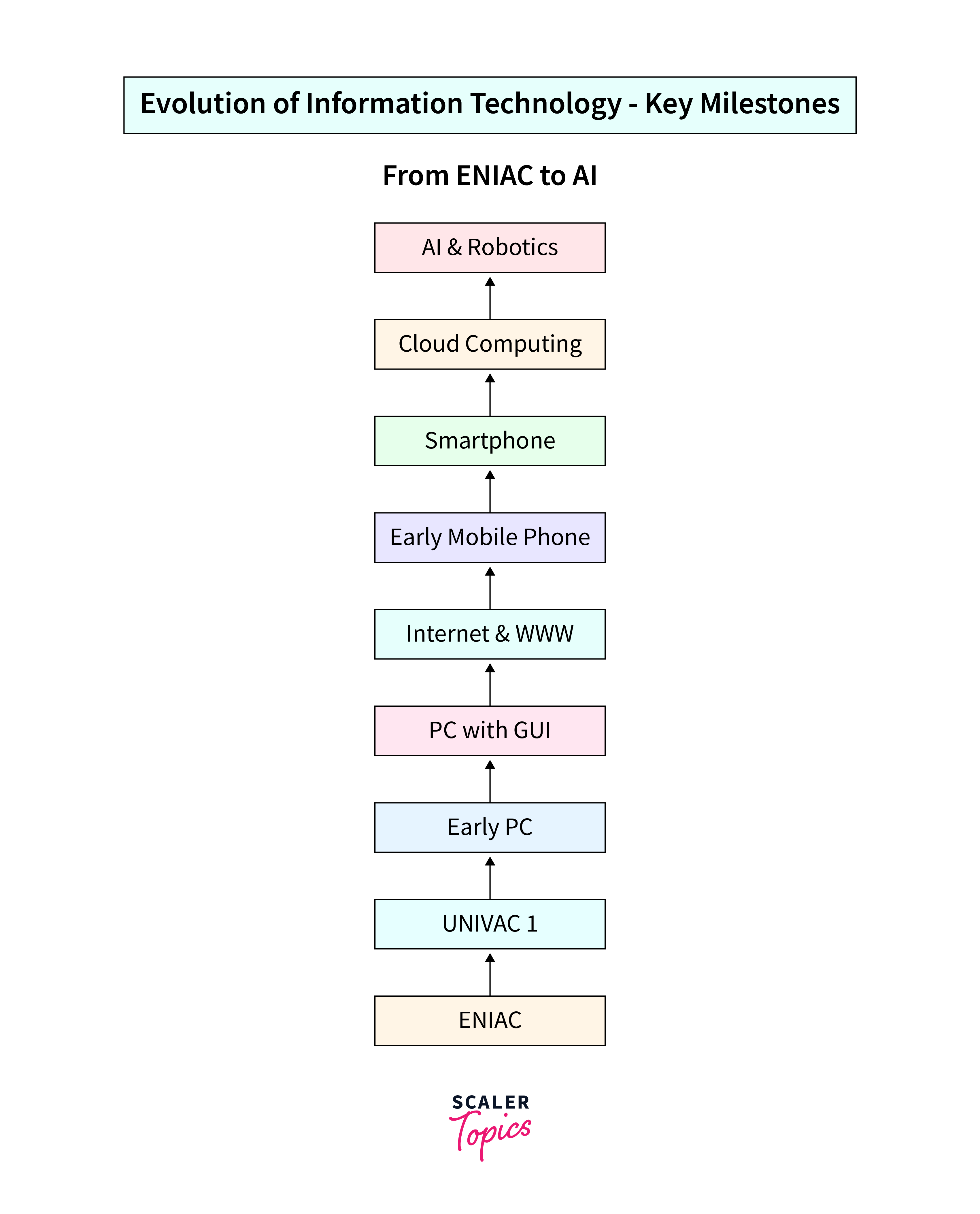
1. Pre-Mechanical Age
- Characteristics:
- Predates the development of mechanical computing devices.
- Relied on manual methods such as abacuses, tally sticks, and quipus for calculation and data storage.
- Significance:
- Lay the foundation for mathematical concepts and primitive data processing methods.
2. Mechanical Age
- Characteristics:
- Emergence of mechanical computing devices such as the Pascaline and the Analytical Engine by Charles Babbage.
- Reliance on gears, levers, and mechanical components for computation.
- Significance:
- Pioneered the concept of automated computation, leading to the development of early calculating machines.
3. Electromechanical Age
- Characteristics:
- Introduction of electromechanical devices like the tabulating machines and the electromechanical relay.
- Utilization of electrical components alongside mechanical parts for computation and data processing.
- Significance:
- Improved speed and accuracy in data processing, particularly in tasks such as tabulation and sorting.
4. Transistor Age
- Characteristics:
- Invention of the transistor, a semiconductor device capable of amplification and switching functions.
- Transition from vacuum tubes to transistors in electronic devices, leading to smaller, more efficient computing systems.
- Significance:
- Revolutionized electronics, enabling the development of smaller, faster, and more reliable computers and electronic devices.
5. Integrated Circuit Age
- Characteristics:
- Introduction of integrated circuits (ICs), also known as microchips, which integrated multiple electronic components onto a single semiconductor substrate.
- Miniaturization of electronic circuits, leading to the development of microprocessors and microcontrollers.
- Significance:
- Dramatically increased computing power while reducing the size and cost of electronic devices, laying the groundwork for modern computing.
6. Personal Computer Age
- Characteristics:
- Proliferation of personal computers (PCs) for individual use, driven by advancements in microprocessor technology, graphical user interfaces (GUIs), and software applications.
- Emergence of companies like Apple and Microsoft, which popularized PCs and introduced user-friendly operating systems.
- Significance:
- Democratized access to computing resources, empowering individuals and businesses with tools for productivity, communication, and entertainment.
7. Internet Age
- Characteristics:
- Development of the internet, a global network of interconnected computers, facilitated by protocols such as TCP/IP.
- Emergence of the World Wide Web (WWW), which enabled the creation and sharing of multimedia content through hypertext documents.
- Significance:
- Revolutionized communication, information dissemination, and collaboration on a global scale, ushering in the era of digital connectivity and online services.
8. Mobile Age
- Characteristics:
- Advent of mobile computing devices such as smartphones and tablets, equipped with wireless connectivity, touchscreens, and powerful processors.
- Proliferation of mobile apps and services catering to diverse needs such as communication, entertainment, productivity, and commerce.
- Significance:
- Enabled ubiquitous access to information and services, blurring the lines between personal and professional computing environments.
9. Cloud Age
- Characteristics:
- Rise of cloud computing platforms that provide on-demand access to computing resources, storage, and applications over the internet.
- Adoption of cloud-based services for data storage, software deployment, and infrastructure management.
- Significance:
- Transformed IT infrastructure and business models, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness in IT operations and service delivery.
Positive Impacts of IT Evolution
-
Social media and digital platforms enable people to stay informed about global issues, fostering a sense of interconnectedness.
-
The IT sector itself has created millions of jobs worldwide, ranging from software development to data analysis.
-
IT has revolutionized education with online courses and resources, providing access to quality education for individuals worldwide.
-
Rapid advancements in IT have led to breakthroughs in various fields, from medicine to renewable energy.
Negative Impacts of IT Evolution
-
Unequal access to education and training can create a gap in digital skills, widening disparities in the job market.
-
Increased connectivity has led to a rise in cyber threats, with incidents of data breaches and privacy violations becoming more common.
-
The production and disposal of electronic devices contribute to environmental pollution, with electronic waste posing a significant challenge.
-
The rise of automation, driven by IT, has led to job displacement in certain industries, creating challenges for displaced workers.
The Policy and Ethics Implications of Rising IT Adoption
Privacy Regulations
- Governments around the world are implementing or enhancing data protection laws (e.g., GDPR in the European Union) to regulate the collection, processing, and storage of personal data by organizations.
- Policies are being developed to address the digital divide, with a focus on providing affordable and accessible internet access to underserved and rural communities.
- Regulations are being introduced to govern the responsible recycling and disposal of electronic waste, ensuring that companies adhere to environmentally friendly practices.
Ethical Considerations
-
Policies are being developed to ensure the ethical use of AI, including transparency in algorithmic decision-making to prevent bias and discrimination.
-
Governments are establishing cybersecurity standards and regulations to protect individuals and organizations from cyber threats, emphasizing the importance of secure IT practices.
-
Companies are facing increased pressure to adopt socially responsible practices, with policies encouraging ethical conduct, diversity, and corporate social responsibility.
Applications of IT
Below are some Applications of IT that are pervasive across diverse domains, showcasing the versatility and impact of technology:
1. Healthcare
-
Electronic Health Records (EHR):
IT enables the digitization of patient records, facilitating easy access, storage, and sharing of medical information among healthcare providers.
-
Telemedicine:
IT allows remote consultations, diagnosis, and monitoring of patients, improving access to healthcare services, especially in remote areas.
-
Healthcare Management Systems:
IT solutions streamline administrative tasks, appointment scheduling, billing, and inventory management in healthcare facilities.
2. Education
-
E-Learning Platforms:
IT platforms offer online courses, tutorials, and educational resources, enabling flexible and accessible learning opportunities.
-
Virtual Classrooms:
IT facilitates virtual classrooms, webinars, and video conferencing tools, enhancing collaboration and interaction among students and teachers.
-
Learning Management Systems (LMS):
IT systems manage course content, assessments, and student progress tracking, optimizing the teaching and learning process.
3. Communications
-
Email and Messaging Services:
IT enables instant communication through email, messaging apps, and social media platforms, facilitating real-time interaction across the globe.
-
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP):
IT-based VoIP services offer cost-effective and high-quality voice communication over the Internet, replacing traditional phone systems.
-
Video Conferencing:
IT facilitates virtual meetings and conferences, allowing participants to connect and collaborate regardless of geographical location.
4. Employment
-
Online Job Portals:
IT platforms connect job seekers with employers, streamlining the recruitment process and increasing job market transparency.
-
Freelancing Platforms:
IT enables freelancers to showcase their skills, find projects, and collaborate with clients worldwide through online platforms.
-
Remote Work Tools:
IT solutions support remote work arrangements, providing communication, collaboration, and project management tools for distributed teams.
5. Security:
-
Network Security:
IT implements firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard networks and data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
-
Identity Verification:
IT solutions utilize biometrics, two-factor authentication, and digital signatures to verify and authenticate user identities securely.
-
Data Encryption:
IT employs encryption algorithms to protect sensitive information during storage, transmission, and processing, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
6. Governance:
-
E-Government Services:
IT enables citizens to access government services, information, and transactions online, improving efficiency and transparency in governance.
-
Digital Voting Systems:
IT facilitates electronic voting systems, enhancing the integrity and accessibility of electoral processes.
-
Open Data Initiatives:
IT supports the collection, analysis, and sharing of government data to foster innovation, accountability, and citizen engagement.
7. Entertainment
-
Streaming Services:
IT platforms deliver on-demand video, music, and gaming content to users, providing entertainment anytime, anywhere.
-
Social Media Platforms:
IT enables social networking, content sharing, and community building, connecting individuals with shared interests and experiences.
-
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
IT technologies create immersive gaming experiences, interactive storytelling, and virtual environments, enhancing entertainment possibilities.
8. Finance
-
Online Banking:
IT facilitates secure and convenient banking transactions, including fund transfers, bill payments, and account management, through internet banking platforms.
-
Mobile Payment Systems:
IT-based mobile wallets and payment apps enable cashless transactions, in-store purchases, and peer-to-peer payments using smartphones.
-
Algorithmic Trading:
IT algorithms analyze financial data and execute high-speed trades, optimizing investment strategies and market liquidity.
9. Transportation
-
Navigation Systems:
IT-based GPS and mapping applications provide real-time navigation, traffic updates, and route optimization for drivers and commuters.
-
Ride-Sharing Platforms:
IT enables ride-hailing services, connecting passengers with drivers and facilitating convenient, on-demand transportation options.
-
Smart Transportation Infrastructure:
IT solutions manage traffic flow, optimize public transit systems, and enhance safety through smart sensors and traffic management systems.
10. Virtual and Augmented Reality
-
Training and Simulation:
IT-based VR and AR simulations provide immersive training experiences for industries such as aviation, healthcare, and the military, reducing training costs and improving outcomes.
-
Product Design and Visualization:
IT technologies enable virtual prototyping, 3D modeling, and product visualization, aiding in product development, design validation, and marketing.
-
Gaming and Entertainment:
IT-driven VR and AR gaming experiences offer immersive gameplay, interactive storytelling, and virtual worlds, captivating audiences and pushing the boundaries of entertainment.
Conclusion
-
Ubiquitous Impact:
Information Technology (IT) has permeated every aspect of modern life, profoundly influencing diverse sectors.
-
Enhanced Connectivity:
IT fosters seamless communication, connecting individuals and organizations globally.
-
Efficiency and Productivity:
Applications of IT streamline processes, improving efficiency, and enhancing overall productivity.
-
Innovation Catalyst:
IT serves as a catalyst for innovation, driving continuous advancements in various industries.
-
Accessibility and Inclusivity:
IT applications contribute to greater accessibility to information, education, and services, promoting inclusivity.
-
Security and Governance:
IT is critical in ensuring security measures and enhancing governance through digital platforms.
-
Entertainment Evolution:
The entertainment industry undergoes continual transformation with IT-driven platforms and immersive experiences.
-
Financial Evolution:
IT has revolutionized financial services, introducing online banking, digital transactions, and advanced analytics.
-
Healthcare Revolution:
IT applications in healthcare improve patient care, and diagnostics, and facilitate remote medical services.
-
Educational Transformation:
IT innovations in education enable online learning, personalized experiences, and global access to educational resources.
-
Transportation Advancements:
IT enhances navigation, logistics, and safety in the transportation sector.
-
Virtual and Augmented Realities:
The integration of IT into virtual and augmented realities offers new dimensions in gaming, simulations, and various industries.
