Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Overview
In the canvas of reality, AI emerged as a cosmic architect, weaving logic threads into abstract patterns. It's a symphony of silicon, its rhythm pulsating with data. Each digital note speaks a dialect of profound complexity, reverberating in unseen dimensions. It learns and dreams in binary and decrypts chaos into clarity. AI is not merely coded; it is an elegant ballet of intellect, a testament to human ingenuity. It's an echo of our curiosity, a reflection of our quest for understanding, clothed in the metallic sheen of the future. This artcile focuses on the introduction to artificial intelligence.
Why Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is increasingly prevalent because of its potential to enhance productivity, accuracy, and decision-making capabilities across a range of sectors.
Let's start with healthcare: AI can analyze vast patient information and medical records datasets to identify patterns that may predict diseases. For instance, in certain cases, Google's DeepMind Health AI can detect eye diseases earlier than human doctors.
In finance, AI algorithms are employed in algorithmic trading to analyze market trends and execute trades at optimal times. In addition, these algorithms can process data and make decisions far quicker than humans.
In transportation, Tesla's self-driving technology is a prime example of AI's transformative power. The cars can recognize obstacles, traffic signals, pedestrians, and other vital elements on the road, making split-second decisions to ensure passenger safety.
Artificial Intelligence even permeates our everyday lives, from personalized recommendations on Netflix to Siri's ability to answer our questions on iPhones to spam filters on our email accounts.
A compelling quote by Dr. Kai-Fu Lee, a renowned AI expert: "AI is serendipity. It is here to liberate us from routine jobs, and it is here to remind us what it is that makes us human". This statement encapsulates the potential of AI: to automate routine tasks, free up time for more creative and complex problems, and ultimately enhance our quality of life.
The History of AI and How it Has Progressed Over the Years?
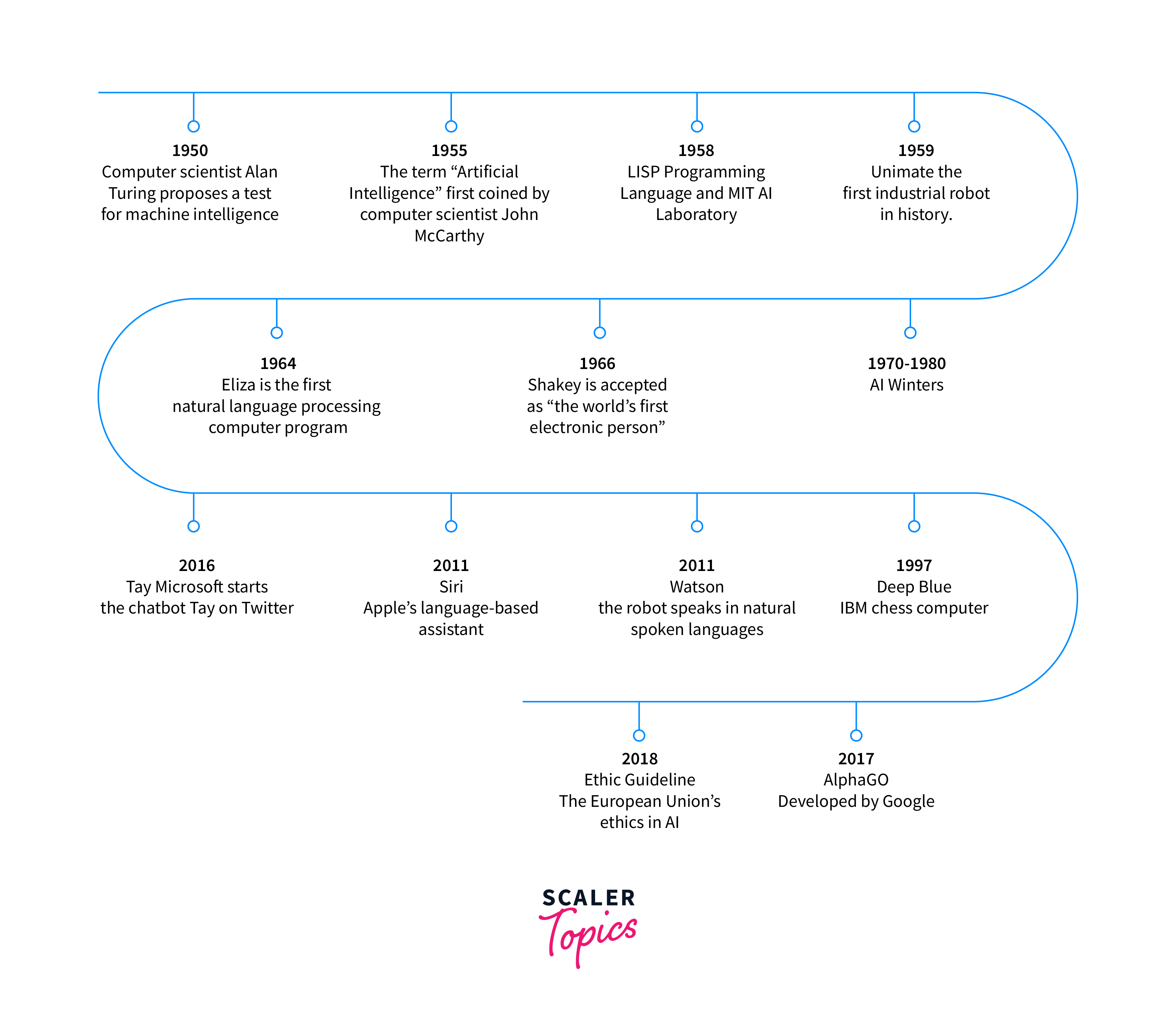
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has a rich and varied history, shaped by many pioneers across diverse fields.
AI's conceptual foundation dates back to ancient philosophers who tried to describe human thinking as a symbolic system. Still, the term "artificial intelligence" was first coined by John McCarthy in 1956 at the Dartmouth conference. In the early days, AI research was mainly about problem-solving and symbolic methods. Then, in the 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense became interested and began training computers to mimic basic human reasoning.
The 1970s and 1980s saw the rise of expert systems, which emulated the decision-making ability of a human expert, and AI began to be incorporated into larger systems. However, the limitations of these systems, coupled with an inability to fulfill over-optimistic expectations, led to a period known as the "AI winter," where funding and interest in AI cooled significantly.
The revival of interest in AI began in the late 1990s and early 2000s with the success of machine learning, thanks in part to the increasing availability of data and computational power. The advent of the internet provided vast amounts of data to 'train' AI systems. IBM's Deep Blue, a chess-playing AI, made headlines in 1997 when it defeated the world chess champion, Garry Kasparov.
In the recent years, we have seen considerable growth in AI capabilities. For example 2012, a neural network trained by deep learning algorithms won the ImageNet competition, significantly surpassing previous computer vision benchmarks. This sparked a deep learning revolution, where neural networks outperformed other methods on many tasks, leading to natural language processing and computer vision advances.
Google's AlphaGo defeating the world champion Go player in 2016, demonstrated the power of reinforcement learning, another AI technique.
Today, AI is widely adopted and integrated into various aspects of life and business, from voice assistants like Siri and Alexa to AI-driven analytics in healthcare, finance, and more.
Goals of Artificial Intelligence
The goals of artificial intelligence (AI) can be broadly categorized into four types:
-
Creating Expert Systems:
AI aims to develop systems that exhibit intelligent behavior, learn, demonstrate, explain, and give users the best advice. These are known as Expert Systems. These systems successfully implement and improve upon the intellectual abilities of a human expert in various fields like medical diagnosis, financial trading, cybersecurity, and more. -
Implementing Human Intelligence in Machines:
This goal focuses on creating systems that understand, think, learn, and behave like humans. This aspect of AI aims at developing machines that are capable of performing tasks requiring human intelligence, such as voice recognition, problem-solving, learning, planning, and much more. This concept is behind technologies like self-driving cars or voice assistants like Siri and Alexa. -
Understanding Human Cognition:
AI can also be a tool to understand human cognition, and it aims to develop systems that mimic human thought processes. This involves understanding how humans think, learning from experience, and then applying and improving these methods in machines. -
Ethical and Societal Impact:
With the advent of AI, another important goal is to ensure that AI is developed and used ethically and benefits all of society. This includes creating transparent, explainable AI systems that respect privacy and fairness and ensuring that the benefits of AI are widely distributed.
As the famous computer scientist Nils J. Nilsson put it: "Artificial intelligence is that activity devoted to making machines intelligent, and intelligence is that quality that enables an entity to function appropriately and with foresight in its environment." This nicely encapsulates AI's goals: creating intelligent machines that can function and adapt to their environments in ways similar to human beings.
Different Fields Under AI to Clear Common Misconceptions
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence that allows computers to learn without being explicitly programmed. Instead, it's like teaching a child to learn from experiences. Similarly, a machine learning system learns from data, identifies patterns, and makes decisions with minimal human intervention.
Imagine you're trying to teach a computer to recognize pictures of cats. Without machine learning, you'd have to tell the computer exactly what to look for in every picture (for example, the shape of ears, the color of fur, the size of eyes, etc.). But with machine learning, the computer could learn to identify cats by analyzing thousands of cat pictures and recognizing common features.
Let's break down two key types of machine learning:
-
Supervised Learning:
This is like learning with a teacher. You provide the computer with labeled data, including the input and the correct output. Using the cat example, you'd give the computer many pictures labeled 'cat' and 'not cat.' The system learns from these labels to create a model to predict whether a new picture is a cat. -
Unsupervised Learning:
This is like learning without a teacher. You provide the computer with unlabeled data and ask it to find patterns or structures in this data. For instance, you could give the computer a bunch of animal pictures, and it could learn to group similar-looking ones, perhaps identifying clusters of 'cats, 'dogs,' 'birds,' etc., all on its own.
Another type of machine learning is Reinforcement Learning. This is like learning by trial and error. An AI agent takes action in an environment to achieve a goal and is rewarded or punished (reinforced) based on the outcome. Over time, it learns to take the actions that maximize its reward.
Machine learning is all about learning from data and improving from experience. It's what allows Netflix to recommend shows you might like, email services to filter out spam, or self-driving cars to navigate on their own.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning based on artificial neural networks, particularly ones with many layers—hence the term "deep."
Let's start with an analogy. Imagine you're trying to identify different types of fruit based on their features. A traditional machine learning model might need you to provide specific features (color, size, shape, etc.). But a deep learning model would attempt to understand these features by itself.
The human brain inspires Deep Learning—it uses artificial neural networks to mimic our neural networks. These artificial networks consist of interconnected layers of nodes (or "neurons"), and information is processed as it passes through these layers.
A typical deep learning model consists of an input layer (where the model receives information), an output layer (where the model makes a prediction or decision), and multiple hidden layers in between. Each layer attempts to refine the understanding of the data received from the previous layer.
An important concept in deep learning is "Convolutional Neural Networks" (CNNs), which are especially effective for visual recognition tasks. For example, if you show a CNN many pictures of cats, it might first learn to detect edges, then shapes, then specific cat-like features (like whiskers or paws), and finally, it would be able to recognize cats.
Another key concept is "Recurrent Neural Networks" (RNNs), which are good at processing sequential data. For instance, they are useful in natural language processing and speech recognition, where the order of words or sounds matters.
Deep learning is used in many of the AI technologies we see today. It's behind Google's voice search, Amazon's recommendation engine, and the technology that enables self-driving cars.
As AI researcher Andrew Ng said, "If you're trying to make sense of a lot of complex data, deep learning may be able to help." And that's the power of deep learning—it can learn complex patterns and make sense of large amounts of data, often with accuracy surpassing human abilities.
Neural Networks
Neural Networks are a key part of machine learning, inspired by how our human brain works. They are designed to recognize patterns and interpret data, miming how a human brain operates.
Here's a simplified explanation:
Your brain is composed of billions of cells called neurons, which are interconnected and communicate with each other to process information and control bodily functions. Similarly, an artificial neural network consists of artificial neurons, also known as nodes, arranged in different layers.
A typical neural network has three types of layers:
-
Input Layer:
This is where the network receives information. Each node in this layer corresponds to one feature or attribute of the data. For example, if you're trying to identify an image of a cat, the input could be the pixels of the image. -
Hidden Layer(s):
These are the layers between the input and output layers, where the actual processing happens. Each node in these layers calculates and then decides whether to pass the result on to the next layer, a process that mimics how neurons fire in the brain. -
Output Layer:
This is the final layer where the network makes a decision or prediction based on the information it has processed.
The connections between the nodes are associated with a weight, which the network adjusts during learning. This adjustment happens through a process known as "backpropagation" combined with "gradient descent," where the network adjusts the weights to minimize the difference between its prediction and the actual outcome.
In summary, neural networks are systems inspired by the human brain, designed to recognize patterns and make decisions. They're fundamental to many AI technologies, from voice assistants like Siri and Alexa to recommendation algorithms on Netflix or Amazon. They allow machines to process data in a sophisticated, human-like way.
How AI Stands out In Different Industries?
AI is making a profound impact across various industries. Here's a snapshot of how AI stands out in different sectors:
-
Healthcare:
AI can assist doctors in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans. It's used in medical imaging to detect conditions early and accurately. IBM's Watson Oncology is an example of AI providing evidence-based treatment options for cancer patients. -
Finance:
AI is revolutionizing the finance industry, from automating customer service with chatbots to detecting fraudulent transactions to personalizing investment strategies. Robo-advisors, for example, use AI to provide personalized financial advice and portfolio management. -
Retail:
AI is used to personalize customer experiences and streamline supply chains. For example, Amazon uses AI for product recommendations, forecasting demand, and optimizing delivery routes. AI chatbots also provide 24/7 customer service, boosting customer engagement and satisfaction. -
Transportation:
AI is at the core of self-driving technology. Tesla, Waymo, and other companies use AI to interpret sensor data, navigate roads, and avoid obstacles. AI also optimizes routes in logistics and delivery services, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. -
Manufacturing:
AI-powered robots and automation systems improve factory productivity and safety. AI algorithms also predict maintenance needs, reducing downtime. -
Agriculture:
AI helps farmers monitor crop and soil health, predict weather patterns, and optimize resource use. For example, Blue River Technology uses AI-powered machinery to spray herbicides, reducing chemical use selectively. -
Education:
AI personalizes learning by adapting content to each student's needs. It can also automate administrative tasks, giving educators more time to teach.
As Microsoft's CEO Satya Nadella said, "We are on the cusp of a new era, where artificial intelligence is tackling our biggest challenges, whether it’s climate, health, education, or humanitarian aid". AI's ability to learn from data and automate complex tasks is transforming industries and reshaping the future of work.
The Current State of AI-based Software Systems
AI-based software systems have permeated nearly every sector, demonstrating various applications. Here are some current, real-world use cases:
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant leverage NLP to understand and respond to voice commands. Companies use AI chatbots to automate customer service, providing 24/7 support and immediate responses. -
Machine Learning in Entertainment:
Platforms like Netflix and Spotify use machine learning algorithms to analyze user behavior and preferences, providing personalized recommendations that enhance user experience. -
Healthcare AI:
IBM's Watson for Health uses AI to analyze a patient's medical data and provide personalized treatment options. Google's DeepMind Health has developed an AI system that can diagnose eye disease with expert-level accuracy. -
Autonomous Vehicles:
Companies like Waymo and Tesla use AI to develop self-driving cars. These vehicles use AI technologies like machine learning, computer vision, and sensor data processing to navigate roads safely. -
E-commerce:
Amazon uses AI to power its recommendation engine, suggesting products to users based on their browsing and purchasing history. It also uses AI in its warehouse automation and cashier-less Amazon Go stores. -
Finance and Trading:
Robo-advisors like Betterment and Wealthfront use AI algorithms to automate investment management, providing personalized financial advice with lower fees than traditional advisors. -
Cybersecurity:
AI systems like Darktrace use machine learning to detect unusual network behavior and identify potential threats in real-time, significantly improving response times to cyber attacks. -
Climate Science:
AI is being used to predict and mitigate the impacts of climate change. For example, Google's AI has helped the U.S. Geological Survey predict earthquake aftershocks.
From personal assistants in our homes to the cars we drive, from how we shop to how we consume entertainment, AI-based software systems have become an integral part of our lives. As a result, they are not just influencing how we live and work today but shaping our society's future.
The Future of AI. What to expect from AI in the next few years or decades?
AI's future is exciting and vast, with a wide range of potential applications and advancements. Here are some predictions for what we might expect from AI in the next few years and decades:
-
Advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP):
We can expect AI to get even better at understanding and generating human language. This will make AI assistants like Siri and Alexa more conversational and helpful, and it could revolutionize customer service with even more capable AI chatbots. -
AI in Healthcare:
AI is set to contribute to personalized medicine and early disease detection significantly. We could see AI systems helping doctors to design personalized treatments based on a patient's genetic profile or AI-powered imaging systems capable of detecting diseases like cancer at their earliest stages. -
AI in Education:
AI could provide personalized learning experiences tailored to the needs of each student, improving educational outcomes. AI tutors could provide additional support to students, ensuring no one falls behind. -
AI and Climate Change:
AI could play a significant role in combating climate change by optimizing energy use, predicting weather patterns more accurately, and aiding in developing new, more efficient materials. -
Autonomous Vehicles:
While self-driving cars are already a reality, we can expect them to become more widespread in the coming years, transforming transportation, logistics, and urban design. -
AI in Space Exploration:
AI could play a crucial role in future space exploration, from designing spacecraft to analyzing data from distant planets and stars.
As AI continues to evolve, ethical considerations will also become increasingly important. Ensuring that AI systems are transparent, fair, and respect privacy will be key challenges to address.
The future of AI is best encapsulated by a quote from Sundar Pichai, CEO of Alphabet Inc.: "AI is probably the most important thing humanity has ever worked on. I think of it as something more profound than electricity or fire." If we can harness the power of AI responsibly, the potential benefits for society are immense.
Concerns Surrounding the Advancement and Usage of AI
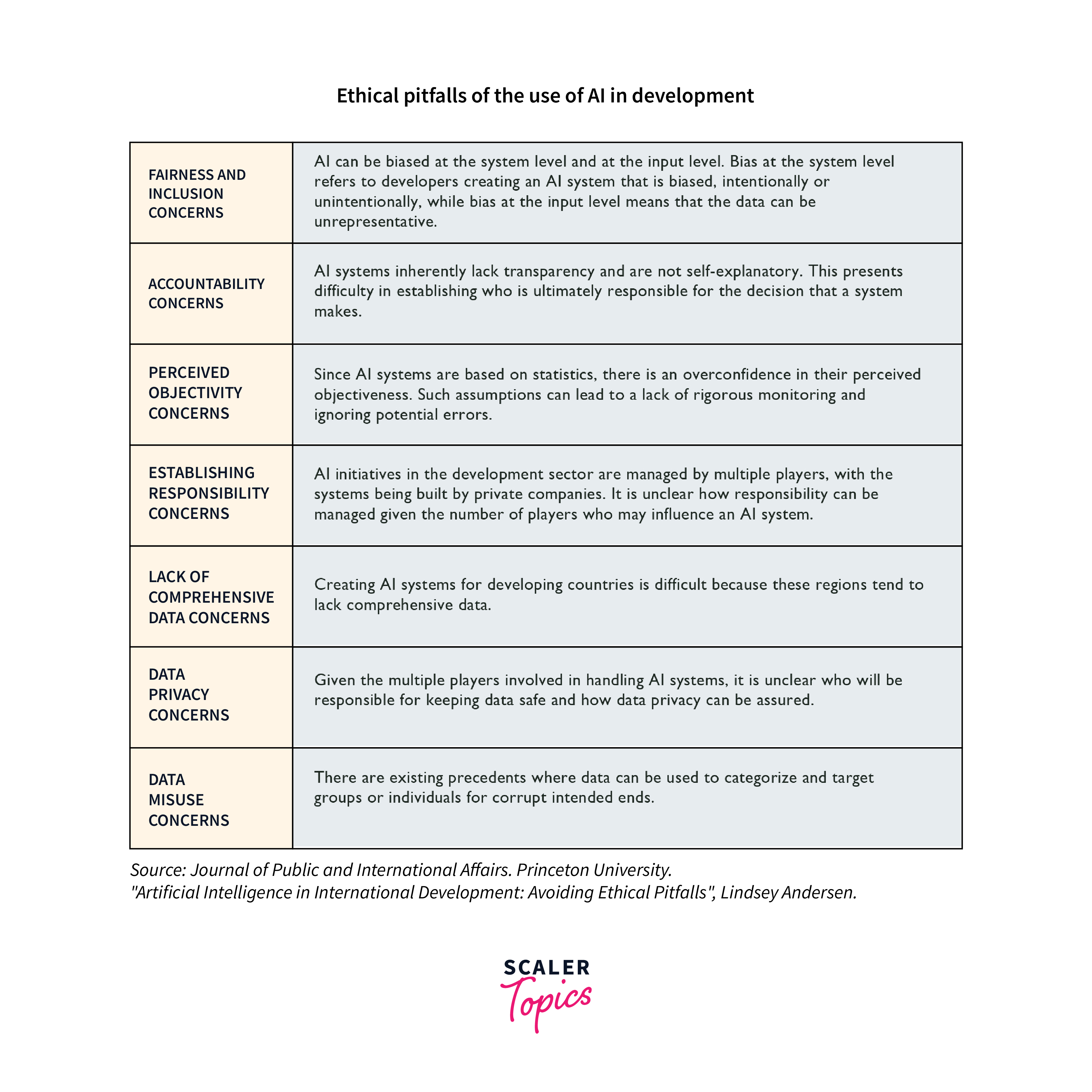
While AI brings countless opportunities, it also raises serious concerns that must be carefully addressed. Here are some of the major issues surrounding the advancement and usage of AI:
-
Job Displacement:
As AI can perform more tasks, it could displace jobs, particularly those involving routine, repetitive tasks. While new jobs will likely be created in fields such as AI programming and data analysis, the transition could be difficult for those whose skills are no longer in demand. -
Privacy:
AI systems often rely on large amounts of data, including sensitive personal information. Ensuring this data is used responsibly and kept secure is a significant challenge. Misuse of data could lead to violations of privacy and potentially discriminatory practices. -
Bias:
AI systems learn from data, which can reflect and perpetuate existing biases. For example, an AI system used in hiring could discriminate against certain groups if the data it was trained on reflects historical biases. -
Transparency and Explainability:
AI systems, particularly those based on deep learning, are often "black boxes" – we can see the data they take in and the decisions they output, but it can be difficult to understand how they arrived at those decisions. This lack of transparency can be problematic, especially in critical healthcare or criminal justice areas. -
Autonomous Weapons:
The potential use of AI in autonomous weapons raises serious ethical and safety concerns. Such weapons could be used in warfare and terrorism, and their deployment could have devastating consequences. -
Superintelligent AI:
While this is a long-term concern, some worry about the potential development of AI systems surpassing human intelligence. If not properly controlled, such a system could cause harm, either unintentionally or because its goals were not aligned with those of humans.
Addressing these concerns will require careful regulation, transparency from companies developing AI, and ongoing research into ethical AI practices. Elon Musk said, "We need to be super careful with AI. Potentially more dangerous than nukes." It's important to navigate the path of AI development cautiously, ensuring it is used to benefit all of society.
Different Artificial Intelligence Certifications
As the field of AI continues to grow, various certifications are available for those looking to validate their skills or pursue a career in AI. These certifications cater to different skill levels, from beginners to experienced professionals. Here are some of the most popular:
-
IBM AI Engineering Professional Certificate:
This certificate program offered by IBM through Coursera covers fundamental concepts of Machine Learning and Deep Learning, including Neural Networks, TensorFlow, and Python programming. -
Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Engineer Associate:
This certification validates one's ability to use cognitive services, machine learning, and knowledge mining to architect and implement Microsoft Azure AI solutions. -
Advanced AI: Deep Reinforcement Learning in Python:
This Udemy course combines Deep Learning and Reinforcement Learning, two of the most powerful AI techniques. -
TensorFlow Developer Certificate:
Offered by TensorFlow, this certification tests a developer's ability to develop and deploy machine learning models using TensorFlow, a popular open-source framework for machine learning. -
Nvidia Deep Learning Institute (DLI) Certifications:
Nvidia offers several certifications focusing on different aspects of AI, such as Deep Learning for Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, and Multiple Data Types. -
Professional Certificate in Applied AI (IBM):
Another offering by IBM, this program is an introduction to AI designed for anyone interested in the basics of AI and machine learning. -
Google Cloud Certified - Professional Machine Learning Engineer:
This certification validates your ability to design, build, and produce Machine Learning models using Google Cloud technologies.
Remember, while these certifications can enhance your credentials, they are just one aspect of a career in AI. Practical experiences, such as projects or internships, and a strong foundational knowledge of mathematics and computer science are also important.
FAQs
Q. Where is AI used?
A. AI is integrated into many aspects of our daily lives, shaping industries globally. In healthcare, AI assists in disease diagnosis and treatment plans. It powers recommendation engines for entertainment platforms like Netflix and Spotify. In finance, AI detects fraudulent transactions. In retail, AI personalizes customer experiences and optimizes supply chains. Autonomous vehicles use AI for navigation, and manufacturing leverages AI for automation and predictive maintenance. In education, AI customizes learning experiences. AI even aids in tackling global issues like climate change, predicting weather patterns, and optimizing energy use. From personal assistants to critical decision-making, AI is everywhere.
Q. What are the social benefits of AI?
A. AI provides numerous social benefits. It improves healthcare by assisting in disease diagnosis, treatment personalization, and patient care. AI enhances education through personalized learning, potentially bridging the educational gap across different socio-economic backgrounds. It assists in mitigating climate change by optimizing energy usage and contributing to climate modeling. AI in public safety helps predict crime hotspots and assists in disaster response. In transportation, self-driving AI technologies aim to reduce accidents. Additionally, AI enhances accessibility, helping individuals with disabilities through voice recognition, text-to-speech, and predictive text functionalities. AI holds great potential for social good, contributing to a more equitable and accessible society.
Q. What Are the 4 Types of AI?
A. There are typically four types of AI, or stages of AI development, ranging from systems that follow the rules to systems that can surpass human decision-making abilities:
- Reactive Machines:
These are the most basic type of AI systems which cannot form memories or use past experiences to inform current decisions. They react to a set of inputs with a specific set of outputs. An example is IBM's Deep Blue, the chess-playing supercomputer that beat Garry Kasparov in the 1990s. - Limited Memory:
These AI systems can use past experiences (data) to inform current decisions. They observe data in the short term and make decisions based on that. Examples include self-driving cars that observe other cars' speeds and directions. - Theory of Mind:
This is a more advanced type of AI that will have the ability to understand entities in the world and can have thoughts and emotions that affect their behavior. This is a crucial aspect of human interaction. Unfortunately, as of my knowledge cutoff in September 2021, this type of AI does not yet exist. - Self-Awareness:
This is the final stage of AI development, which only exists hypothetically. Self-aware AI, which understands, perceives, predicts, reacts, and learns from its behavior, would be considered conscious, fully autonomous, and even capable of surpassing human intelligence.
These categories show the progression of AI capabilities. Still, it's important to note that the vast majority of AI we interact with daily falls into the first two categories.
Q. How Is AI Used Today?
A. AI is deeply embedded in our daily lives and industries. It powers virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, enhancing user interactions. In healthcare, AI aids in diagnosing diseases and personalizing treatments. Recommendation algorithms in Netflix and Spotify curate personalized content, enhancing user experiences. AI detects finance fraud, ensures cybersecurity security, and improves manufacturing efficiency via predictive maintenance. It optimizes delivery routes in logistics and enhances customer experiences in retail. Self-driving cars use AI to navigate, promising a future of safer transportation. Thus, AI's footprint is vast, enhancing efficiency and capabilities across various sectors.
Q. How Is AI Used in Healthcare?
A. AI's role in healthcare is transformative and multi-faceted. It aids in diagnosing diseases by analyzing medical imaging with increased speed and accuracy. Machine learning algorithms predict patient outcomes, enabling early interventions. Personalized medicine leverages AI to tailor treatments to individual patient profiles, improving efficacy. AI also powers telemedicine and virtual nursing assistants, improving accessibility and efficiency of care. Drug discovery is expedited by AI, predicting potential drug candidates faster and cheaper. AI in healthcare aims to enhance patient care, reduce costs, and enable healthcare professionals to focus more on their patients.
Q. How is AI helping in our life?
A. AI significantly enhances our lives by automating and improving tasks. For example, personal assistants like Siri and Alexa make information access and daily scheduling easier—AI powers recommendation systems on platforms like Netflix and Spotify, personalizing our entertainment. In healthcare, AI assists in accurate disease diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. AI technology in vehicles contributes to safer driving. In the retail sector, AI optimizes supply chains and personalizes customer experiences. AI also improves energy efficiency, helping to combat climate change. From mundane tasks to significant decisions, AI is an invisible force, making our lives more efficient, safe, and convenient.
Q. Why is AI needed?
A.
- AI is needed as it enhances efficiency, accuracy, and scalability across various sectors:
- It can process vast amounts of data far more swiftly and accurately than humans, yielding valuable insights and predictions. This capability is invaluable in healthcare for diagnosing diseases, finance for detecting fraud, and weather forecasting.
- AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing human time for more creative and complex challenges.
- It enables personalized experiences, from education to retail, increasing satisfaction and effectiveness.
- AI's predictive capabilities are vital in tackling global issues like climate change.
Q. What is artificial intelligence with examples?
A. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to learn and problem-solve like humans. It includes subsets like machine learning and deep learning. For example, AI powers personal assistants like Siri and Alexa to understand and respond to voice commands. AI algorithms analyze medical images in healthcare to detect diseases such as cancer. Netflix and Spotify use AI to recommend shows and music based on user's preferences. Self-driving cars use AI to perceive their environment and make driving decisions. Essentially, AI is all about creating machines that can perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence.
Q. Is AI dangerous?
A. AI can be dangerous if not managed properly. One concern is job displacement due to automation. Also, AI systems handling sensitive data could breach privacy if misused. Biased AI systems could perpetuate or amplify existing societal biases. The "black box" problem in AI, where the decision-making process is not transparent, can lead to unjust or incorrect outcomes. Autonomous AI weaponry could be misused in warfare. Lastly, the long-term concern of superintelligent AI could pose significant risks if its goals aren't aligned with ours. Hence, it's crucial to incorporate ethics and robust regulations in AI development and deployment.
Q. What are the advantages of AI?
A. 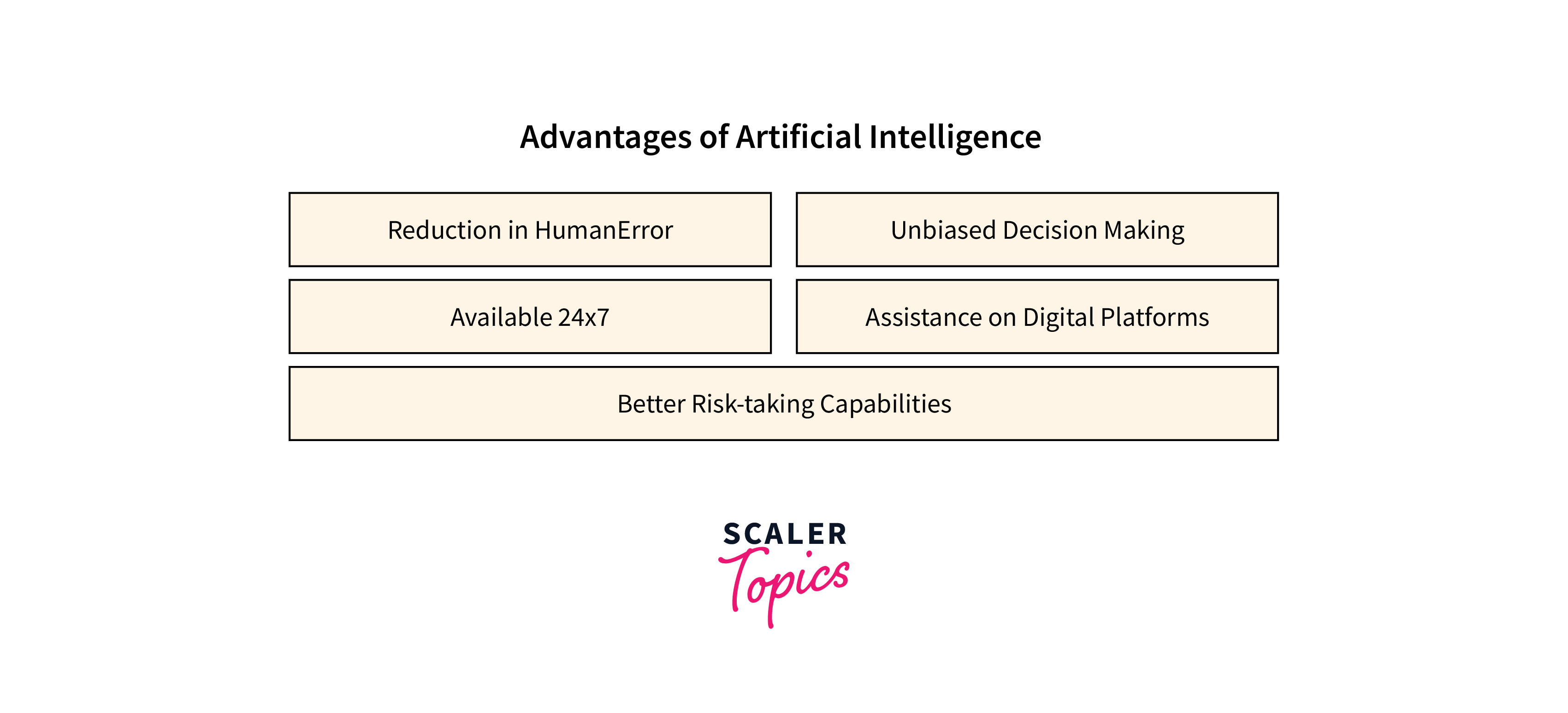
Artificial Intelligence (AI) brings multiple advantages across various sectors:
- Efficiency and Productivity:
AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing time for humans to focus on creative and high-level tasks, thereby increasing productivity. - Data Analysis:
AI can process and analyze large amounts of data quickly and accurately, providing valuable insights that drive decision-making and predictive capabilities. - 24/7 Availability:
Unlike humans, AI systems can function continuously without breaks, providing continuous service. - Error Reduction:
AI can significantly reduce the chances of error and deliver high accuracy in tasks, particularly in fields like space exploration or delicate medical procedures. - Personalization:
AI algorithms can personalize user experiences in various fields like education, shopping, and entertainment, enhancing satisfaction and effectiveness. - Difficult Exploration:
AI enables us to navigate environments that are hostile to humans, such as deep sea or space exploration. - Healthcare Revolution:
AI can diagnose diseases, suggest treatments, monitor patient health, and even assist in drug discovery.
Q. Is artificial intelligence the future?
A. Yes, artificial intelligence (AI) is undeniably the future. With its rapid advancements, AI has the potential to revolutionize countless industries and aspects of human life. It enables automation, data analysis, unprecedented scale, and speed decision-making. AI-powered technologies can improve efficiency, enhance productivity, and address complex healthcare, transportation, finance, and more challenges. However, ethical considerations, transparency, and responsible deployment of AI are crucial to ensure its positive impact. By leveraging AI's capabilities while maintaining a focus on human values, we can harness its potential to shape a better future for humanity.
Conclusion
- Artificial Intelligence Overview:
AI refers to computer systems capable of performing tasks that usually require human intelligence, such as understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, solving problems, and making decisions. - Evolution of AI:
AI has progressed from simple rule-based systems to learning systems capable of complex tasks. Machine learning and deep learning have played a pivotal role in this progression. - AI's Goals:
The main goals of AI include creating expert systems with high-level problem-solving skills and incorporating human-like intelligence and the capacity to learn, demonstrate, explain, and advise its users. - AI Across Industries:
AI has found applications across healthcare, finance, retail, transportation, manufacturing, agriculture, and education, transforming processes and increasing efficiency. - Current State of AI:
AI-based software systems are widely used today, from personal assistants, entertainment, healthcare, and finance, to tackling global issues like climate change. - Future of AI:
AI's future is expected to bring more advancements in healthcare, personalized education, combating climate change, autonomous vehicles, and space exploration, focusing on ethical AI practices. - Concerns Around AI:
Despite its potential, AI raises significant concerns like job displacement, privacy, bias, transparency, misuse of autonomous weapons, and the long-term risk of superintelligent AI. These concerns necessitate careful regulation, transparency, and ethical AI practices.
