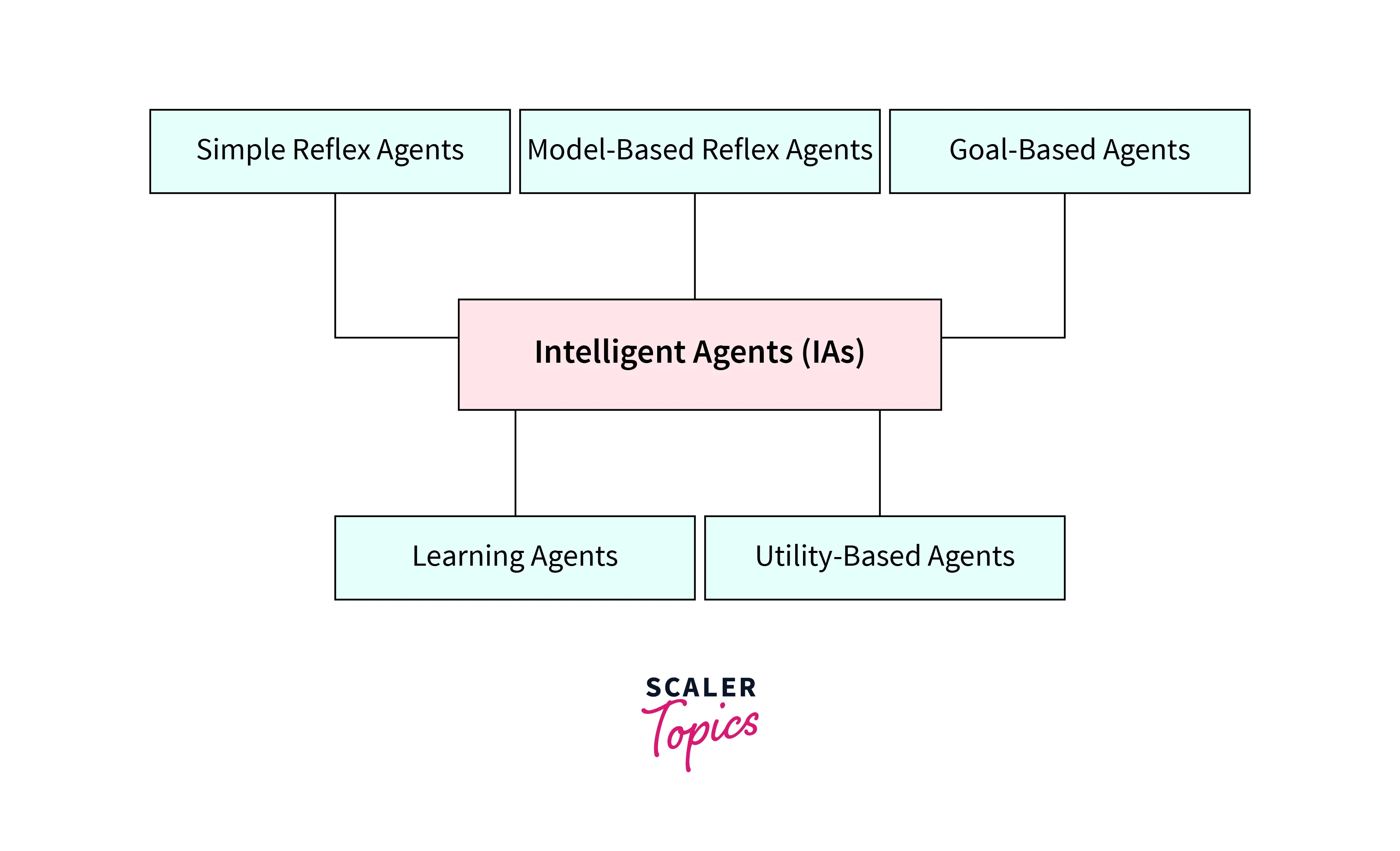
Types of AI Agents
Overview
Artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly transformed human-machine interaction by imparting machines the capability to make judgments and execute jobs to assist humans. At the core of AI, we will find AI agents. These are intelligent entities known as Intelligent Agents (IAs), capable of perceiving their environment and analyzing it to take rational actions to achieve goals.
Different AI agents are designed to solve particular challenges and work on specific tasks. A deeper understanding of the types of agents in AI is essential for building effective and efficient AI systems.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly grown in the recent past by helping to build intelligent machines capable of performing complex tasks which traditionally require human intelligence. We can implement complex AI systems operating effectively in dynamic environments with various AI agents.
Let us understand the different types of agents in AI and how they are being used in real-world applications.
How do the IAs Interact with Their Environment?
The AI agent has to behave similarly to human beings who act on the perception of conditions seen in the environment. Hence these types of agents in AI also need to perceive the current or likely future of the environment and then take suitable actions for the necessary outcome. They need sensors for observation and, after perceiving, take the necessary action through actuators respectively. Hence, we need to understand the two important factors.
- Perception:
It is an activity of registering some observed phenomenon and storing it so that it could form some opinion for action. - Action:
It is the performing activity resulting in some observable change in the environment. The AI agent brings out effective changes in the environment after the perception and analysis of sensor feedback. Different actuators like motors, transmission units, and linkages get activated through instructions from pre-designed programs to bring the required changes to the environment as per the target.
How should the Agents Act in AI?
All the types of agents in artificial intelligence should act rationally and intelligently so that they almost mimic human behavior. They should properly perceive and analyze sensor information and be competent to take necessary actions to achieve the best performance.
Types of AI Agents
- Simple Reflex agents:
These types of agents in AI can take action by reflex on perceiving the current status of the environment. Their action is not based on any set model or previous information. Their success depends on full observability of the environment. Also, they follow the condition action rule, which means they will take action according to what condition it perceives. e.g., applying car brakes on seeing a large pothole on the road.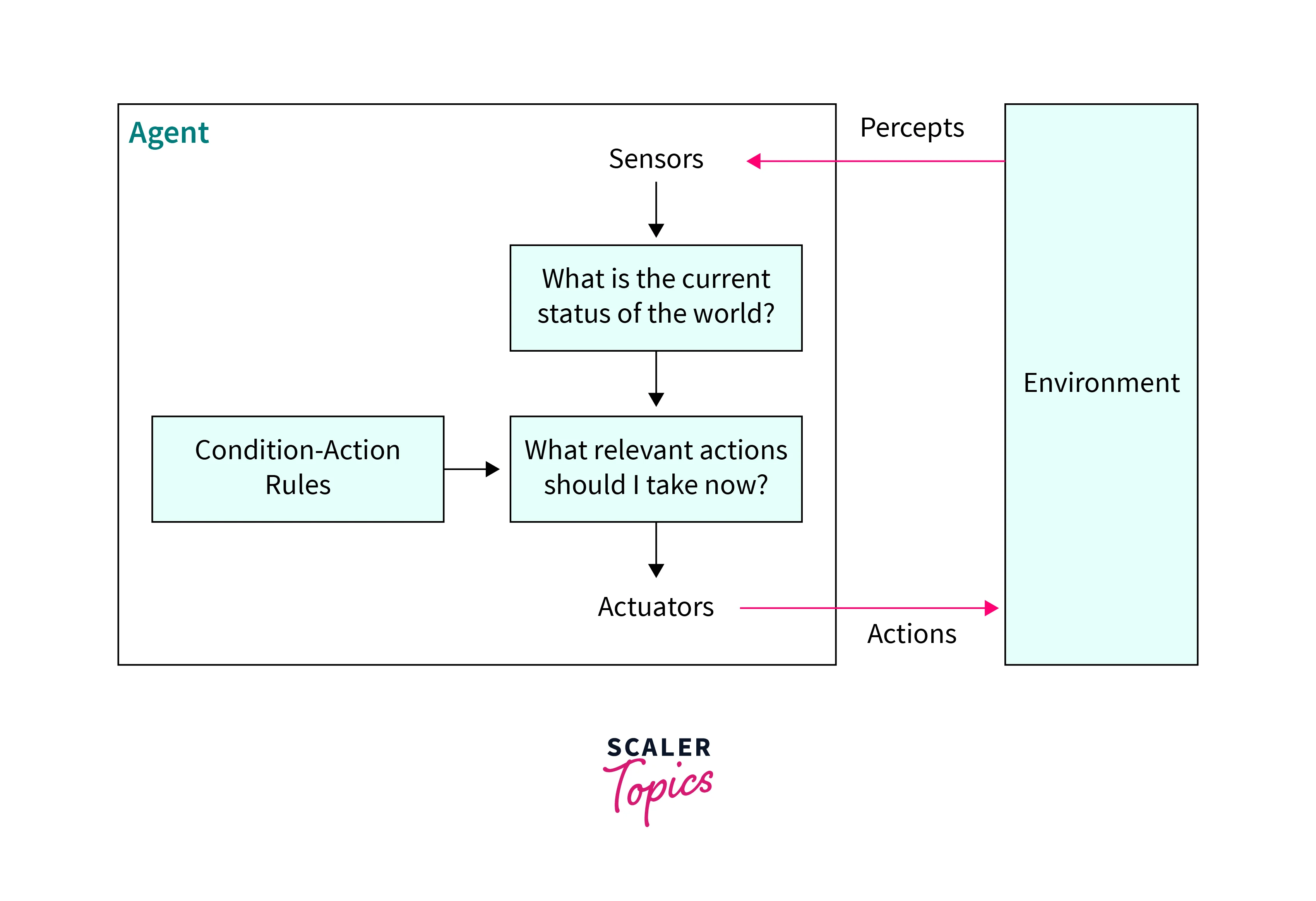
Problems with the simple reflex agent design approach
- Since they are built for simple condition action rules, they possess limited intelligence.
- They need full observability and hence cannot act on non-perceivable parts of the current state of the environment.
- They cannot adapt to the changes in the environment.
- Model-based Reflex agents:
These types of agents in AI are an improved or modified version of simple reflex agents. Their action is based on models built on previous experience and can take necessary action when required, even in a partially observable environment. e.g., a thermostat device that operates on previous history-based models for values of hot conditions of the surface of iron so that it goes on and off when ironing a variety of clothes or a control device that can monitor the speed of cars on highways as per the limit set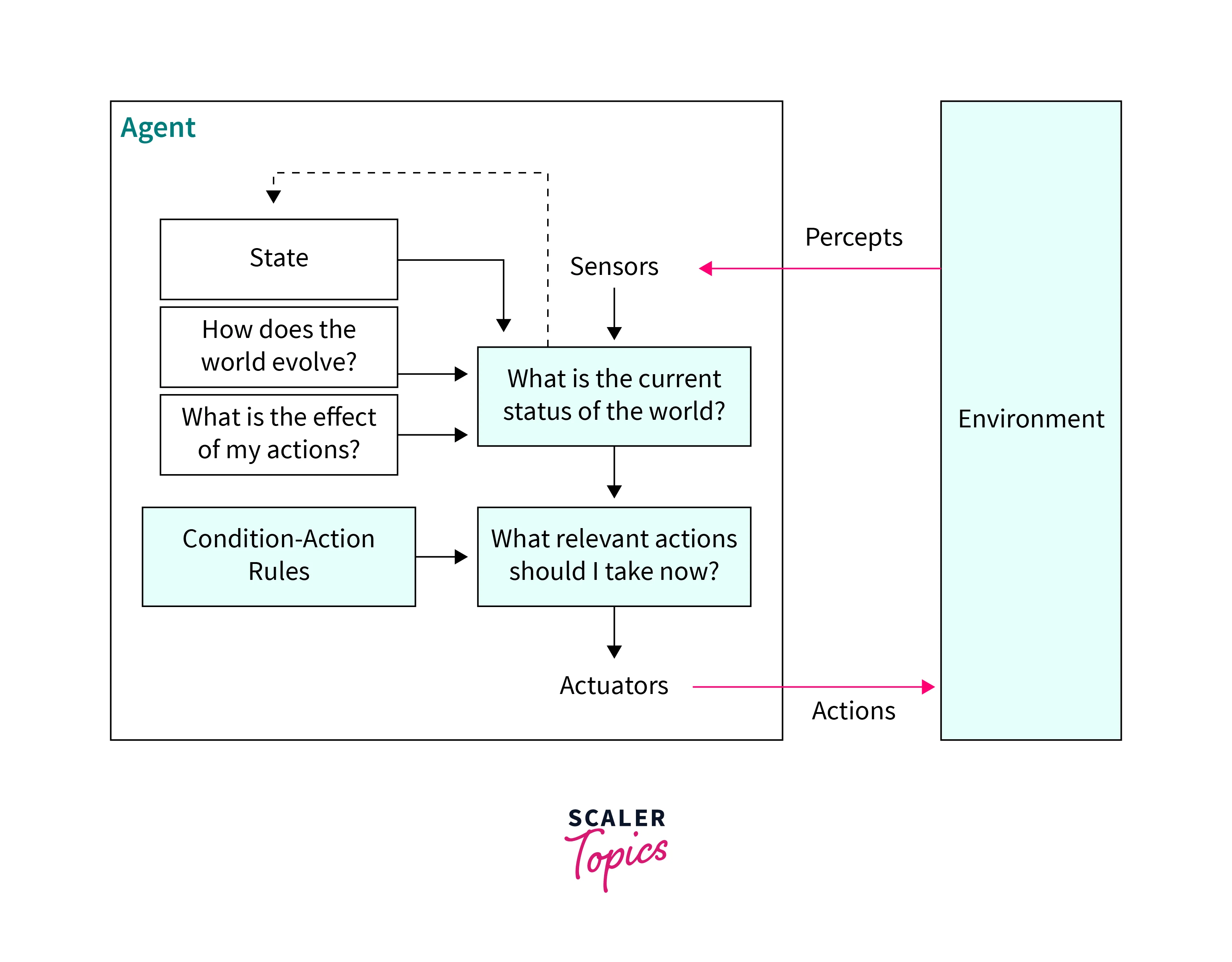
A model-based agent has two essential factors:
- Model:
It works by finding a rule whose condition matches the current situation. The model has some inbuilt history and information regarding the environment. These types of agents in AI can use more than one condition-related action based on the model. A model-based agent can perform in partially observable environments. - Internal state:
The agent has to be aware of the internal state, which is registered and recorded by each present and past percept. The present state is stored inside the agent, a typical structure describing the unseen part of the environment. For updating the internal state, it is essential to have information about how the world evolves on its own regardless of the agent and further how the actions of the agent will affect the world.
-
Goal-based agents:
They are trained to achieve a particular goal based on a previous set program with specific inputs like images, diagrams, or maps that help them reach the expected goal. Searching and planning are additional tasks that need to be performed by these types of agents in AI to reach the goal that is the required outcome. A sorting robot will separate and put a particular part in its designated bin. Similarly, a searching agent can suggest a proper surgeon from an available pool of expert surgeons for a specific surgery needed by a patient.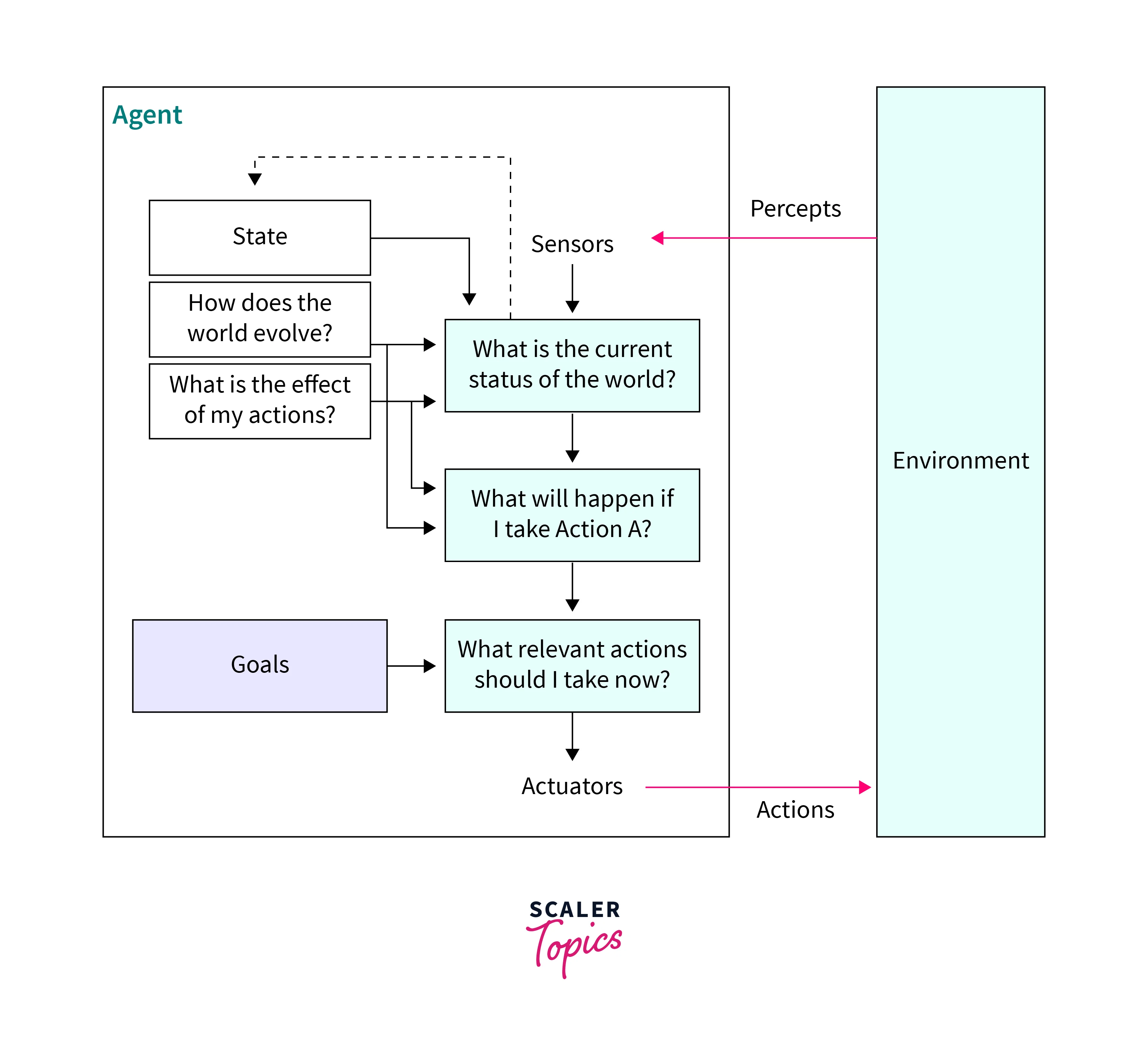
-
Utility-based agents:
These types of agents in AI are like goal-based agents but have the additional capability to try options for better performance. Here the focus is on acquiring a happy state by taking action. They can try different options one at a time and prefer the one that results in an accurate outcome. For example, in a navigation program, to find the path of the shortest distance to reach a particular destination from your starting point, it can choose an alternative option. If the utility is not going to achieve happiness, another better option will be selected, and so on.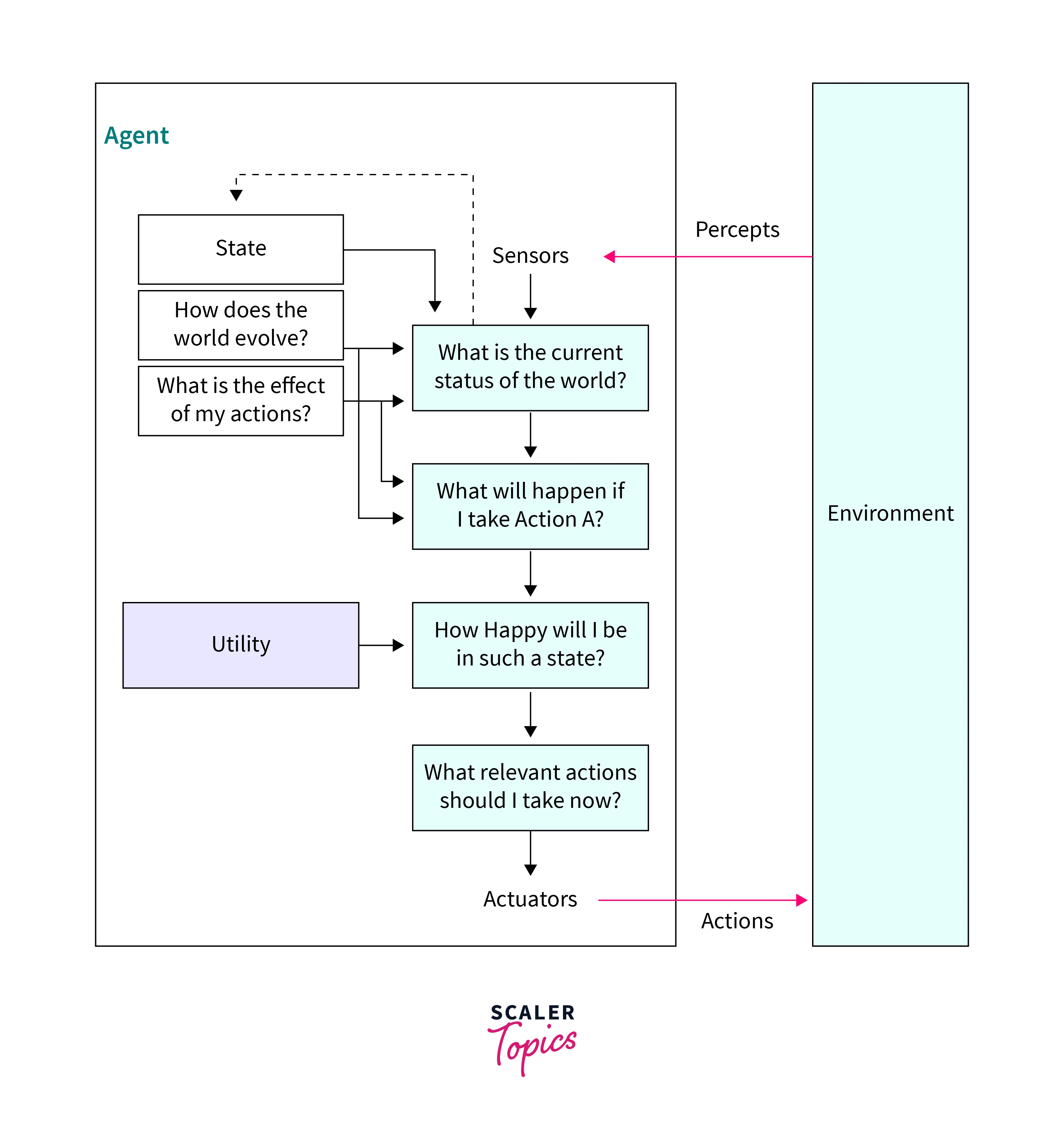
-
Learning agents:
These are advanced types of agents in AI who can learn new options to improve performance by avoiding unwanted things based on current and previous experiences. It adds percepts to the internal state of earlier unseen observations of the environment, which become useful in the future. Hence research and planning are additional responsibilities of this agent. For example, an autonomous car can avoid traffic jam routes or automatically change controlling parameters like speed, cabin temperature, etc., by using the internal state and adding some new percepts to it through learning.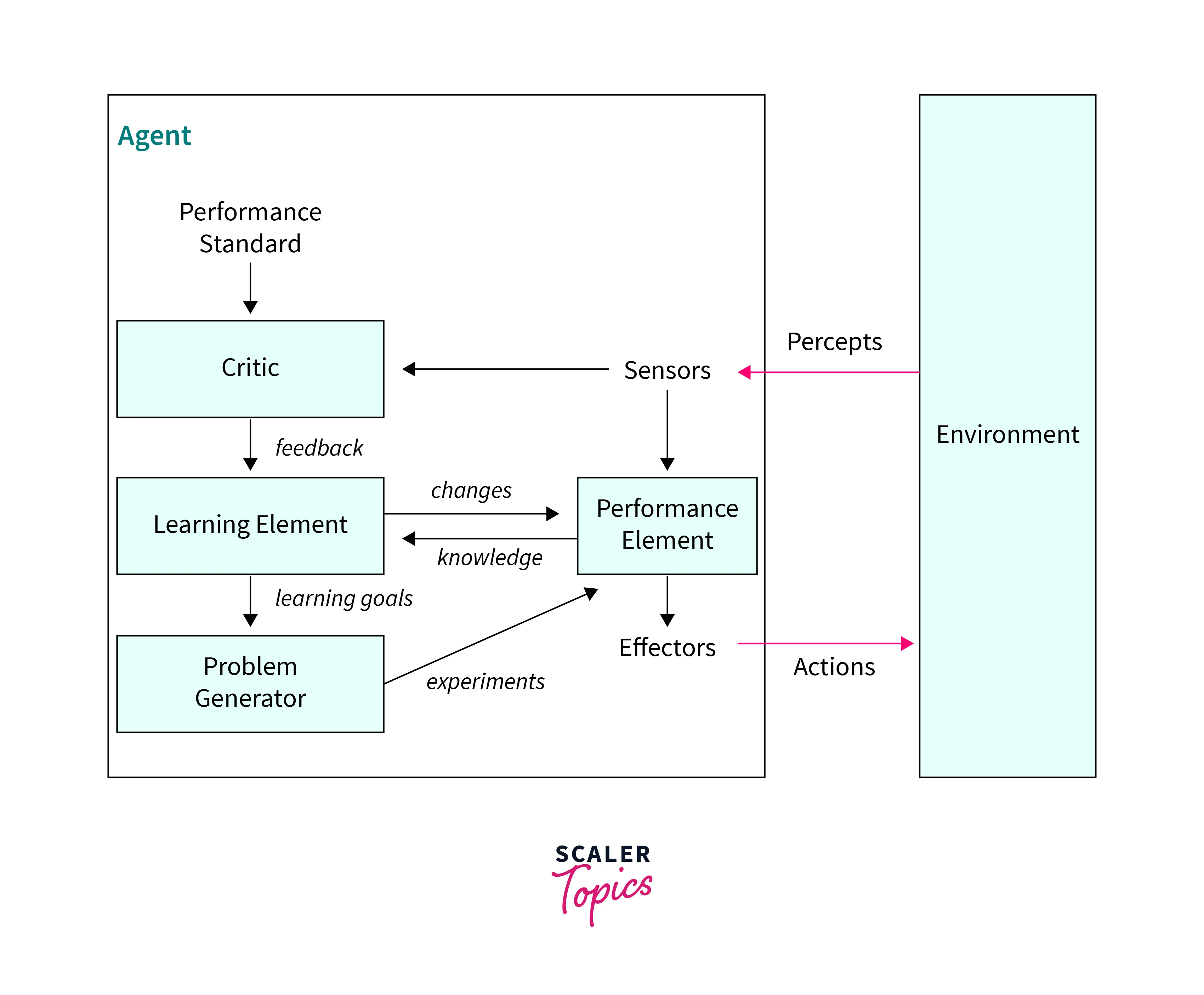
A learning agent comprises four main components which contribute to overall learning.
a. Learning element:
This is the main element of a learning agent. It helps itself with the feedback obtained from the critic element. It also observes the performance and compares it with the performance standard. Overall, coordinating all elements of this agent to learn and improve performance is the responsibility of the learning element.
b. Critic:
This element gives proper feedback to the learning element about the actions taken by the performance unit against set standards and their effectiveness. It can help the learning element to make necessary alterations in the internal state for better performance.
c. Performance element:
This unit takes actual external actions bringing changes in the environment through the actuators. The learning unit can ask to modify the actions of the performing element as per feedback from the critic element. Hence this element is vital in designing and modifying the learning element.
d. Problem Generator:
Actually speaking, it does not generate problems but provides new situations for the agent to gain more information from the external environment. It exposes the learning element to add a more useful set of instructions to the elements and helps learn better.
Conclusion
To summarize:
- It is essential to understand the various types of agents in AI for developing intelligent systems capable of handling challenging tasks.
- We discussed five types of AI agents- simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents.
- Each AI agent discussed in the article has particular elements that make it suitable for specific applications.
- A final takeaway from this article is we need to carefully select the appropriate type of agent based on its capabilities for achieving the best results.
