Attributes in DBMS

In a relational database, attributes are the characteristic properties that collectively define an entity. The attributes are further categorized into six different types: Composite attribute, Atomic attribute, Single valued attribute, Multi-valued Attribute, Stored and Complex Attribute.
What are the Attributes in DBMS?
In the relational database, attributes are the characteristic properties that define all the items belonging to a specific category applied to every column cell. We can think of attributes as the values that are used to describe a specific member or attribute as a column in an entity table.
Suppose we have several students in a class; we can uniquely identify a student by the properties associated with a student, like a student roll number, name, branch, age, etc. These properties that describe an entity are attributes for students.
Example
Take a look at the following database table "student" when students' information is stored.
| student_id | student_age | student_name | student_branch |
|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | 21 | Aryan | Civil Engeneering |
| 102 | 22 | Eshaan | Electonics and Communication Engineering |
| 103 | 24 | Divyansh | Computer Science Engineering |
| 104 | 21 | Vaibhav Singh | Chemical Engineering |
Here, to store information about every student, we are storing his name, id, age, and branch of each student in four columns. The properties of student that are student_id, student_age, student_name, and student_name are the attributes for the student.
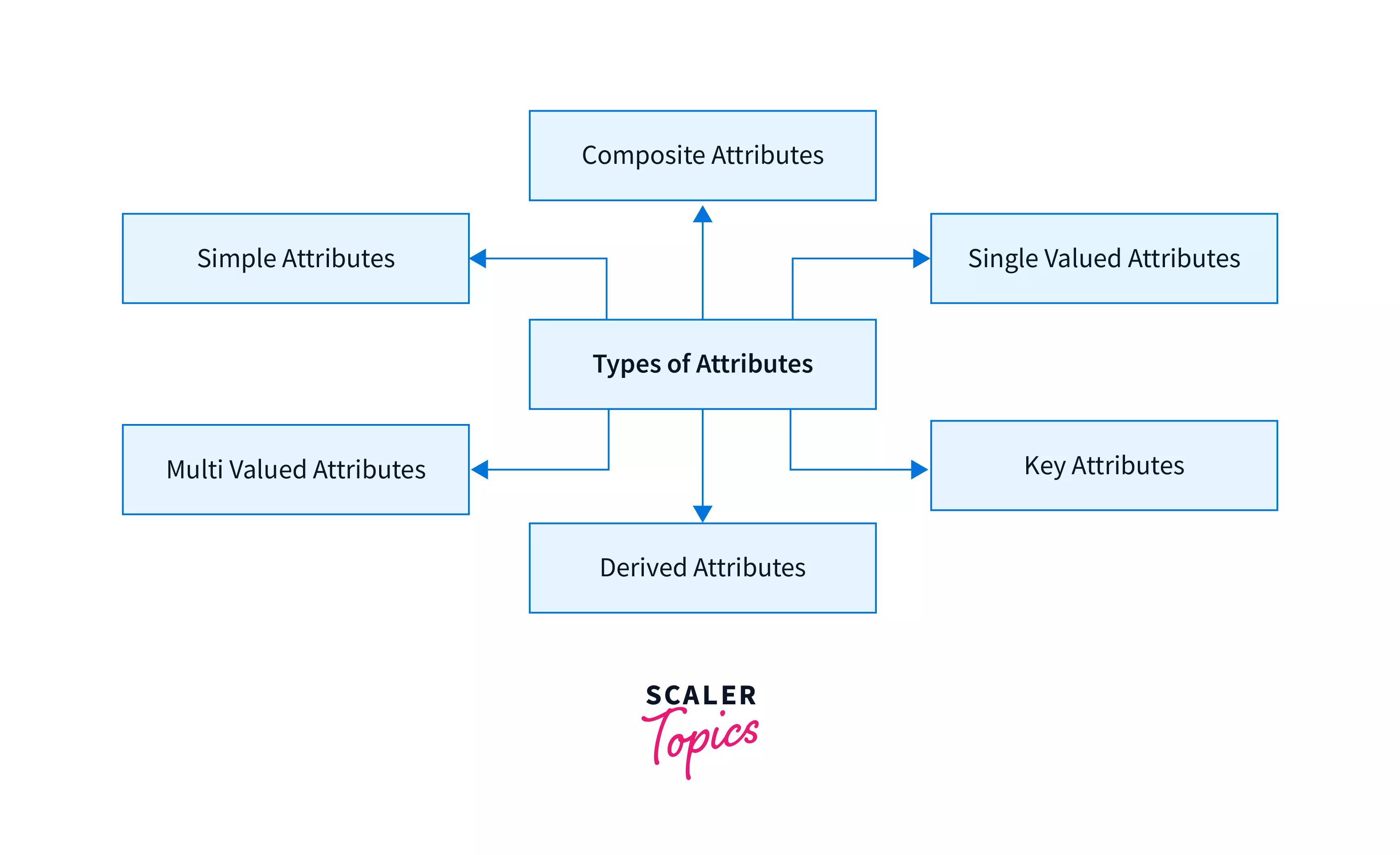
Types of attributes in DBMS
There are six different types of attributes in DBMS.
Let us discuss each of them briefly-
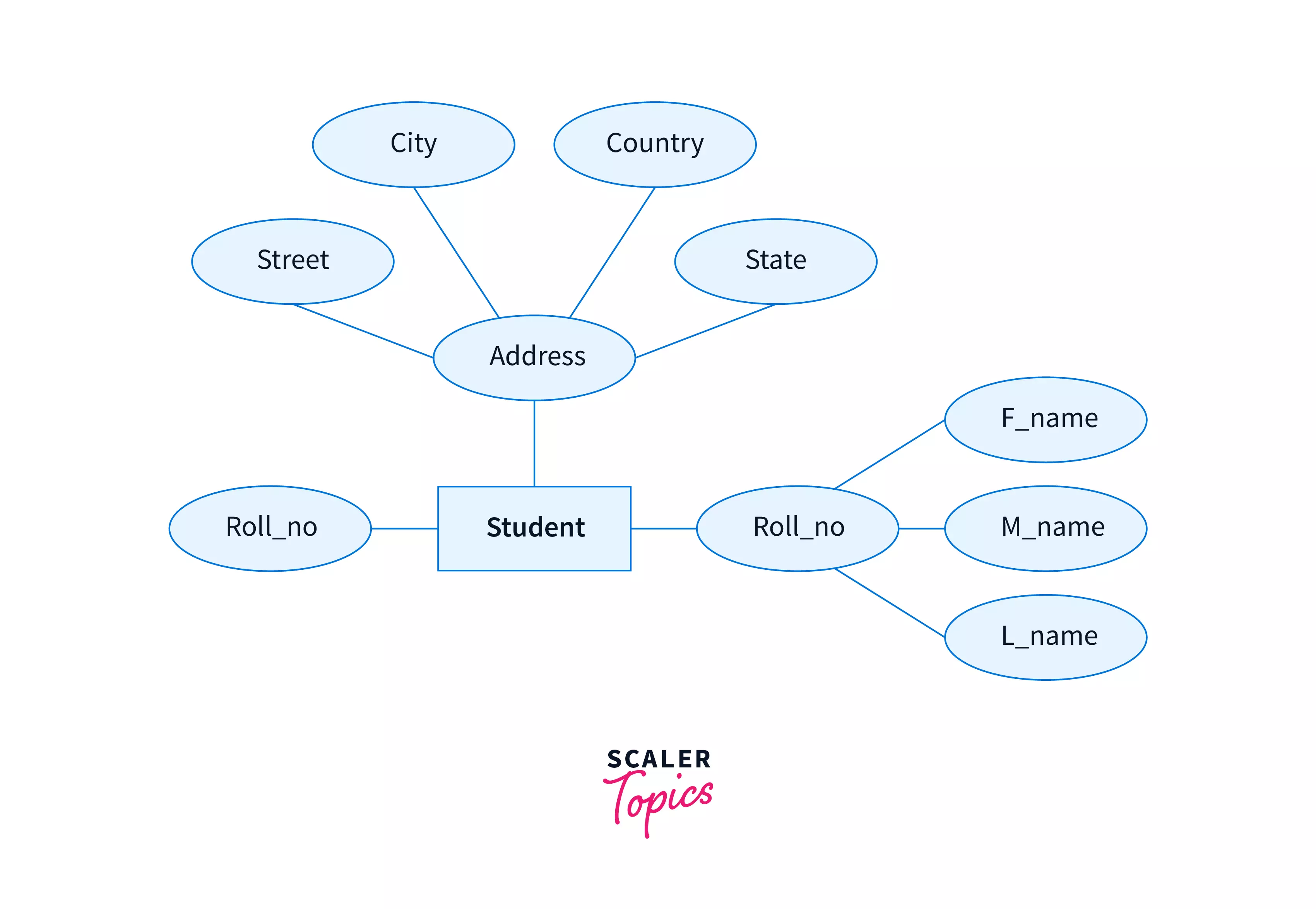
Composite Attribute
As the name suggests, those attributes composed of many other simple attributes are called composite attributes in DBMS.
Properties like student_name can be further divided into sub-parts like first_name, middle_name, and last_name where each sub-part can form an independent attribute. Similarly, address property can be composed of state, city, country etc.
Simple/Atomic Attribute
Such attributes that cannot be further subdivided into several attributes are called simple attributes. For example, attributes like the current class and branch of a student have an absolute value, and they cannot be further sub-divided into other parts like we divided full_name into first_name, middle_name, and last_name.
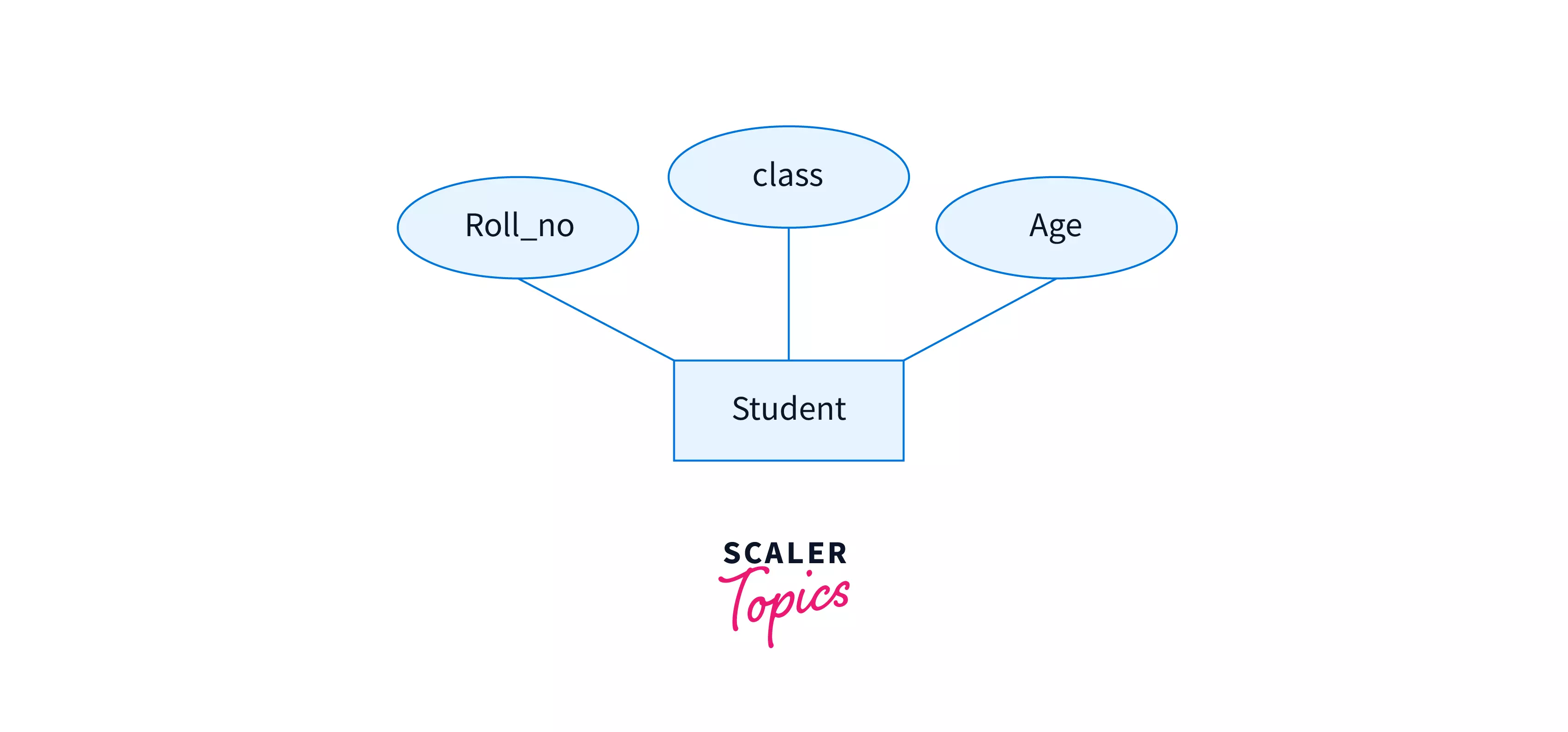
Single-valued Attribute
Single-valued attributes are properties that have a single particular value for a particular entity. This means that single-valued attributes don't have more than one value for an item.
For example, attributes like age, roll number, and gender associated with the student can only have a single value for an individual student.
Multi-valued Attribute
Attributes that can have multiple sets of values for a single entity are known as Multi-valued attributes. They are enclosed inside double bounded ovals in the ER diagram (ER diagram stands for entity relation diagram that displays the relationship of entity sets stored in a database.)
For example, attributes like phone_number, email_id, and hobbies are categorized as multi-valued attributes because a single student in the class can have more than one phone number, email_id, and hobbies.
Here, a single student Eshaan in the database, has a set of different hobbies mentioned above, and hence hobbies is a multi-valued attribute for the students.

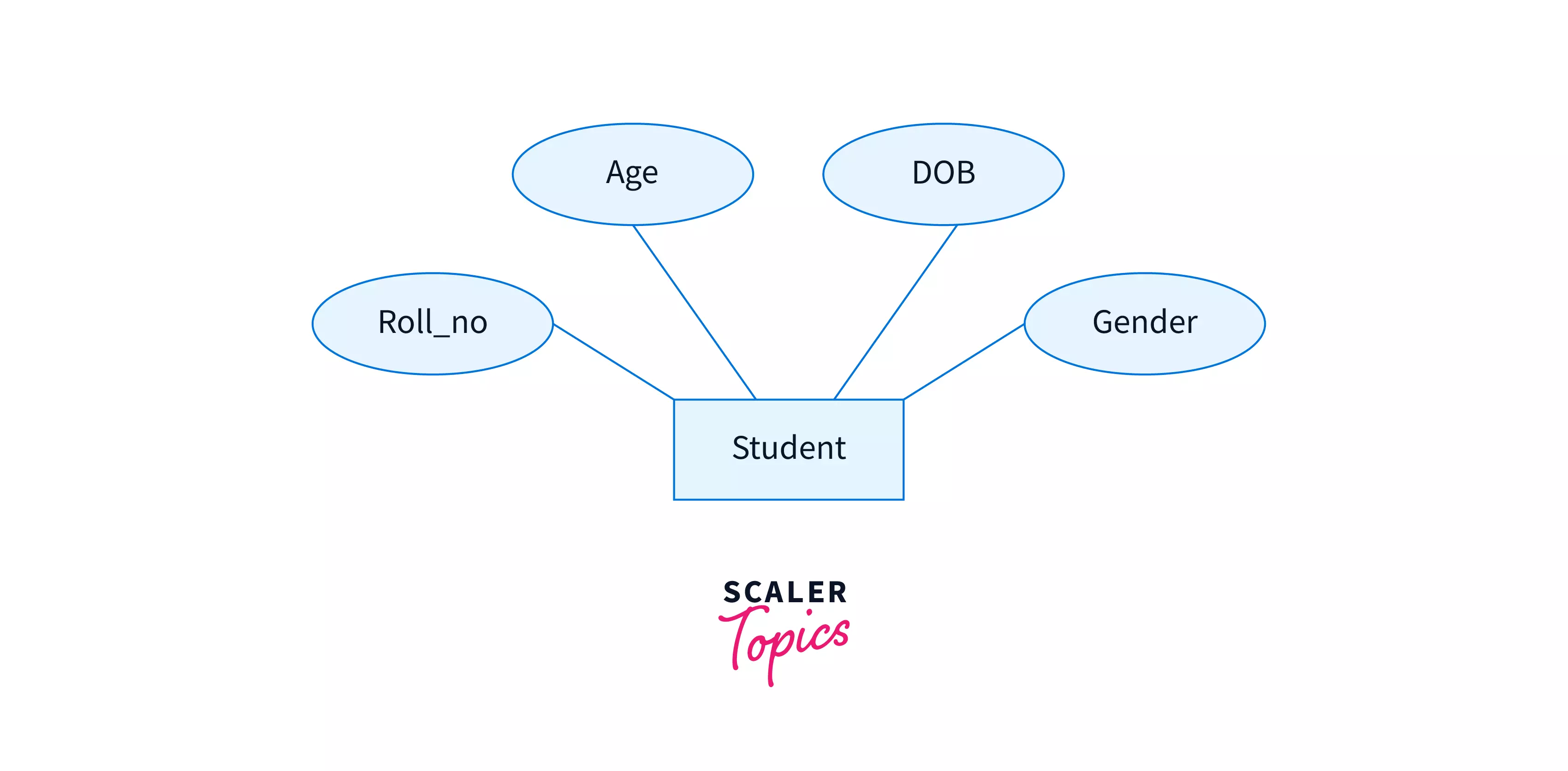
Derived/Stored Attributes
Such attributes whose value can be derived from other attributes of the entity are called derived attributes in DBMS. Valued stored in derived attributes can be obtained from processing other attributes.
For example, properties like age of a student can easily be obtained by subtracting the current day from the date of birth attribute of the student entity. So, age is a derived attribute in the student table.
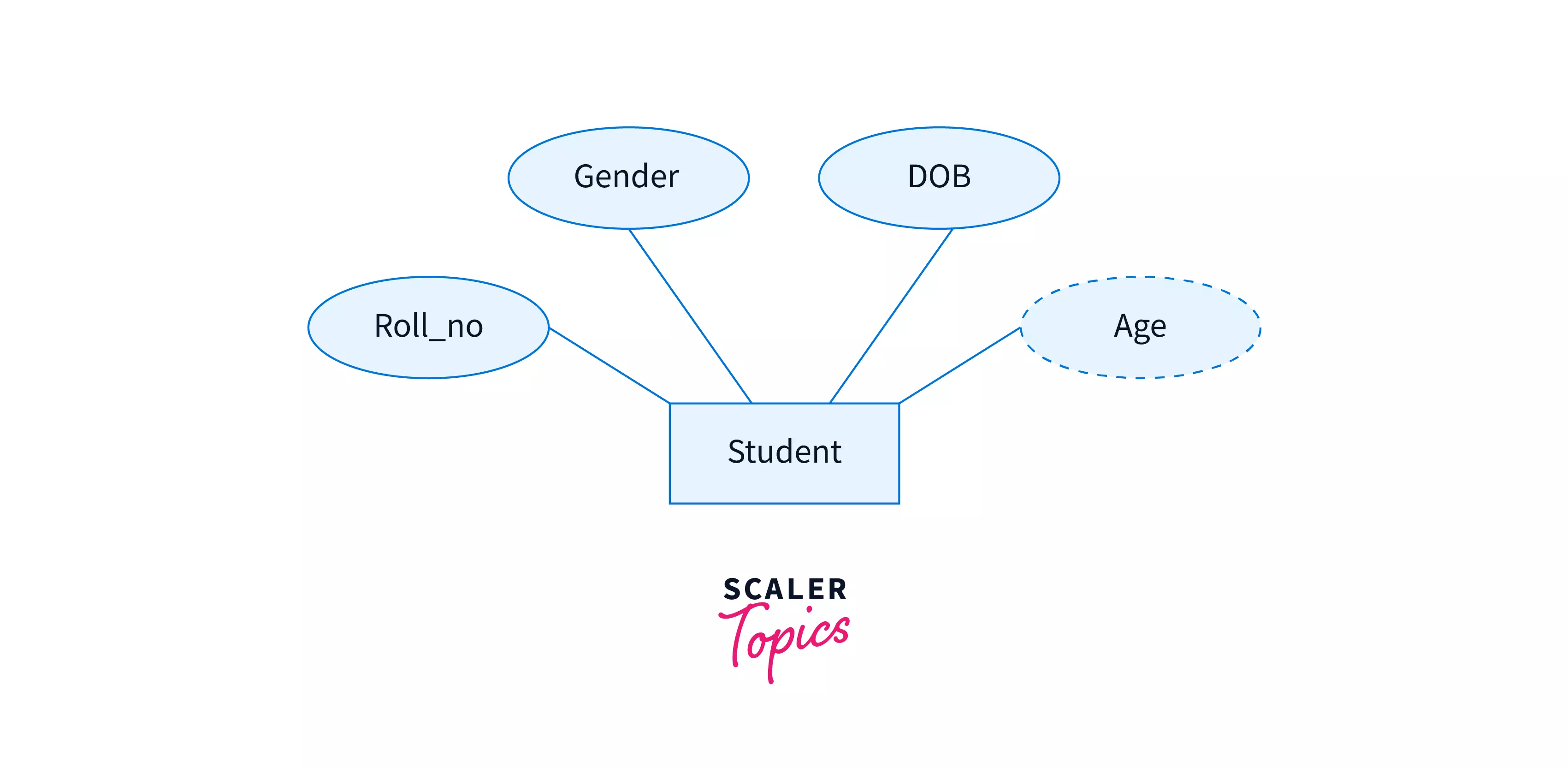
Note: Derived attributes are marked using dotted boundaries.
Complex Attribute
Nesting multi-valued and composite attributes together form a complex attribute. Complex attributes are formed by arbitrarily nesting the composite and multi-valued attributes.
For example, a person owns more than one house, and each house has more than one phone number. Then, the attribute phone is represented as a complex attribute.
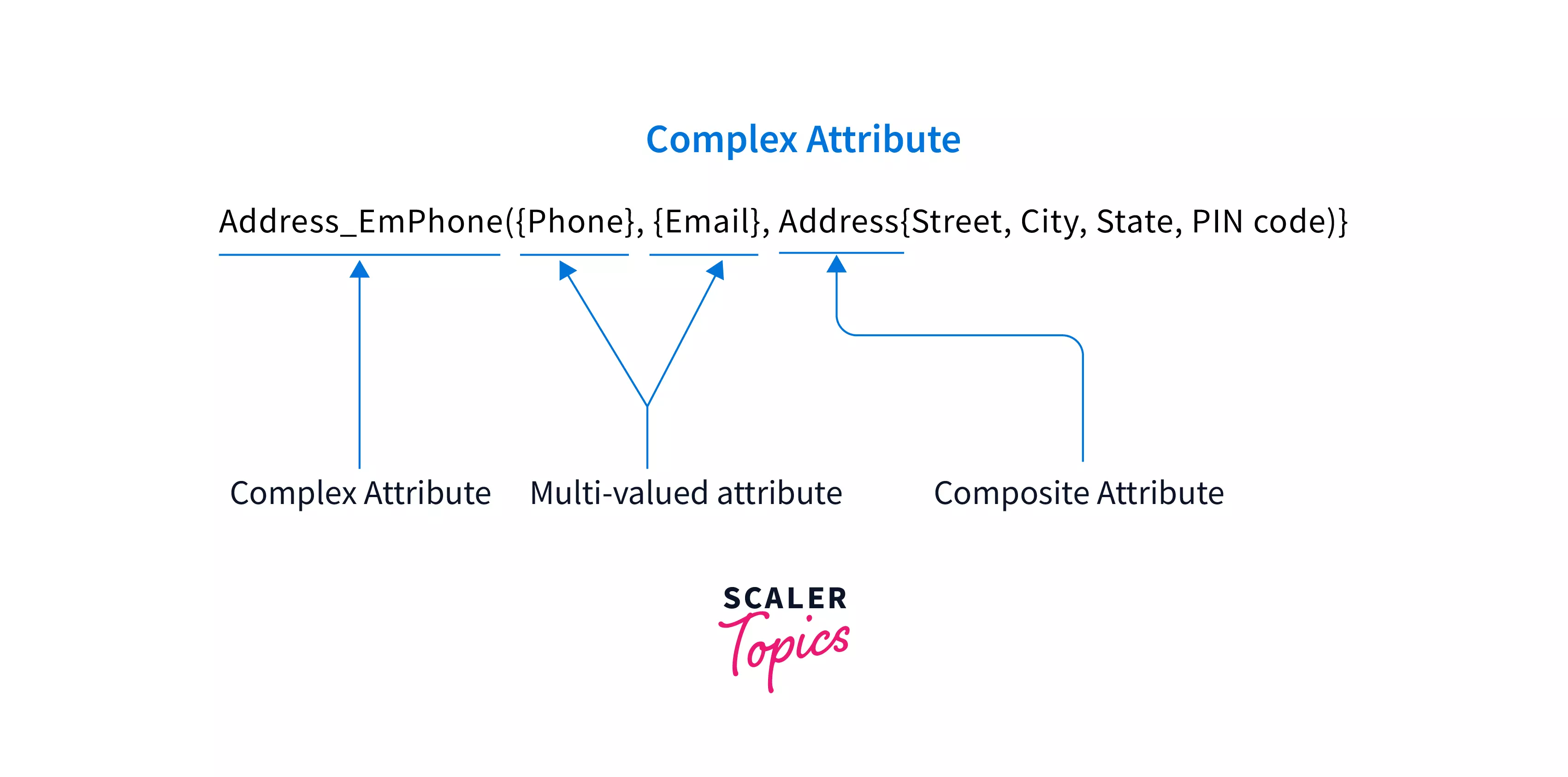
Here, in the above image, the attribute Address_EmPhone is used to store the email, phone number, and address of the employee. We are enclosing multi-valued attributes inside braces {} and composite attributes inside parentheses ().
Conclusion
- Attributes are the characteristic properties that collectively define an entity. We can also think of attributes as the values that are used to describe a specific member or attribute as a column in an entity table.
- Attributes are categorized into six different types -
- Composite attribute: Attribute composed of more than one simple attribute.
- Atomic attribute: Attributes that cannot be further subdivided.
- Single valued attribute: Such attributes don't have more than one value for an item.
- Multi-valued attribute: These attributes have multiple sets of values for a single entity.
- Derived attribute: Values of these attributes can be derived from other entity attributes.
- Complex attribute: Nesting multi-valued and composite attributes form complex attributes.
