AWS Backup
Overview
AWS Backup is a data protection solution that uses AWS services and hybrid workloads to consolidate and automate data protection. AWS Backup is a low-cost, fully managed, policy-based solution for scalability in data protection.
What is AWS Backup?
It is simple to consolidate and automate data protection across AWS services, in the cloud, and on-premises with the help of AWS Backup, a fully-managed solution. With this service, you can manage backup procedures and track your AWS resources activity. It eliminates the requirement for writing unique scripts and manual procedures by enabling you to automate and combine backup actions previously carried out service-by-service. Your data protection schedules and policies can be automated with a few mouse clicks in the AWS Backup dashboard.
AWS Backup does not govern the backups you do in your AWS environment outside AWS Backup. So, start utilizing AWS Backup right away if you want a consolidated, all-encompassing solution for business and regulatory compliance requirements.
How Does AWS Backup Work?
AWS Backup allows you to build backup rules known as backup plans. These plans can describe your backup needs, such as how frequently you should back up your data and how long you should keep those backups.
By simply labeling your AWS resources, you can apply backup plans to them. AWS Backup automatically backs up your resources based on the backup schedule you choose.
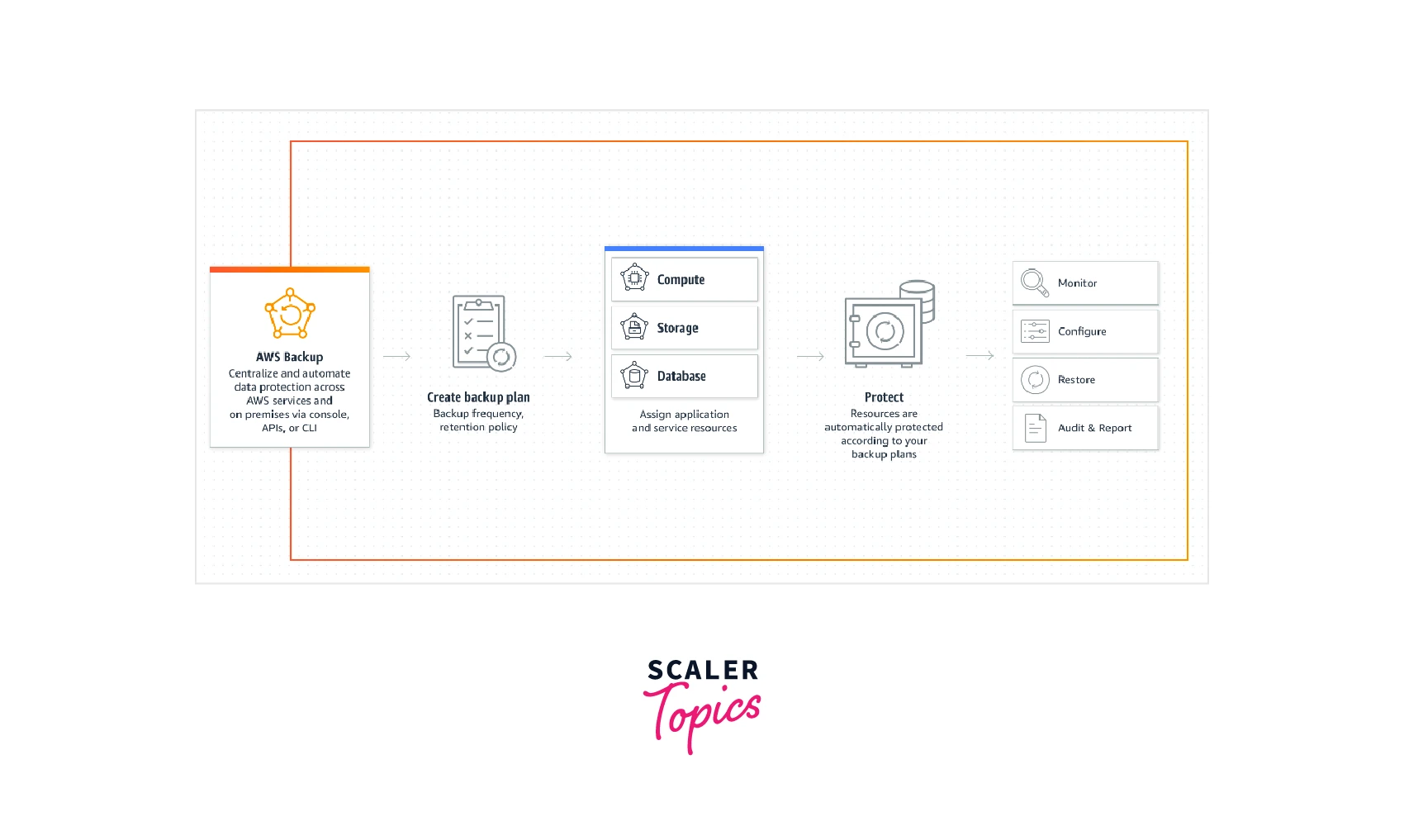
You can create a backup of various applications related to computation, storage, databases, etc. AWS Backup helps you easily create a backup plan and use multiple protection methods.
AWS Backup Features
Numerous services and capabilities are offered by AWS Backup, including:
-
Centralized Backup Administration AWS Backup provides a centralized backup panel, a set of backup APIs, and the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) to manage backups across the AWS services that your applications utilize. With AWS Backup, you centrally control backup rules that satisfy your backup needs. Then, you can use them to back up your application data consistently and legally across all of your AWS resources and services.
-
Back Up Based on Policy You can build backup plans, sometimes referred to as backup policies, using AWS Backup. Apply these backup plans to the AWS resources you want to protect across the AWS services you use after using them to specify your backup requirements. You might develop different backup plans that adhere to particular legal and corporate compliance standards. This makes it possible to guarantee that your needs back up each AWS resource. A scalable implementation of your backup strategy across your company and applications is made simple by backup plans.
-
Backup Procedures Based on Tags Your AWS resources can be applied to backup plans in various ways, including labeling using AWS Backup. Using tags, you can ensure that all of your AWS resources are backed up and protected while making it simpler to deploy your backup plan across your apps. Your AWS resources can be arranged and categorized beautifully using AWS tags.
-
Policies for Lifecycle Management By storing backups in a cheap cold storage tier, AWS Backup helps you to meet compliance requirements while reducing backup storage expenses (backups to cold storage are full backups). According to the timetable, you can automatically establish lifecycle policies to move backups from warm to cold storage.
-
Account-to-Account Backup and Administration All of the AWS accounts inside of your AWS Organizations hierarchy can have their backups managed using AWS Backup. Cross-account management enables you to automatically apply backup policies to backup plans across your company's AWS accounts. As a result, operational overhead is decreased while compliance and data protection become scalable. Additionally, it aids in preventing manual replication of backup plans across many accounts.
-
Continual Backups Your routine backups are efficiently incrementally stored via AWS Backup. A complete copy of your data is backed up on the initial backup of an AWS resource. Your AWS resources are only changed for each subsequent incremental backup. You can benefit from frequent backups' data protection and lower storage costs by using incremental backups (backups to cold storage are full backups).
-
Maintenance of All AWS Backups Some resource types fully support AWS Backup management. The advantages of comprehensive AWS Backup management include: Unbiased encryption Instead of utilizing the same encryption key as the source resource, AWS Backup encrypts your backups automatically using the KMS key of your AWS Backup vault. This adds to the already present layers of defense.
-
Put Backup Vaults for Your Data in Place. Each backup created by AWS Backup has immutable content, which means it cannot be changed. AWS Backup further secures your backups by being safely separated from their source instances in backup vaults. For example, even if you destroy the source Amazon EC2 instance and Amazon EBS volumes, your vault will continue to store your Amazon EC2 and Amazon EBS backups following your select life policy.
Getting Started with AWS Backup
For AWS resources like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances, Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes, Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) databases, Amazon DynamoDB tables, Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) file systems, Amazon FSx file systems, and AWS Storage Gateway volumes, AWS Backup makes it simple to centrally configure backup policies and monitor backup activity.
- Get Started with AWS Backup To start with AWS Backup, sign in to your AWS account, and launch the AWS Backup console.
- Make a Backup Strategy A backup strategy establishes guidelines, including how regularly to back up your resources and how long to keep backups on hand.
- Assign Resources to AWS As soon as you assign resources to backup plans, AWS Backup will begin backing up those resources automatically and handling backup retention on your behalf.
- Monitor, Alter, and Restore After backing up your resources, you can check, edit, or restore your backups.
1: Service Opt-in
- Open the AWS Backup console at here after logging into the AWS Management Console.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Settings.
- Under service opt-in, choose Configure resources.
- Opt into all AWS Backup-supported Resources by moving all the toggles to the right.
- Choose Confirm.
2: Create an On-demand Backup
- Open the AWS Backup console at here after logging into the AWS Management Console.
- Select Create an on-demand backup under Protected resources from the navigation pane.
- Select the resource type you wish to backup on the Create on-demand backup page, such as DynamoDB for Amazon DynamoDB tables.
- Choose the resource's name (or) ID if you wish to protect it. Make sure the resource you select is what you need.
- Make sure that Create backup immediately is chosen. Doing this allows you to view your stored resource on the Protected resources page, and a backup is started immediately.
- Include an expiry value and a transition to cold storage value (if necessary).
- Decide on a current backup vault. After you select Create a new backup vault, a new page to create a vault appears, and when you are done, you are sent back to the Create on-demand backup page.
- Select the Default role from the list of IAM roles.
- Enter a key and an optional value before selecting and Adding a tag to tag your on-demand backup with one (or) more tags.
- Decide whether to build an on-demand backup. This leads you to the Jobs page, which features a list of available positions.
- The Advanced backup options section will show if your resource type is EC2. If your EC2 instance is running Windows, pick Windows VSS. Thanks to this, you may now make Windows VSS backups that are application-consistent.
- To view the specifics of the task, choose the Backup job ID for the resource you selected to back up.
3: Create a Scheduled Backup
- Open the AWS Backup console at here after logging into the AWS Management Console.
- Select Manage Backup plans from the dashboard. Alternately, select Backup plans from the navigation pane and then select Create a Backup plan.
- Starting with the template, select a plan from the list and type a name into the Backup plan name box.
- Select the desired backup rule on the plan summary screen, then click edit.
- Examine and select the values you wish to use for your rule. For instance, you may change the Monthly rule's one-year backup retention term to three years. If your strategy calls for Amazon EFS backups, you may automatically set up lifecycle rules to move these backups from your plan to Amazon EFS.
- To build a new backup vault, select Create a new Backup vault or Default for the backup vault.
- Select the Save Backup rule when you have completed modifying the rule.
4: Create Amazon EFS Automatic Backups
- Go to here to access the Amazon EFS interface.
- Select a file system on the file system to enable automatic backups.
- In the General settings panel, select edit.
- Select Enable automatic backups to activate automatic backups.
5. View Your Backup Jobs and Recovery Points Using AWS Backup
- Navigate to here to access the AWS Backup interface. Go to the dashboard option in the navigation pane.
- Choose Backup jobs information to see the status of your backup tasks. After clicking here, you may examine the backup and restoration jobs tables on the Backup jobs page.
- The jobs that are listed can be filtered by time. For instance, the number of jobs produced during the previous 24 hours, seven days, or 30 days. You may set the number by selecting the gear icon.
6: Restore a Backup
- Visit here to access the AWS Backup interface.
- Select Protected resources and the resource ID you want to restore from the navigation pane.
- Resource ID lists your recovery points and the resource type. To access the Resource information page, select a resource.
- To restore a resource, select the radio button next to its recovery point ID in the Backups window. Select Restore from the menu in the pane's top right corner.
- Set the settings for the restoration. The selected resource type is represented by the restoration parameters that are displayed.
- See Restoring a backup for advice on how to restore specific resources. Select Default role under Restore role.
7: Create an Audit Report
- Open the AWS Backup console at here after logging into the AWS Management Console.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Reports.
- Choose to Create a report plan.
- Select the Backup job report from the dropdown list.
- For the Report plan name, enter TestBackupJobReport.
- For File format, choose both CSV and JSON.
- For the S3 bucket name, select the destination for your reports from the dropdown list.
- Choose to Create a report plan.
8: Clean Up Resources
- Open the AWS Backup console at here
- In the navigation pane, choose Backup plans.
- On the Backup plans page, choose the backup plan you want to delete.
- To delete the resource assignments for your plan, choose the radio button next to the assignment name, and then select Delete.
- To delete the backup plan, choose to Delete in the page's upper-right corner.
- On the confirmation page, enter the plan name, and choose to Delete plan.
Benefits of AWS Backup
- Centralized Backup Management Create backup rules from a centralized console, streamlining backup administration and making it simple to guarantee application data's backup and protection across all AWS services.
- Streamline Backup Procedures. It assists customers in lowering costs and saving time by automating schedules and managing retention, minimizing the requirement for users to do self-service procedures. Users may utilize tags to apply backups, which allows them to efficiently back up all of the resources required by the apps.
- Increase Backup Compliance Users can simply back up their essential AWS resources via a single portal, protecting it from manual updation and assisting in meeting compliance needs. Amazon backup protects user data with robust encryption, which helps safeguard data from various attacks.
Use Cases
- Cloud-Native Backup AWS Backup offers a single platform for automating and managing backups across several services. It supports AWS S3, AWS Elastic Block Store, AWS Relational Database Service, AWS DynamoDB, AWS Neptune, AWS Elastic File System, AWS FSx, AWS Lustre, and Amazon Elastic Compute cloud. AWS Backup allows you to back up essential data stores like instances, files, databases, and various services mentioned above.
- Hybrid Data Protection Amazon Backup integrates data security and compliance management for your hybrid-environment applications. AWS Backup can safeguard on-premises VMware workloads and data held by Storage Gateway volumes. AWS Backup may automatically duplicate backups to many unique AWS Regions as part of a scheduled backup strategy (or) on demand. Cross-Region backup is useful if your business continuity (or) compliance requirements need backups to be held at least a specified distance away from production data.
Supported AWS Resources and Third-party Applications
You may use AWS Backup with AWS Organizations to configure, administer, and govern backup activity across your company's AWS accounts and resources by managing and deploying data protection policies. The following are some useful resources:
- AWS EC2 instances
- Windows Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) supported applications
- AWS EBS volumes
- AWS S3 buckets
- AWS RDS database
- AWS DynamoDB tables
- AWS Neptune databases
- AWS DocumentDB databases
- AWS EFS
- Amazon FSx
- AWS Storage Gateway volumes
- VMware workloads
AWS Backup Pricing
You only pay for the backup storage you utilize, the backup data moved between AWS Regions, the backup data you restore, and the number of backup assessments while using AWS Backup. There is no setup cost, and there is no minimum fee.
Pricing for AWS Backup Storage
The cost of backup storage is determined by how much storage space your backup data requires. Based on the typical storage space utilized during the month, a monthly storage fee is charged (billed as GB-Month).
Restore Pricing
The quantity of data recovered during the month determines the restored amount billed for the month. The total amount of data from all the backups restored in a month is measured in GB.
Pricing for Cross-Region Data Transfers
The amount of data transported between two Regions, whether inside a single AWS account (or) between two AWS accounts, is the cross-Region amount invoiced in a month. Data transfer charges apply when you move data outside of an AWS Region. Transfers within the same AWS Region are free. The AWS account that is sending the data will be charged for data transport, and the AWS account that is receiving the data will be charged for backup storage.
Cost of AWS Backup Audit Manager
AWS Backup Audit Manager offers predefined and customized restrictions to ensure that your backup conforms with your established regulations. The cost of AWS Backup Audit Manager is divided into two parts: fees for backup analyses and configuration items saved by AWS Config. With AWS Backup Audit Manager, there are no minimums or up-front obligations; you pay for what you use.
- Backup Assessments Backup assessments are incurred when a specific AWS resource, such as a backup vault or backup plan, is compared to a control.
- Items for Configuration Evaluations conducted by AWS Backup Audit Manager use configuration elements saved by AWS Config. These assessments need AWS Config, and AWS Backup Audit Manager setup items are billed individually. AWS Config keeps track of one configuration item for each backup evaluation. When modifications are made to the underlying backup resources, you will additionally be charged for configuration item recording (such as changes to backup plans or the creation of a recovery point.)
Conclusion
-
AWS Backup allows you to build backup rules known as backup plans, which can use to describe your backup needs, such as how frequently you should back up your data and how long you should keep those backups.
-
Using tags, you can ensure that all of your AWS resources are backed up and protected while making it simpler to deploy your backup plan across your apps.
-
Cross-account management enables you to automatically apply backup policies to backup plans across your company's AWS accounts, resulting in decreased operational overhead.
-
You can save time and money with the fully managed, policy-based solution from AWS Backup's automated backup scheduling, retention management, and lifecycle management features.
-
AWS Backup centralizes data protection management and compliance for your applications. AWS Backup can use to safeguard VMware workloads running on-premises and in VMware CloudTM on AWS.
-
You only pay for the backup storage you use, the backup data sent between AWS regions, the restored backup data, and the number of backup assessments.
