RDS Billing and Provisioning
Overview
The RDS (Amazon Relational Database Service) allows AWS customers to operate, manage, and scale their databases. RDS is a managed service that offers various instance sizes and types, seven database engines, and seven database engines for use with relational databases. In RDS Billing and Provisioning in AWS, You can pay according to the actual resource usage with the on-demand rates offered by AWS RDS pricing models. No minimum payment is required. The pricing structure for RDS Reserved Instances offers substantial savings in exchange for a long-term commitment.
How Does Amazon RDS Pricing Work?
The cost of Amazon RDS depends on a number of factors, such as the database region, database instance, database engine, and purchase type that you select (On-Demand or Reserved Instance).
Deployment type, Additional Storage, Outbound Data Transfers, DB Instances, and also the other aspects that affect the cost of Amazon RDS. However, you only pay for the relational DB resources including data transfer, operations, storage, and hosting that you use during your Amazon RDS billing period.
Based on the following components Amazon RDS instances are billed in RDS Billing and Provisioning in AWS:
1. Amazon RDS Free Tier
The AWS RDS Free Tier offers the following resources on a monthly basis. 20 GB of SSD storage for your database and an additional 20 GB for database backups or snapshots are both included in the free tier. As part of the Free Tier, the database service, compute instance, and storage are all provided without charge.
A single Availability Zone (AZ) of the db.t2.micro instances, running any open source database engine, SQL Server Express, or Oracle Bring Your Own License, is available for 750 hours per month.
2. Amazon RDS Pricing By Database Engine
Seven different relational database engines are supported by Amazon RDS: MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server. Amazon Aurora and Amazon Aurora with PostgreSQL compatibility are also supported. Amazon RDS can also be installed on OutPosts (on-premises).
Amazon Aurora is AWS’s proprietary relational DB, provides high availability at scale. It can help you save money when dealing with intermittent usage or when you require quick failovers and numerous read replicas. It is compatible with both PostgreSQL and MySQL databases.
In RDS Billing and Provisioning in AWS, When using provisioned Aurora, selecting On-Demand Instances enables hourly billing. No long-term commitments. zero upfront costs.
Aurora storage is billed by Amazon RDS in GB-monthly increments and I/Os usage in increments of one million requests. Neither storage nor I/O require any prior provisioning. Both of them scale automatically.
Open-Source Databases
The cost of provisioned I/O, RDS data transfer fees, and storage for MySQL, Postgres, and MariaDB open-source databases is comparable to one another. The only distinction is that PostgreSQL instances are typically between 5 and 10 percent more expensive per hour.
Proprietary Databases
An exclusive database provided by AWS is called Amazon Aurora. It has a number of features, such as serverless option and Multi-zone backup.
Using features like Data Transfers, Backtrack, Snapshot Export Global Database, and out of Aurora attract additional charges. You can save more money by selecting Reserved Instances (committed use for 1 or 3 years). Instead, choosing Aurora Serverless enables you to pay for the capacity that you actually use while automatically scaling capacity up and down as needed by your application.
3. Amazon RDS Pricing By Database Instance
Following engine selection, you will select an RDS instance type and size with the required amount of memory (GiB RAM) and compute (vCPU) for your workload with an appropriate networking capacity (Mbps).
From db.m5.24xlarge( with 96 vCPUS, 384 GiB RAM, and does 19,000 Mbps) to db.t3.micro (which has 2 vCPUS, 1 GiB RAM, and supports 2085 Mbps), Amazon RDS offers a range of instances.
4. Amazon RDS Pricing By Database Region
A database instance may be deployed in various Availability Zones (Multi-AZ deployment). In this case, RDS automatically creates and runs backup database instances in a different Availability Zone. These secondary DB instances are located in different AZs and replicate the primary DB instance across them.
Each Availability Zone (AZ) in an Amazon Region has its own set of pricing options and supports failure isolation. Regardless of your choice of DB engine, instance type, payment option, storage, etc., you must always select a region, an AZ, or a local zone in order to calculate RDS costs.
In addition to backing up the system, this offers lowers latency spikes, failover support, reduces I/O freezes, and data redundancy. Read traffic is also served by secondary DB instances in Multi-AZ DB cluster deployments.
5. Amazon RDS On-Demand Instance Pricing vs Amazon RDS Reserved Instance Pricing
On-Demand Instance Pricing
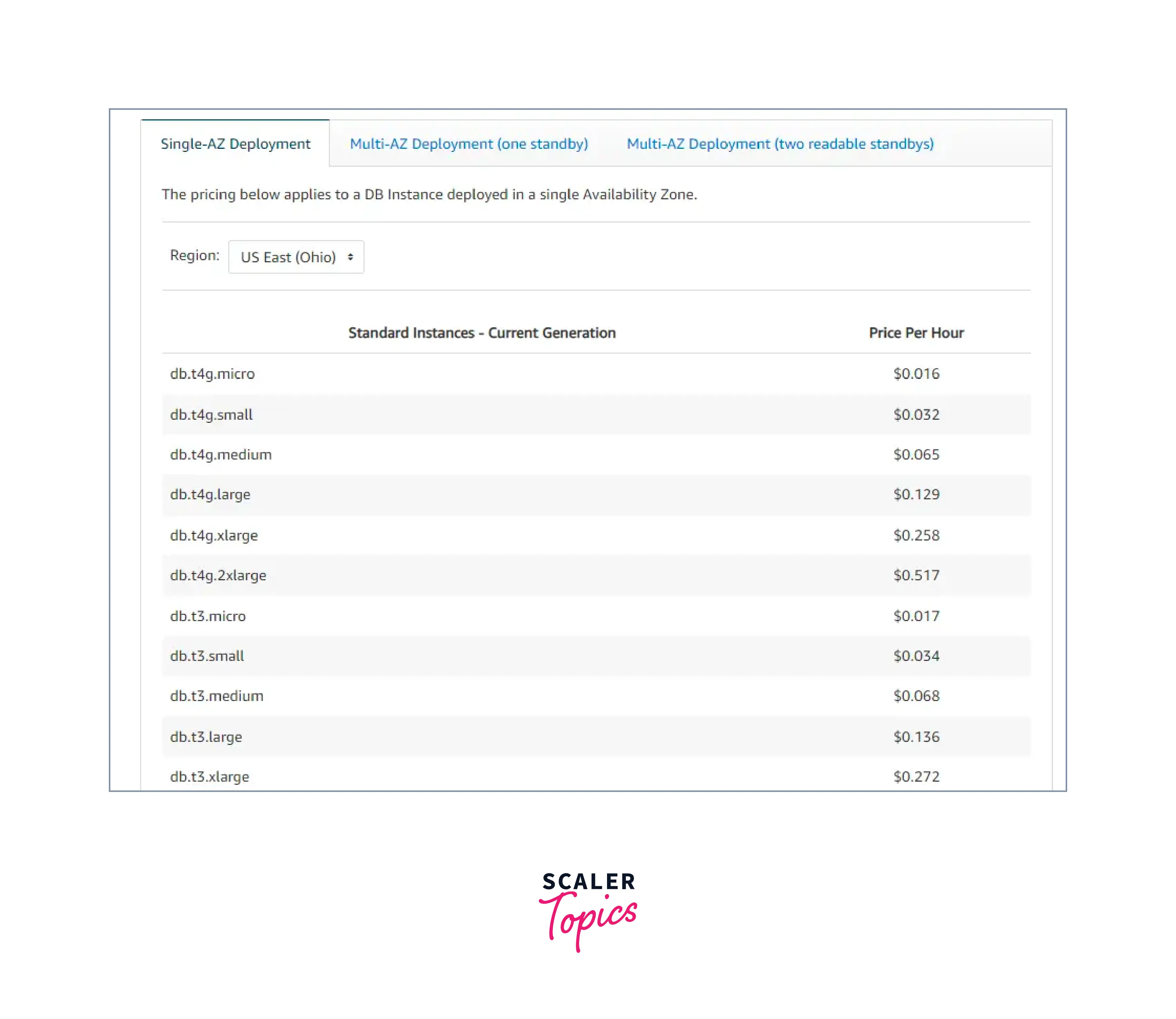
For the DB instance hours you use, you pay by the hour. Although bills are calculated down to the second and display times in decimal form, pricing is listed on an hourly basis. RDS usage is now billed in 10-minute blocks with 1-second increments.
The default billing method in RDS is On-Demand instance pricing by the hour of DB usage. No long-term commitments or upfront payments are necessary in this situation.
In RDS Billing and Provisioning in AWS, Pricing for Amazon RDS On-Demand instances by availability zone, instance size, and location is shown below:
Reserved Instance Pricing
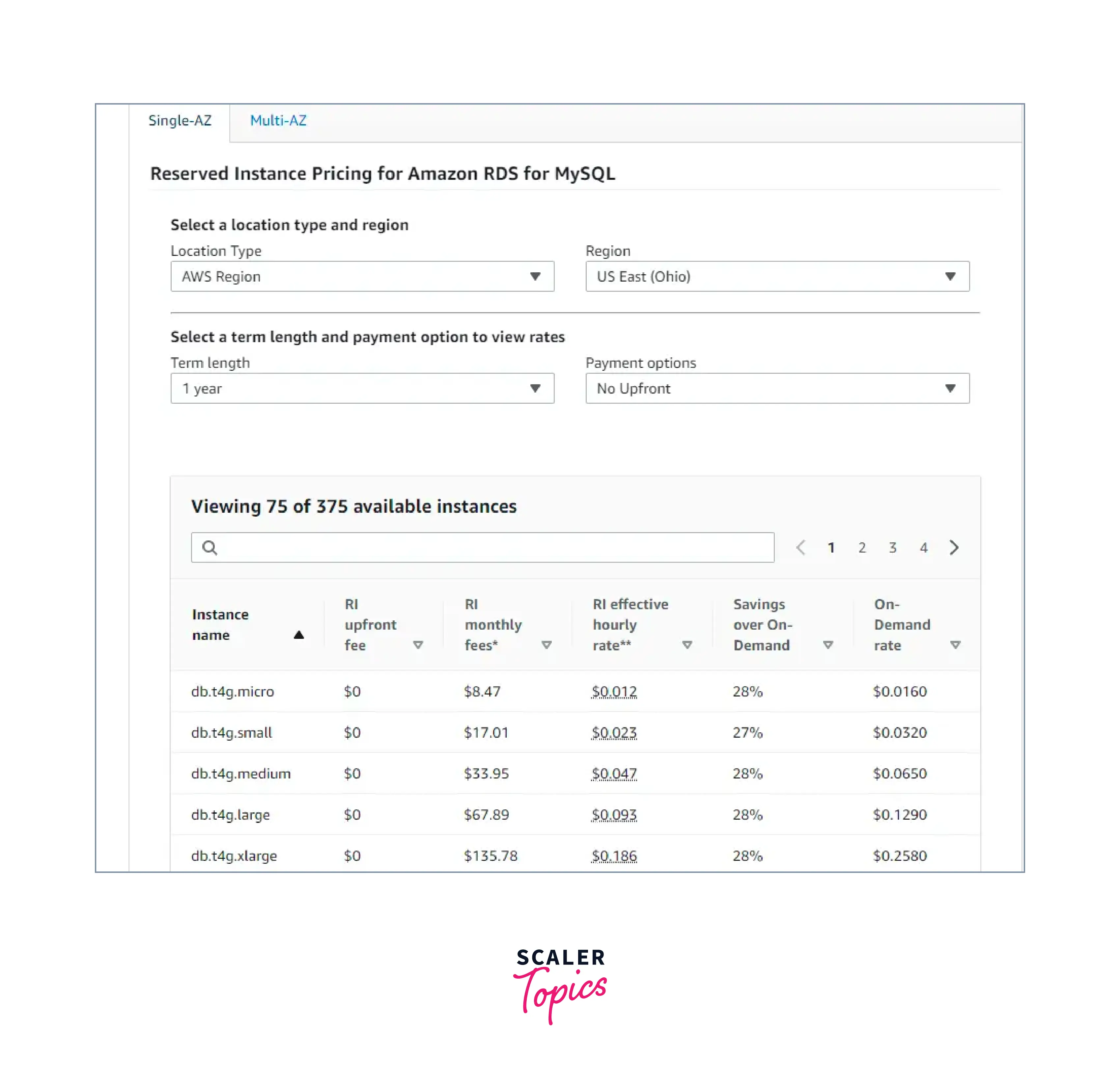
In comparison to the on-demand DB instance pricing, reserve a DB instance for one or three years and receive a sizable discount. You can use Reserved Instances to launch, delete, start, or stop multiple instances within an hour while still receiving the Reserved Instance benefit for each instance.
Here is an example of Pricing for a standard three-year term is:
- Partial Upfront Payment: 2.993 (effective hourly rate of $0.008).
- Full Upfront Payment: 0 a month (effective hourly rate of $0.008), and 53% less expensive than on-demand.
Pricing for a typical one-year term for a MySQL db.t3.micro Instance deployed within a single AZ in the US East region:
- No Upfront Payment: 0 KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '%' at position 59: …ervice costs 29%̲ less at8.76 per month ($0.012 effective hourly rate).
- Partial Upfront Payment: 50 4.161 (effective hourly rate of $0.011), and a 33% savings over on-demand.
- Full Upfront Payment: 98 per month (effective hourly rate of $0.011), and a 34% savings over on-demand.
6. Amazon RDS Pricing By DB Storage
In RDS, there are three different types of storage available and these choices affect how much you pay each month.
General Purpose (SSD) Storage
The general-purpose storage rate is $0.115/GB-month.
For a primary dataset, RDS offers a range of General Purpose (SSD) storage capacities from 20 GiB to 64 TiB. General Purpose (SSD) only charges for the storage you provide; no additional fees are assessed for I/Os used.
Provisioned IOPS (SSD) Storage
The provisioned IOPS rate is 0.125/GB-month.
RDS allows you to allocate I/O capacity in accordance with particular database needs. From 1,000 IOPS to 80,000 IOPS and 100 GiB to 64 TiB of storage can be scaled and provisioned.
Magnetic Storage
The I/O rate is 0.10/GB-month.
For the primary dataset of your account, RDS offers a selection of magnetic storage capacities ranging from 20 GiB to 3 TiB. For backward compatibility, this storage option is supported.
7. Additional Amazon RDS Pricing Factors
Data Transfer, Snapshot export, and Backups are subject to additional charges in RDS Billing and Provisioning in AWS.
-
Additional Backup Storage Fees: Additional costs for provisioned database storage are billed at $0.095 per GiB-month. Backup storage is the space connected to any active database snapshots you've taken as well as automated database backups.
-
Snapshot Export Pricing: In RDS, Snapshots pricing starts at $0.01/GB of snapshot size. Data from RDS or Aurora snapshots can be automatically exported to Amazon S3 in a Parquet format using RDS Snapshot Export. This format can unload up to twice as quickly. Compared to text formats, it uses almost six times less storage in Amazon S3. Additionally, it enables you to analyse exported data using AWS services like Amazon Athena, Amazon SageMaker, and Amazon EMR.
-
RDS Data Transfer Pricing: RDS data transfer cost only applies to data transfers made from RDS to the internet, not the other way around. For the first 10 TB per month, the tier-based pricing is $0.09 per GB. For 100GB each month, across all AWS locations, data transport out to the internet is free.
To know more about Amazon RDS Pricing, Please Click on This Link: https://aws.amazon.com/rds/pricing/
So, How Much Does Amazon RDS Cost?
In RDS Billing and Provisioning in AWS, The cost of RDS is affected by ten main factors:
Database engine, snapshot export option, instance type, backup option, instance size, payment option ( Reserved versus On-Demand Instance Pricing), Amazon region or availability zone, storage option, whether you use multiple AZs or one AZ, and whether you transfer data out of or into RDS are all factors to consider.
It can be difficult to obtain an accurate estimate, particularly if you haven't used Amazon RDS before. Even if you have, it is simple to ignore some cost centres because of the variety of pricing components.
How To Understand And Control RDS Costs?
RDS pricing must be measured precisely in order to be optimised. This calls for a system that can transform the information in your RDS bill into insights that are simple to understand, relevant, and useful.
CloudZero can be useful. Your RDS costs are mapped to the people, processes, and goods that produce them by CloudZero's cloud cost intelligence platform.
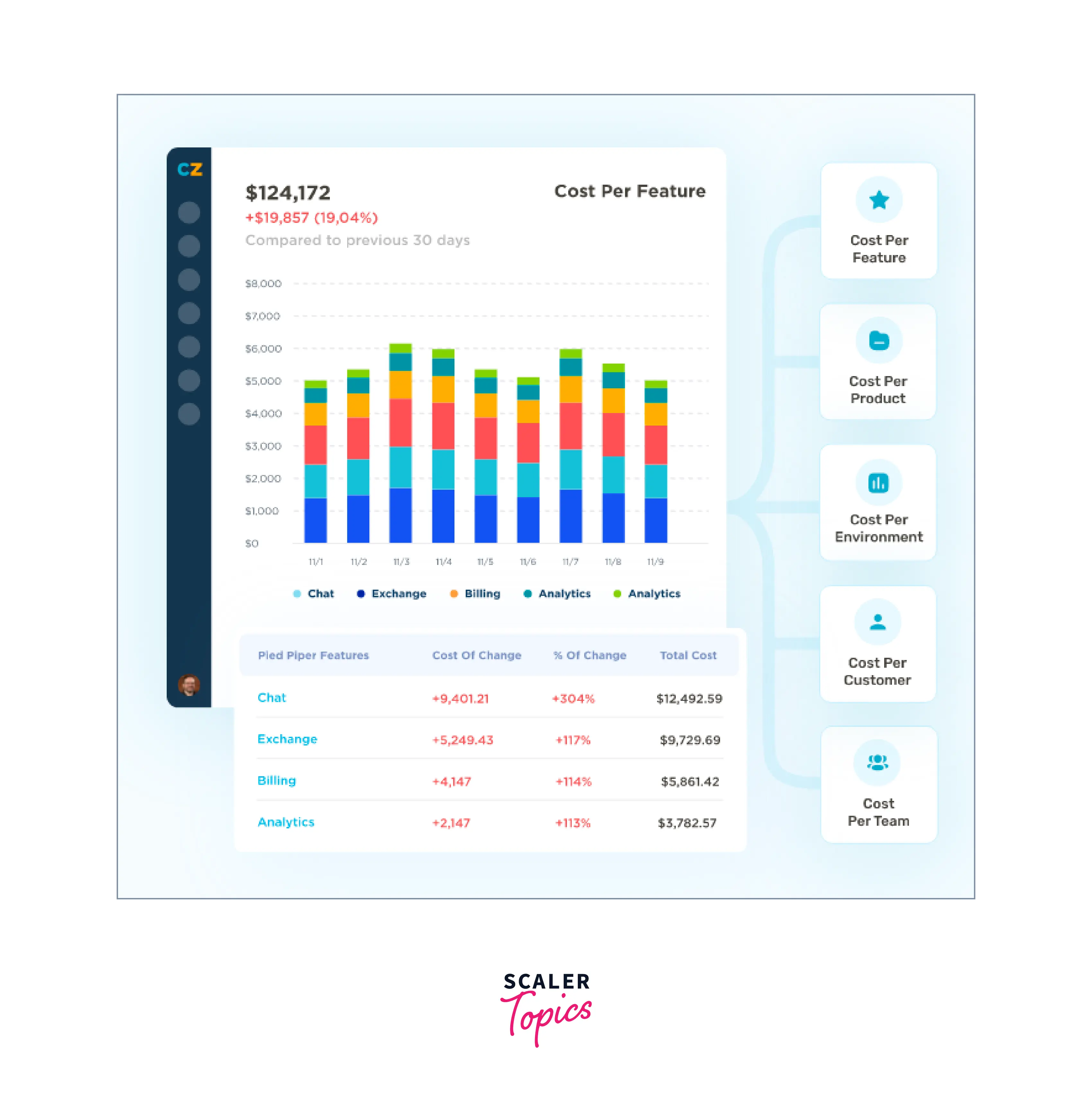
As a result, you are given the ability to evaluate Amazon RDS prices based on business metrics that are important to you, like environment, project, team, software feature, product, cost per customer, and more.
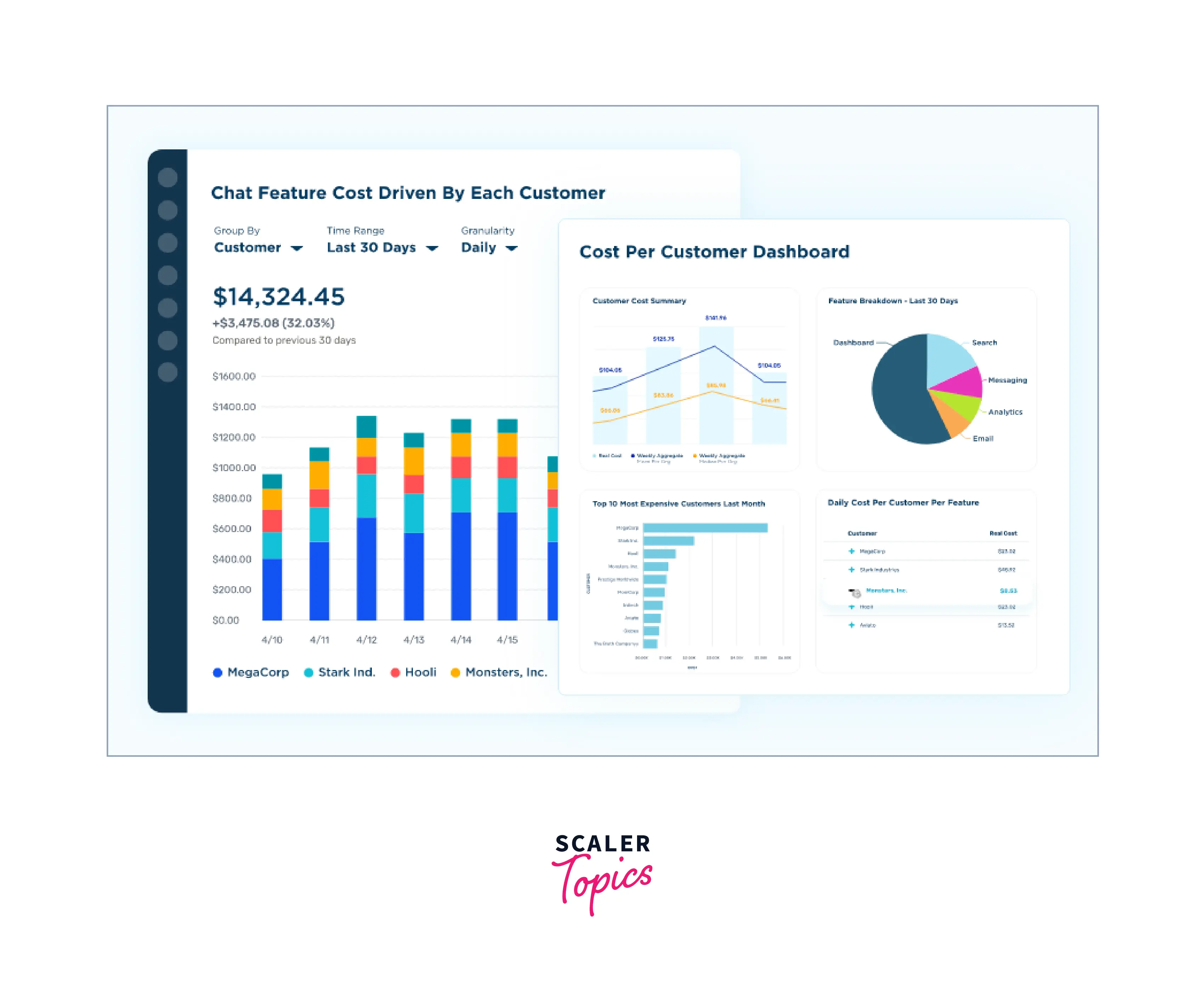
You can choose what to cut to cut costs or what to increase to improve performance or returns by identifying your top Amazon RDS cost drivers.
Conclusion
- The RDS (Amazon Relational Database Service) allows AWS customers to operate, manage, and scale their databases.
- RDS is a managed service that offers various instance sizes and types, seven database engines, and seven database engines for use with relational databases.
- You can pay according to the actual resource usage with the on-demand rates offered by AWS RDS pricing models. No minimum payment is required.
- Deployment type, Additional Storage, Outbound Data Transfers, DB Instances, and other aspects also affect Amazon RDS costs.
- Seven different relational database engines are supported by Amazon RDS: MariaDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server.
- Additional costs for provisioned database storage are billed at $0.095 per GiB-month in RDS Billing and Provisioning in AWS.
- The cost of Amazon RDS depends on a number of factors, such as the database engine, database instance, database region, and purchase type that you select (On-Demand or Reserved Instance).
