Disaster Recovery in Azure
Overview
Disaster Recovery in Azure is a comprehensive solution for safeguarding data and applications against unforeseen disruptions. It offers replication, failover, and recovery capabilities to ensure business continuity. Azure provides multiple disaster recovery options, including Azure Site Recovery and Azure Backup, allowing organizations to design and implement robust recovery strategies tailored to their specific needs.
What is Azure Site Recovery?
Azure Site Recovery enables organizations to replicate their on-premises physical servers, virtual machines, and workloads to Azure or a secondary data center for business continuity and disaster recovery purposes.
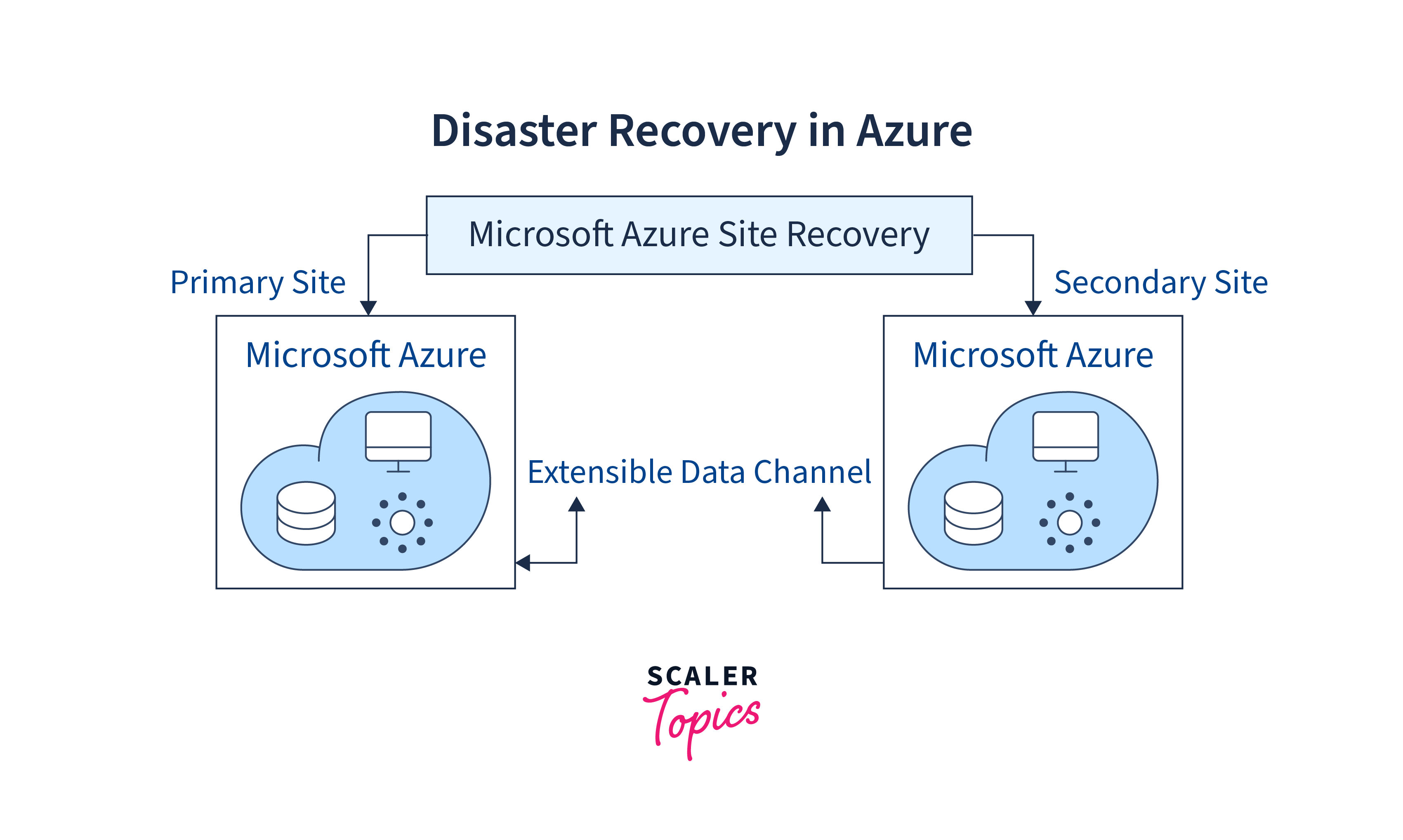
With Azure Site Recovery, in the event of a disaster or system failure, organizations can fail over their applications and data to the replicated environment, minimizing downtime and ensuring data integrity. It supports a variety of replication scenarios, including Hyper-V, VMware, and physical servers, and offers features like automated failover, testing, and monitoring to ensure recovery readiness.
Azure Disaster Recovery: Two Solution Architectures
Azure Disaster Recovery offers two primary solution architectures to meet different recovery needs:
- SMB Disaster Recovery
- Enterprise-scale Disaster Recovery
SMB Disaster Recovery in Azure
The SMB Disaster Recovery solution in Azure offers cost-effective cloud-based disaster recovery options for small businesses. It leverages partner solutions like Double Take DR, which utilizes Azure services such as Traffic Manager, Azure Virtual Network, and Site Recovery in a highly available environment.
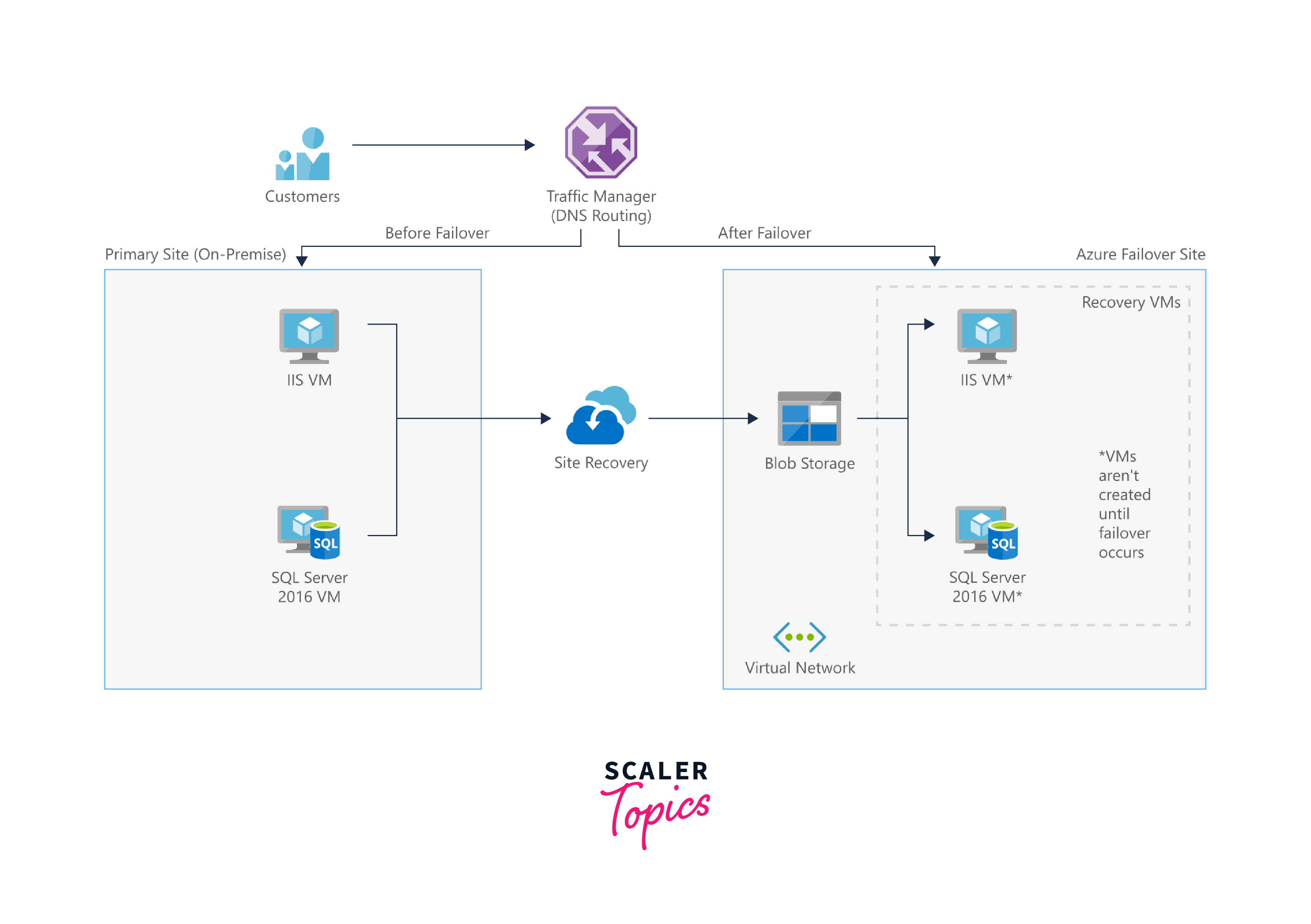
Here's how the solution works:
-
Traffic Manager:
The traffic Manager plays a crucial role in managing DNS traffic. It dynamically routes traffic between different sites based on policies defined by the organization. This ensures that users are directed to the appropriate site, whether it's the primary or failover location.
-
Azure Site Recovery (ASR):
Azure Site Recovery is responsible for orchestrating machine replication and managing the configuration of failback procedures. It ensures that critical workloads and virtual machines are continuously replicated to Azure, providing a failover option in case of a disaster.
-
Virtual Network:
Azure Virtual Network serves as the location where the failover site is created during a disaster. It ensures that the necessary network infrastructure is in place to support the failover of workloads to Azure.
-
Blob Storage:
Blob Storage is used to store replica images of all machines protected by Azure Site Recovery. These images are essential for the recovery process, allowing organizations to restore their systems quickly in the event of a disaster.
Enterprise-scale Disaster Recovery in Azure
Enterprise-scale Disaster Recovery in Azure is designed for large organizations with complex infrastructure and stringent disaster recovery requirements. It enables the failover of critical systems such as SharePoint, Linux, and Dynamics CRM web servers from an on-premises data center to Azure infrastructure.
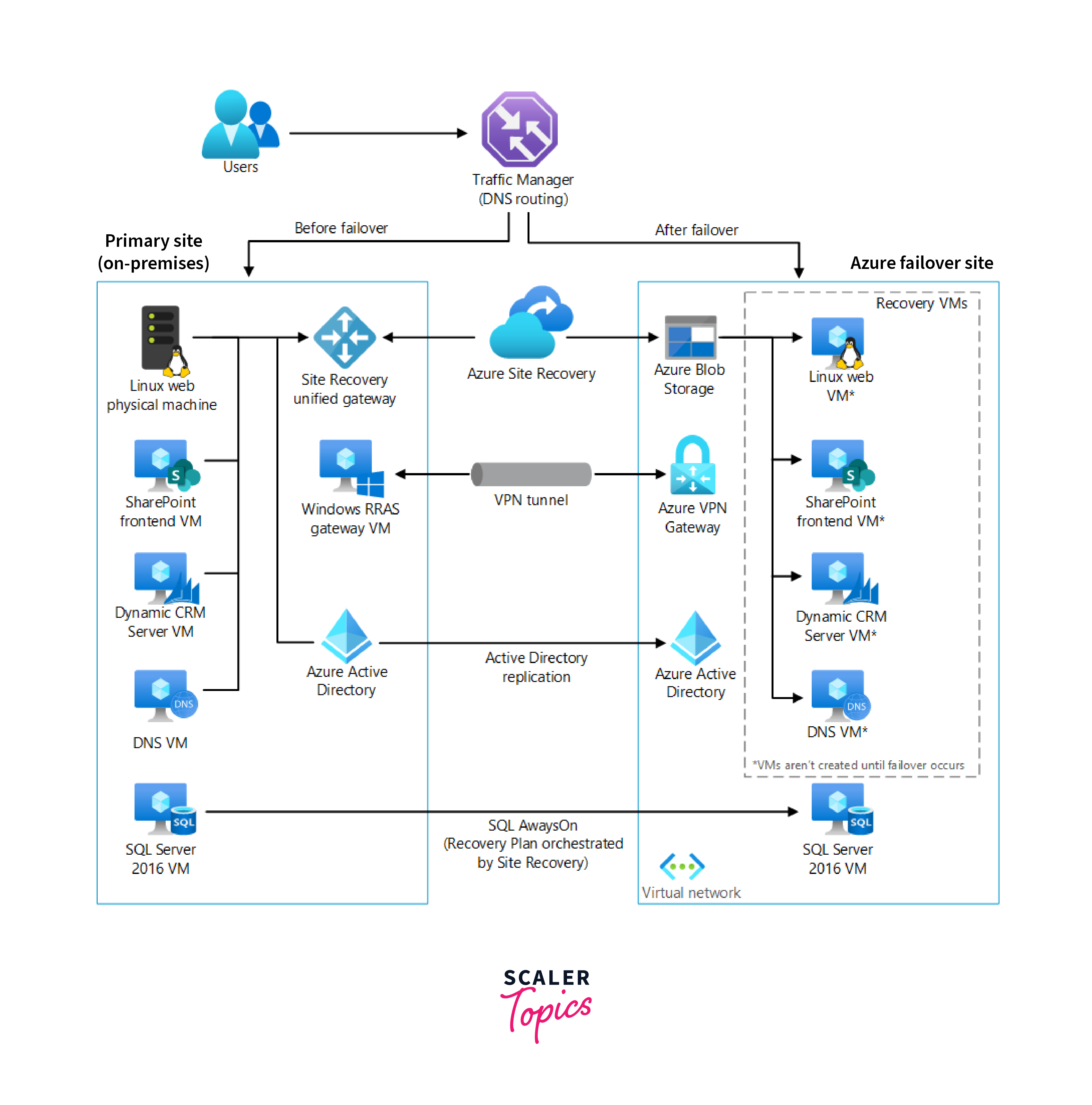
Here's how this solution works:
-
Traffic Manager:
Traffic Manager is a critical component that manages DNS traffic routing based on policies defined by the organization. It ensures efficient traffic distribution between different sites, whether they are on-premises or in Azure.
-
Azure Site Recovery (ASR):
Azure Site Recovery plays a central role in orchestrating the replication of machines and managing the configuration of the entire disaster recovery process. It ensures the continuous replication of workloads, allowing for seamless failover in case of a disaster.
-
Blob Storage:
Blob Storage is used to store replica images of all machines protected by Azure Site Recovery. These images serve as the foundation for recovery operations, enabling the rapid restoration of systems and data.
-
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD):
Azure AD acts as a replica of the on-premises Azure Active Directory service. It provides authentication and authorization capabilities for cloud applications, ensuring secure access during the recovery process.
-
VPN Gateway:
The VPN Gateway facilitates secure and private communication between on-premises and cloud networks. It ensures that data transmission remains protected while enabling seamless connectivity between environments.
-
Virtual Network:
Azure Virtual Network is the designated location where a failover site is created in the event of a disaster. It ensures that the necessary network infrastructure is available to support the failover and operation of critical workloads in Azure.
Best Practices for Azure Disaster Recovery
Best practices for implementing Azure Disaster Recovery to ensure the highest level of preparedness and resilience include:
-
Define Clear Objectives:
Clearly state recovery objectives, RTOs, and RPOs to guide your planning efforts.
-
Prioritize Critical Workloads:
Identify and prioritize critical systems and applications for recovery.
-
Data Replication:
Implement data replication strategies, such as Azure Site Recovery, to ensure up-to-date and consistent data in Azure.
-
Failover and Failback Procedures:
Develop detailed procedures for initiating failover and failback operations.
-
Application Recovery:
Document recovery procedures for critical applications, testing their functionality in Azure.
-
Network Connectivity:
Ensure network connectivity by configuring Azure Virtual Networks, VPNs, or ExpressRoute.
-
Regular Testing:
Schedule regular disaster recovery tests to validate the plan's effectiveness.
-
Monitoring and Alerting:
Set up continuous monitoring and alerting to quickly detect and respond to issues.
Azure Disaster Recovery Plan
A well-structured Azure disaster recovery plan is crucial for businesses seeking to mitigate the impact of unexpected disruptions. It begins with defining clear objectives, identifying critical systems, and assessing risks. Key components include strategies for data replication, application recovery, and network connectivity. Regular testing, monitoring, and documentation ensure the plan's effectiveness, allowing organizations to recover swiftly and maintain business continuity in Azure.
Operational Readiness Testing
Operational Readiness Testing (ORT) is a critical phase in the implementation of a disaster recovery (DR) solution, including those hosted on Azure. The primary goal of ORT is to ensure that your DR plan is fully prepared and operational, ready to be executed in the event of a disaster. In the context of Azure disaster recovery, ORT involves validating the readiness of your Azure-based DR solution to ensure a smooth and effective response to any disruptive event.
Dependent Service Outage
A dependent service outage refers to a situation where a particular service or application becomes unavailable or experiences disruptions due to a failure or issue with another service, system, or component it relies upon. This can occur in complex technology ecosystems, such as cloud-based applications, where multiple interconnected services work together to deliver a complete solution.
When a dependent service fails or experiences downtime, it can have a cascading effect, causing interruptions or degradation of the functionality of the services that rely on it. To mitigate the impact of dependent service outages, organizations often implement redundancy, failover mechanisms, and thorough monitoring to quickly identify and address issues to maintain service availability and reliability.
Network Outage
A network outage refers to a disruption or loss of connectivity within a computer network, which can be caused by various factors such as hardware failure, software issues, cyberattacks, or infrastructure problems. During a network outage, users may experience an inability to access online resources, communicate with remote devices, or use internet services.
These outages can have significant consequences for businesses, leading to downtime, loss of productivity, and potential data loss, emphasizing the importance of robust network monitoring, redundancy, and disaster recovery plans to minimize the impact of such events.
Plan For Regional Failures
A plan for regional failures is a comprehensive strategy developed by organizations to address and mitigate the potential impacts of disruptions or disasters that affect an entire geographic region. These regional failures can include natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods, or man-made events like power outages, cyberattacks, or public health crises.
Key components often involve data replication to remote locations, redundant infrastructure, off-site backups, and well-defined procedures for evacuating or relocating critical operations if necessary.
Conclusion
- Azure Site Recovery is a Microsoft Azure service that provides VM and application replication for disaster recovery.
- Two Solution Architectures: Azure offers both SMB and Enterprise-scale solution architectures for disaster recovery, catering to different organizational needs.
- SMB Disaster Recovery in Azure is a cost-effective solution tailored for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Enterprise-scale Disaster Recovery offers advanced features for larger organizations with complex IT environments.
- Best practices for Azure disaster recovery include clear objectives, regular testing, and robust data replication and recovery procedures.
- An Azure disaster recovery plan outlines strategies for maintaining business continuity through Azure resources and services.
- Operational Readiness Testing validates disaster recovery plans and systems for effective readiness.
- A dependent service outage occurs when one service disruption impacts other interconnected services.
- A network outage is the loss of connectivity within a computer network due to various factors, resulting in service disruption.
- A plan for regional failures outlines strategies for mitigating the impact of large-scale disruptions that affect entire geographic regions.
