What is Azure Site Recovery and How do you use it?
Overview
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, ensuring business continuity is paramount. This article provides a detailed overview of Azure Site Recovery, Microsoft's robust solution for safeguarding your data, applications, and operations. Explore how Azure Site Recovery offers seamless disaster recovery, efficient data replication, and the confidence to thrive in an ever-evolving business environment. Azure Site Recovery is a Microsoft service enabling seamless business continuity and disaster recovery.
What is ASR in Azure?
Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is a pivotal cloud-based service within Microsoft's Azure ecosystem that plays a vital role in ensuring the resilience, continuity, and disaster recovery preparedness of organizations. ASR serves as a safeguard against a multitude of potential disruptions, ranging from hardware failures and software glitches to site-wide outages and catastrophic events.
At its core, ASR enables seamless replication of an organization's critical workloads, applications, and data from on-premises environments to Azure cloud or secondary data centers. This replication process is designed to be highly efficient and near-real-time, assuring that the replicated data remains current and consistent with the source. In the event of an unforeseen disruption, ASR enables orchestrated failover and failback procedures, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss.
ASR's capabilities extend beyond just recovery. It empowers organizations to define customized recovery plans that encapsulate the steps to take during a disruption. Furthermore, it allows for non-disruptive testing of these plans, enabling organizations to practice recovery procedures without affecting live environments.
The integration of ASR with Azure services and Azure Virtual Machines ensures a seamless experience during recovery operations. This integration further streamlines hybrid cloud strategies, enabling businesses to maintain a balance between on-premises and cloud resources.
The Advantages of ASR
- Cost Effectiveness: ASR offers a cost-effective approach to disaster recovery. Traditionally, setting up and maintaining a secondary data center for disaster recovery purposes can be expensive. ASR eliminates the need for such significant investments by leveraging the cloud's scalability and pay-as-you-go model. Organizations can replicate their critical workloads to Azure without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure. This approach reduces capital expenditures and allows businesses to optimize costs based on actual usage.
- Data Resilience: One of the primary goals of disaster recovery is to ensure data resilience. ASR accomplishes this by continuously replicating data from on-premises environments to Azure or secondary data centers. This replication process is designed to be near-real-time, minimizing the risk of data loss during unexpected disruptions. By maintaining up-to-date copies of data, ASR ensures that businesses can recover their operations with minimal data loss, thereby enhancing data protection and integrity.
- Heterogeneous Workload Support: Modern IT environments are often heterogeneous, with a mix of virtual machines, physical servers, and various operating systems. ASR excels in this regard by offering support for a wide range of workloads. It can replicate virtual machines running on VMware or Hyper-V, as well as physical servers. This versatility allows businesses to protect their diverse IT landscape with a single, unified solution.
- Application Consistency: Successful disaster recovery extends beyond data replication—it also involves ensuring application consistency. ASR goes beyond copying data; it ensures that applications are replicated and recovered in a consistent state. This ensures that applications function as intended after recovery, without data corruption or inconsistencies, enabling businesses to resume operations seamlessly.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) Integration: ASR is an integral part of a comprehensive Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) strategy. It enables organizations to create customized recovery plans that align with their specific business needs. These recovery plans define the sequence of steps to be taken during a disruption, facilitating orchestrated failover and failback procedures. This integration ensures minimal downtime, efficient recovery, and a structured approach to managing disruptions.
- Non-Disruptive Testing: ASR provides a critical feature for preparedness: non-disruptive testing of recovery plans. Organizations can simulate recovery scenarios without affecting live systems. This allows IT teams to refine their recovery processes, validate their strategies, and identify any gaps before an actual disruption occurs. Non-disruptive testing enhances the organization's readiness to respond effectively during real-world incidents.
- Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) Customization: ASR empowers organizations to set specific Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) for each workload. RPO defines the maximum acceptable data loss, while RTO outlines the target time for recovery. ASR enables businesses to customize these objectives based on the criticality of applications and data. This level of customization ensures that recovery processes align with the organization's tolerance for data loss and downtime.
- Scalability and Elasticity: Azure's cloud infrastructure provides scalability and elasticity, which ASR leverages during disaster recovery scenarios. In the event of a disruption, businesses can dynamically allocate resources to accommodate increased demand. This ensures that applications perform optimally even during recovery, helping maintain operational efficiency.
- Geographic Distribution and Geo-Redundancy: ASR enhances resilience through geographic distribution and geo-redundancy. By replicating data to Azure's geographically dispersed data centers, ASR ensures that data is stored in multiple locations. This minimizes the impact of regional disruptions and provides an additional layer of protection against unforeseen events.
- Reduced Complexity and Automated Processes: Disaster recovery processes can be complex and time-consuming. ASR simplifies these processes by automating many aspects of replication, failover, and failback. This reduces the potential for human errors, streamlines recovery operations, and allows IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine recovery tasks.
Replicate Data to the Cloud With Azure Site Recovery (ASR)
Organizations today recognize the critical importance of safeguarding their data and ensuring seamless business continuity in the face of disruptions. Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is a comprehensive solution within the Microsoft Azure ecosystem that facilitates the replication of data to the cloud, enabling businesses to prepare for and manage various disaster recovery scenarios. This process involves distinct stages, from planning and preparation to failover and failback, all while requiring efficient management, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Planning Stage:
Effective disaster recovery begins with careful planning. Organizations must assess their critical workloads, applications, and data to determine the most suitable strategy for replication. This involves defining Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) for each workload. RPO establishes the maximum acceptable data loss, while RTO outlines the desired recovery time. During the planning stage, organizations should identify dependencies between applications and systems to create recovery groups. These groups help ensure that related components are recovered together, maintaining application consistency. Additionally, a clear communication plan should be developed to inform stakeholders about recovery processes and expected downtime.
Prepare and Configure:
The preparation and configuration phase involves setting up the necessary infrastructure and defining replication policies. Organizations begin by configuring Azure resources, including Azure Virtual Networks, storage accounts, and target virtual machines. This process establishes the foundation for replication. Next, replication policies are defined to specify which workloads and virtual machines will be replicated, how often replication will occur, and how long data will be retained. ASR provides flexibility to tailor replication to the organization's requirements, allowing customization based on workload criticality and compliance needs.
Failover and Failback:
Failover and failback are crucial stages in the disaster recovery process. Failover refers to the process of transitioning operations from the primary site to the recovery site when the primary site becomes unavailable due to a disruption. Failback, on the other hand, involves returning operations to the primary site after it has been restored.
During failover, ASR ensures that the replicated data is in a consistent state, and the recovery plan is executed as per the predefined sequence. The application dependencies and recovery groups identified earlier play a pivotal role in orchestrating a controlled and efficient failover process. Failover minimizes downtime and data loss, maintaining business continuity.
Once the disruption is resolved, organizations initiate the failback process to return operations to the primary site. ASR ensures that data changes made during the recovery period are synchronized back to the primary site, ensuring consistency across both sites. Proper testing of failover and failback procedures is crucial to validate their effectiveness and uncover any potential issues.
Manage, Monitor, and Troubleshoot:
Ongoing management, monitoring, and troubleshooting are essential to maintaining the effectiveness of the ASR solution. ASR provides a range of tools and capabilities to facilitate these tasks.
- Management: Organizations can use the Azure portal to manage and monitor their replication settings, recovery plans, and ongoing replication health. The portal offers a centralized view of replication progress, failover history, and configuration details, enabling administrators to make informed decisions.
- Monitoring: ASR continuously monitors the health of the replication process and provides alerts for any issues. Automated notifications help administrators identify and address potential problems proactively. Regular health checks ensure that data remains in sync and recovery plans are up to date.
- Troubleshooting: In the event of issues or errors, ASR provides detailed logs and diagnostic information. Administrators can use this information to identify the root cause of problems and take appropriate corrective actions. Azure's extensive documentation and support resources offer guidance for troubleshooting various scenarios.
Protecting Virtual Machines in Azure using Azure Site Recovery (ASR)
In the digital era, the availability and reliability of virtual machines (VMs) are paramount to the success of businesses. Disruptions, whether caused by hardware failures, software glitches, or other unforeseen events, can result in significant downtime and data loss. Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is a robust solution provided by Microsoft's Azure platform that addresses these challenges by offering comprehensive disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities for VMs deployed within the Azure ecosystem.
Assessment and Planning:
Effective disaster recovery begins with a thorough assessment of VM workloads and a well-defined planning phase. Organizations must identify the critical VMs that require protection and evaluate their dependencies to ensure a coherent recovery strategy. Understanding the Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) for each VM is essential. RPO defines the maximum acceptable data loss, while RTO indicates the target time for recovery.
ASR Configuration:
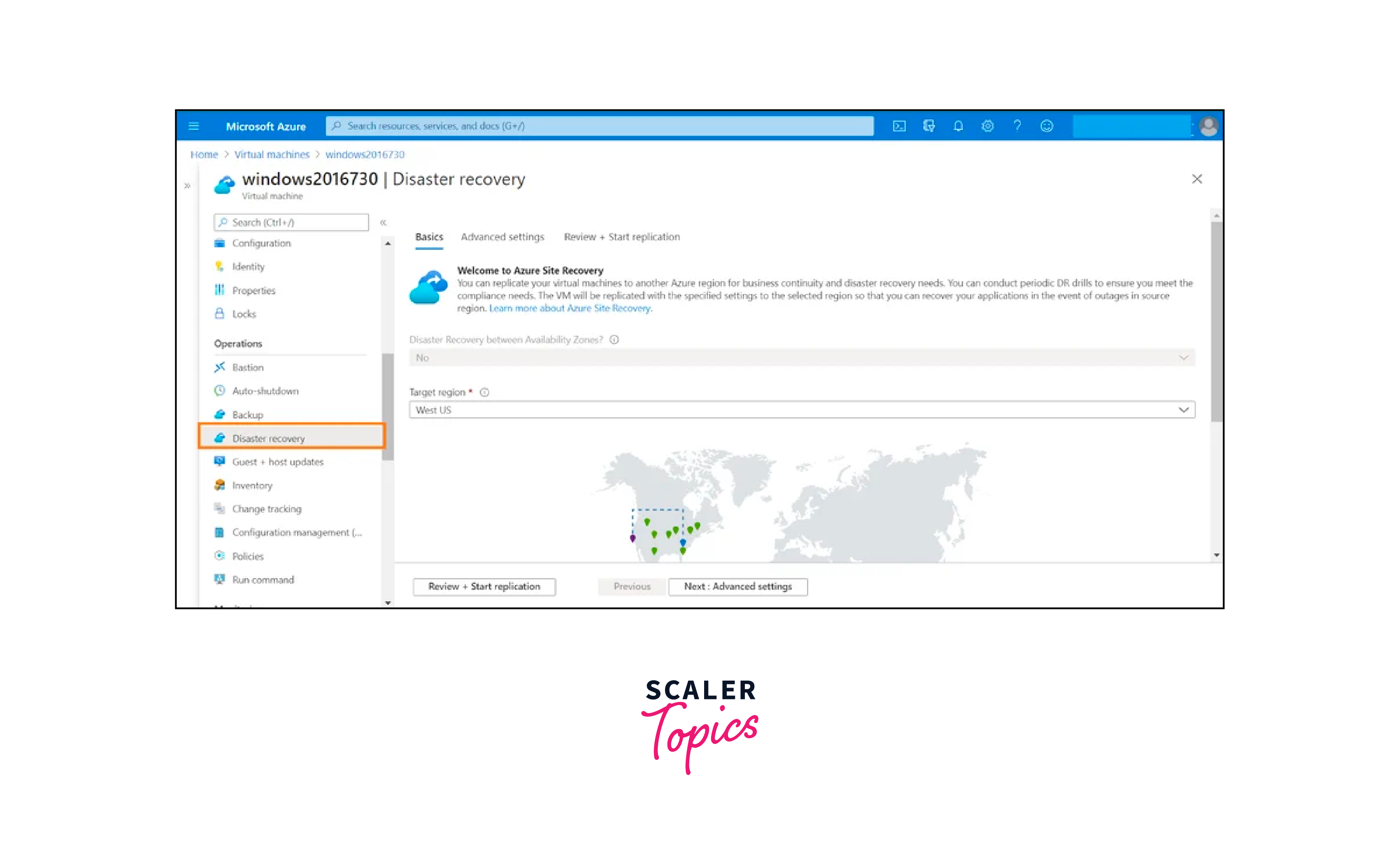
After planning, the ASR configuration phase begins. This step involves setting up the necessary infrastructure and defining replication policies. Organizations configure Azure resources, such as storage accounts and Azure Virtual Networks, that serve as the foundation for replication. Replication policies dictate how often data should be replicated, as well as the retention policies for historical data. These policies are tailored to align with the RPO and RTO requirements determined during the planning phase.
Replication to Azure:
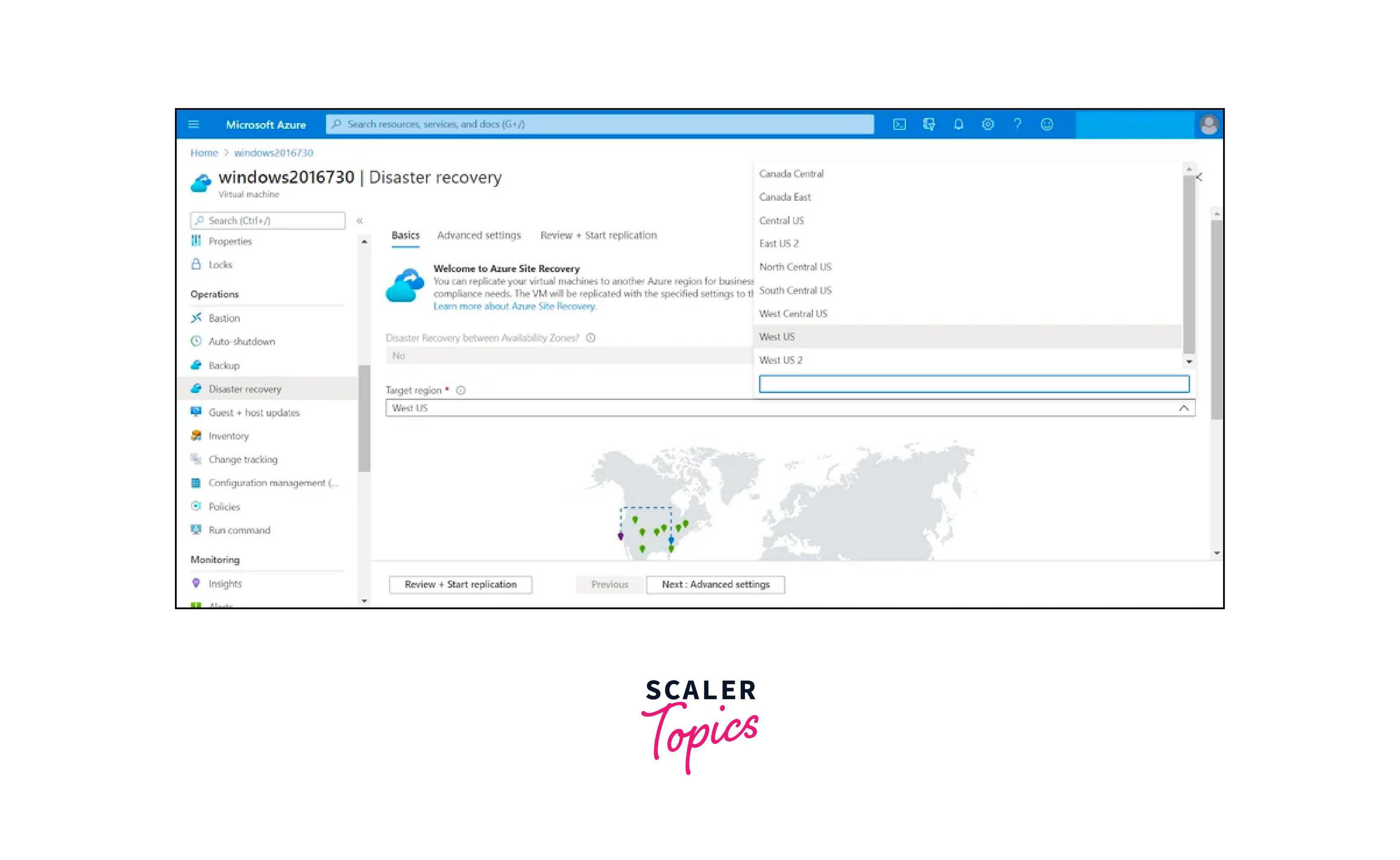
Azure Site Recovery offers multiple replication scenarios, catering to different deployment models. For organizations with primary data centers in Azure, inter-region replication ensures data resilience within the Azure cloud infrastructure. Furthermore, ASR supports hybrid cloud scenarios by replicating VMs from on-premises data centers to Azure. This flexibility enables businesses to maintain consistent protection across various environments.
Orchestrated Failover:
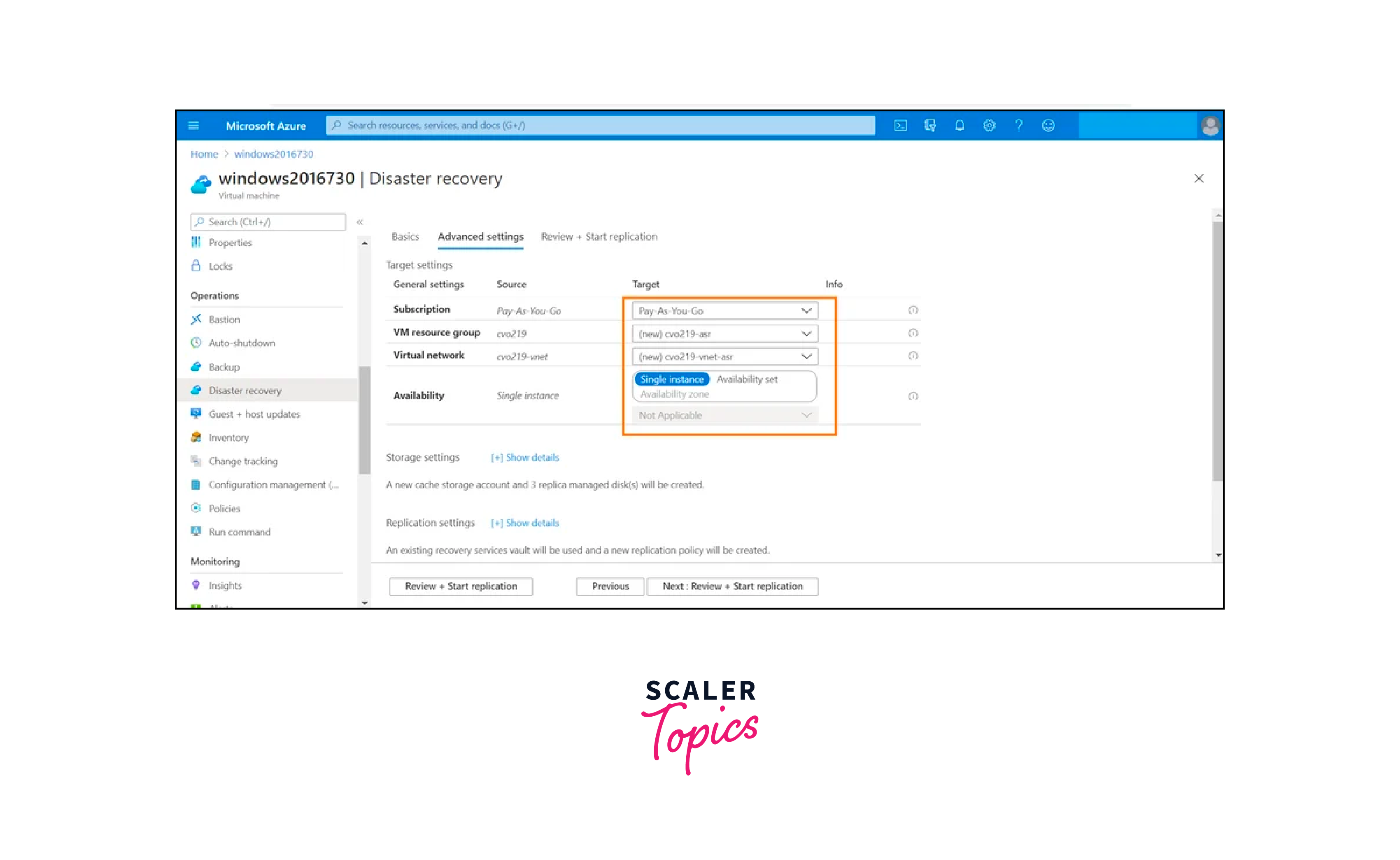
When a disruption occurs, initiating an orchestrated failover is crucial to minimize downtime. ASR's recovery plans facilitate a controlled failover process. These plans define the sequence of actions required to transition from the primary site to the recovery site. By adhering to these predefined sequences, ASR ensures a systematic recovery process that reduces the risk of errors and maintains data integrity.
Application Consistency:
VMs often host complex applications with interdependencies. ASR's capability to ensure application consistency during failover is invaluable. It ensures that VMs and their corresponding applications recover in a consistent state, eliminating data corruption and preserving operational continuity. This guarantees that the recovered systems are fully functional and operational after failover.
Automated Testing and Validation:
The effectiveness of a disaster recovery plan depends on its validation through testing. ASR offers the ability to conduct non-disruptive testing and validation of recovery plans. This simulation allows organizations to evaluate the efficacy of their plans without affecting the production environment. By identifying any potential issues or gaps, organizations can fine-tune their recovery strategies and enhance their readiness for real disruptions.
Recovery Monitoring and Health Checks:
Continuous monitoring is integral to ensuring the ongoing health of the disaster recovery setup. ASR provides real-time visibility into the status of protected VMs, the progress of replication, and the history of failover events. Automated alerts and notifications promptly notify administrators of any deviations from the expected operational state, enabling proactive interventions.
Efficient Failback:
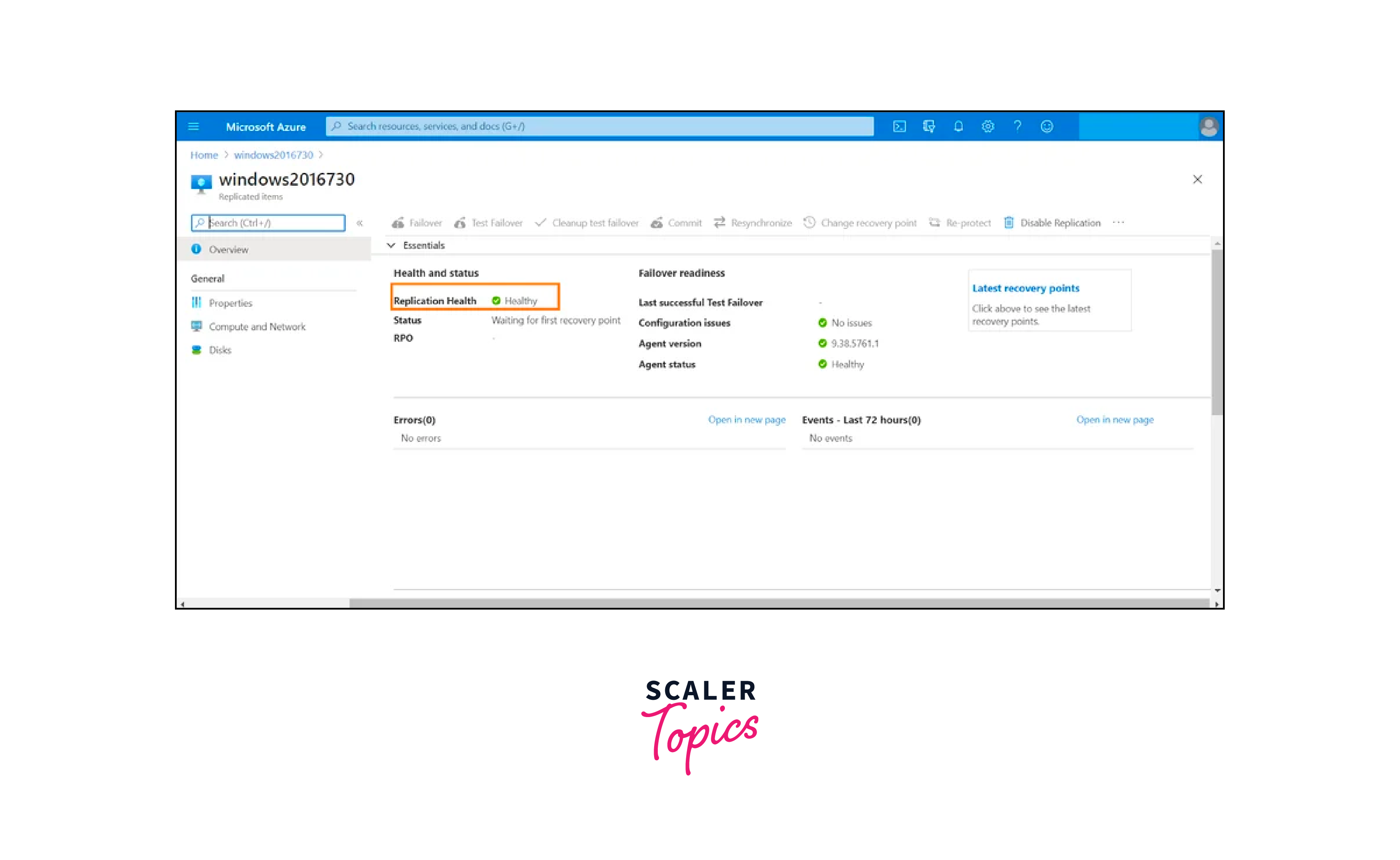
Once the disruption is resolved, the transition back to the primary site, known as failback, must be smooth and efficient. ASR manages the synchronization of data changes made during the failover period, ensuring data consistency between the primary and recovery sites. This process guarantees that the organization's operations are restored to their original state, minimizing any potential data loss.
Resource Optimization and Cost Efficiency:
ASR's capabilities extend to optimizing resource allocation during failover scenarios. It enables organizations to provision resources dynamically based on demand. This adaptive approach eliminates the need for constant over-provisioning, contributing to cost savings and efficient resource utilization.
Compliance and Security:
Azure Site Recovery aligns with Azure's robust security features and compliance certifications. This ensures that data remains protected and compliance requirements are met even during disaster recovery events.
Pricing
Azure Site Recovery pricing can be complex and depends on various factors, including the specific services you use, the amount of data you need to protect, and your replication requirements.
- Pay-as-You-Go Model: Azure Site Recovery typically follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where you pay for the resources and services you use.
- Compute Costs: You are charged for the compute resources (virtual machines) used during replication and recovery processes.
- Storage Costs: Charges apply for the storage of replicated data in Azure storage accounts.
- Network Data Transfer Costs: Data transfer charges apply when replicating data to Azure or between Azure regions.
- Retention Costs: If you want to retain replicated data for a longer period, additional costs may be incurred.
- Configuration Server Licensing: You may need a configuration server on your on-premises environment, subject to licensing costs.
- Licensing Based on Replication Type: Costs may vary based on the type of replication (e.g., Hyper-V, VMware, physical servers) and the replication destination (Azure or another location).
- Data Transfer Costs for Failover/Failback: When performing failover or failback operations, data transfer costs can apply.
- Azure Site Recovery vs. Azure Backup: Azure Site Recovery and Azure Backup are distinct services, and their pricing models differ.
- Azure Calculator: Use the Azure Pricing Calculator to estimate costs based on your specific configuration and requirements. Be sure to check the official Azure pricing page for the most current information.
Conclusion
- Azure Site Recovery is a vital Azure service designed to ensure business continuity and disaster recovery by replicating critical data and workloads to Azure or secondary data centers.
- Azure Site Recovery supports inter-region replication for Azure-based primary data centers and hybrid scenarios, ensuring data resilience across diverse environments.
- Azure Site Recovery provides real-time visibility into the status of VMs, replication, and automated alerts for proactive issue resolution.
- Azure Site Recovery offers resource optimization, aligns with Azure's security features, and complies with regulations during disaster recovery events.
- Azure Site Recovery simplifies the setup and management of disaster recovery scenarios, ensuring seamless failover and failback processes for applications and data.
- Azure Site Recovery ensures application consistency during failover by orchestrating the sequencing of virtual machine failovers and data replication.
- With built-in automation and orchestration capabilities, Azure Site Recovery reduces the complexity of manual recovery processes and minimizes human error.
- Azure Site Recovery offers a cost-effective approach to disaster recovery by leveraging Azure's pay-as-you-go pricing model, eliminating the need for expensive dedicated infrastructure.
