Azure Hybrid Cloud & Multi Cloud
Overview
In the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, businesses are increasingly turning to hybrid and multi-cloud solutions to meet their diverse and dynamic needs. Azure, Microsoft's cloud platform, offers a robust set of services that empower organizations to seamlessly integrate both on-premises and cloud resources. This article delves into the world of Azure hybrid multicloud and cloud deployments, exploring their significance, motivations, concerns, and how unified operations can mitigate potential challenges.
Defining Hybrid and Multicloud
A hybrid cloud is a form of cloud computing that blends public cloud services (provided by third-party providers via the public internet) and private cloud services (on-premises infrastructure). Applications and data can flow between the two cloud environments on a regular basis thanks to hybrid clouds. Because of business needs including satisfying regulatory and data sovereignty requirements, optimizing on-premises technology investments, or resolving latency challenges, many enterprises opt for a hybrid cloud strategy.
Edge workloads are becoming a part of the growing hybrid cloud. The computational capacity of the public cloud is brought to the private cloud by cloud-managed edge computing devices, which are located closer to where IoT devices are located. This includes data that is stored in applications, linked devices, and mobile consumer services. By shifting workloads to the edge, devices can reduce latency by interacting with the cloud less frequently and maintaining reliable operation over prolonged offline times. Experience-driven resources are made available closer to your customers with expanded compute, storage, and service availability.
The usage of several cloud computing services in a heterogeneous environment from different cloud providers (private and public clouds) is referred to as multicloud computing. A multicloud strategy reduces risk and offers more flexibility. Select services from many cloud providers that are most appropriate for a given task, or utilize services provided by a specific cloud provider in a specific region.
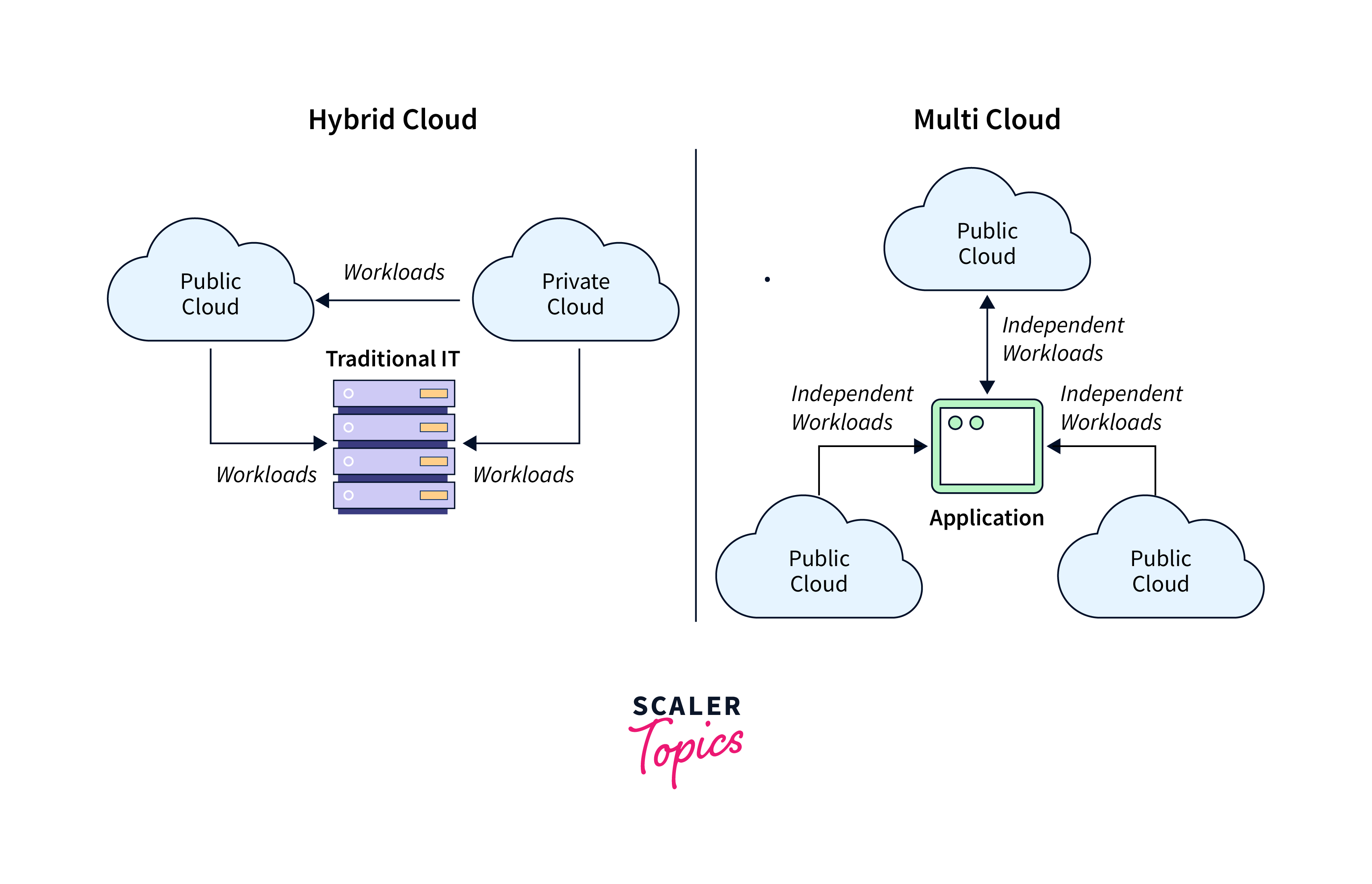
A multicloud strategy involves using multiple cloud providers for enhanced flexibility and resilience. Real-world examples showcase its effectiveness across diverse industries.
Real World Examples
-
Finance and Banking:
Use Case: Trading Platforms
Example: AWS for analytics, Azure for AI, and Google Cloud for storage. Ensures performance, scalability, and compliance.
-
Healthcare:
Use Case: Data Security
Example: AWS for storage, Google Cloud for analytics, Azure for compliance. Balances specialized services and regulatory needs.
-
E-commerce:
Use Case: Scalability
Example: AWS for peak times, Azure for insights, and IBM Cloud for disaster recovery. Optimizes scalability, redundancy, and service diversity.
Practical Insights
-
Avoiding Vendor Lock-in:
Distributing workloads prevents dependence on one vendor, facilitating better negotiations and cost optimization.
-
Optimizing Service Capabilities:
Leveraging provider strengths for specific services. For example, AWS for computing power, and Google Cloud for machine learning.
-
Enhancing Resilience:
Improved resilience by distributing critical workloads, ensuring business continuity during outages.
-
Cost Optimization:
Selecting the most cost-effective services from each provider, optimizing costs based on workload requirements.
Hybrid and Multicloud Narrative
This Azure hybrid multi-cloud scenario offers advice on what you can do differently to succeed in your organization's cloud adoption endeavor while adhering to a typical hybrid and multi-cloud narrative. This broad story takes a look at the whole cloud adoption process rather than focusing on just one methodology.
With more deployment options, global scale, integrated cross-platform security, unified compliance, and enhanced workload, operational, and cost efficiencies throughout the enterprise, a hybrid cloud platform offers your business numerous benefits. It also continuously maximizes the value of its current infrastructure.
Investing in offshore disaster recovery and backup infrastructure is another capital expense that could be cut. For workloads and related data on-premises that are not otherwise prohibited from living in a public cloud, the public cloud for BCDR techniques is an appealing choice. Customers that use the public cloud for BCDR benefit from significant investments in security and privacy, scalability on demand, simplicity, and quick recovery times.
Businesses are dispersing their resources among numerous clouds, the edge, and on-premises environments. We frequently hear about four basic needs that customers have:
- A single pane of glass providing visibility into the state of all current and future infrastructure and applications.
- Integrating cloud infrastructure with on-premises policies and updates can be challenging. Companies are aware of the necessity of putting in place a governance standard,
- A broad spectrum of capabilities from both on-premises and cloud environments, as organizations frequently have distinct application development teams. To standardize development processes, customers want consistent compatibility between the two.
- A desire to control security posture without significantly altering ongoing activities. This difficulty is exacerbated by cloud and multi-cloud, which can erode confidence and foster mistrust.
Hybrid and Multicloud Motivations
Azure hybrid multi-cloud serves your business objectives in public, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments as a real enterprise-grade cloud service. This article will go over several best practices that can support a range of cloud mixes, from environments that have little to no Azure infrastructure in place to environments that are 100% Azure.
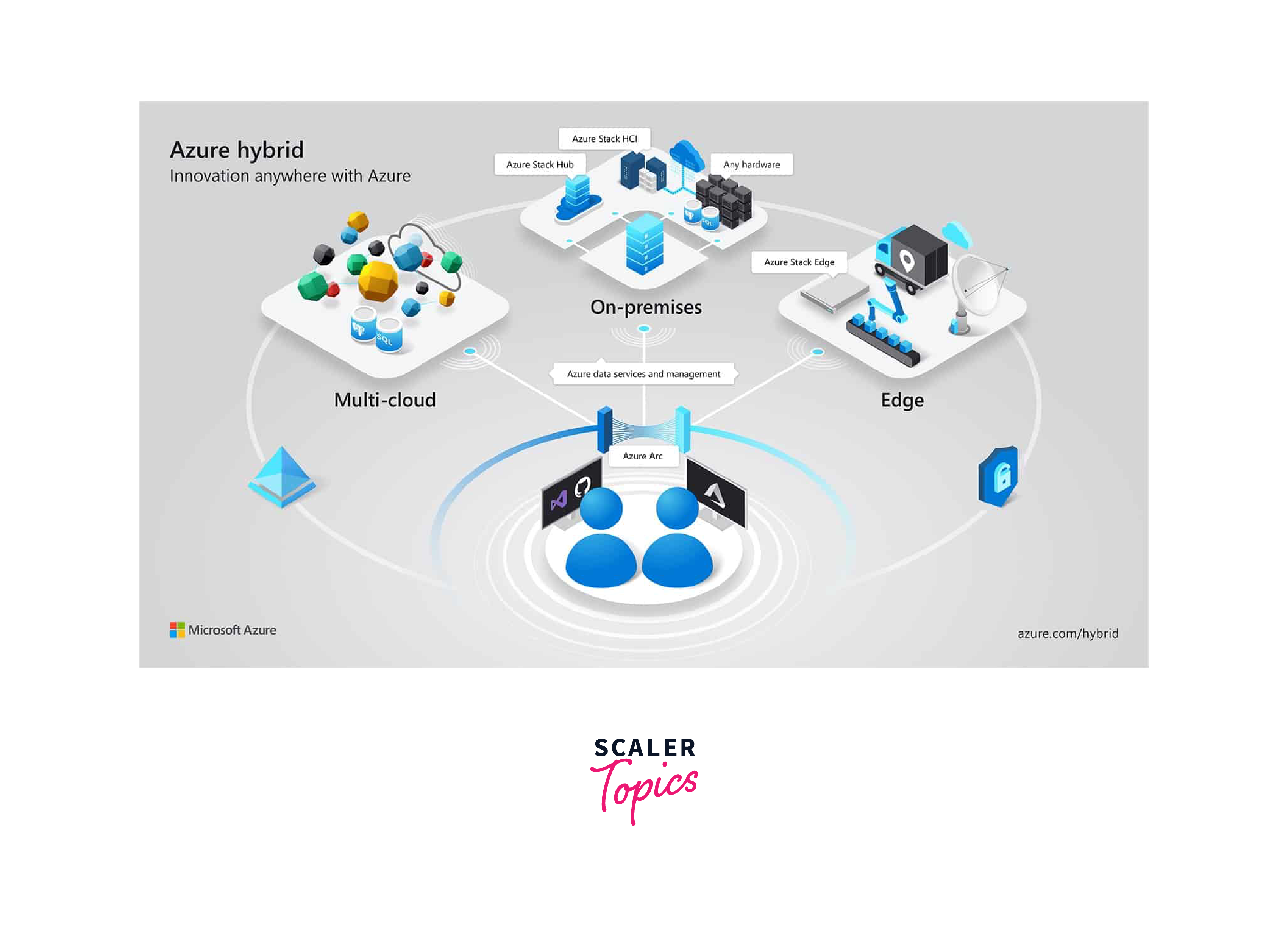
Hybrid cloud computing allows you to easily scale up your on-premises infrastructure to the public cloud to handle any overflow when processing and computing demand varies, all without providing third-party data centers access to all of your data. Your company can benefit from the freedom and innovation offered by the public cloud by running some workloads there while keeping highly sensitive data in your data center to satisfy customer demands or comply with legal restrictions.
We understand that clients opt to disperse their digital estate across multi-cloud and hybrid environments for a variety of good reasons. These are a few typical business motivators:
- Reduce or prevent lock-in to a single cloud provider
- Acquired enterprises, subsidiaries, and business units have already implemented various cloud systems.
- Depending on the geopolitical context, various cloud providers may have varying regulatory and data sovereignty requirements.
- Increase disaster recovery and business continuity by splitting workloads between two cloud providers.
- Run apps close to user locations to optimize performance; this may necessitate adopting multi-cloud or hybrid systems.
- Adopting multi cloud techniques might facilitate the easy migration of certain data platforms or industry-specific applications.
Hybrid and Multicloud Concerns
With a wise approach to adopting multi-cloud and hybrid technologies, several of the aforementioned incentives can develop into business transformations.
Others need substantial pre- and post-deployment work in order to achieve those novel benefits. For example, cloud provider lock-in is a possibility. However companies must narrow their strategy for cloud adoption to prevent lock-in. Numerous of a cloud provider's best offerings are exclusive to that provider and cannot be found with another. Organizations are frequently forced to restrict cloud adoption to the most basic infrastructure as a service (IaaS) capabilities or heavily invest in the use of cloud-native technologies like containers or Kubernetes to achieve mobility and minimize lock-in.
Another typical challenge related to hybrid and multi-cloud adoption arises once workloads are released and put into production: businesses frequently have to immediately reevaluate existing processes when attempting to give operations management support to workloads in new environments. These kinds of settings are not intended for use with the operations management systems that are now in use, nor with the policies and procedures that accompany them. Companies frequently wind up with distinct operations tooling and processes to account for variations in cloud environments, which doubles the cost of operations by the number of cloud environments supported.
Minimize Hybrid and Multicloud Concerns with Unified Operations
Unified operations in Azure are a critical component of minimizing the concerns associated with hybrid and multicloud deployments. These operations provide a consistent and efficient way to manage resources across diverse environments, ensuring that organizations can reap the benefits of Azure hybrid and multi-cloud solutions while mitigating potential challenges. Here are some key ways to minimize these concerns using unified operations in Azure:
1. Azure Arc
Azure Arc is a central piece of the puzzle. It enables organizations to extend Azure services to any infrastructure, whether on-premises, at other cloud providers, or on the edge. This extension allows you to centrally manage and govern resources consistently, regardless of their location. Azure Arc brings various benefits to the table:
-
Inventory and Configuration Management:
Azure Arc provides a unified inventory of all your resources, offering a single pane of glass to view and manage them. This ensures you have a comprehensive view of your resources across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
-
Policy and Compliance Enforcement:
Azure Policy can be used to enforce compliance and configuration standards across all your resources, maintaining consistency and security. You can define policies once and apply them uniformly, which is crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring data security.
-
Automated Deployments:
Azure Arc simplifies the process of deploying and managing resources across different environments. You can use Azure Resource Manager templates to create, update, and delete resources consistently across all your environments.
2. Azure Policy and Blueprints
Azure Policy and Azure Blueprints work in tandem to help organizations maintain consistency and enforce compliance standards in a multi-cloud environment:
-
Azure Policy:
This service allows you to create, assign, and manage policies that define rules and actions for resources. These policies can be applied uniformly across various cloud providers and on-premises environments. For instance, you can define a policy to ensure that all virtual machines have encryption enabled, regardless of where they are deployed.
-
Azure Blueprints:
Azure Blueprints provide a way to package policy definitions, role assignments, and resource templates into reusable artifacts. This ensures that you can consistently apply governance requirements, such as security or compliance, across your multi-cloud landscape.
3. Azure Security Center
Security is paramount in hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Azure Security Center is a unified security management system that offers advanced threat protection across all your workloads. Here's how it helps mitigate concerns:
-
Unified Security Dashboard:
Azure Security Center provides a unified dashboard to monitor and protect resources in hybrid and multi-cloud deployments. It offers visibility into security vulnerabilities, threats, and compliance status, allowing you to take action proactively.
-
Security Recommendations:
The service offers security recommendations and best practices based on the assessment of your resources. This helps organizations identify and address potential security issues consistently.
-
Security Policy Enforcement:
You can use Azure Security Center to enforce security policies uniformly across all your environments, ensuring that security configurations and settings are consistent.
4. Azure Cost Management and Billing
Managing costs in multi-cloud environments can be complex due to different pricing models and billing structures from various cloud providers. Azure Cost Management and Billing provide tools to optimize expenses:
-
Unified Cost Management:
Azure Cost Management offers a unified view of your spending across Azure and other cloud providers. This enables you to track costs consistently and identify areas for optimization.
-
Budgets and Alerts:
You can set up budgets and alerts to keep spending in check across all your cloud environments. Azure will notify you when spending approaches or exceeds defined thresholds.
Benefits of Using Hybrid Cloud
Embracing Azure hybrid multicloud and cloud deployments offers numerous advantages:
-
Flexibility:
Organizations can adapt to changing business needs, scaling resources up or down as required.
-
Cost Efficiency:
By optimizing resource allocation and usage, businesses can realize significant cost savings.
-
Security:
Sensitive data can be kept on-premises while leveraging Azure's robust security features for cloud-based resources.
-
Resilience:
Multicloud strategies enhance redundancy and fault tolerance, reducing the risk of downtime.
-
Scalability:
Azure's extensive service offerings facilitate the development and deployment of diverse workloads.
-
Innovation:
Azure's continuous updates and new services enable organizations to stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Azure hybrid multicloud and cloud solutions offer organizations a powerful and flexible approach to cloud computing. They provide a range of benefits while addressing specific operational, security, and compliance needs. Here are 7-8 key points to sum up the significance of Azure hybrid multicloud:
- Azure empowers businesses to scale resources as needed, ensuring adaptability to changing demands.
- Optimization tools and unified management streamline resource allocation, leading to significant cost savings.
- Organizations can maintain data control and regulatory compliance while benefiting from Azure's robust security features.
- Multicloud strategies enhance fault tolerance, reducing the risk of downtime and service disruptions.
- Azure's global network enables resource deployment in various regions, improving performance and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Continuous updates and new services allow organizations to stay competitive and innovative in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
- Azure Cost Management and Billing provide insights into spending patterns and budgeting to ensure efficient resource usage.
