Azure Virtual WAN
Overview
Azure Virtual WAN simplifies and optimizes connectivity in Azure and on-premises setups. It centralizes management, enhances security, and ensures seamless connectivity to Azure resources and the internet. With improved performance and efficient routing, it simplifies branch connections and enables easy network scaling, offering reliable and secure connectivity for applications and data in Azure.
What is Azure Virtual WAN
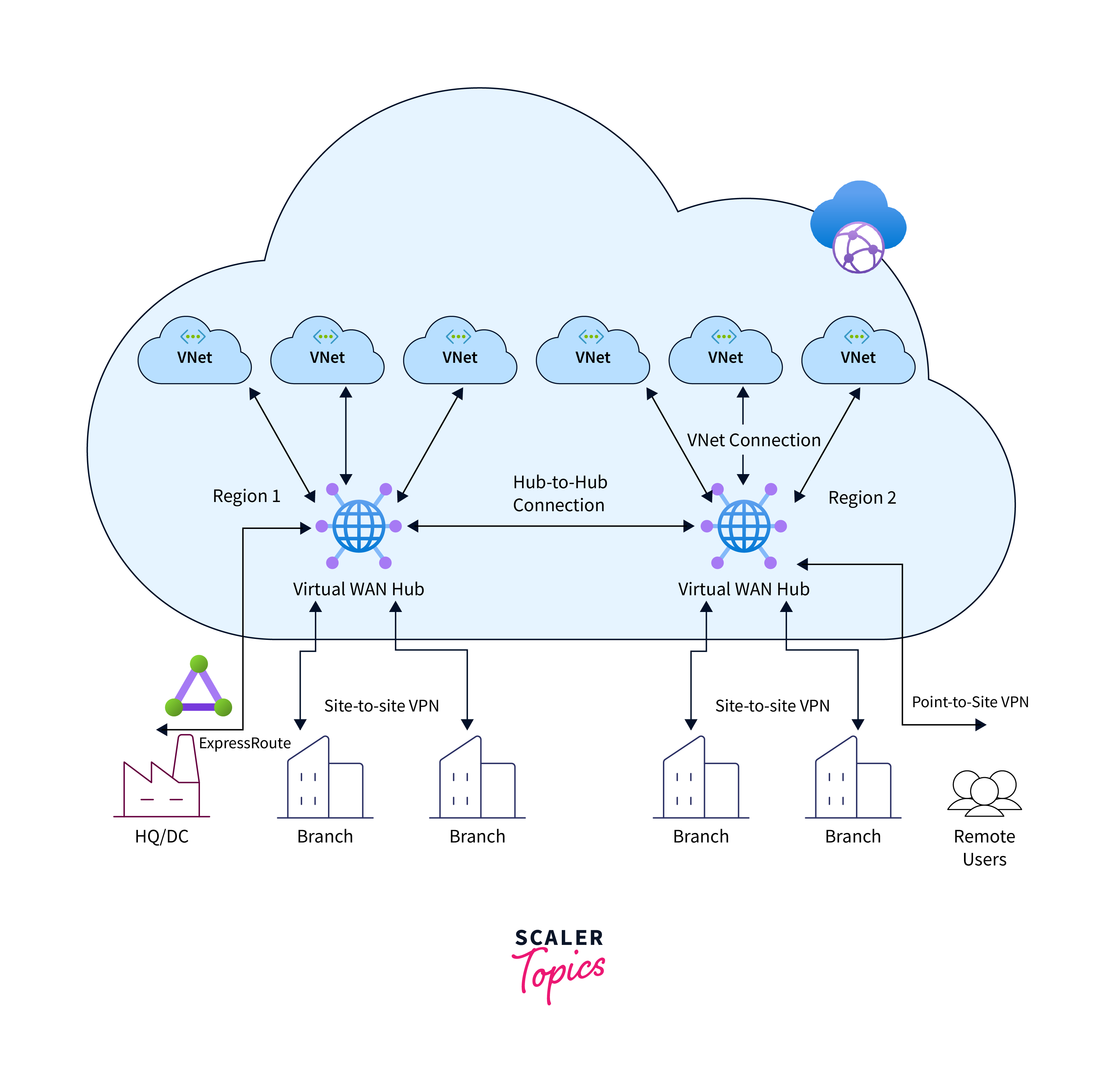
Azure Virtual WAN is a Microsoft Azure service designed to simplify and optimize networking and connectivity in a multi-branch and multi-cloud environment. It provides a centralized hub for network management, allowing organizations to connect their on-premises sites, remote offices, and Azure resources efficiently. Here's a more detailed overview of Azure Virtual WAN:
-
Hub and Spoke Architecture: Azure Virtual WAN employs a hub and spoke architecture for network design. In this model, the hub serves as the central point of connectivity and management, while the spokes represent various locations, such as branch offices or Virtual Networks (VNets). This design simplifies network management by consolidating it at the hub, making it easier to control traffic and security policies.
-
Optimized Routing: Virtual WAN includes routing capabilities that prioritize efficient traffic routing. It ensures that data takes the most direct and optimal path to reach its destination. This optimization is crucial for enhancing network performance and reducing latency.
-
Secure Connectivity: One of the key benefits of Azure Virtual WAN is its ability to provide secure connectivity. Leveraging Azure's robust global network infrastructure, it offers a secure and reliable means of connecting your on-premises sites and branch offices to Azure resources. This reduces the need for maintaining dedicated, expensive VPN connections and enhances the overall security of your network.
-
Site-to-Site VPN: Azure Virtual WAN supports site-to-site VPN connections, enabling secure and encrypted communication between your on-premises locations and Azure. This capability is vital for ensuring that data transmitted between your network and Azure remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
-
Branch-to-Azure Connectivity: Branch offices can seamlessly connect to Azure resources using SD-WAN appliances. SD-WAN technology optimizes network traffic between your branch offices and Azure, enhancing connectivity and ensuring reliable communication.
-
Azure Transit: Azure Virtual WAN allows network traffic to traverse Azure for inspection, filtering, and auditing. This feature, known as Azure Transit, adds an extra layer of security and compliance to your network by routing traffic through Azure, where it can be subjected to various security and monitoring services.
-
Integrated Security Services: Azure Virtual WAN integrates with Azure Firewall, Azure Network Firewall, and Azure Bastion. These security services provide added protection by filtering network traffic, preventing unauthorized access, and securing your virtual network infrastructure.
The architecture of Virtual WAN
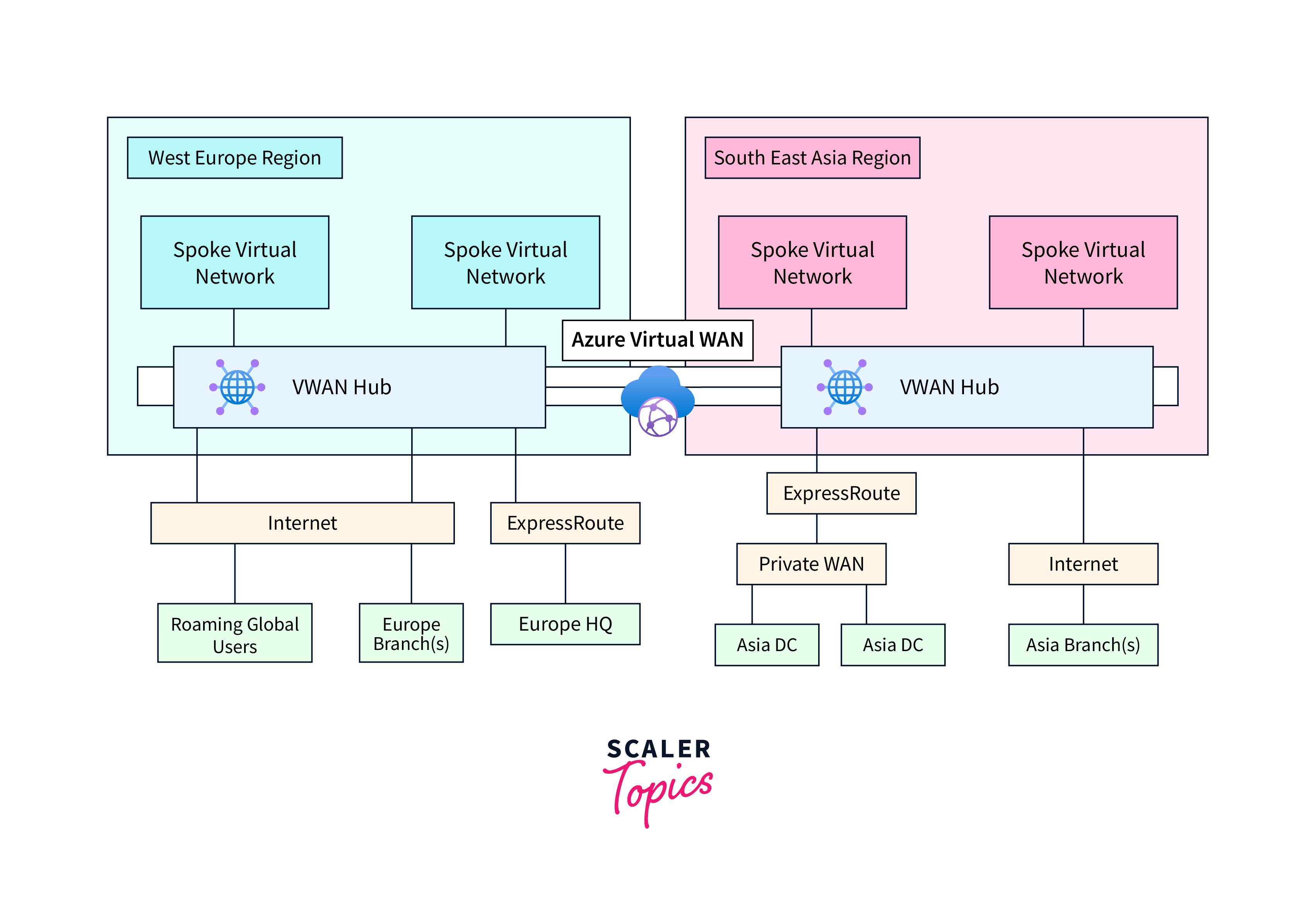
The architecture of Azure Virtual WAN is built on a hub and spoke model, designed to simplify and optimize network connectivity in a multi-branch and multi-cloud environment. Let's explore the architecture in more detail:
-
Hub: The hub serves as the central point of connectivity and management in Azure Virtual WAN. It is typically located in an Azure region and is where network traffic is aggregated and controlled. The hub can be associated with multiple spoke locations, including branch offices and Azure VNets.
-
Spokes: Spokes are the remote locations or Virtual Networks (VNets) that connect to the hub. Spokes can represent branch offices, remote sites, or Azure VNets. Spokes establish connectivity to the hub, allowing them to communicate with each other and with Azure resources through the hub.
-
Hub-to-Hub Connectivity: Azure Virtual WAN supports hub-to-hub connectivity. This means that if you have multiple hubs, they can be interconnected, enabling seamless communication between different hubs. This is useful for organizations with a distributed network architecture.
-
Hub-to-Spoke Connectivity: Traffic can flow from spokes to the hub and vice versa. This connectivity is essential for managing network traffic, enforcing security policies, and optimizing routing through the hub.
-
Hub-to-On-Premises Connectivity: Azure Virtual WAN allows secure connections between on-premises locations and the hub through site-to-site VPNs. This ensures that data can flow securely between your corporate network and Azure resources.
-
Security and Compliance: The hub acts as a control point for network security and compliance. By centralizing network policies and security measures at the hub, organizations can enforce consistent security across all connected spokes. Azure Virtual WAN also integrates with Azure security services to enhance network protection.
-
Optimized Routing: Azure Virtual WAN optimizes the routing of network traffic, ensuring that data takes the most efficient path between spokes, hubs, and Azure resources. This optimized routing enhances network performance and reduces latency.
Resources
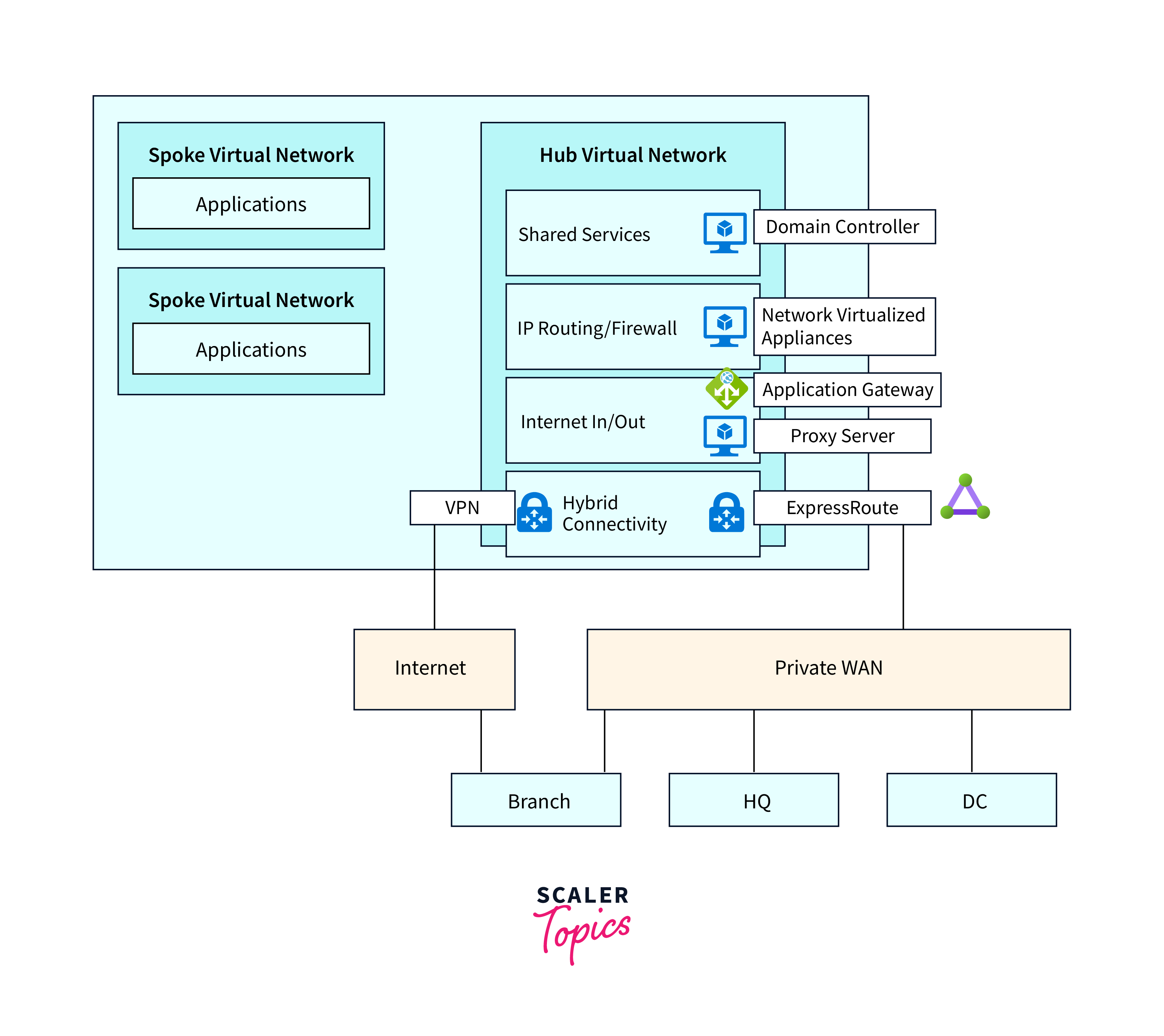
Azure Virtual WAN uses several key resources and components to enable its architecture and functionality. Here are some of the essential resources involved in Azure Virtual WAN:
-
Virtual WAN: The central resource that represents the Azure Virtual WAN itself. It is the primary resource that contains the configuration settings and defines the overall architecture. Virtual WAN is created and managed in the Azure portal.
-
Hubs: Hubs are critical resources within Azure Virtual WAN. They act as the central points for network connectivity and management. Each hub is typically associated with a specific Azure region and serves as the focal point for connecting spokes and on-premises locations.
-
Spokes: Spokes represent remote sites or Virtual Networks (VNets) that connect to the hub. These can include branch offices, remote data centers, or Azure VNets. Spokes establish connectivity to the hub, enabling network traffic to flow between them and with Azure resources through the hub.
-
Site-to-Site VPN Connections: Site-to-Site VPN connections are established between on-premises locations and the hub. These connections ensure secure communication between the corporate network and Azure resources. VPN gateways are used to establish these connections.
-
Hub Virtual Network Gateways: Hub Virtual Network Gateways are used to connect spokes and on-premises locations to the hub. They facilitate the secure and encrypted flow of network traffic between these resources and the hub.
-
Routing: Routing resources play a crucial role in Azure Virtual WAN. They ensure that network traffic is routed efficiently between spokes, hubs, and Azure resources. This includes the routing of traffic from on-premises locations through the hub and to Azure.
-
Network Security Groups (NSGs): NSGs are used to enforce network security policies at the hub and spoke levels. They allow administrators to control inbound and outbound traffic to and from virtual machines and other resources.
-
Azure Firewall: Azure Firewall can be integrated into Azure Virtual WAN to provide network security services. It helps filter and inspect network traffic, adding an extra layer of security to the network architecture.
Types of Virtual WAN
Azure Virtual WAN provides different types of hubs to cater to specific networking needs. These hub types include:
-
Standard Hub: A Standard Hub serves as the central point for connecting branch offices and remote locations to the Azure cloud. It allows for seamless communication between these locations and Azure resources, optimizing routing and security policies.
-
Secured Virtual Hub: A Secured Virtual Hub provides enhanced security features for your network. It includes integrated security services like Azure Firewall and Azure Bastion to safeguard network traffic and protect against security threats.
-
ExpressRoute Hub: An ExpressRoute Hub is designed for organizations that require high-speed, dedicated network connections to Azure. It allows for a direct connection to Azure resources through ExpressRoute circuits, ensuring reliable and low-latency communication.
-
Gateway Transit Hub: The Gateway Transit Hub type is suitable for scenarios where a hub needs to act as a transit point for VPN and ExpressRoute traffic to reach on-premises locations. It facilitates connectivity to the corporate network through VPN and ExpressRoute.
-
Transit Hub: A Transit Hub type enables hub-to-hub connectivity. This is useful for organizations with a distributed network architecture that requires communication between different hubs. It enhances the scalability and reach of the network.
-
Global Transit Hub: A Global Transit Hub is designed for organizations with global operations. It allows for network connectivity across the globe, connecting different locations in a worldwide network. It simplifies network architecture for multinational organizations.
The choice of hub type depends on an organization's specific networking requirements. Standard Hubs are commonly used for connecting branch offices and remote sites to Azure. Secured Virtual Hubs add an extra layer of security. ExpressRoute Hubs cater to high-speed dedicated connections. Gateway Transit Hubs and Transit Hubs facilitate traffic flow between different hubs, while Global Transit Hubs enable worldwide network connectivity.
Each hub type is designed to address specific networking scenarios and requirements, offering flexibility and scalability in Azure Virtual WAN.
Advantages of using virtual WAN
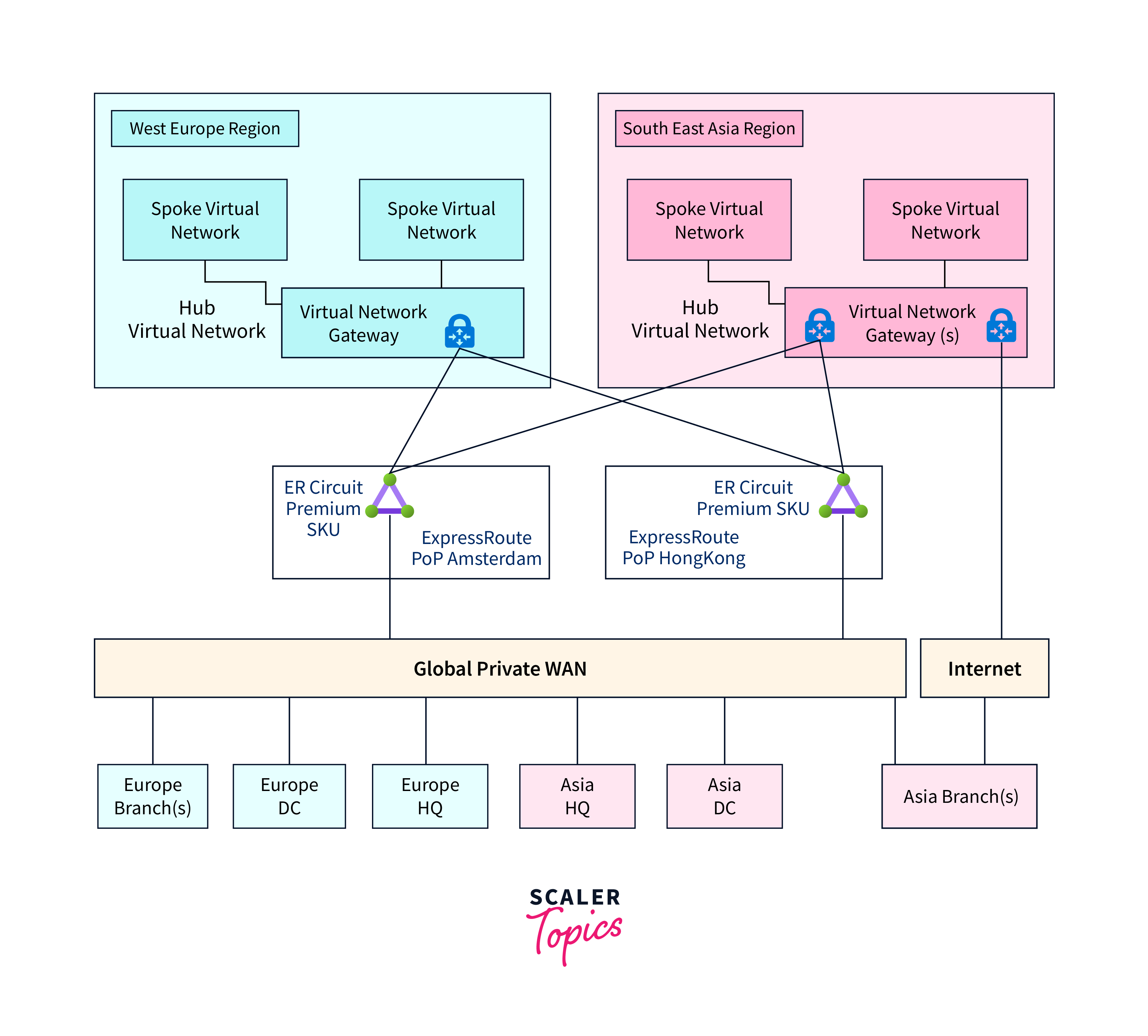
Using Azure Virtual WAN offers several advantages for organizations seeking to simplify, optimize, and secure their network connectivity. Some key advantages include:
-
Centralized Network Management: Azure Virtual WAN provides a hub-and-spoke architecture, allowing for centralized network management. This simplifies the configuration, monitoring, and control of network resources, reducing administrative overhead.
-
Optimized Routing: The service optimizes traffic routing, ensuring data takes the most efficient path. This leads to enhanced network performance, reduced latency, and cost savings in data transfer.
-
Secure Connectivity: Virtual WAN leverages Azure's global network infrastructure, offering secure connectivity. This reduces the need for costly dedicated VPN connections and enhances network security.
-
Seamless Branch Connectivity: Branch offices and remote locations can connect to Azure efficiently through SD-WAN appliances, ensuring reliable and efficient communication.
-
Site-to-Site VPN: Azure Virtual WAN supports site-to-site VPN connections, enabling secure and encrypted communication between on-premises locations and Azure.
-
Disaster Recovery: Azure Site Recovery, integrated with Virtual WAN, provides disaster recovery capabilities. VMs can failover to a secondary Azure region, ensuring business continuity.
-
Cost Efficiency:
- Reduced Hardware Costs: Virtual WAN solutions often eliminate the need for dedicated, expensive hardware appliances, as they leverage software-defined networking (SDN) and virtualization technologies.
- Optimized Bandwidth Utilization: Virtual WAN can optimize bandwidth usage through intelligent routing and traffic management, potentially reducing costs associated with data transfer.
- Flexibility and Scalability:
- Elasticity: Virtual WAN allows for easy scalability, enabling organizations to adjust their network resources based on changing demands without the need for significant infrastructure changes.
- Agility: Virtual WAN can adapt quickly to changes in network configurations or business requirements, providing greater agility compared to traditional networking solutions.
- Disaster Recovery and Redundancy: Virtual WAN allows for the implementation of redundant connections and failover mechanisms, enhancing resilience and ensuring business continuity in the event of network failures or disasters.
- Integration with Cloud Services:
- Cloud-native Integration: Virtual WAN solutions are often designed to integrate seamlessly with cloud platforms, supporting direct connections to cloud services and optimizing performance for cloud-based applications.
- Multi-Cloud Support: Virtual WAN can provide connectivity and optimization for organizations using multiple cloud providers, offering flexibility and avoiding vendor lock-in.
Conclusion
- Azure Virtual WAN simplifies and optimizes network connectivity with a hub-and-spoke architecture. It offers centralized network management, reducing administrative complexity.
- Optimized routing enhances network performance and reduces latency. Secure connectivity is achieved through Azure's global network infrastructure.
- Branch offices can connect efficiently through SD-WAN appliances. Site-to-site VPN connections ensure secure communication with on-premises locations. Azure Site Recovery provides disaster recovery capabilities for business continuity.
- Compliance certifications make it suitable for organizations with regulatory requirements. It can lead to cost savings in network operations. Scalability and flexibility make it adaptable to organizations of all sizes and complexities.
- ExpressRoute hubs offer high-speed, dedicated connectivity to Azure resources. Azure Virtual WAN streamlines network operations in multi-branch and multi-cloud environments.
