B Tree in DBMS
Indexing is the first thing that comes to mind when we consider a database's performance. In this article, we'll learn about B-trees and how database indexing using B-tree in DBMS can improve the databases' performance.
An m-way tree that self-balances itself is called a "B-tree." Due to their balanced structure, such trees are frequently used to manage and organize enormous databases and facilitate searches. In a B-tree, each node can have a maximum of m child nodes.
Definition of B-tree
B-tree in DBMS is an m-way tree that balances itself. Due to their balanced structure, such trees are frequently used to manage and organize enormous databases and facilitate searches. In a B-tree, each node can have a maximum of n child nodes. In DBMS, B-tree is an example of multilevel indexing. Leaf nodes and internal nodes will both have record references. B-Tree is called a Balanced stored tree as all the leaf nodes are at the same levels.
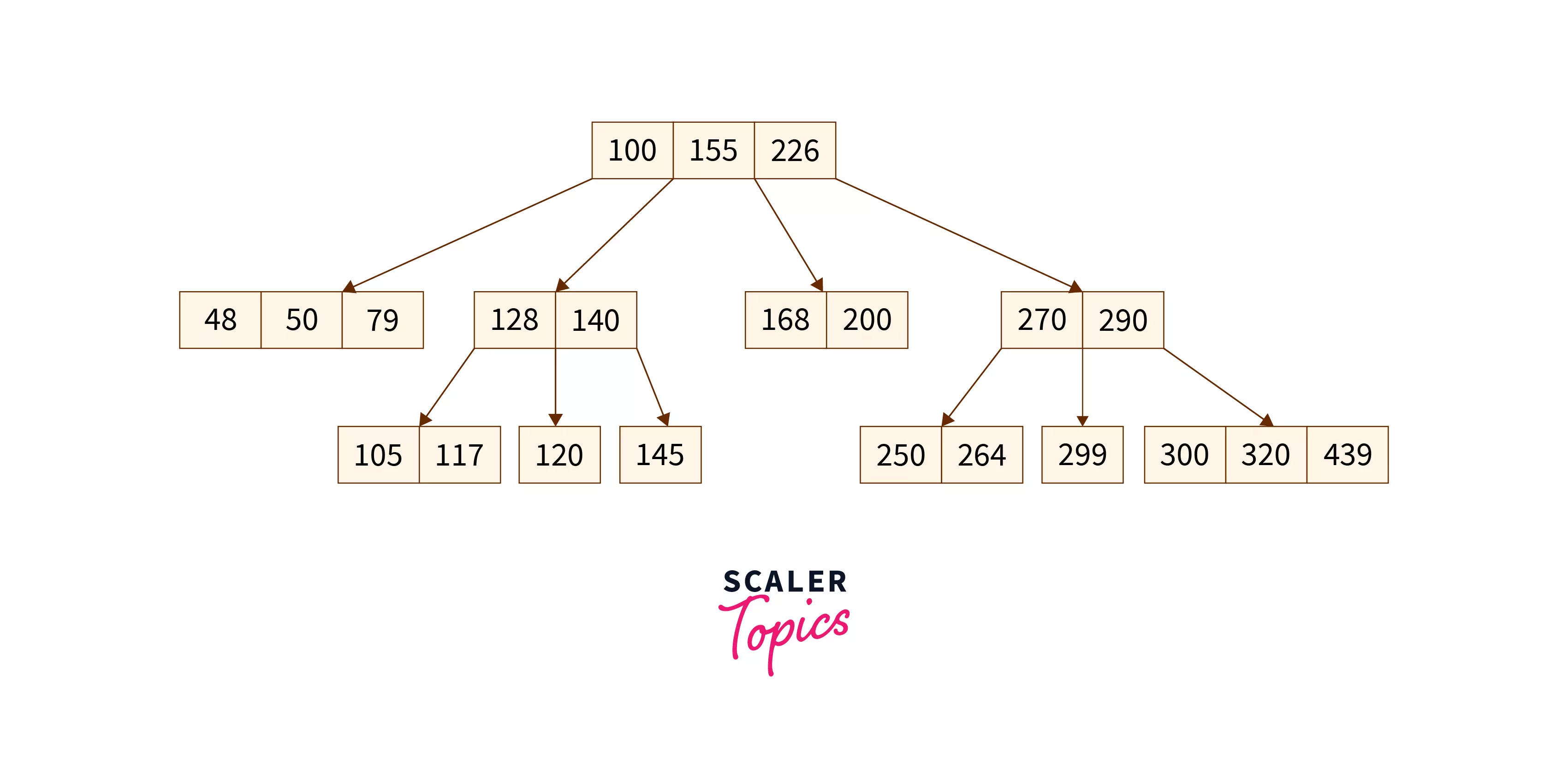
Properties of B-tree
Following are some of the properties of B-tree in DBMS:
- A non-leaf node's number of keys is one less than the number of its children.
- The number of keys in the root ranges from one to (m-1) maximum. Therefore, the root has a minimum of two and a maximum of m children.
- The keys range from min([m/2]-1) to max(m-1) for all nodes (non-leaf nodes) besides the root. Thus, they can have between m and [m/2] children.
- The level of each leaf node is the same.
Need of B-tree
- For having optimized searching we cannot increase a tree's height. Therefore, we want the tree to be as short as possible in height.
- Use of B-tree in DBMS, which has more branches and hence shorter height, is the solution to this problem. Access time decreases as branching and depth grow.
- Hence, use of B-tree is needed for storing data as searching and accessing time is decreased.
- The cost of accessing the disc is high when searching tables Therefore, minimizing disc access is our goal.
- So to decrease time and cost, we use B-tree for storing data as it makes the Index Fast.
How Database B-Tree Indexing Works
- When B-tree is used for database indexing, it becomes a little more complex because it has both a key and a value. The value serves as a reference to the particular data record. A payload is the collective term for the key and value.
- For index data to a particular key and value, the database first constructs a unique random index or a primary key for each of the supplied records. The keys and record byte streams are then all stored on a B+ tree. The random index that is generated is used for indexing of the data.
- So this indexing helps to decrease the searching time of data. In a B-tree, all the data is stored on the leaf nodes, now for accessing a particular data index, the database can make use of binary search on the leaf nodes as the data is stored in the sorted order.
- If indexing is not used, the database reads each and every record to locate the requested record and it increases time and cost for searching the records, so B-tree indexing is very efficient.
How Searching Happens in an Indexed Database?
The database does a search in the B-tree for a given key and returns the index in O(log(n)) time. The record is then obtained by running a second B+tree search in O(log(n)) time using the discovered index. So overall approx time taken for searching a record in a B-tree in DBMS-indexed databases is O(log(n)).
Examples of B-Tree
Suppose there are some numbers that need to be stored in a database, so if we store them in a B-tree in DBMS, they will be stored in a sorted order so that the searching time can be logarithmic.
Let's take a look at an example:
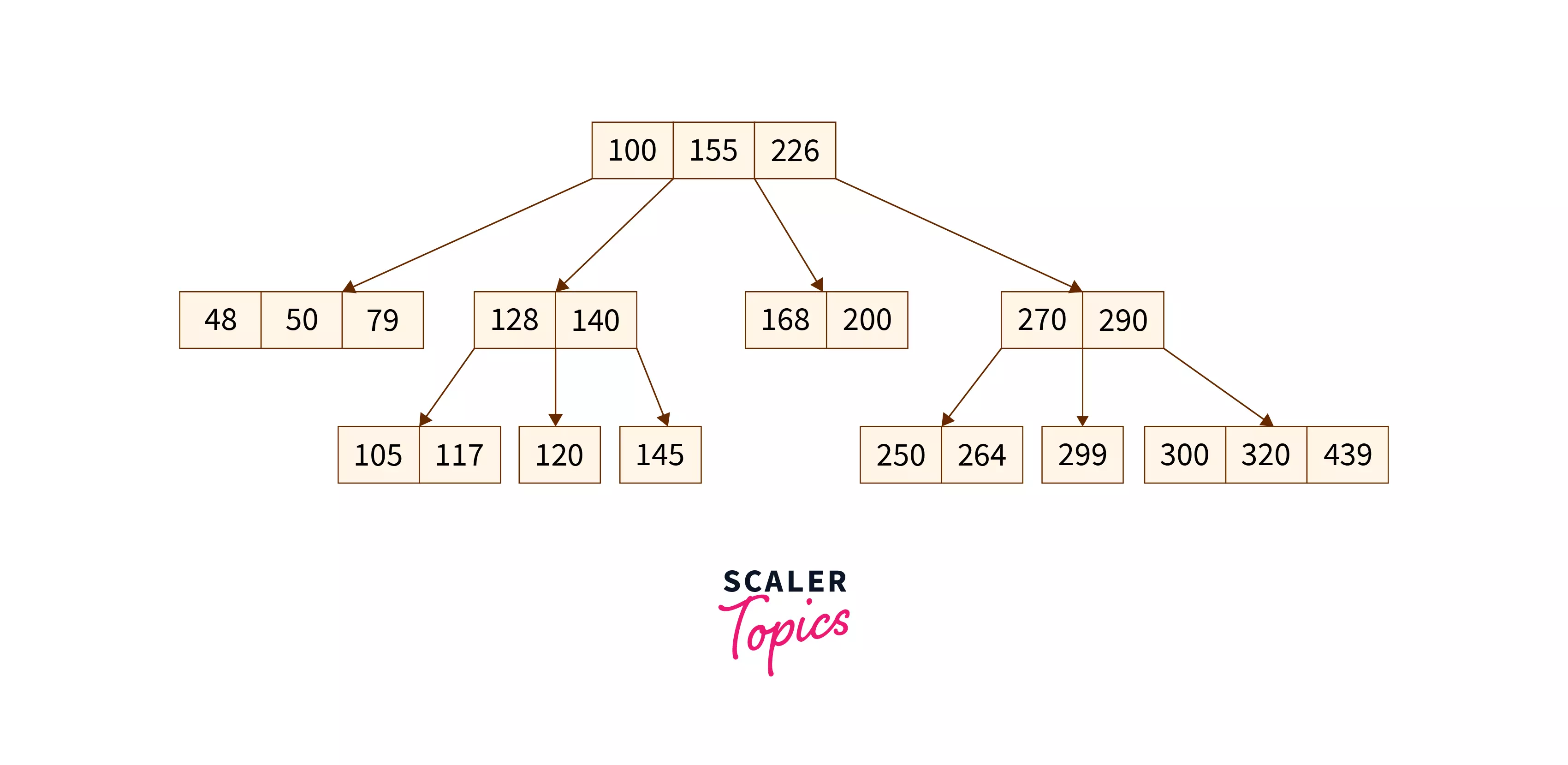 The above data is stored in sorted order according to the values, if we want to search for the node containing the value 48, the following steps will be applied:
The above data is stored in sorted order according to the values, if we want to search for the node containing the value 48, the following steps will be applied:
- First, the parent node with a key having data 100 is checked, as 48 is less than 100 so the left children node of 100 is checked.
- In left children, there are 3 keys, so it will check from the leftmost key as the data is stored in sorted order.
- The leftmost element is having key value as 48 which matches the element to be searched, that we wanted to search.
Learn more
You can learn more about B-tree in DBMS:
Conclusion
- An m-way tree that self-balances itself is called a “B-tree”.
- Due to their balanced structure, such trees are frequently used to manage and organize enormous databases and facilitate searches.
- B-tree is an example of multilevel indexing.
- Use of B-tree is needed for storing data as searching and accessing time is decreased.
- B-trees can be used for database indexing to improve searching and storing time of database.
- While using B-tree, the database can make use of binary search on the leaf nodes as the data is stored in the sorted order.

