base Tag in HTML

Overview

The <base> HTML tag specifies a base URL or URL for relative links within an HTML page. This URL will serve as the base URL for all links on the page and will appear before each of them.
For example, we can set the base URL once in the header area of our page, and all subsequent relative links will utilize that URL as a starting point.
The following tutorial provides information about this element, including, attributes, examples of its usage, related properties, and browser compatibility.
Syntax
Note :
- The <head> tag contains the HTML <body> element.
- A page can have only one <base> element.
Attributes
Attributes are applied to tags to provide more information to the browser about how the tag should appear or behave. You can use one or more attributes with HTML tags. Attributes are made up of a name and a value separated by an equals sign (=), with the value enclosed in double quotes.
For example, <base target = "\_blank" >
Element - Specific Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| href | URL | Specifies the base URL for relative URLs throughout the page. Absolute and relative URLs are also permitted. |
| target | _blank, _parent, _self, _top | Specifies where the linked resource should be displayed. |
The following are explanations of target values :
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| _blank | Opens the target URL in a new window. |
| _parent | Opens the target URL in the parent frame. |
| _self | Opens the target URL in the current window. |
| _top | Opens the target URL in the full width of the window. |
Global Attributes
Global attributes are properties that can be applied to all HTML elements and are shared by all of them. As both standard and non-standard HTML elements support them, they're referred to as global. However, they may not affect some.
Global properties can be applied to any HTML element, including ones that aren't mentioned in the standard. This means that even if utilizing non-standard elements causes the content to be non-HTML5 compliant, some characteristics must be allowed. Despite the fact that <foo hidden>...</foo> is not a valid HTML element, HTML5-compliant browsers conceal content marked as <foo hidden>...</foo>.
List of Global Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accesskey | shortcut key | It guides how to create a keyboard shortcut for the currently selected element. The browser should use the first one on the computer keyboard layout. |
| autocapitalize | off / none, on / sentences, words, characters | Controls whether or not text input is automatically capitalized when entered/edited by the user and how it is capitalized. |
| autofocus | false | Indicates that an element will be highlighted when the page loads or when the <dialogue> in which it is included is displayed. |
| class | classname | It is a list of classes for the element, separated by spaces. CSS and JavaScript use classes to identify and access specific components using class selectors or functions. |
| contenteditable | true/false | An enumerated attribute that indicates whether or not the element should be user-modifiable. If this is the scenario, the browser modifies its widget to allow customization. |
| contextmenu | menu-id | The context menu of an element is defined. A context menu appears when the user clicks the right mouse button on an element. |
| data-* | data | Custom data attributes allow private information to be communicated between HTML and its DOM representation, which scripts can use. All such custom data can be accessed using the HTML Element interface of the element on which the attribute is set. |
| dir | ltr / rtl / auto | Specifies the element's text's base direction of directionality. |
| draggable | true/false / auto | An enumerated attribute is used to specify whether or not the element may be dragged using the Drag and Drop API. |
| dropzone | copy/move/link | This parameter determines whether dragged data is copied, relocated, or linked when it is dropped. |
| enterkeyhint | On virtual keyboards, this value indicates the action label (or icon) for displaying the enter key. | |
| exportparts | It can be used to transitively export shadow components from a nested shadow tree to a contained light tree. | |
| hidden | hidden | The value of a Boolean attribute indicates whether or not the element is still relevant. For example, It can be used to hide parts of a website that can't be accessible until the login procedure is finished. Such things will not be rendered by the browser. |
| Id | name | Defines a distinct/unique identifier (ID) that must be consistent and unique throughout the document. It identifies the element when linking (through a fragment identifier), scripting, or styling (with CSS). |
| lang | language-code | It is used to specify the primary language for the element's text content. |
| Spellcheck | true/false | It is used to specify whether or not the element should be checked for spelling mistakes. |
| tabindex | number | It is used to specify the tabbing order of an element. |
| title | text | It includes text that presents advisory information about the element to which it belongs. Generally, but not always, such information is given to the user in the form of a tooltip. |
| slot | The slot established by the element whose name attribute matches the value of the slot property is assigned to an element with a slot attribute. | |
| Style | style | Inline CSS is applied to the currently chosen element using style. It is recommended that styles should be defined in separate files or files. This attribute and the <style> element are designed for quick stylings, such as for testing purposes. |
| translate | yes/no | It is used to specify whether or not the content of the element should be converted when the page is localized. |
| xml | language-code | It is used to specify the predominant language for the element's text content in XHTML documents. |
How to Use <base>Tag in HTML ?
- The <base> tag in HTML provides the base URL that all relative URLs in a document should use. Using the target attribute, we can also indicate how additional links should open (in the same window, in another window, etc.).
- A document can only have one <base> element, which is contained inside the <head> tag. The tag must include either a href, a target attribute, or both. <base> tag in HTML is a self-closing tag and does not contain any content.
Examples of <base> Tag in HTML
Example 1:
In this example, we will specify a default URL and a default target for all links on a page.
Output
Example 2:
In this example, we will open the target URL in the same window (by default).
Output

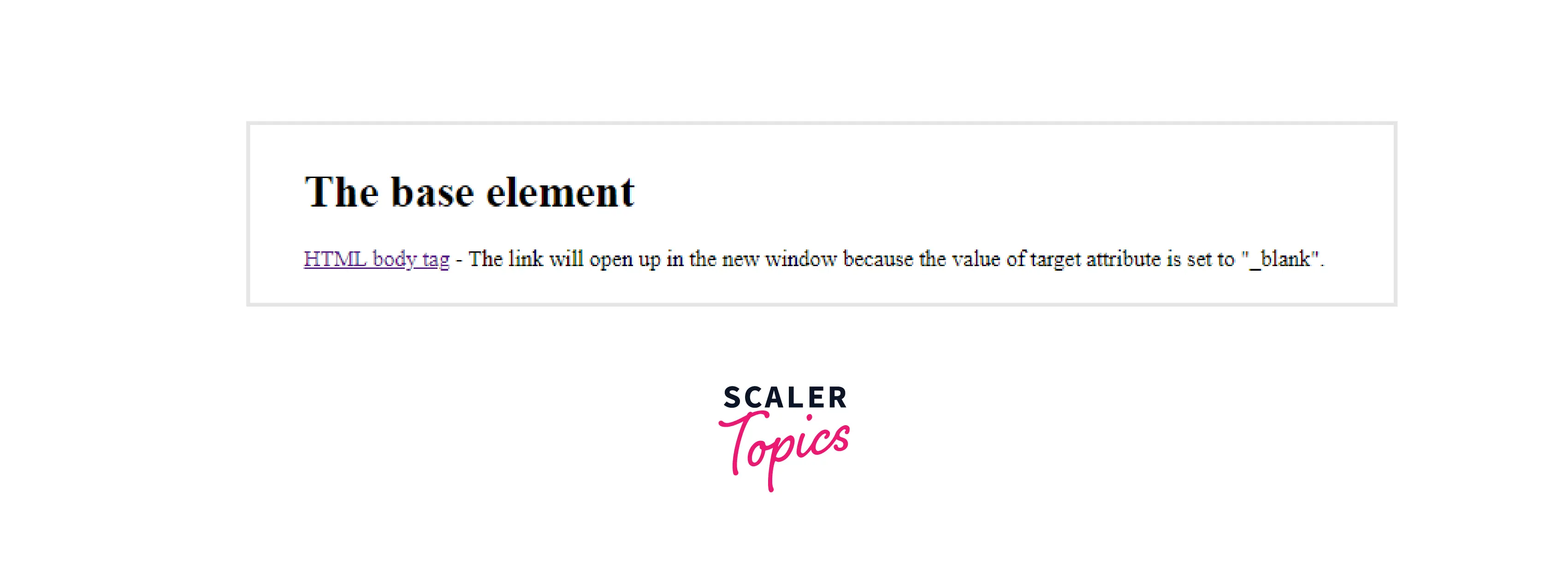
Example 3:
In this example, we will use the _blank atrribute with the <base> tag.
Output

Accessibility Concerns
While the <base> URL can be useful, one of its downsides is that once you define it, you're locked with it. It can only be used once, and after that, all URLs will be impacted. Linking to in-page anchors might also be challenging while using the <base> tag.
Browser Support
The <base> tag in HTML is supported by the following browsers :
| Browser | Google Chrome | Internet Explorer | Microsoft Edge 12+ | Firefox | Opera | Safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Learn More
Conclusion
- The <base> tag in HTML is used to specify the base URL for all the URLs in the HTML document.
- Suppose a single webpage contains numerous URLs for the same domain name. In that case, the base URL can be specified using the <base> tag in the HTML document head, and the relative paths can subsequently be added in the HTML document body. All the relative URLs on the webpage will automatically include the base URL.
- The <base> element is defined in the <head> section and is only allowed to be used once per document.
- The <base> tag in HTML has two event-specific attributes. One is the href attribute, which specifies the base URL for relative URLs throughout the document, while the other is the target attribute, which specifies where the linked resource should be displayed.
Related Tags
- <head>
- <a>
- <meta>
