Linux Binary Directories
Overview
In the world of Linux, the file system is organized hierarchically, and each directory has a distinct purpose. One crucial aspect of Linux is the presence of binary directories, which house executable files. These bin directories in linux serve as storage locations for important commands and programs. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Linux's principal binary folders, particularly /bin, /sbin, /lib, and /opt. Each directory serves a certain purpose and contains a specific type of binary.
Introduction to Linux Binary Directories
As previously mentioned, the Linux operating system employs a hierarchical file system structure, with various directories serving specific functions. Bin directories in Linux are dedicated areas for storing executable files, commonly known as binaries. These binaries are required for the execution of different commands and programs on a Linux system. The binary folders ensure that these executables are easily accessible to users. These directories serve as storage locations for important commands and programs. This article describes the primary bin directories in Linux. Each directory serves a certain purpose and contains a specific type of binary.
Binary directory contains the following directories:
- /bin
- /sbin
- /lib
- /opt
/bin
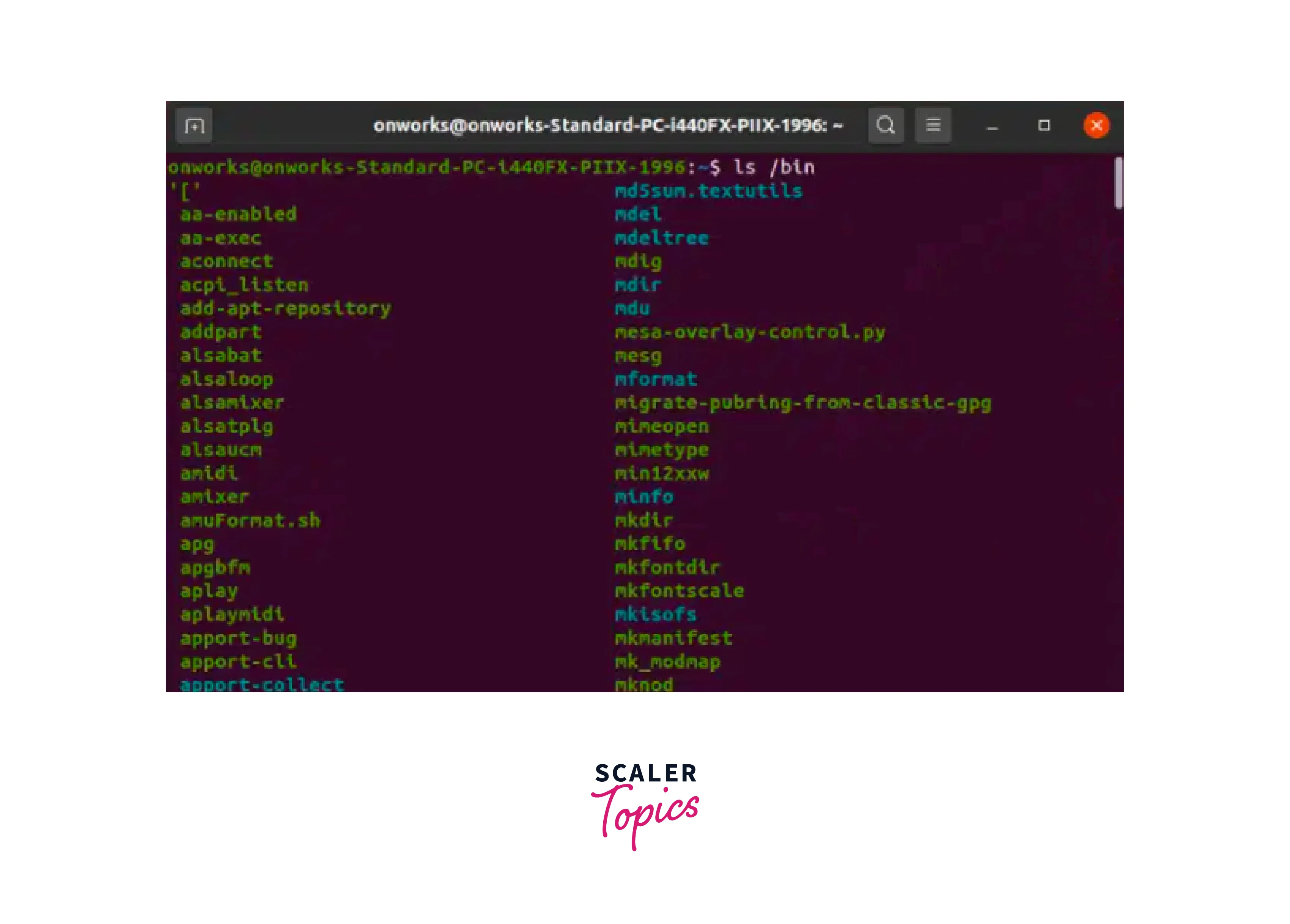
The /bin directory, which stands for "binary" includes basic binaries that are required for the system's basic function. These binaries are available to all users and are required for the system to function properly. In other words, /bin contains the basic commands that users utilize on a daily basis. Binaries contained in /bin include commands like ls, cp, mv, mkdir, and rm. The ls command displays a list of files and directories, cp copies files, mv moves or renames files, mkdir creates directories, and rm deletes files and directories. These commands are essential for doing daily chores because they allow users to explore the file system, change files and directories, and conduct basic operations.
We can use the following command to see /bin directories:
Output:
/sbin
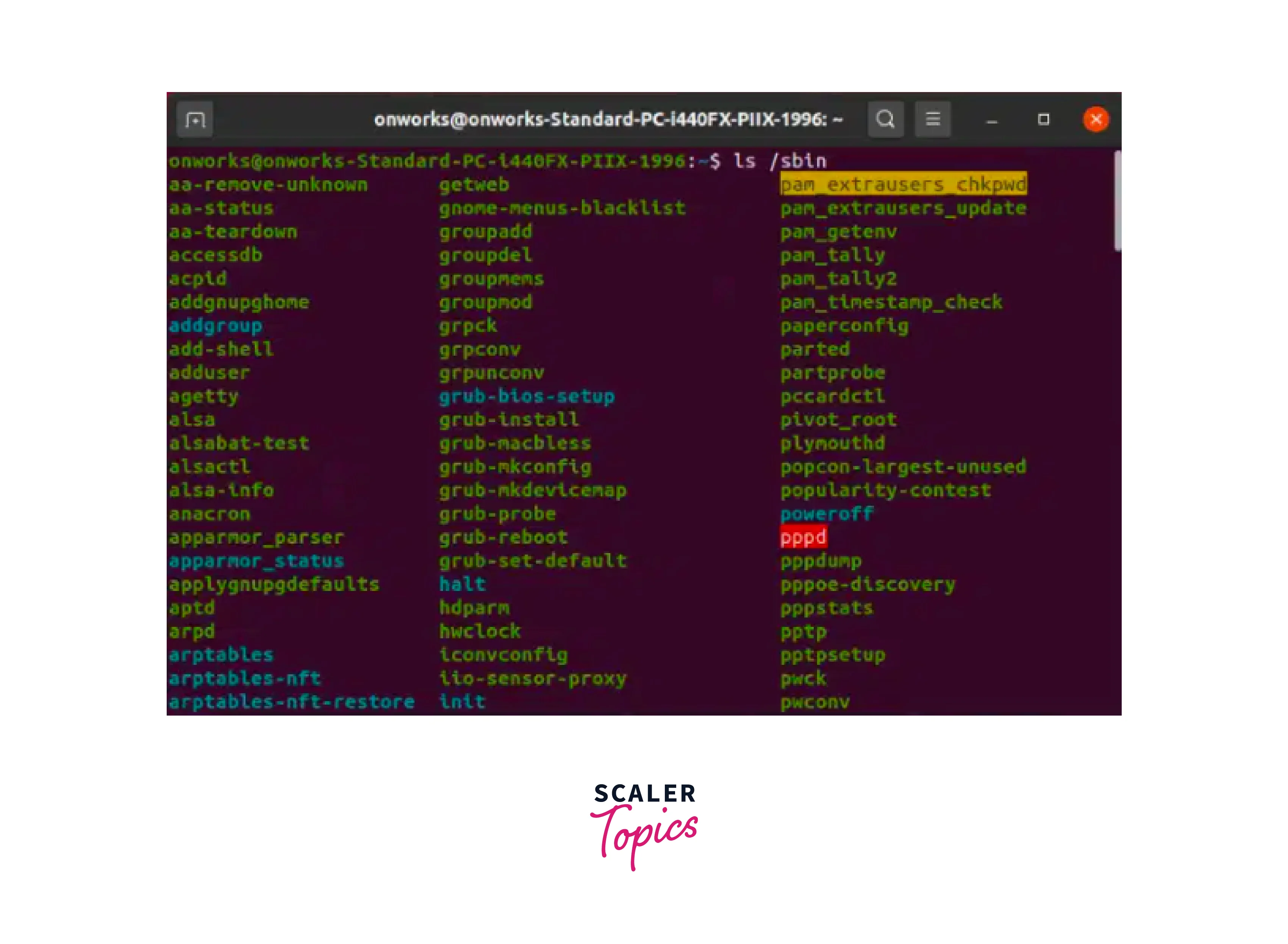
The /sbin directory, which stands for "system binary," includes binaries that are required for system administration and maintenance operations. Unlike the /bin directory, the binaries in /sbin are typically used by the system administrator or root user. These binaries are essential for administering and configuring the system, as well as executing complex administrative activities. Binaries found in /sbin include commands like ifconfig, fdisk, init, and shutdown. The ifconfig command is used to setup network interfaces, fdisk is used to manage disc partitions, init is used to handle the system's startup process, and shutdown is used to shut down the system. These commands are essential for maintaining and controlling the system's infrastructure and operations.
We can use the following command to see /sbin directories:
Output:
/lib
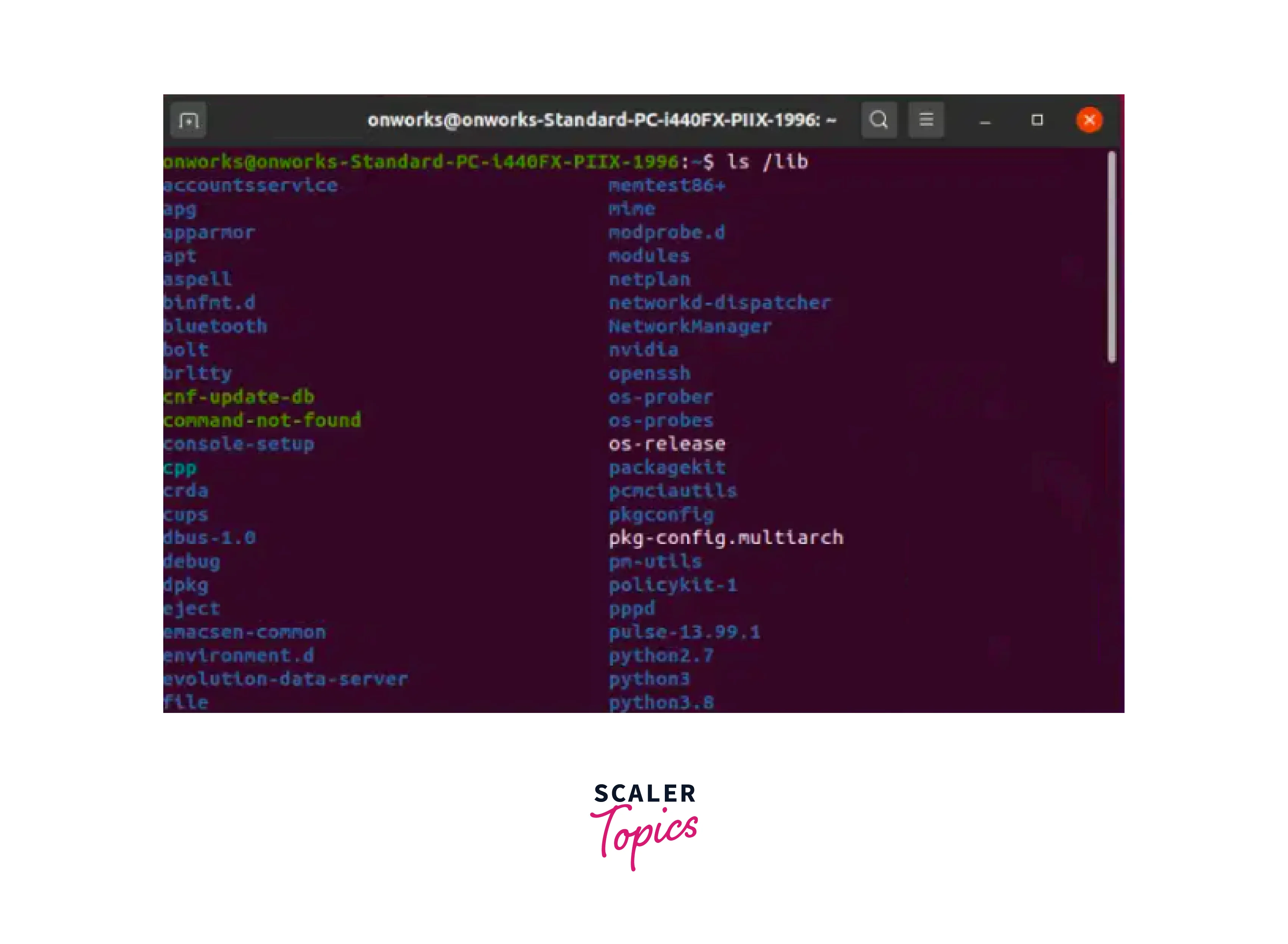
The /lib directory, short for "library," includes shared libraries that are required for the proper operation of the system's many programs and binaries. Shared libraries provide reusable code that may be used by different programs, eliminating redundancy and increasing efficiency. These libraries are dynamically loaded during program execution, allowing programs to use common functions and resources without having to include the complete code in their binaries. Libc.so, libpthread.so, and libm.so are examples of shared libraries located in /lib. The libc.so package contains C programming language functions, while libpthread.so contains threading support, and libm.so contains mathematical functions. These libraries are required for programs to function properly and efficiently.
/lib has following modules:
- /lib/modules:
The /lib/modules directory acts as a repository for kernel modules. It stores the compiled kernel modules in a structured manner, making them easily accessible for the system when needed. - /lib32:
The /lib32 directory is found in 64-bit Linux distributions and contains 32-bit libraries. These libraries are necessary to support the execution of 32-bit applications on a 64-bit operating system. - lib64:
The /lib64 directory, on the other hand, is present in 64-bit Linux distributions and contains 64-bit libraries. These libraries are essential for running 64-bit applications on a 64-bit operating system.
We can use the following command to see /lib directories:
Output:
/opt
The /opt directory, which stands for "optionalk", is used to install software packages that are not available through the Linux distribution's package manager. This directory is used for installing optional or third-party software. While the package manager is used to install most software, some programs or packages may not be available through this system. As a result, the /opt directory provides a dedicated location for installing such software. Each software package usually has its own subdirectory within /opt, making it simple to organize and maintain separate software installs. Examples of software installs within /opt include proprietary applications, commercial software, and manually installed software packages. The /opt directory allows users to keep these optional software items in a clean and distinct installation environment.
We can use the following command to see /opt directories:
Output:
Add-on applications from individual vendors should be installed in '/opt'. And so in some systems '/opt' is empty as they may not have any add-on application.
conclusion
- Understanding the purpose and organization of Linux binary directories is vital for efficient system administration and usage.
- In this article, we have discussed what are Bin directories in Linux in detail.
- We discussed what is /bin.
- We discussed what is /sbin.
- We discussed what is /lib.
- We discussed what is /opt.
- By knowing the functions of bin directories in Linux, Linux users can navigate and utilize their systems effectively.
