What are the Characteristics of the Database Approach?

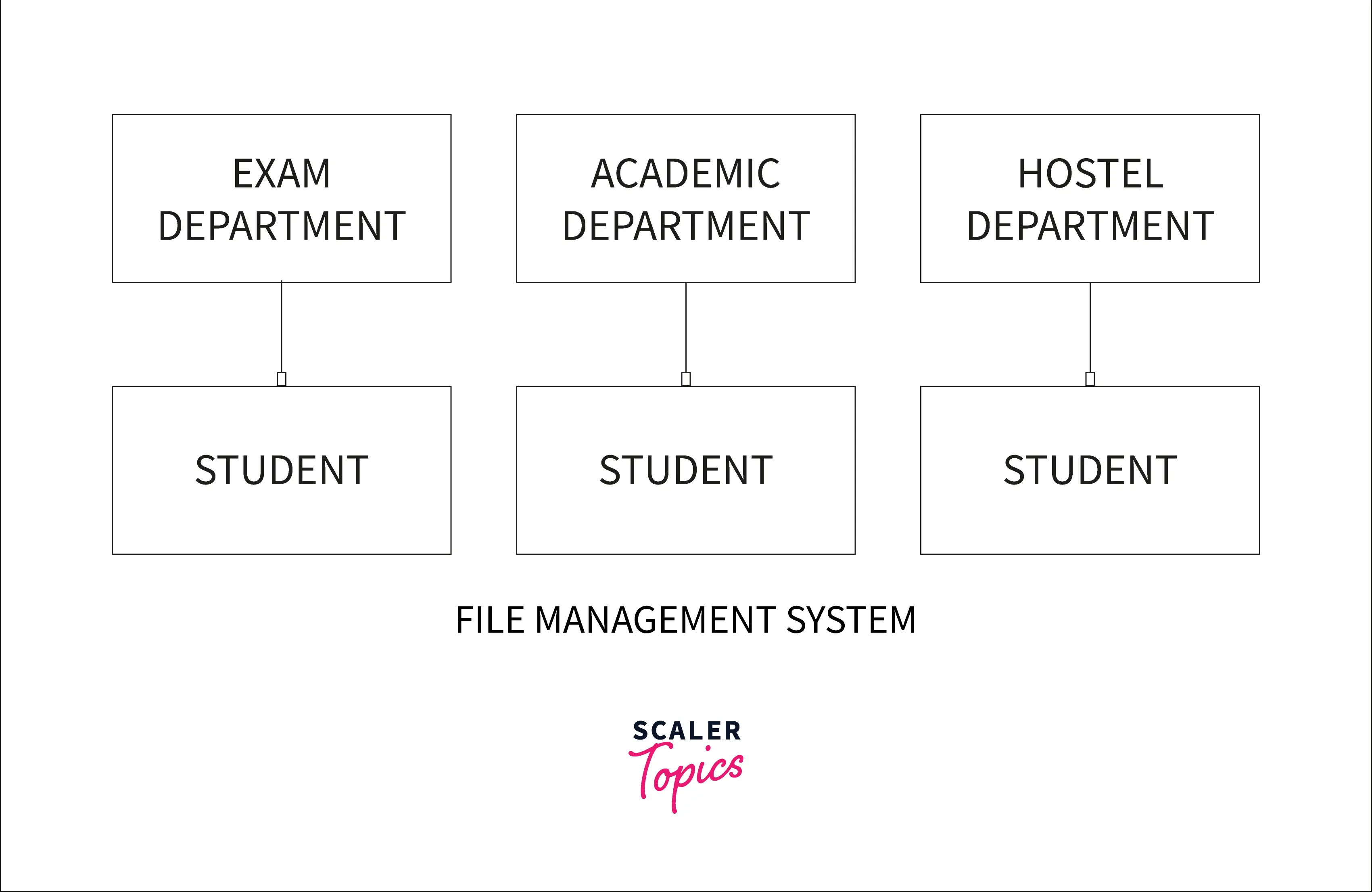
In File Management System, each user stores separate data for the application even if the same data is stored by another user.
Like in a university, there are multiple departments such as Exam Department, Academic Department, Hostel Department, etc. In the traditional File Management System, we have to maintain separate records of the students in each department.
So if there are 100 students in the university and there are 5 departments, we will be storing 100x5 = 500 records. This causes repetition of data and wastage of resources.
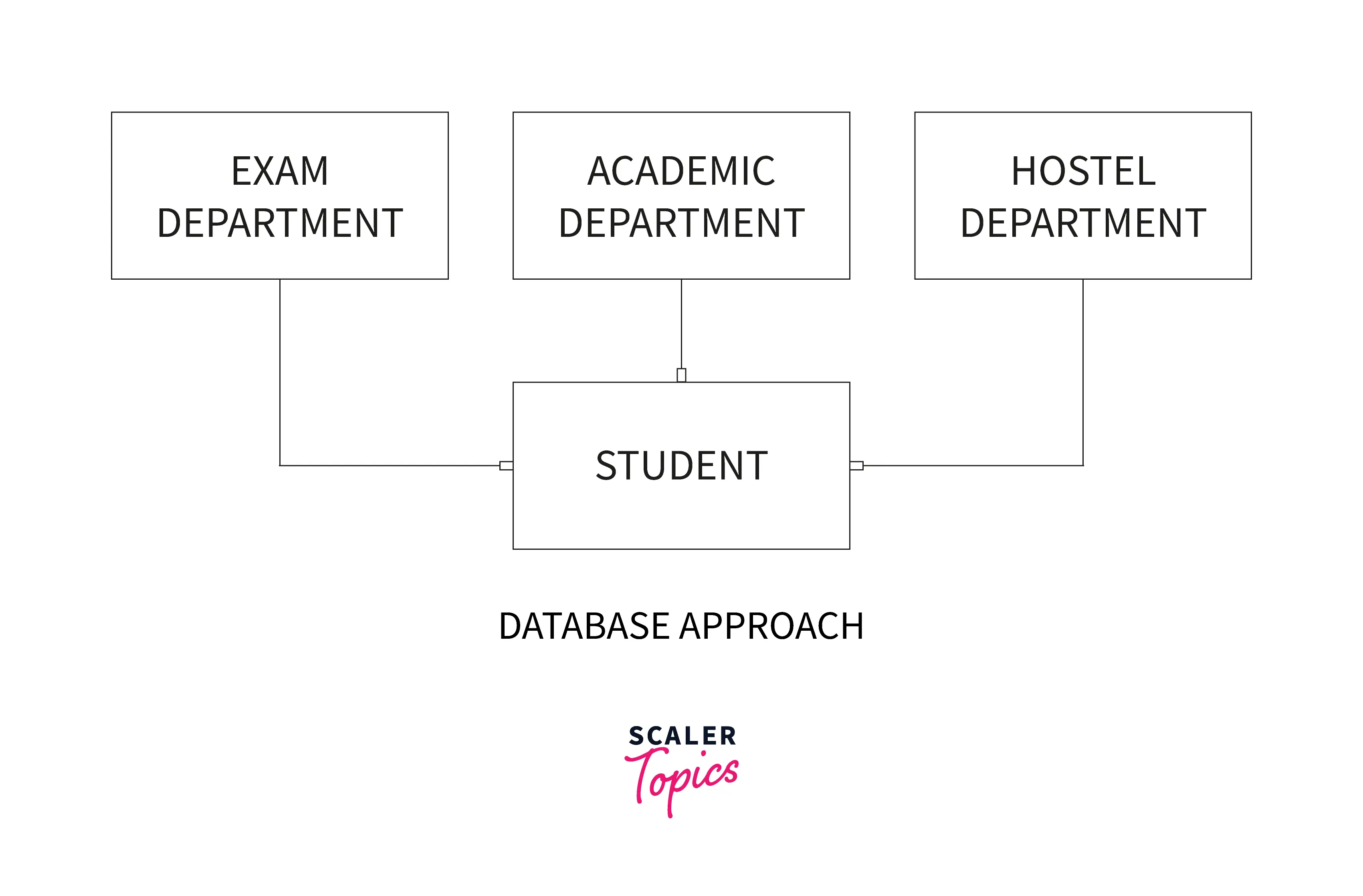
Due to this major drawback, the Database Approach is used for storing and maintaining the data where the data is defined once and stored in a single location and accessed by multiple users from this location.
Various Characteristics of Database Approach
As you have seen above, the database approach is far more efficient and robust than the traditional file management system. Let's discuss the characteristics of the Database Approach. But before moving to the characteristics of the Database Approach, let's have a sample database of Students enrolled in a university.
| ROLL_NO | NAME | DEPARTMENT |
|---|---|---|
| 901 | Amit | CSE |
| 835 | Anant | ECE |
| 908 | Deepak | CSE |
| 704 | Hari | EE |
| 516 | Karan | CE |
Self-Describing Nature of a Database System
In the traditional file management system, data definition was not a part of the application, but in the database approach, the data is defined by the users and this defined data describes itself. Now, what do I mean by defining itself? It means that the metadata or data about data is also stored in the database, specifically in the DBMS catalog.
Now, what is this metadata? Metadata means data about data, like the constraints in the database, the structure of the database, the columns of the database, etc. In the introduction section, we used the STUDENTS database and in the STUDENTS database ROLL_NO acts as the primary key, hence the information that "ROLL_NO is the primary key of STUDENTS" is the metadata of the STUDENTS database.
Insulation between Programs and Data, and Data Abstraction
Suppose we want to change the structure of the STUDENTS database by adding a new column of MOBILE_NO. Now in the file management system, we may require to update the structure of the STUDENTS database in every program that is accessing this database. But this is not the issue with the Database Approach.
In the database approach, the structure of the database is stored in the DBMS catalog. So next time when we will access the data, the new structure from the DBMS catalog will be used.
The DBMS or Database Management System provides the conceptual view of the data that is easily readable to the user and hides many details of the data such as how the data is stored or the constraints used on the data. This conceptual view is known as the data model. Hence the data model hides the implementation and storage details of the data thus creating insulation between the program and the data.
For example, following details of the STUDENTS database will be shown to the user,
and the following details will not be shown as these are unnecessary for the user,
Support of Multiple Views of the Data
In a university portal, there can be many types of users such as students, teachers, heads of department, deans, etc. So having a separate database for each type of user will lead to repetition of the data and wastage of resources.
In the Database Approach, a single database is implemented and multiple users access this database. For example for the STUDENTS database, the Head of the Department of CSE will only access the students having CSE as their department, the dean can access the student details of every student in the STUDENTS database.
Sharing of Knowledge and Multi-user Transaction Processing
Sharing of knowledge means that multiple users are accessing common data like a dean and the head of the department are accessing the STUDENTS database. Hence both users are sharing the student records.
A transaction is a process that is accessing one or more databases by reading, writing, or deleting the data records.
Multi-user Transaction Processing as the name implies that the database must allow multiple users to process their respective transactions. But it should also ensure that the transactions are processed concurrently so that multiple users can't change a record at the same instant. For example, consider a Movie Ticket Booking scenario where the DBMS should ensure that only one user can book a seat at a given instant.
These were the main Characteristics of the Database Approach, now let's discuss some other Characteristics of the Database Approach.
Security
A database should be secure so that it remains protected from any internal or external threats. Security comprises safeguarding the database, the data contained inside it, the database management system, and the different applications that utilize the database. Consider a case where a user is trying to update some records in the database as follows,
At 10:45, the user begins to update the records.
At 10:47, the database experienced a power failure while the user was updating the records.
So when the power is restored the transaction should start from the beginning i.e. the state of the database should be 10:45, not 10:47. Either the transaction is completed or it is not completed, there can't be a partially completed transaction.
Query Language
A query in the database is a request for data from the database so that we can read, write, or delete the data in the database. A query performs similar action to that of the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operation. A query allows us to access specific data from the database based on some conditions or constraints.
For example, if the Head of the Department of CSE is trying to fetch student details from the STUDENTS database, then we will perform the query as,
The above query will return us to the following table,
| ROLL_NO | NAME | DEPARTMENT |
|---|---|---|
| 901 | Amit | CSE |
| 908 | Deepak | CSE |
Bridge between Program and Data
The bridge between Program and Data is Data Abstraction or hiding unnecessary data from the user. In data abstraction, we hide unnecessary details such as the type of values, number of columns, the structure of the database, etc are hidden from the user. These details are very crucial for the database admin but not for normal users.
Learn More
We have used some database terms that are closely related to this article and going through them once will increase your understanding of the Characteristics of the Database Approach.
Conclusion
- Earlier, a File Management System was used to manage data needed for a specific application. In the File Management System, each user stores separate data for the application.
- Presently, the Database Approach is used for storing and maintaining the data where the data is defined once and stored in a single location and accessed by multiple users from this location.
- The main characteristics of the Database Approach are the database is Self Describing in Nature, Insulation between Program and Data, Supports Multiple Views of Data, Sharing Knowledge, and Multi-User Transactions in the Database.
- Apart from the main characteristics there are some other characteristics too such as, Security, Query Language, and Bridge between Program and Data.
