12 Essential Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Overview
Cloud computing has emerged as a revolutionary paradigm in the world of information technology, offering scalable and flexible solutions to individuals and businesses alike. This article dives into the 12 essential characteristics of cloud computing that define its uniqueness and value proposition.
For a comprehensive introduction to cloud computing, you can refer to introduction to cloud computing.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
1. On-Demand Self-Service
Without the assistance of service providers, cloud computing enables users to deploy and manage computing resources as needed. This means users can quickly access and configure resources like storage, processing power, and applications through a self-service portal. For instance, consider a startup needing to scale up its website's server capacity during a sudden traffic spike; cloud computing allows it to do so instantly rather than going through a lengthy procurement process.
2. Broad Network Access
One of the remarkable aspects of cloud computing is its ability to provide services over the Internet. Using regular web browsers or specialized programs, users can access cloud services from a range of devices, including computers, smartphones, and tablets. This universal accessibility ensures that resources are available to users wherever they are, promoting seamless collaboration and data sharing.
3. Resource Pooling
Cloud computing utilizes a multi-tenant model where resources are shared among multiple users. This pooling of resources enables higher efficiency and utilization rates. Virtualization technologies ensure that underlying physical resources are abstracted and allocated as needed so different users can operate on the same hardware without interfering with each other. Think of it as a communal swimming pool where each swimmer enjoys the water without owning the entire pool.

4. Rapid Elasticity
When demand changes, cloud services can scale up or down quickly. Resource automated allocation and release as required allows for this elasticity. An e-commerce website can see a dramatic increase in traffic, say, during the holiday shopping season. Cloud infrastructure can instantly provision additional servers to accommodate the increased traffic, and once the rush subsides, the excess resources are automatically released to conserve costs.
5. Measured Service
In cloud computing, users are billed for the actual resources they consume. Instead of making upfront investments in expensive infrastructure, this pay-as-you-go strategy makes sure that firms only pay for what they use. This characteristic aligns with the economic principle of efficiency, as resources are allocated optimally, and organizations can easily monitor their resource consumption and costs.
6. Service Models: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
Cloud computing offers different service models catering to various user needs. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, Platform as a Service (PaaS) delivers a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications, and Software as a Service (SaaS) offers complete applications accessible via the cloud. For example, a company might use IaaS to set up virtual servers, PaaS to develop a custom application, and SaaS for email or customer relationship management.
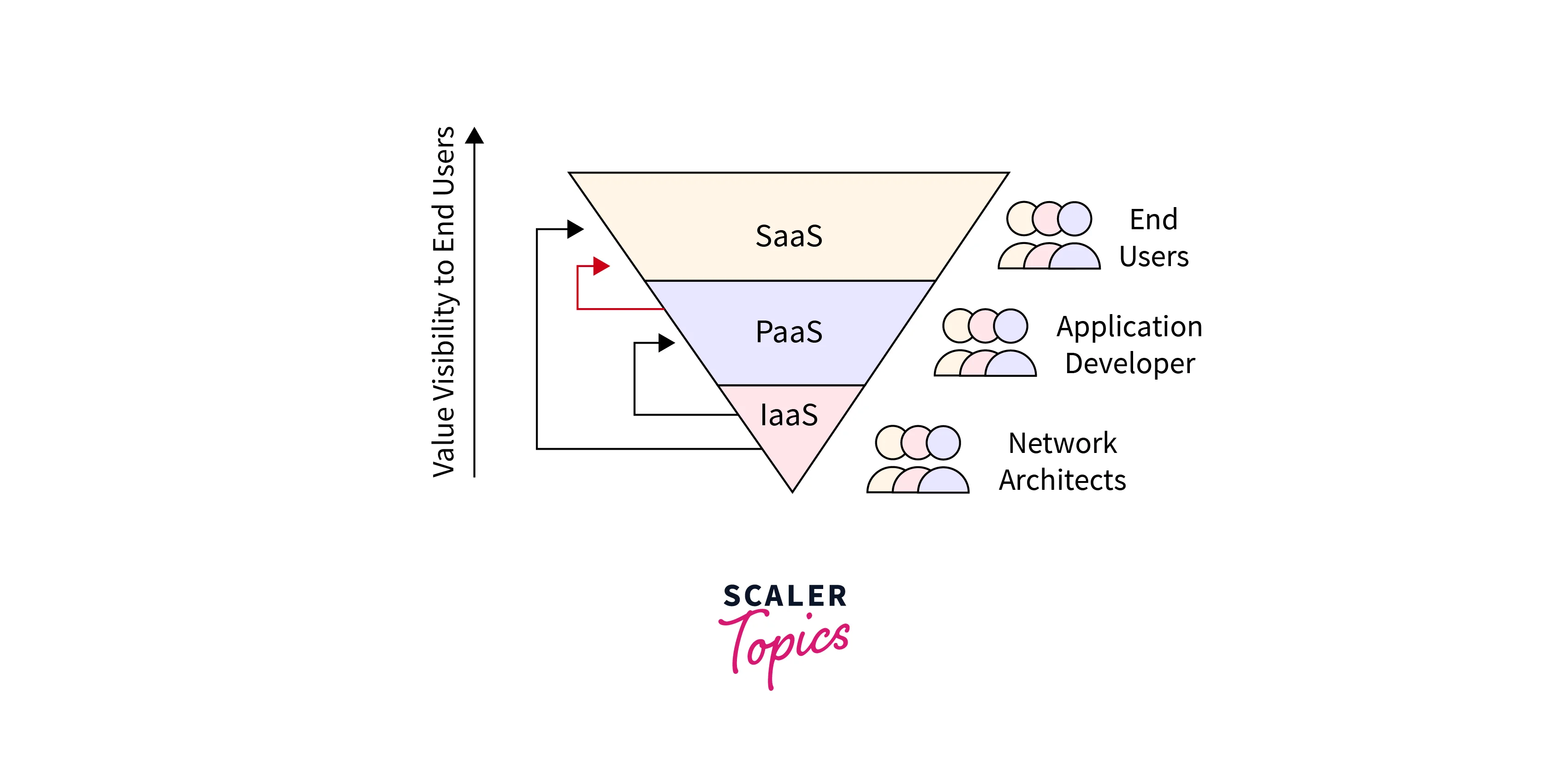
7. Ubiquitous Network Access
With an internet connection, cloud services are available from anywhere. This characteristic enables remote work, collaboration, and data sharing among individuals and teams spread across different geographical locations. A sales team can access the latest customer data from a SaaS-based CRM system while on the go, enhancing productivity and customer service.
8. Shared Responsibility
Security and compliance are shared responsibilities with cloud computing, with the customer and cloud provider each playing a part. The customer is in charge of protecting their applications, data, and access credentials, while the provider is in charge of maintaining the security of the underlying infrastructure. This coordinated approach ensures a more thorough security posture.
9. Scalability and Performance
The flexibility to scale resources either horizontally or vertically is provided by cloud computing. To share the load, horizontal scaling involves setting up more instances of resources, such as servers. Vertical scaling is about increasing the strength of specific resources, such as improving the CPU and RAM of a server. Applications can function effectively even under varying workloads thanks to the scalability property of cloud computing.
10. Disaster Recovery and Redundancy
Cloud providers typically offer built-in disaster recovery solutions and data redundancy. Data is automatically backed up and stored in multiple geographical locations to ensure high availability and integrity. If one data center experiences an outage, services can seamlessly switch to another center, minimizing downtime.
11. Automation and Management
Cloud computing leverages automation to streamline processes and reduce manual intervention. Infrastructure provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment can be automated, leading to faster and more consistent operations. Automation also enhances resource utilization by dynamically adjusting resources based on demand.
12. Flexibility and Customization
Cloud services provide flexibility in terms of resource selection and customization. Users can choose the amount of storage, processing power, and other resources that suit their specific needs. This flexibility also extends to software choices; users can opt for different operating systems, databases, and application frameworks to build tailored solutions.
FAQs
Q. What are the key characteristics of cloud computing?
A. On-demand self-service, widespread network access, resource pooling, quick elasticity, measured service, service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), always-on network access, shared responsibility, scalability and performance, disaster recovery, automation, and flexibility are characteristics of cloud computing.
Q. How does cloud computing promote cost efficiency?
A. Cloud computing follows a pay-as-you-go model, where users are billed only for the resources they use. This efficient resource allocation eliminates the need for upfront investments in hardware and reduces the wastage of unused resources.
Q. What is the significance of the shared responsibility model in cloud security?
A. The shared responsibility model ensures that both cloud providers and customers collaborate to maintain a secure environment. While providers secure the infrastructure, customers are responsible for securing their applications, data, and access controls, creating a layered security approach.
Conclusion
- The way that people and organizations access and manage resources has been revolutionized by cloud computing, which has grown to be a crucial component of contemporary IT infrastructure.
- The 12 essential characteristics of cloud computing outlined in this article showcase its versatility, efficiency, and adaptability.
- As technology continues to evolve, cloud computing will likely remain a cornerstone of innovation, providing solutions that empower businesses and individuals in an ever-changing digital landscape.
