Digital Signature in Computer Network
Overview
Digital signatures allow us to verify the author, date, and time of signatures and authenticate the message contents. To verify the integrity and validity of digital messages and documents, it employs a cutting-edge mathematical technique. It helps us combat the issue of impersonation and tampering in digital communications and ensures that the contents of a message are not changed while in transit. Additionally, digital signatures offer details about the message's origin, status, and signer's agreement. By guaranteeing that the information was written by the signer and was not altered, this signature establishes the legitimacy of the company that produced the digital signature. Any modification to the signed data renders the entire signature invalid.
What is Digital Signature in Computer Network?
 Alice adds an encrypted version of a message—"Hello Bob!"—to the original message before signing it. The message and the signature are delivered to Bob. He checks the message's authenticity using Alice's public key to ensure that the encrypted duplicate, when decoded with the public key, perfectly matches the original message.
Alice adds an encrypted version of a message—"Hello Bob!"—to the original message before signing it. The message and the signature are delivered to Bob. He checks the message's authenticity using Alice's public key to ensure that the encrypted duplicate, when decoded with the public key, perfectly matches the original message.
A personal signature on a written document is the same as a digital signature for an electronic message, which is produced by utilizing a type of cryptography. A message's digital signature offers a special electronic link tying the signer's identity to the message's origin. A digital signature offers evidence of the message's author as well as a way to check the message's consistency. A digital certificate holder combines the data to be signed with their private key before subjecting the data to an algorithmic transformation. The signature is decrypted by the message's recipient using the public key for the matching certificate. The public key decryption also validates the signed message's integrity and the sender's identity. Digital signatures can only be produced by the company that has the private key. But a person who has the relevant public key at their disposal can check the digital signature.
Why Should We Use a Digital Signature?
Here are the top five reasons why your company should consider getting a digital signature:
- Fast turnaround In organizations that use traditional signatures, signing and returning an email-received document requires several actions from the employee. With the press of a mouse, any kind of paperwork and contract can be signed. As a result, you save time because these codes enable you to switch out the paper-based clearance procedure for a wholly digital one that is both quicker and more affordable. With the help of a tablet, phone, or computer, papers can now almost quickly be signed off on from anywhere thanks to digital signatures.
- Cost savings Putting digitalization into practice costs money, but you'll end up saving money in the long term. Paper documents do not need to be sent when using a digital signature. Printing and shipping/delivery expenses will decrease as a result. Additional indirect costs including those associated with tracking, archiving, rekeying data, filing, and the handling of confidential papers will be reduced as well. As a result of the substantial reduction in paper use your company will experience, the use of digital signatures will also aid in reducing environmental waste.
- Workflow efficiency These signatures guarantee greater workflow efficiency with fewer delays. Document management and tracking have gotten simpler and quicker. From the time a document is requested until it is obtained, processes that once took months can now be completed in a lot less time. They also facilitate information and document organization as there are no tangible papers to sort through. Compared to searching through paper papers kept in file cabinets or boxes, searching through digital documents is simpler and faster. You will be able to trace documents more effectively, which is another advantage. If a document is still unsigned, some software even emails signers a reminder.
- Strengthen security Because each signature is secured with a tamper-evident seal that notifies you if any part of the document has been modified after signing, digital signatures minimize the danger of duplication or alteration of the document itself and ensure that signatures are verified and valid. Additionally, PINs, passwords, and codes are given to signers so they can authenticate their identities, confirm their signatures, and approve documents. Your signature is secure thanks to digital encryption and audit trails, which also safeguard your data and prevent fraud at your firm.
- Increase storage space You don't need to keep your workplace storage cabinets loaded with paper files because digital files are saved on virtual servers linked to the IT network or in the cloud, freeing up more room for other uses in your office. Physical documentation takes up a lot of room and promotes paper usage, which is bad for the environment.
How Digital Signature Works?
The document is digitally signed by the sender. The signature is confirmed by the document's recipient.
The steps in the algorithm for digital signatures are:
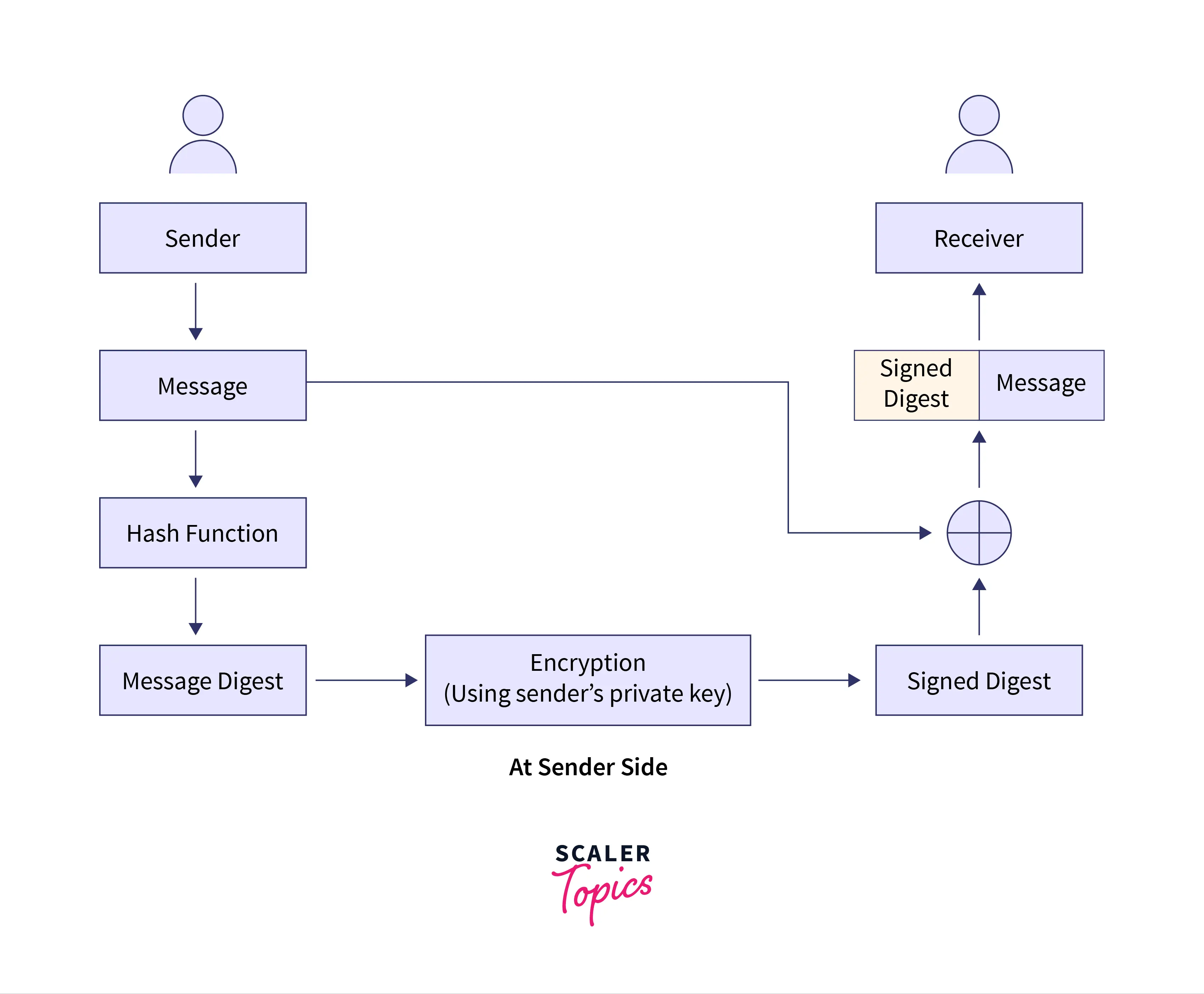
At sender's side:
- The sender transforms the message to be sent into a digested form using a hash function.
- Many hashing algorithms may be utilized, including SHA-1, MD5, and others.
- The term "message digest" refers to the message in its digested form.
- The message digest is encrypted with the sender's private key.
- The signed digest of encrypted communication, also known as the sender's signature, is used.
- Along with the original communication, the sender also sends the recipient the signed digest.
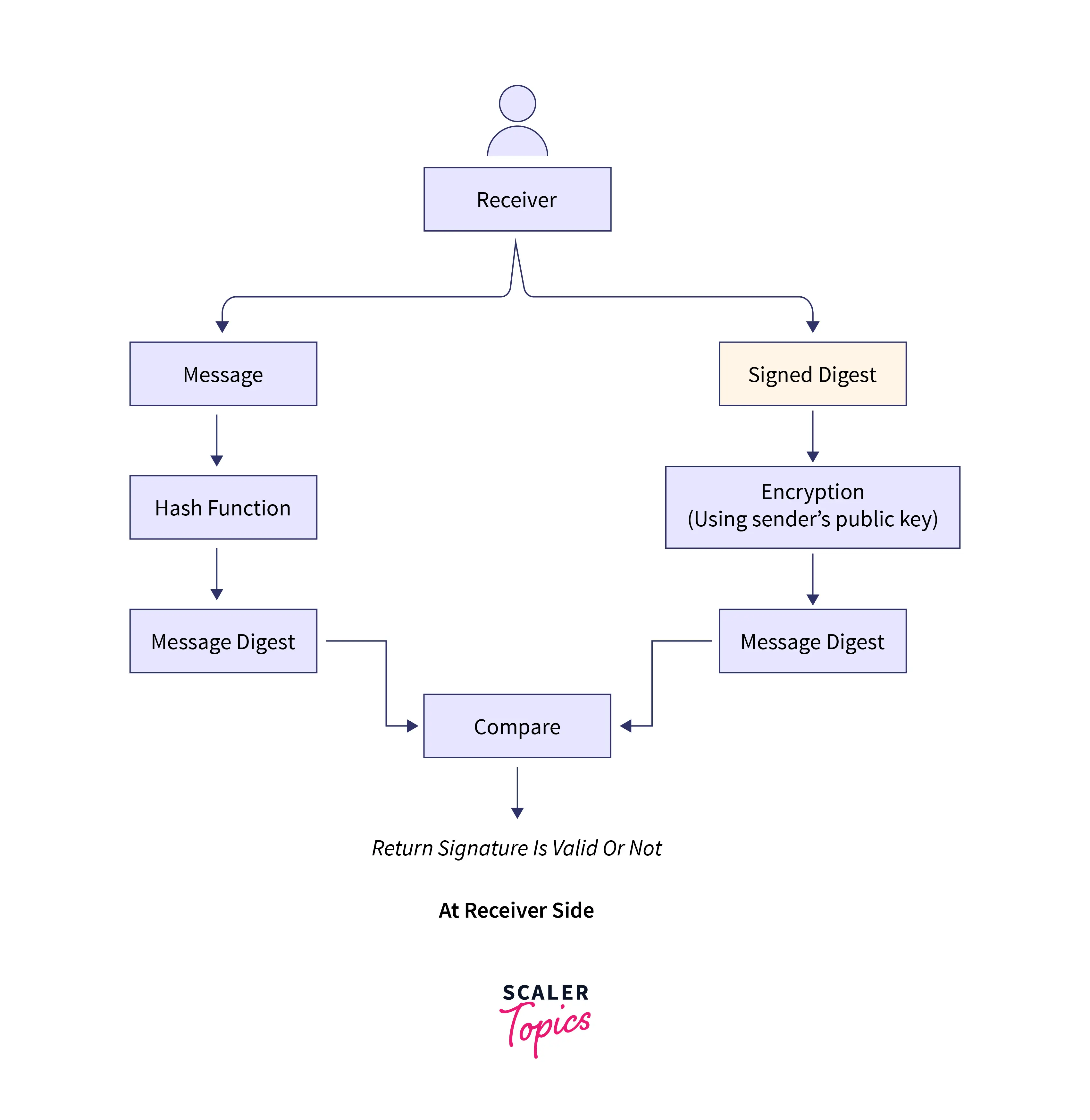
At Receiver Side--
- Receiver receives both the signed digest and the original message.
- Receiver transforms the original message into a message digest using a hash function.
- Additionally, the recipient decrypts the signed digest that was sent using the sender's public key.
- Receiver gets the message digest after decryption.
- The receiver is now comparing the two message digests.
- If they match, it is demonstrated that the document originates from the right source.
Steps Followed in Creating Digital Signature
The user's name, nationality, email address, the date the certificate was issued, and the name of the certifying authority are all included in the digital signature certificate. For several things, such as performing secure web-based transactions, signing documents like MS Word, MS Excel, and PDFs, eTendering, eProcurement, and submitting income tax returns, you need a digital signature certificate. A person or organization may easily sign a document digitally by following a few easy steps if they are requested to. Here is what you should do when you get an email with a link to a document that has to be digitally signed:
Step 1: The document should open in an application for electronic signing when you click the link.
Step 2: The user must consent to electronic signing before using it. The user would need to follow specific steps to start or sign after confirming consent.
Step 3: The user can add the digital signature by selecting each tag and following the guidelines.
Step 4: Verifying one's identification and according to the instructions to add the digital signature are the final and most crucial steps.
What does Signing a Document Mean?
A mark or sign made by a person to denote understanding, consent, acceptance, or responsibility on a piece of paper or another object. Document signing is the process of adding an electronic or digital signature to a document to confirm the sender's identity. Electronic document signing removes the need for actual paper papers and significantly accelerates the signature procedure.
Deal management software and proposal software both place a lot of emphasis on document signature, which is frequently a crucial component of any contract. With several features created to make document production easier, organize processes, and remind participants to submit signed papers, document signing simplifies the flow of documents. Document signing is essential to many businesses, like banking and real estate, to support daily operations and swiftly complete transactions. To be associated with a document while using a digital signature, users must possess a digital certificate. A digital signature is frequently approved by certification authorities, who are in charge of offering digital certificates that are comparable to licenses or passports and are responsible for issuing them. A digital certificate is used to authenticate the document and validate it. This is crucial in confirming the legitimacy of the original signer of the document. Different standards for document signing have been established in terms of security and validity in addition to software.
The advantages of the document signing procedure are outlined in detail:
- Provides users with the ability to verify a legal agreement or contract
- Offers a mechanism of communication between a buyer and seller and gives users a record of record to prove what was agreed upon.
- Reduces bottlenecks, offers real-time regulatory compliance, and has a quicker contract turnaround time.
What Does Signing a Digest Mean?
A message digest is a one-way hash function used in cryptography that contains a string of numbers.
- By detecting modifications and adjustments to any component of a message, message digests are intended to safeguard the integrity of a piece of data or media. They are a kind of encryption that uses hash values to alert the owner of the copyright to any alterations made to their work.
- Specific files that contain the protected works are identified by message digest hash codes. To a certain piece of data content, one message digest is allocated. It can be used to refer to an intentional or unintentional alteration, but it forces the owner to specify both the modification and the person or people who made it. Calculated numbers are used in message digests.
- Along with the message itself, the message digest is transmitted. To compare it to the sender's digest, the receiver might create a digest for the message. When both message digests are identical, the message's integrity is confirmed. Any message manipulation during transmission leads to a different message digest virtually definitely.
- The term "message authentication code" (MAC) refers to a message digest that was generated using a symmetric secret key and may guarantee that the message has not been altered.
- A digital signature may also be created by the sender by creating a message digest and encrypting it with the private key of an asymmetric key pair. After that, the receiver must decode the signature before comparing it to a locally created digest.
Steps Taken While Signing Digest
The stages involved in creating a digital signature are as follows:
- The digital signature is created when the sender uses their private key to encrypt the message digest after computing it (using an algorithm like RSA or SHA1) to create the message digest. A message may have several signatures and signature formats attached, each referencing various (or even overlapping) elements of the message.
- The sender sends the message together with the digital signature.
- The message digest is generated once the receiver decrypts the digital signature using the sender's public key.
- The receiver generates a message digest from the received message data and confirms that the two digests are identical. The message is both intact and legitimate if these digests agree.
Advantages of Digital Signatures
We'll go through the key benefits of digital signatures and why businesses that still use paper-based document procedures should consider investing in them.
- More protection PKI technology, a type of encryption that makes it impossible to change or delete the signature from the final document, is the foundation upon which digital signatures are created. The signers identify themselves while signing digitally using their respective national electronic IDs. Your clients will view eIDs as a reliable form of identification because they are increasingly being used to access both public and private services online. Additionally, when a digital signature is generated, the time and IP address are noted in an audit trail that is integrated into the document. The digitally signed PDF is the sole acceptable form of evidence in court.
- Adherence to law and widespread support The fact that digital signatures are enforceable in nearly all industrialized nations globally is one of its many benefits. Does your company ever conduct business abroad? Do you have any international partners, clients, or suppliers? Because digital signatures are equally legally binding as handwritten ones, there are even more reasons to use them. Digital signatures, which are accepted for use on the majority of papers in the European Union, are seen to be the most secure kind of e-signatures.
- Savings in time Your day will be taken up with manual operations like drafting, printing, scanning, and mailing when dealing with paper-based document transactions. Not to mention that getting them signed and returned takes days, sometimes even weeks. Additionally, if a signature is absent, you will need to wait again while you contact for clarification and resend the document. Processes for digital signatures streamline manual work and cut the lengthy wait time to a few hours.
- Workflow automation Coordination, precision, and manual tracking are needed for paper processes. especially when it's important to guarantee that the paperwork is signed in a specific sequence and that data confidentiality is maintained. Errors can arise when people manage papers. Delays, errors, and the potential for policy violations are all normal parts of the process. However, they are eliminated when employing a digital solution that standardizes, maintains, and ensures error-free workflow.
- Cost savings The economic convenience of turning digital grows as the volume of transactions rises. The savings a typical medium-sized corporation may realize by converting to digital processes are summarised in the table below, which combines the results of many US studies.
- Happier end-users Your clients, business partners, and stakeholders will also profit from digital signatures. They may sign online, on any device, and at their leisure rather than traveling to your branch, office, or store. In addition to resulting in quicker response times, this improved experience also increases customer happiness and retention.
- Enhanced brand recognition and CSR Digital signatures reduce your company's environmental impact. The Minnesota Office of Environmental Assistance estimates that the average office worker uses 20 reams of paper annually (10,000 sheets). On the other hand, since 2014, we believe we have helped save more than 74 tonnes and 2 million sheets of paper annually.
Conclusion
- We now understand the meaning of asymmetric cryptography, how digital signatures operate, how DSA works, how to verify a signature, and why it is better than competing technologies.
- Digital signatures are advantageous in situations when security is crucial because they are more convenient, more effective, and enable remote teamwork. Traditional wet-ink signatures, which require that all parties be present in person to sign documents and aren't precisely reliable, stand in striking contrast to this. What they are and how they function are explained in depth in this article.
- Due to the advantages of digital signatures, more businesses and offices are implementing them to increase workplace security and efficiency.
- Digital document management solutions may reduce paperwork, increase productivity, and improve security while saving your company time, money, and space.
- Digital signatures can assist you in securing and preserving the integrity of your data as more and more paperless, online interactions are employed. Your information, documents, and transactions will be better protected if you comprehend and use digital signatures.
- In this article, we outlined a few typical advantages of implementing and using various kinds of signatures. However, any company or organization may discover its unique advantages by taking into account its goals, its budget, and the system's flexibility.
