What is Bandwidth in Computer Network?
Overview
Bandwidth, or network bandwidth, is the maximum data transfer rate of a network or Internet connection. It determines how much information can be sent over a particular connection in a certain amount of time. The higher bandwidth of a network, the larger amount of data it can send to and from across its path. Be careful not to confuse bandwidth with terms like data rate and throughput, which are very similar. Instead of dealing with the speed of data transfer, bandwidth deals with the measurement of capacity.
What is Bandwidth in Computer Network?
A measurement of the maximum capacity of a wired or wireless communications link to transmit data over a network connection in a specific amount of time is known as bandwidth in a computer network. Usually, bandwidth is expressed in the number of bits, megabits, kilobits, or gigabits that can be transmitted in one second. If a person has a bandwidth rate of 25 Mbps, their household and devices can only receive a maximum of 25 megabits of information per second. It is a common misconception that bandwidth is a measure of network speed. It only measures the maximum amount of data transmitted over an internet connection in a given amount of time.
Importance of Bandwidth
The bandwidth determines how quickly a web page will load on your browser. It is one of the most important factors to take into account when choosing a platform for your website because of this. A website with lots of large photos and long videos would often require a higher bandwidth of 25 Mbps or more. Comparatively, websites that are mostly text-based will require less bandwidth. Multiple devices that are using the same connection must share bandwidth. Some devices use a lot of bandwidth, such as TVs that stream 4K videos. In comparison, a webinar usually consumes much less bandwidth. While bandwidth and speed cannot be compared, greater bandwidth is necessary to maintain multiple devices operational at tolerable speeds. Here is an example of how much bandwidth is often used by various services to help you understand this:
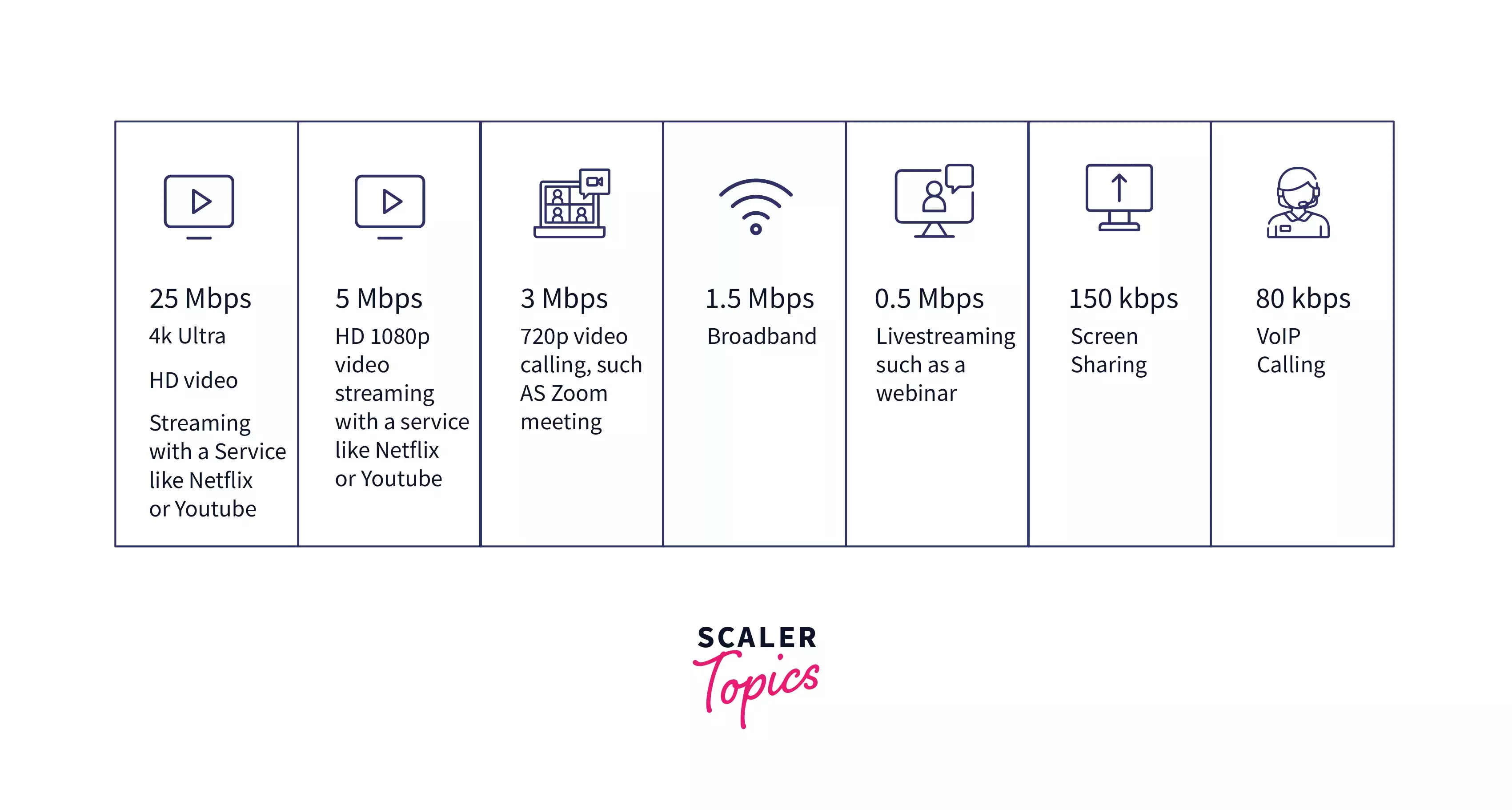
How is Bandwidth Measured?
In general, bandwidth is measured in bits per second (bps). Kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), and gigabits per second (Gbps) are often used to refer to larger units. It's critical to understand the difference between bits per second (bps) and bytes per second (Bps). There are 8 bits in every byte. Bandwidth connections can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. In symmetrical connections, the data capacity is the same in both directions (upload and download). In asymmetrical connections, the data capacity is not the same in both directions (upload and download). The upload capacity is usually less than the download capacity in asymmetrical connections, which are common in consumer-grade internet broadband connections. Measuring bandwidth is typically done by combining firmware or software with a network interface. It will count up all the traffic sent and received over a predetermined period of time, and the result will be expressed as a per-second number. Some of the tools used to measure bandwidth include the Test TCP utility (TTCP) and PRTG Network Monitor.
Methods of Optimizing Bandwidth in Computer Networks
When we want to make the network suitable for quick and efficient communication, we frequently focus on network speed optimization, but bandwidth optimization is equally crucial. This is due to the reason that a network's poorly-optimized bandwidth can surely have a negative impact on the network's overall performance, severely reducing the efficiency and user experience. The following methods are used to optimize the bandwidth of a network:
- Using the QoS (Quality of service) settings, network traffic policies can be set up, and traffic can be prioritized according to its type, ensuring that high-maintenance applications are well-equipped with the bandwidth required to function effectively.
- Using public and private clouds to deploy applications that will offload the network as lesser traffic maintenance needs to be done in the specific network being optimized.
- Eliminating any kind of unnecessary, non-productive traffic that uses up bandwidth on irrelevant operations.
- The strain on network bandwidth can be significantly reduced by scheduling updates, installing software patches, or creating backups outside peak hours.
Conclusion
- Bandwidth, or network bandwidth, is the maximum data transfer rate across any particular path of the network.
- Data rate and bandwidth differ from one another. Data rate describes the actual amount of data transferred, whereas bandwidth describes the number of bits per second that a link can send or receive at one time.
- Bandwidth connections can be symmetrical or asymmetrical. In symmetrical connections, the download and upload speeds are the same, while in asymmetrical connections, the upload and download speeds differ.
- The common units of bandwidth are bps (Bits per second), Mbps (Megabits per second), and Gbps (Gigabits per second).
- An internet connection with a larger bandwidth allows for much faster data transmission than one with a lower bandwidth.
