How to Disable Scrolling on a Webpage with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript?

Overview
Scrolling a webpage while navigating can be controlled by using some JavaScript and CSS or either one of them as well. We shall explore different methods to disable and enable the scrolling functionality of a webpage along with some example code snippets.
Pre-requisite
The prerequisite for understanding this article is the basic understanding of CSS and JavaScript DOM methods like querySelector, and getElementById as well as adding the event listeners to HTML elements.
By Overriding the window.onscroll Function
One of the ways to disable scroll on a webpage is using the window.onscroll event. Let's understand this event.
window.onscroll
The onscroll event on windows is triggered when the window's scrollbar is being scrolled.
We can set the position of this windows.onscroll event to a fixed value then it will prevent the page from scrolling in the vertical or horizontal direction or both.
To do this we need to fix the vertical and horizontal position of the page to the current values which can be done using the following JavaScript functions.
Calculating the current vertical position of the page: To calculate the current vertical scroll position of the web page in pixels document.documentElement.scrollTop and window.pageYOffset functions are used with OR (|) operator because one of them may return 0 value in some of the browsers.
document.documentElement.scrollTop method of JavaScript calculates the number of pixels from the top of the webpage by which the page is scrolled down.
The window.pageYOffset method of JavaScript also calculates the number of pixels from the top of the webpage by which the page is scrolled down. Since some of browsers do not support the former method then this method comes as an alternative.
Calculating the current horizontal position of the page:
To calculate the current horizontal position of the webpage in pixels document.documentElement.scrollLeft and window.pageXOffset values functions are used with the OR (|) operator because one of them may return 0 value in the browsers.
The document.documentElement.scrollLeft method is used to get the number of pixels to the left of the page by which the webpage is displaced to the right.
window.pageXOffset values method is also used to get the number of pixels to the left of the page by which the webpage is displaced to the right but the former method is not supported by some of the browsers, therefore, this method comes as an alternative.
Now, to assign the above-calculated values to the windows.scroll event we may use the window.scrollTo() function and pass the calculated values in this function as arguments to fix the horizontal and vertical position of the webpage.
Let's see the implementation of the above functionality.
Let's try to understand the above snippet. The output of the above code looks like this.
Output:
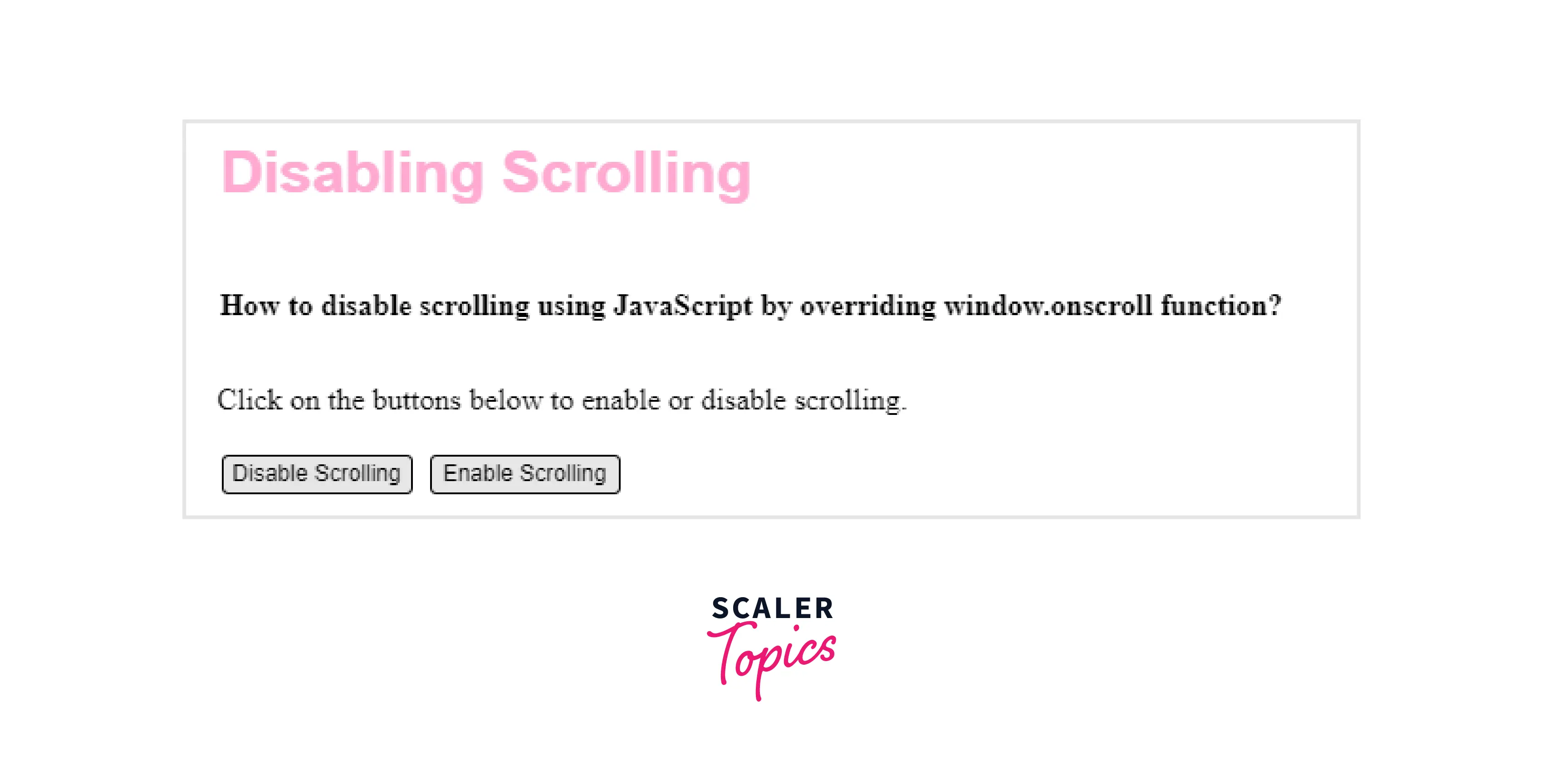
Here, when we click the Disable Scrolling button then we trigger the function disableScroll() where we are calculating the scroll position in the vertical direction in the scrollTop variable and the scroll position in the horizontal direction in the scrollLeft variable. After calculating these values we assign them to the scroll event of the window using the function called window.scrollTo(scrollTop,scrollLeft).
When the Enable Scrolling button is clicked then we trigger the function enableScroll() which simply puts the value of the window.scroll event to blank and enables scrolling.
By Setting the Height of the Body to 100% and Overflow to Hidden
Scrolling of the webpage can also be disabled by using only the CSS using the overflow property. In this method, we set the height of the element for which the scroll is disabled to 100% such that it covers all the space of its parent container, and then we set the overflow property to hidden.
For the horizontal scrolling, we use the property overflow-x and set it to hidden.
We shall use JavaScript to add these properties to the HTML document.
Let's see the implementation
Output:
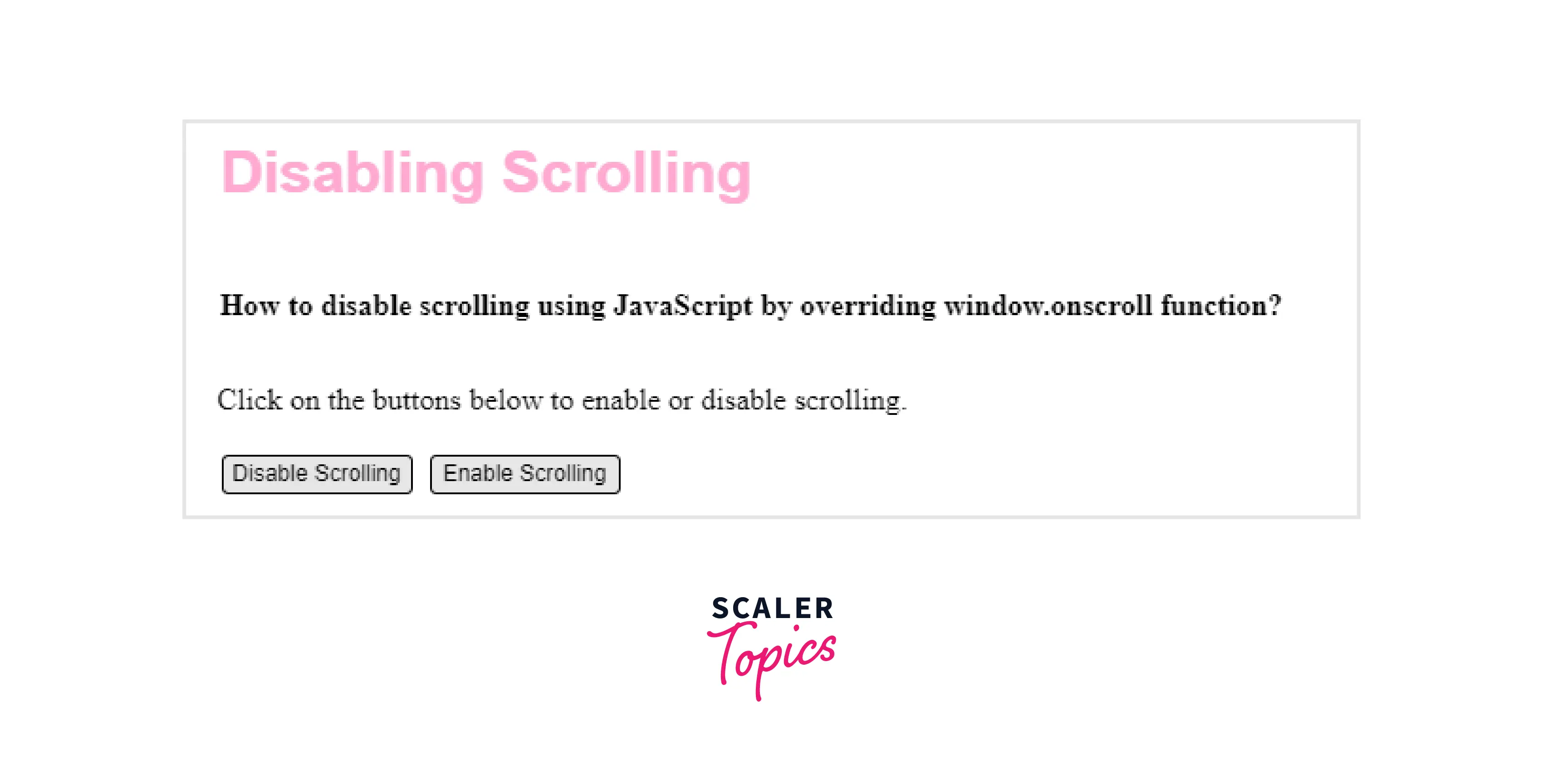
It will have the same effect as with the window.onscroll but with a few differences. Let's discuss those differences.
- It will disable the keyboard scrolling as well. Therefore we won't be able to move up and down using a keyboard, mouse or spacebar, etc.
- It will disable the touch scroll as well
- It will disable the scroll up and down by selecting the text.
Set overflow-x to Hidden to Disable Horizontal Scroll Bar in CSS
For disabling the horizontal scrolling we can set the property overflow-x to hidden along with the height is set to 100%. Everything else remains the same. Let's see the implementation for this.
Output:
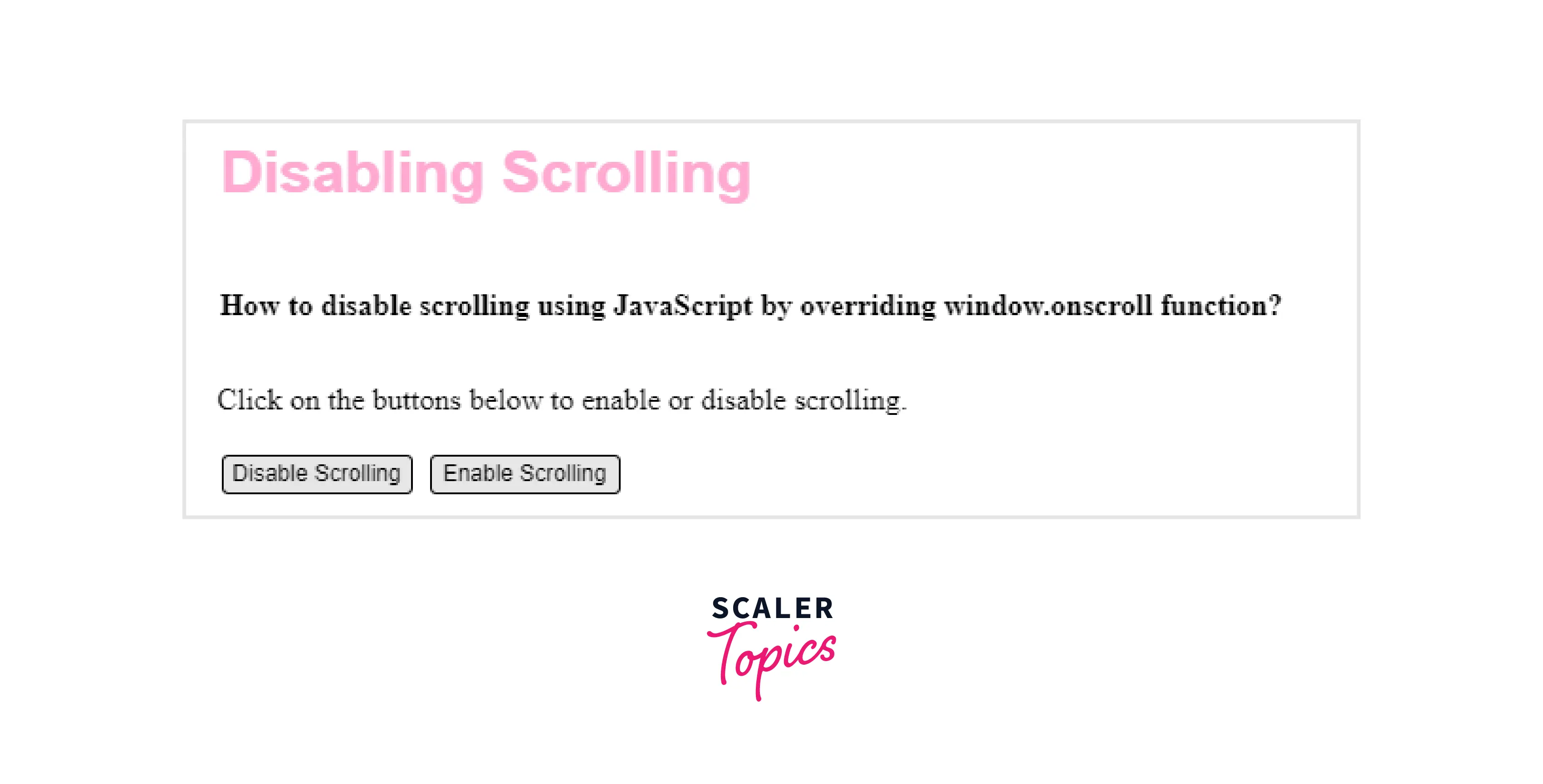
Preventing Keyboard Scroll Using JavaScript
Suppose, we want to prevent only the keyboard scroll but want to keep other scrolls, in that case, we need to add a keydown event Listener because this will detect which key is pressed and we can prevent the default behavior of the document if the key pressed is keyboard arrows, spacebar, shift+space bar, pageup, pagedown, etc.
We create an event Listener which takes an event argument and checks if the event(button pressed) has a keyCode equal to some of the keycodes already stored in an array. If it matches with one of them then we call the function preventDefault() and return false. This will disable the scrolling effect using that key.
To enable the scrolling effect we simply remove that eventListner added with that particular keypress.
Let's see the implementation of the above strategy.
Output:
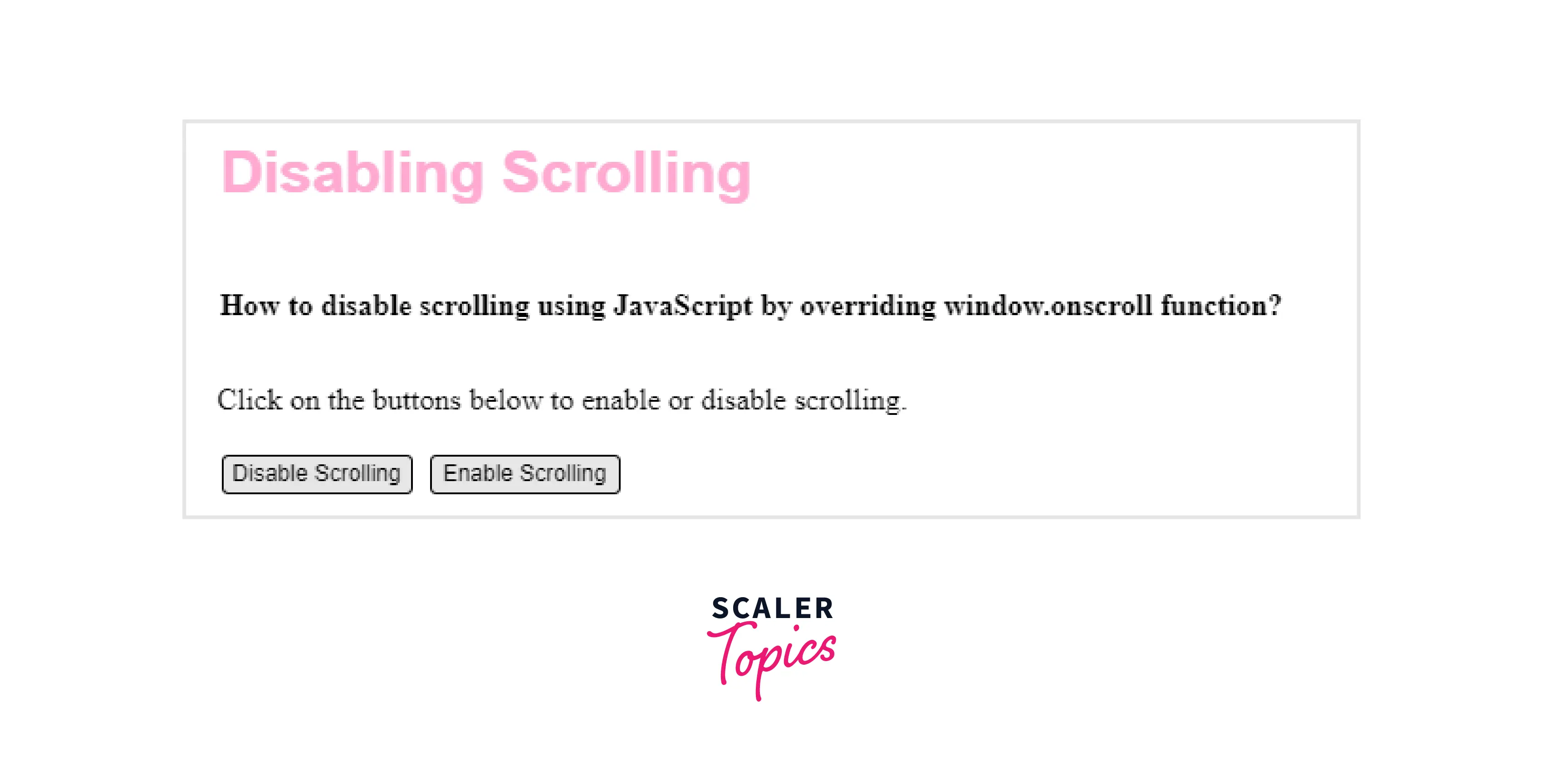
Preventing Touch Scroll Using JavaScript
To prevent the touch scroll, we need to add a touchmove event listener which prevents the default behavior while we perform touch scroll. This can be accomplished by creating a function called disableTouchScroll() which takes a touchmove event and prevents the default behavior using the function preventDefault() and stops the propagation using the stopPropagation() function of the event.
This can be implemented as follows
Applying CSS to Hide the Scrollbar in Website's Code
To hide the scrollbar in the website's code we can use the -ms-overflow-style property in the body element where we can set it to node as well as the -webkit-scrollbar property where we set the display property for this as none, this ultimately hides the scrollbar.
Let's understand this with the implementation:
Using the above css one can hide the scrollbar.
Conclusion
- We conclude that the scrolling effect of a webpage can be controlled using CSS and JavaScript.
- One of the methods to disable and enable scrolling is to override the window.onscroll method.
- We can also control specific scroll events like touch scroll, keyboard scroll, etc.
- Scrolling is controlled in two directions i.e. vertical and horizontal.
- Some of the important functions involved in the calculation of the scrolled amount of webpage are as follows.
- document.documentElement.scrollTop.
- document.documentElement.scrollLeft.
- window.pageYOffset.
- window.pageXOffset.
