Difference Between Steganography and Cryptography
Overview
Steganography and cryptography are both ways to protect information when it comes to data security and privacy. But they are used for different things and work in different ways. In this article we will discuss steganography and cryptography in a thorough way, and will also find the difference between steganography and cryptography, and how they each help in protecting our sensitive data.
Steganography
Steganography is the process of hiding information in data that looks harmless. With this method, secret messages are hidden in different types of carriers, such as text, audio, video, pictures, and even network protocols. The main goal of steganography is to hide the message itself so that it can't be found by people who shouldn't know about it. Steganography uses the changes in carrier data that can't be seen to send secret messages while making it look like nothing is wrong.
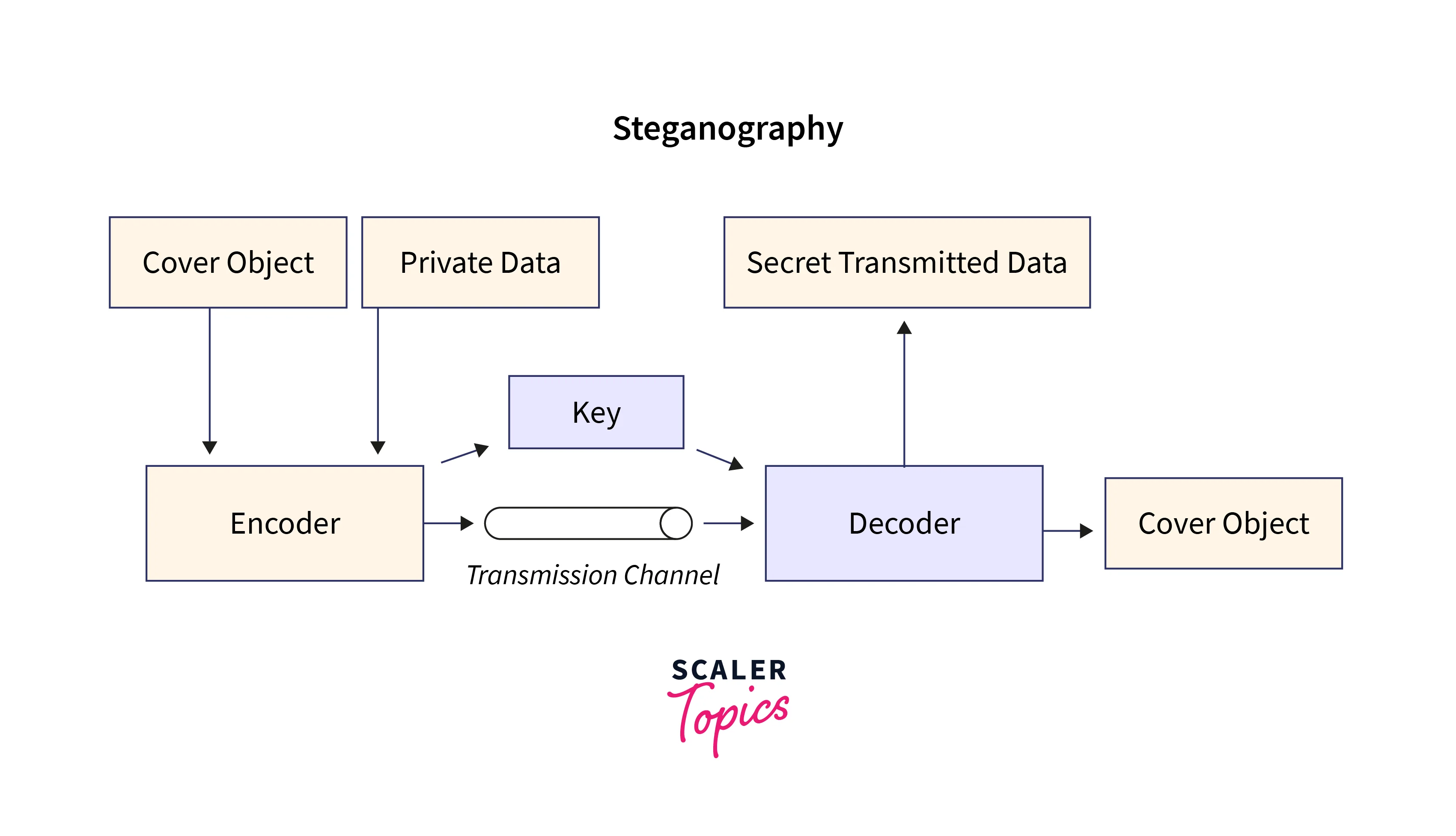
Text
In the context of steganography, "text" refers to any written or typographic content that is used as a carrier for concealing hidden messages or information. Textual data can include letters, words, sentences, paragraphs, or any other form of human-readable characters. In steganography, text can be manipulated in various ways to embed secret information while maintaining the appearance of a normal text document.
Audio
Audio steganography is a technique used to hide secret information or messages within audio files, such as music or speech, without visibly altering the perceptual quality of the audio. It is a form of data hiding that can be used for various purposes, including secure communication, watermarking, and covert data transmission.
Video
Video steganography is a method of hiding secret information within video files without noticeably affecting the video's visual or auditory quality. Similar to audio steganography, video steganography aims to embed data covertly within a carrier video, making it challenging for anyone without the appropriate decryption method to detect or access the hidden information.
Images
Images in steganography involve hiding secret information within image files without altering their visual appearance significantly. Techniques include LSB substitution, frequency domain methods, and more. These methods embed data within the image's pixels, and extraction is needed to retrieve the hidden information. Image steganography has uses in secure communication and watermarking, but it should be used responsibly and ethically.
Network or Protocol
Networkrefers to the communication infrastructure over which steganographic data is transmitted or shared. This includes the internet, local area networks (LANs), or any other interconnected system of devices. Steganography can utilize existing network protocols for covert data transmission, but it may also involve the development of specialized steganographic protocols to ensure the hidden data remains undetected during transit.
Cryptography
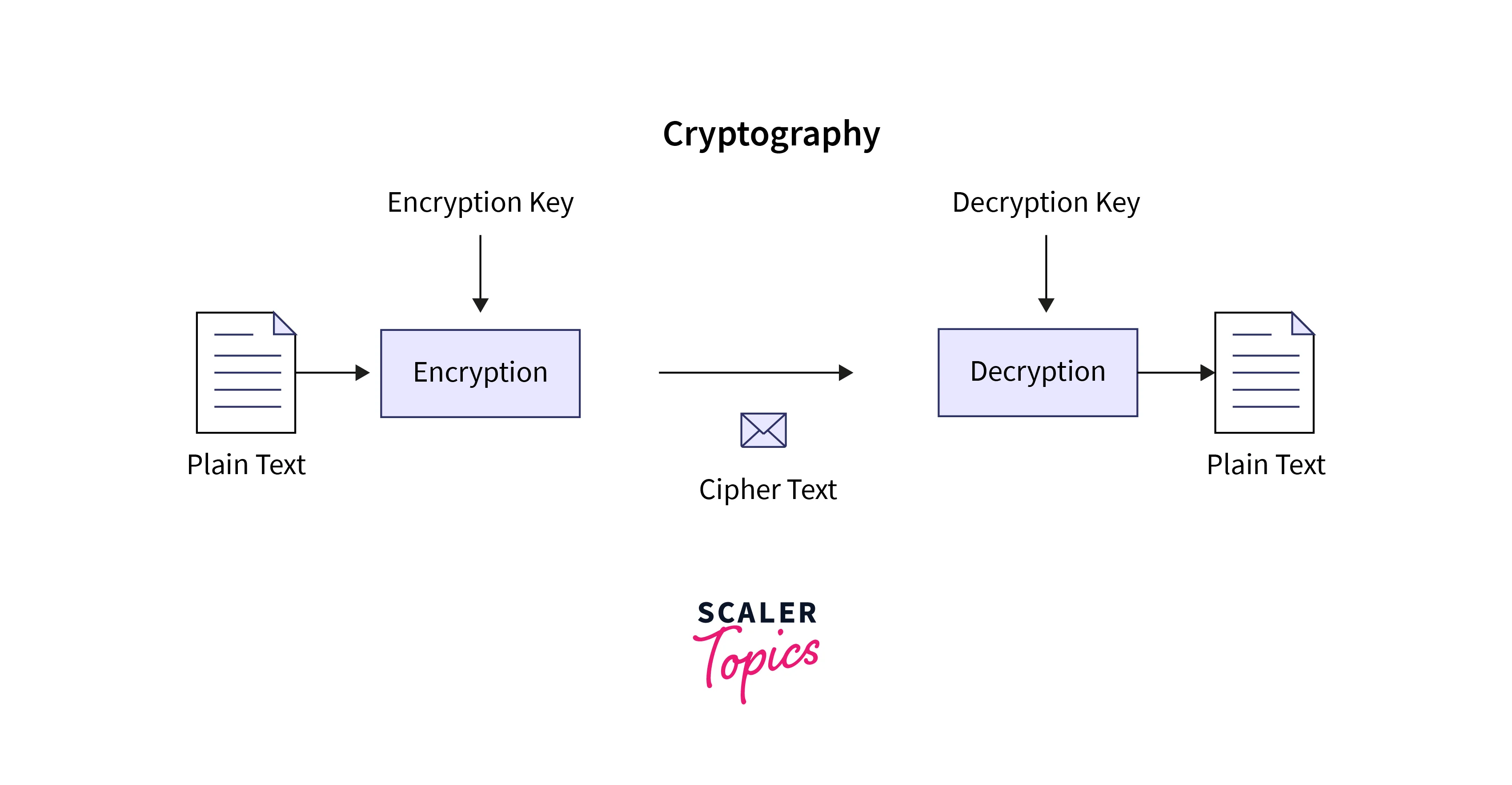
Cryptography is the practice of securing information by converting it into an unreadable format, known as ciphertext, using mathematical algorithms and keys. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data.
Symmetric key cryptography
Symmetric key cryptography is a method where the same secret key is used for both encrypting and decrypting data. It's efficient but relies on securely sharing the secret key. It's widely used for data encryption in secure communication and storage. Popular algorithms include AES and DES.
Asymmetric key cryptography
Asymmetric key cryptography, also known as public-key cryptography, is a cryptographic technique that uses a pair of mathematically related keys for securing communication and data. There are two keys are involved.
Public Key: This key is freely shared with anyone and used for encryption. It allows anyone to encrypt data that can only be decrypted by the corresponding private key.
Private Key: This key is kept secret and used for decryption. It's mathematically linked to the public key but cannot be easily derived from it. It's used to decrypt data that was encrypted with the corresponding public key.
After we have learnt the definition and concept, let's find out the difference between steganography and cryptography below.
The Difference Between Steganography And Cryptography
| Aspect | Steganography | Cryptography |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Hide the existence of secret information within a cover medium (e.g., image, audio) without raising suspicion. | Securely transform and protect the content of the message from unauthorized access. |
| Main Purpose | Concealment and secrecy of the message itself. | Data protection, confidentiality, and security. |
| Visibility | Conceals the presence of the message. | Typically, the presence of encrypted data is evident, but the content is protected and unreadable without the key. |
| Key Role | Usually not directly related to steganography. | Essential for both encryption and decryption processes. |
| Technique | Embeds secret data within a cover medium (e.g., LSB encoding in images). | Mathematically transforms the original data into ciphertext using an algorithm and a secret key. |
| Reversibility | Can be reversible (original data can be extracted). | Often reversible (with the correct decryption key), but can also be designed for one-way functions (e.g., hashing). |
| Security Focus | Focuses on hiding the message's existence. | Focuses on securing the content of the message against unauthorized access or tampering. |
| Authentication | Typically does not provide authentication of the sender or recipient. | Can incorporate authentication through digital signatures. |
Conclusion
- Steganography and cryptography are two distinct approaches to safeguarding information in the realm of data security and privacy.
- Steganography focuses on concealing the very existence of secret information within seemingly harmless carriers like text, audio, video, images, or network protocols. Its primary aim is to hide messages, making them undetectable to those who shouldn't have access.
- Cryptography, in contrast, revolves around transforming data into unreadable ciphertext using mathematical algorithms and keys. Its core objectives are ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity.
- This article also discusses the difference between steganography and cryptography.
