Difference Between Information Security and Cyber Security
Both information security and cyber security terms seem to be synonyms of each other. Both deal with the protection and security of the computer system to keep it safe from information breaches and threats. Both terms can be used interchangeably but information security mainly deals with the protection of data availability, integrity and confidentiality. On the other hand, cyber security mainly deals with the protection and security of mobile and electronic devices from cyber attacks. Following are some of the examples of cyber security:
- Critical Infrastructure
- Cloud Security
- Application Security
- Network Security
Following are some of the examples of information security:
- Compliance Controls
- Technical Controls
- Access Controls
- Procedural Controls
Information Security Vs Cyber Security
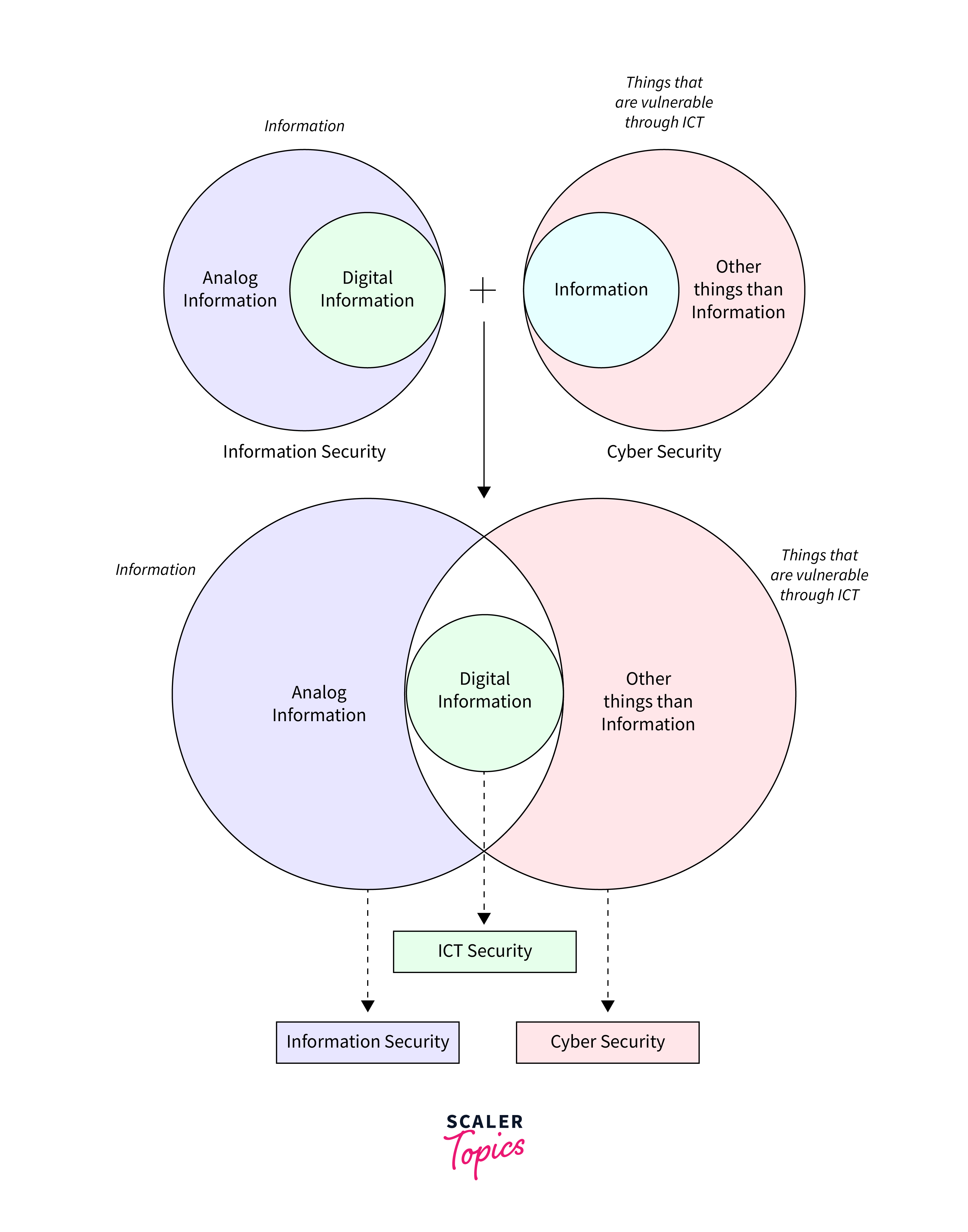
The difference between information security and cyber security is explained below:
| Parameter | Information Security | Cyber Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It deals with providing the availability, integrity and confidentiality of the information by protecting it from unauthorized access, users and modifications of data. | It mainly deals with the protection of the data on the internet from external resources. |
| Protection | Protects the data from any kind of threat. | Protects cyberspace from all kinds of cyber attacks. |
| Scope | Information security deals with the protection of information. | Protects anything in the cyberspace |
| Threat | Information security revolves around data protection from any type of threat. | Cyber security revolves around the protection from cyber attacks or threats. |
| Attacks | Information security protects from disruption, modifications, disclosure, unauthorized access and unauthorized users. | Cyber security protects from law enforcement, cyber fraud and cyber crimes. |
| Professionals | Professionals in information security are the foundation of data security and information security professionals deal with the responsibilities, organizational roles, processes and policies that guarantee information confidentiality, integrity, and availability | Professionals in cyber security are concerned with the protection from the Advanced Persistent threats (APT) or active threats. |
| Deals with | Information security concerned with information assets and confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. | Cyber Security concerned with threats of cyberspace like protection of personal information, social media accounts, etc. |
| Defence | It comes in a scenario when the security is broken. | It comes as a first line of defence. |
| Threats | Deals with multiple threats like human error, espionage and physical theft. | Addresses digital threats like phishing, malware and hacking. |
| Goal | The Main aim of information security is to protect information confidentiality, integrity and availability without considering the medium in which data is stored. | The Main aim of cyber security is to protect from unauthorized users, access, modification, disruption, and disclosure of digital information. |
| Technologies | Use multiple technologies such as data loss prevention tools, access controls and encryption. | Use multiple technologies such as intrusion detection systems, antivirus software and firewalls. |
| Skills required | Needs knowledge of regulatory issues, legal, compliance and risk management and also technical knowledge | Needs knowledge of computer networks, systems, and software development and also requires programming skills. |
| Focus on data | Mainly focuses on the protection of information assets which along with data also involves other information like confidential customer data, trade secrets, and intellectual properties. | Mainly focuses on the protection of data instead of focusing on how it is transferred and stored. |
| Threat landscape | Focuses on multiple threats such as social engineering attacks, insider threats and security breaches | Focuses on constantly evolving threats like emerging cybercrime techniques, and new kinds of malware. |
| Incident | Deals with the incidents that come from sources like insider threats, physical breaches, etc. | Deals with the incidents that come from digital environments like malware attacks, network intrusion, etc. |
| Response | Includes rules and policies to manage the threats related to the integrity, confidentiality and availability of data. | Mainly focus on the protection of digital systems from cyber threats. |
| Network Security | It deals with the security of the whole network infrastructure. | Focus on protecting the network from cyber threats such as malware, etc. |
| Mobile Security | Focuses on protecting data stored and transmitted by mobile devices to ensure privacy. | Focuses on protecting mobile devices from various cyber threats. |
| Cloud Security | Deals with the protection of data and applications hosted in the cloud to ensure integrity, confidentiality and availability | Deals with the protection of cloud infrastructure and services from cyber threats. |
FAQs
Q. What is the difference between information security and cyber security?
A. Information security mainly deals with the protection of information availability, integrity and confidentiality. On the other hand, cyber security mainly deals with the protection and security of mobileandelectronic devices` from cyber attacks.
Q. Can cyber security be considered as a subset of information security?
A. Yes, cyber security is generally considered a subset of information security. While information security encompasses the protection of all types of information, including physical and analogue forms, cyber security specifically focuses on protecting digital information and systems from cyber threats.
Q. How cyber security is different from information security?
A. Cyber security focuses on protecting digital information and systems from cyber threats, while network security specifically deals with securing networks and their infrastructure from unauthorized access, misuse, and other cyber threats.
Conclusion
- The main difference between information security and cyber security is that information security mainly deals with the protection of data availability, integrity and confidentiality but cyber security deals with the protection and security of mobile and electronic devices from cyber attacks.
- Critical Infrastructure, Cloud Security, etc. are some of the examples of cyber security.
- Compliance Controls, Technical Controls. etc. are some of the examples of information security.
