Difference between JDK, JRE and JVM

Overview
Java is one of the most important programming languages in today's era. Java is also very versatile as it serves as a programming language for Android development, web development, desktop applications, and much more. But before delving into the world of Java, let us understand the basic yet important concepts of Java- the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM. This article deals with the differences between these components.
Java Development Kit (JDK)
- As the name suggests, the Java Development kit is used for developing Java applications and applets.
- It consists of Java Runtime Environment (JRE), interpreter, compiler, and other tools like archiver, document generator, etc.
- It is responsible for compiling, debugging, and executing.
- It is platform-dependent as a different JDK is required for every platform.
Working
-
Compilation-
It consists of a Java compiler (javac) which is responsible for translating the Java code to the bytecode. The bytecode is an intermediate code that is understood by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
-
Execution-
The Java code is executed by the JVM which is a part of JDK.
-
Debugging-
There might be errors and bugs in our Java code which is debugged using the tools provided by JDK.
Importance
- It is important as it is used to maintain the compatibility between various versions of Java.
- It is mainly used for development, compiling, and debugging.
- JDK is mainly responsible for compiling as it contains the compiler javac. It makes JDK essential for development.
- The JDK version represents the Java version.
- It ensures consistent behavior across all platforms by enforcing the standard Java syntax.
- Also, multiple versions of JDK can exist on the same machine, allowing developers to work with different Java versions simultaneously.
Use Cases
- It provides different tools and libraries for building frameworks, Android applications, desktop applications, etc.
- Some of the popular JDK include- OpenJDK and Oracle JDK.
JDK architecture

The various components of JDK are- JVM, development and debugging tools, etc.
Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
-
As you must have rightly guessed from the name, Java Runtime Environment is provided by Java to run the applications.
-
It is an implementation of JVM. It consists of run-time libraries.
-
JRE Architecture

The components of JRE include-
- JVM- the most important component of JRE
- Deployment technologies
- Class Loader Subsystem
- Bytecode verifier
- Interpreter
- Libraries
- User Interface Toolkits
Working
-
To understand the workings of JRE, we need to know JVM. Here, we will understand it in short and discuss it in depth later in this article.
-
JVM is Java Virtual Machine which is the core component of JRE.
-
Consider an example- We have created a file "index.java". After it is compiled by the compiler (javac), as byte code and that code is stored in a class called "index. class".
-
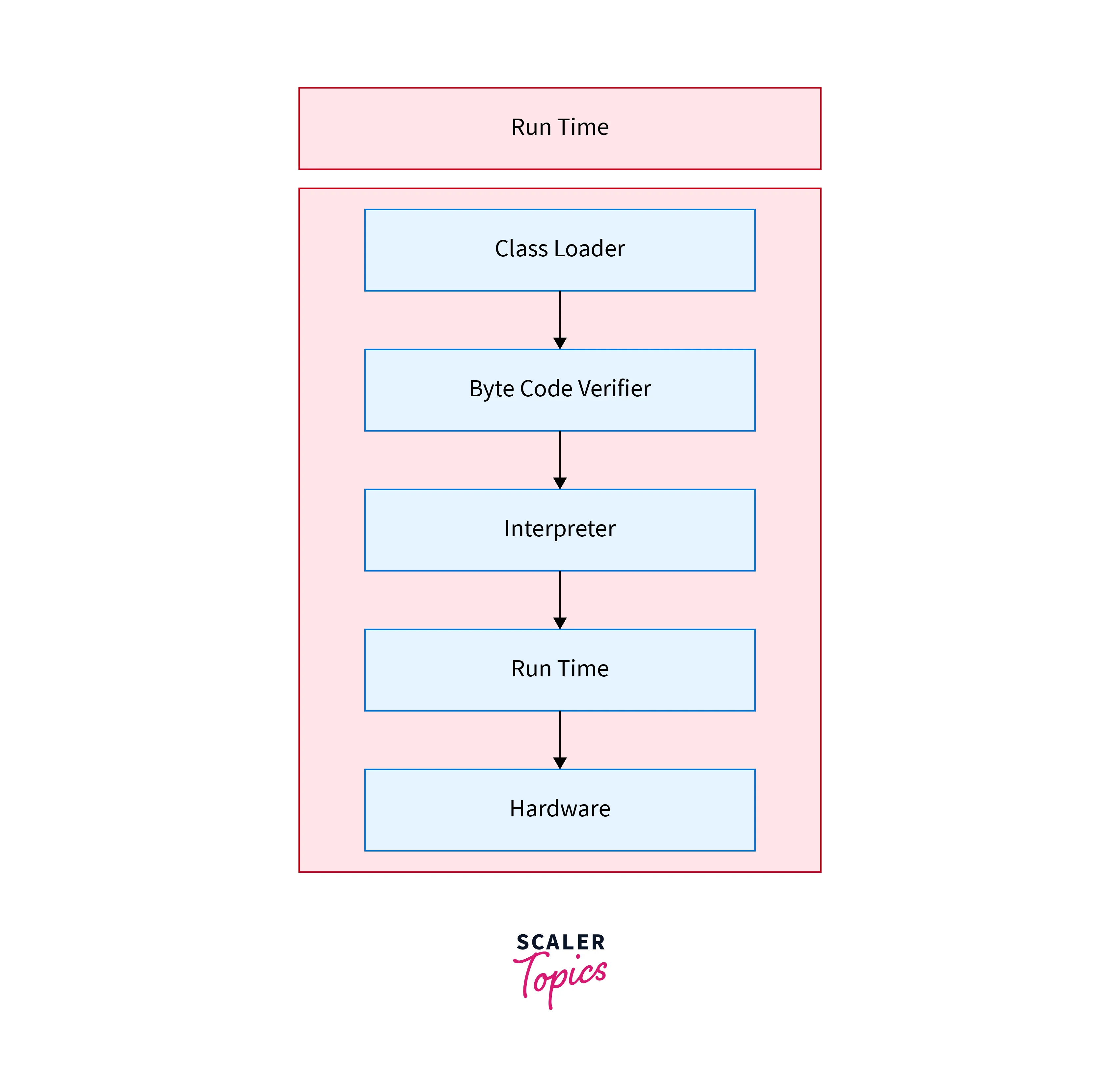
From this we can understand that the important components are- ClassLoader, Bytecode verifier, and Interpreter.
-
ClassLoader-
Classes are loaded into the memory as per their requirement. So, the Java ClassLoader is used to load the required classes to run a Java program. When the JVM is initialized, the following classes are loaded-
- Bootstrap class loader
- Extensions class loader
- System class loader
-
Bytecode verifier-
Before the code is passed to the interpreter, the bytecode verifier is used to verify the format of the Java code.
-
Interpreter-
When the byte code is loaded successfully, the Java interpreter creates an object of JVM because of which the Java code can run on the underlying machine.
Importance
- It is majorly responsible for running the Java applications
- It also ensures the safe execution of the Java program by using features like sandboxing.
- It consists of various integration libraries like- Java Database Connectivity(JDBC), JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface), RMI (Remote Method Invocation) etc.
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
- Java Virtual Machine is a part of the JRE.
- It is a specification that provides a run-time environment for Java applications.
- JRE provides the resources and libraries to run Java applications and JVM is the core component within it responsible for executing bytecode.
- JVM is responsible for converting the byte code to machine-specific code.
- As it is a part of JRE, it gets installed when JRE is installed.
- It is known as a virtual machine as it is not present physically.
- It is a document that describes the requirements of JVM implementation.
JVM Architecture
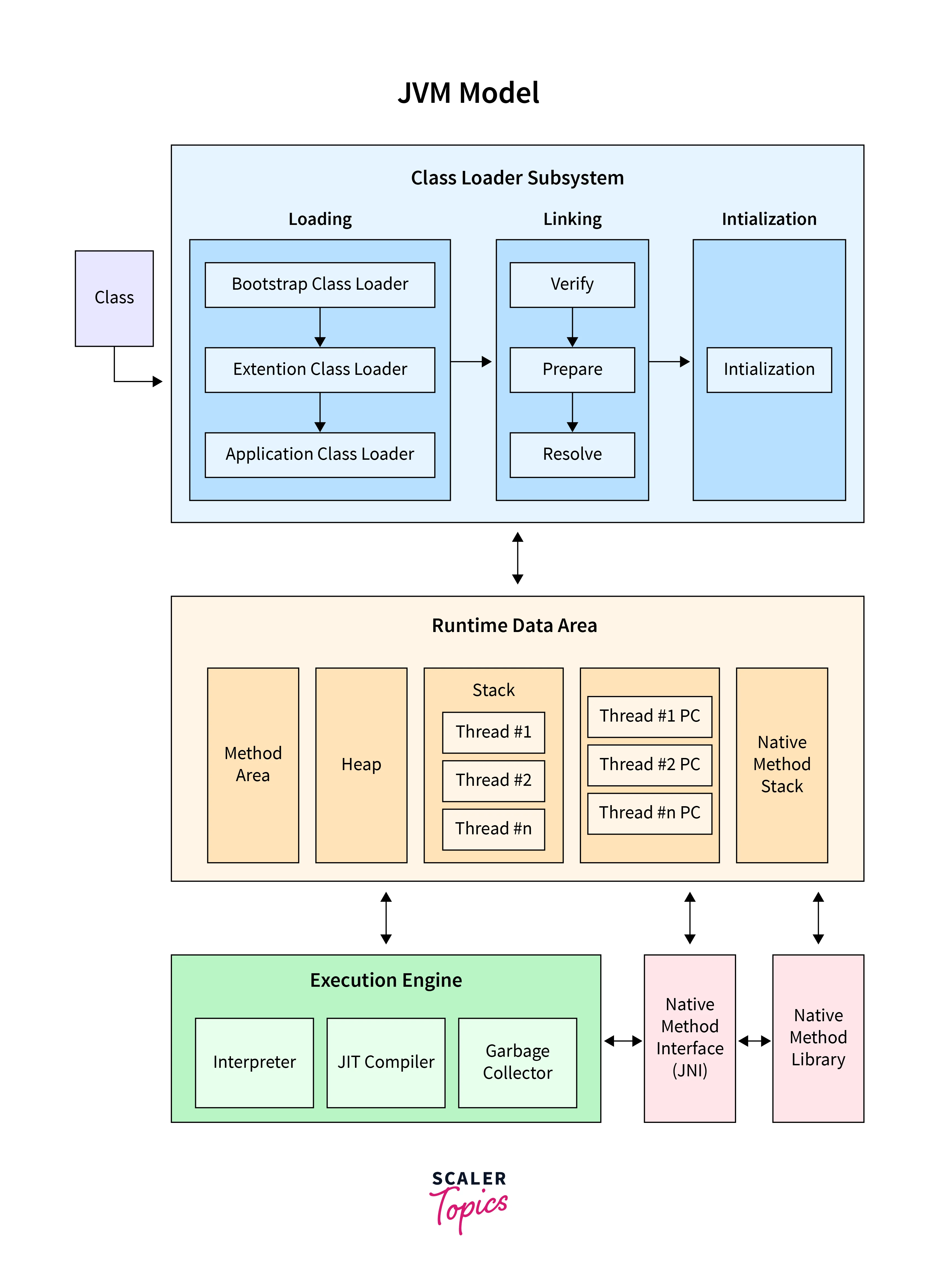
The components of JVM are as follows-
-
Class Loader Subsystem-
The class loader subsystem ensures that the class is loaded into memory. It is an on-demand process that prevents unnecessary work and redundancy. It handles the process of Loading, Linking, and Initialization.
-
Runtime Data Area-
It is the area where the memory is used during the execution. The sub-components of the Runtime Data Area are as follows-
- Method Area- It is used to store the class metadata.
- Heap- It is used to dynamically allocate and deallocate memory of objects.
- Stack- In Java, each thread has a stack dedicated. It is used to store particular data related to methods. It is also used to manage method calls.
-
Execution Engine-
It is used to interpret and execute bytecode. The instructions are read and executed. The sub-components of the execution engine are as follows-
- Interpreter- It is used to execute the instructions line-by-line. It allows step-by-step execution of the program.
- JIT Compiler- It is used to translate the bytecode into machine code. This can result in faster performance and better runtime.
- Garbage Collector- It is used to automatically manage the memory. It is used to allocate and deallocate memory. The developers do not have to look into the allocation and deallocation of memory.
-
Java Native Interface (JNI)-
It is a Java framework that allows the code running in the JVM to interact with the native libraries. The performance is also optimized.
Working
-
The JVM is responsible for loading, linking and initialization.
-
During runtime, JVM becomes an instance of JRE.
-
Loading-
Loading involves bringing the bytecode of a class into memory. It is the first step of execution in JVM.
-
Linking-
Here, the bytecode verification takes place. The class file is parsed by the JVM and divided into basic elements like methods, fields, etc. It is important to verify the bytecode to prevent unauthorized access and ensure memory safety.
Linking has 3 sub-stages.
-
Verification-
It verifies and ensures that the bytecode adheres to the structural rules for JVM's security. The rules like proper data type handling and valid references to objects are checked.
-
Preparation-
Memory is allocated to the static fields and they are initialized with the default values. It ensures that the static data of the class can be used.
-
Resolution-
It is used to resolve the symbolic references to concrete references.
-
-
Initialization-
During initialization, the sequence of static initializers and static fields' execution follows the order they are defined in the code. This is to make sure that the classes are properly initialized before they are put into use.
Importance
- The feature of Write Once Run Anywhere or WORA is possible because of JVM. Java code can be developed on one platform but it can be run on different platforms also.
- JVM is actually responsible for calling the main() method of Java.
- It also provides abstraction by hiding the inner implementation from the developers utilizing libraries from JVM.
- JVM enhances security by enforcing bytecode verification and runtime access controls, ensuring that Java applications operate in a secure sandboxed environment. It results in a safe application execution.
JDK Vs JRE Vs JVM
The difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM is as follows-
| JDK | JRE | JVM |
|---|---|---|
| JDK stands for Java Development Kit | JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment | JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine |
| Java Development kit is used for developing Java applications and applets. | Java Runtime Environment is provided by Java to run the applications. | Java Virtual Machine is a specification that provides a run-time environment for Java applications and describes the requirement of JVM implementation. |
| It is platform-dependent. | It is platform-dependent. | It is platform-independent. |
| Implementation is JDK=JRE+Development tools | Implementation is JRE=JVM+libraries | Implementation is only a runtime environment to execute the code. |
| JDK consists of many development tools. | JRE consists of class libraries and other files. | JVM does not consist of any software tools. |
FAQs
Q. What is the Difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM in Java?
A. JDK is the Java Development Kit used for development, JRE is the Java Runtime Environment used to run Java applications, and JVM is the Java Virtual Machine responsible for executing Java bytecode.
Q. What is the Role of JVM in Achieving Platform Independence?
A. JVM interprets bytecode and converts it into machine-specific instructions, enabling Java code to run consistently across various platforms.
Q. Can Different Versions of JDK Exist on the Same Machine?
A. Yes, multiple versions of JDK can exist on the same machine, allowing developers to work with different Java versions simultaneously.
Conclusion
- Java Development kit is used for developing Java applications and applets. It consists of Java Runtime Environment (JRE), interpreter, compiler, and other tools like archiver, document generator, etc. It is responsible for compiling, debugging, and executing.
- In JDK, compilation involves using the Java compiler (javac) to translate code into bytecode, which is understood by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The execution is carried out by the JVM within JDK, whereas the debugging tools are provided to identify and rectify errors and bugs in Java code.
- Java Runtime Environment is provided by Java to run the applications. It is an implementation of JVM. It consists of run-time libraries. t consists of various integration libraries like- Java Database Connectivity(JDBC), JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface), RMI (Remote Method Invocation) etc.
- The important JRE components are- ClassLoader, Bytecode verifier, and Interpreter. It is a specification that provides a run-time environment for Java applications.
- JVM is responsible for converting the byte code to machine-specific code. It is known as a virtual machine as it is not present physically.
- The feature of Write Once Run Anywhere or WORA is possible because of JVM. Java code can be developed on one platform but it can be run on different platforms also. JVM is responsible for calling the main() method of Java.
