What is the Difference Between Linux and Ubuntu?
Delve into the nuances of Linux and Ubuntu in this enlightening article, tailored for developers, system administrators, and Linux aficionados. We'll unpack their distinct features and functionalities, enhancing your understanding of each. Initially, familiarize yourself with essential concepts: the kernel', the OS's core managing resources and hardware-software interactions, and the operating System' (OS), the user-hardware interface encompassing the kernel. Additionally, we'll explore the 'Rolling Release Model' and 'Fixed Release Schedule', pivotal in distinguishing Linux and Ubuntu.
Ready to deepen your knowledge? Let's get started on this insightful journey into their unique worlds.
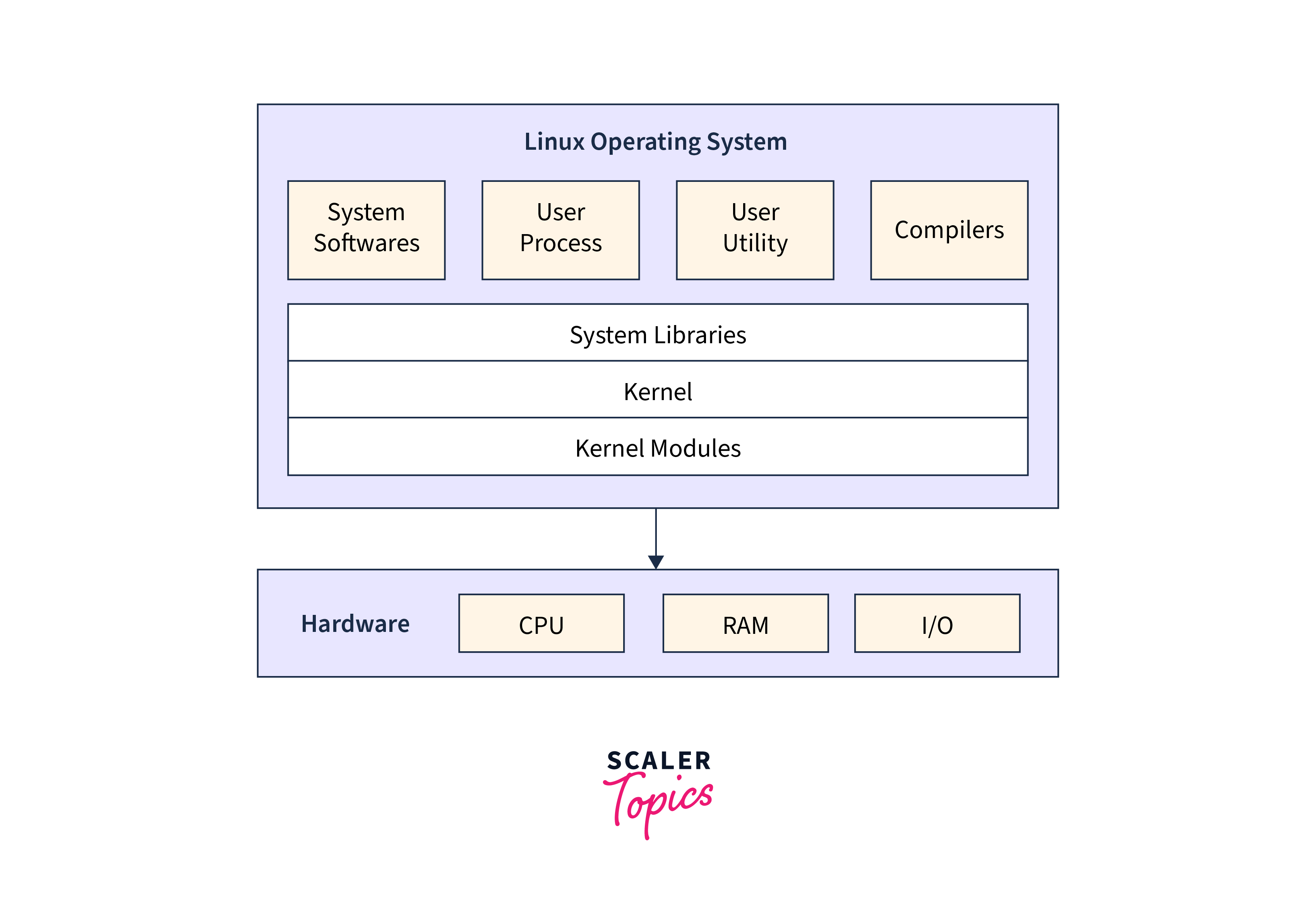
What is Linux ?
Linux refers specifically to the kernel of the operating system, which is the core component responsible for managing system resources, facilitating communication between hardware and software, and providing essential functionalities.
However, the term "Linux" is often used more broadly to refer to an entire operating system that is built around the Linux kernel. This complete operating system, often referred to as a Linux distribution or simply a distro, includes not only the Linux kernel but also a collection of software packages, utilities, libraries, and graphical interfaces.
The Linux kernel itself was initially developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991 and released under an open-source license, which allowed developers around the world to contribute to its development and create their own Linux distributions. As a result, there are now numerous Linux distributions available, such as Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, and CentOS, each with its own set of features, package management systems, and user interfaces.
So while Linux technically refers to the kernel, it is commonly used to describe the entire operating system built around the Linux kernel. Also, when we say Linux OS, it means the OS has Linux as its kernel.
Here are some of the benefits of using Linux:
- Free and open-source: Linux is built on the principles of open-source software, which means that its source code is freely available for anyone to view, modify, and distribute.
- Stable and secure: Linux is known for its stability and security. It is a good choice for organizations that need a reliable and secure operating system.
- Flexible: Linux is a very flexible operating system. Users can utilize it on a diverse range of hardware platforms.
- Customizable: Linux is made up of a collection of independent components. It makes it easy to customize and extend Linux to meet the needs of different users and organizations.
- Command-Line Interface: Linux offers a powerful command-line interface (CLI) that allows users to interact with the system through text commands. It provides advanced control and flexibility, making it a preferred choice for system administrators, developers, and power users.
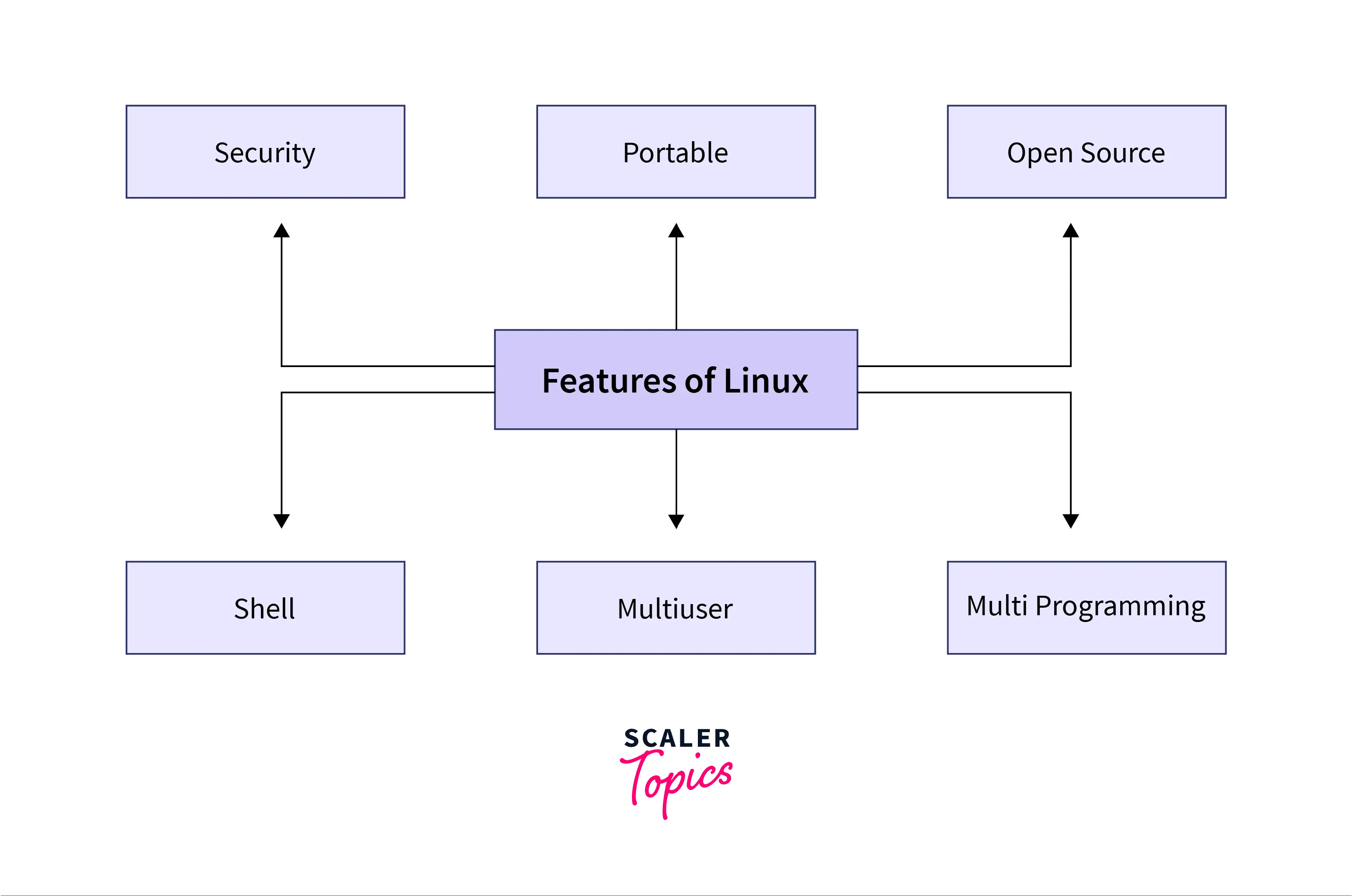
To deepen your understanding of Linux features, you can read the Features of Linux Operating System article.
Understanding the fundamentals of Linux is essential for comprehending the difference between Linux and Ubuntu.
What is Ubuntu ?
Ubuntu is a popular Linux distribution that has gained widespread popularity for its user-friendly approach and extensive community support.
Users can utilize Ubuntu as their primary operating system for work, school, or personal use. Ubuntu is an ideal choice for developers and game developers, providing them with extensive development tools and resources.
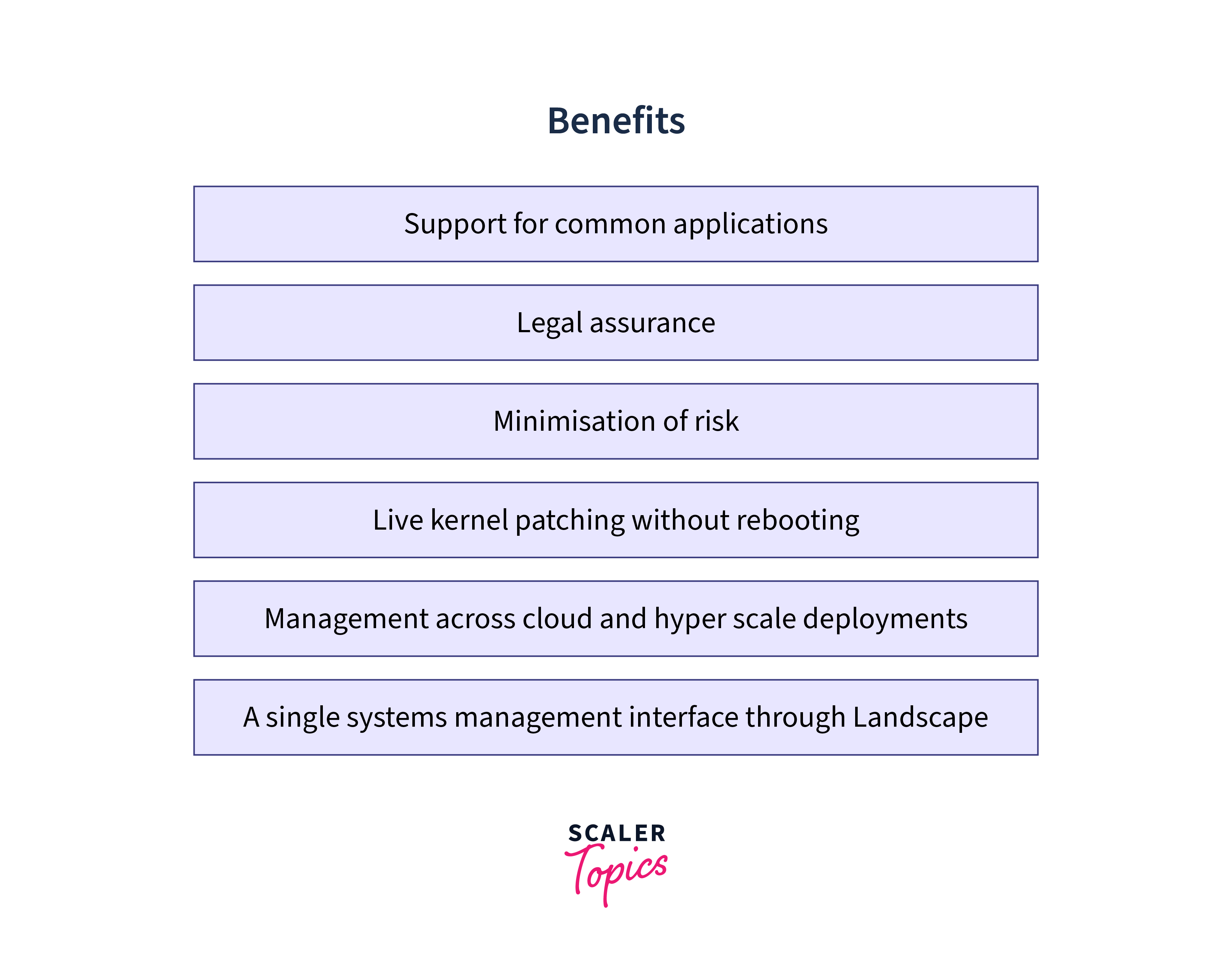
Here are some of the benefits of using Ubuntu:
-
Free and open-source: Ubuntu is free to download and use. There are no licensing fees or hidden costs.
-
Secure: Ubuntu is constantly updated with security patches and improvements. It makes it one of the most secure operating systems available.
-
Easy to use: Ubuntu is designed to be easy to use, even for beginners. The user interface is simple and intuitive. It offers a visually appealing desktop environment and a range of applications for productivity, multimedia, and entertainment purposes.
-
Wide range of software: Ubuntu offers a complete operating system with pre-installed software and applications, including popular applications like Firefox, LibreOffice, and GIMP. You can also install software from the Ubuntu Software Center or from third-party repositories.
-
Versatile: Users can employ Ubuntu on various devices, such as desktops, laptops, servers, and even Raspberry Pi, offering versatility and adaptability across different hardware platforms.
-
Support: Ubuntu has a large and active community of users and developers.
Overall, Ubuntu offers a user-friendly and feature-rich Linux distribution.
Key Differences Between Linux vs Ubuntu
In this section, we will explore the difference between Linux and Ubuntu.
Here is a comprehensive table that shows the key difference between Linux and Ubuntu:
| Parameter | Linux | Ubuntu |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An open-source kernel | A Linux-based open-source operating system |
| Distributions | Various distributions of Linux are available | One of the popular Linux distributions |
| Customizability | Highly customizable | Customizable with different desktop environments and themes |
| Package Management | Package manager varies by distribution | Uses the APT package manager |
| User-Friendliness | May require advanced technical knowledge | User-friendly and suitable for beginners |
| Release Cycle | Rolling release and fixed release models available | Fixed release cycle with LTS versions |
| Community Support | Large and active community | Strong community support and resources |
| Hardware Compatibility | Wide range of hardware support | Focuses on compatibility with popular hardware |
| Pre-installed Software | Minimal software pre-installed | Includes a selection of software for various use cases |
| Target Audience | Suitable for both servers and desktops | Primarily designed for desktop use |
Understanding the difference between them empowers users to make informed choices based on their needs and preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between Linux and Ubuntu is essential for individuals navigating the world of operating systems. Here are the key takeaways from the article:
- Linux is a free and open-source kernel that forms the foundation for numerous operating systems, including Ubuntu.
- Ubuntu, on the other hand, is a Linux distribution that provides a complete operating system package with a user-friendly interface and a range of pre-installed software.
- Linux offers high customization and flexibility, allowing users to tailor the system to their specific needs and preferences.
- Ubuntu focuses on accessibility and ease of use, providing a polished desktop environment and a vast software repository.
- Linux encompasses a wide range of distributions beyond Ubuntu, each with its own characteristics, target audience, and use cases.
- Both Linux and Ubuntu benefit from active developer communities and regular updates.
In conclusion, Linux and Ubuntu provide distinct approaches to the operating system landscape, catering to a range of users and requirements.
