Escape Sequence in Python

Abstract
An escape sequence is a sequence of characters that, when used inside a character or string, does not represent itself but is converted into another character or series of characters that may be difficult or impossible to express directly, like newline (\n), tab (\t), and so on.
In the escape sequence, a character is preceded by a backslash (\) followed by the character you want to represent for the new line. We have something like this \\\n.
This character serves as an escape sequence initiator, and every character (one or more) following it is considered an escape sequence.
Introduction to Escape Sequence in Python
Suppose you have the string containing a double backslash (\\\\), and you want to print the string with a double backslash, but it is impossible to print it directly. So here comes the role of escape sequences.
Firstly, understand sequences. A sequence is just a set of two or more characters and an escape where the sequence begins with a backslash (\\) and other characters in the set follow that backslash.
An escape sequence is a sequence of characters that, when used inside a character or string, does not represent itself but is converted into another character or series of characters. So escape sequences are formed using two things: the first is a backslash (\\), and the second is the set of one or more characters following that backslash (\\).
List of Escape Sequence Available in Python
| Escape Sequence | Meaning |
|---|---|
| \’ | Single quote |
| \\’ | Double quote |
| \\ | Backslash |
| \n | Newline |
| \r | Carriage Return |
| \t | Horizontal Tab |
| \b | Backspace |
| \f | Formfeed |
| \v | Vertical Tab |
| \0 | Null Character |
| \N{Name} | Unicode character Database named lookup |
| \uxxxxxxxx | Unicode character with a 16-bit hex value |
| \Uxxxxxxxx | Unicode character with a 32-bit hex value |
| \000 | Character with octal value ooo |
| \xhh | Character with hex value hh |
How to escape single quotes in Python
As we know, if we use a single quote inside the string directly, and that string is closed inside a pair of single quotes, then the interpreter will get confused and give an error output.
For Example,
We want to print who's this.
If we execute this directly, we get an error message -
Why this error occurred?
The interpreter needs clarification. It can't find the starting position of a single quote since it occurred three times.
How to overcome?
To overcome this problem, we can use escape sequences here.
Output:
The above examples show how a single quote is printed in (Who’s) using a backslash (‘\’).
It happened because of the backslash (‘\’) before any character tells the interpreter that this combination is an escape sequence in python, removing the backslash from the string and putting the quote inside the string.
n Escape Sequence in Python
Suppose I give a string, so it will not be considered a new line. What if we want to print some part of the particular string in the new line?
We can use “\n” here, which tells the interpreter to print some characters in the new line separately.
Example:
Output:
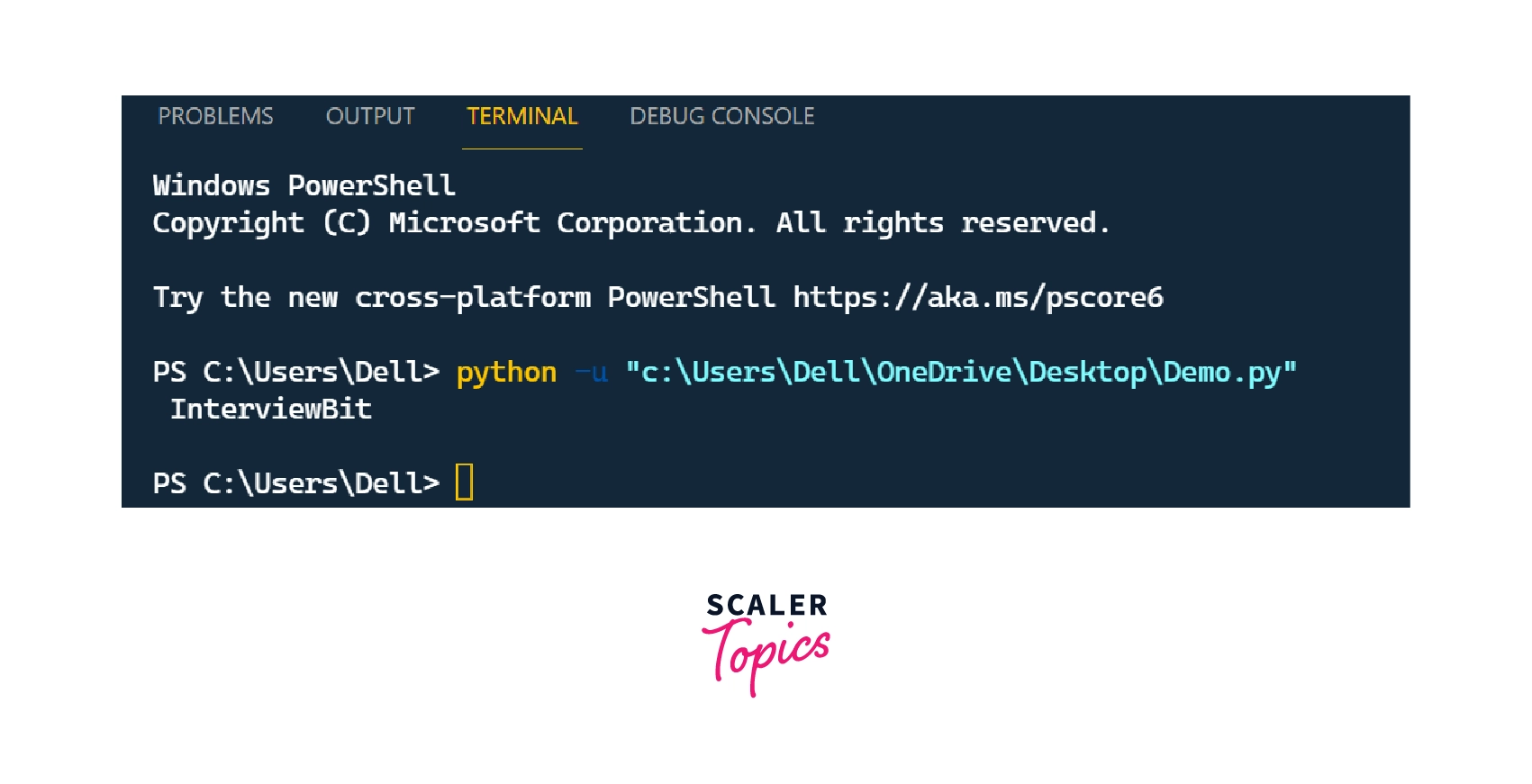
The above example shows that "Bit" is printed in a new line.
So we can say that we will get the new line when we type \n in the string before any word or character.
Backslash Escape Sequence in Python
What if we want to print a single backslash? We can't do it by just writing "", so we'll use "\\".
Example:
Output:
Python escape sequence for Space
If we want to add tab space between words, then this escape sequence will give the tab space between the words or characters using “\t”.
Example:
Output:
From the above screenshot, you can see that if we want a tab space between two words, we can use this ‘\t’ escape sequence to print the spaces.
Backspace Escape Sequence in Python
This escape sequence is used to remove the space between the words.
Example:
Output:
Python escape sequence for Hexa value
Now, there may be a situation where we have Hexa values, and we want to print alphabets using their Hexa values? In such a case, we can use “\xhh”, where hh is the unique Hexa value of the alphabet.
Example:
Output:
As you can see in the above example, the characters are printed according to their respective Hexa values, followed by the ‘\x’.
Python escape sequence for Octal value
Now, what if we want to print alphabets using their octal values? So for that, we will use “\ooo”, where ooo is the unique octal value of the alphabet.
Example:
Output:
As you can see in the above example, the characters are printed according to their respective octal values, followed by the ‘\’.
Remove all escape sequences from a list
Now, what if we want to remove all the escape sequences from the list? So let’s take an example:
Example:
Output:
In the above example, there is a list that contains two Hexa values (‘x50’ and ‘x44’), so if we just put a "\" before them, then we can escape them all. As you can see, “x50” is replaced by its Hexa value ‘P’, and “x44” is replaced by ‘D’ by putting "\" before them.
Python escape sequence ignore
To ignore all the escape sequences in the string, we have to make a string as a raw string using ‘r’ before the string. After that escape sequence will also be considered normal characters. Let's take an example.
Example:
Output:
From the example above, you can observe that when we typed ‘r’ before the string, it ignored the escape sequence, which is a new line “\n” in the string.
Python escape sequence remove
To remove all the characters from the left and right of an argument string, we will use the string.strip() function.
Example:
Output:
Escape Sequence Interpretation
When a backslash appears in a string, the escape sequence is interpreted. After encountering a backslash (inside a string), we would check the subsequent character (with the (\)) on the escape sequence table, which is the table mentioned earlier. The sequence is removed from the string if a match is detected in the table. And it is translated into a normal character. If no match is detected, no lookup is performed, and the control sequence is copied as it is.
Example:
Output:
As seen in the above output, the first print statement produced output with one tab space because \t is present in the table. On the other hand, in the second print statement, the \c persists, as no legal resolution for that sequence exists.
Preventing Escape Sequence Interpretation
There are some situations where we don't want the string to behave as shown above (which means printing the translation of the sequence present in the sequence table). Some situations are shown below where we must print the same sequence instead of its translation.
- A string contains a network or a local path.
- The strings that contain regex, which the regex engine would further process.
Methods of Prevention
-
Method 1
It is tedious and only advised if the string size is less. Just doubling the backlash allows us to overcome such issues. In this method, we manually find the single backslash and concatenate it with another backslash.
Example:
Output:
In the first case, "\t" was considered a tab space, but in the second one, "\t" was printed as a normal literal.
-
Method 2
We can use the concept of raw string, i.e., adding r or R before the string, which will preserve the escape sequences as literals.
Example:
Output:
In raw string, as you can see that, escape sequences are preserved as literals.
Conclusion
- Escape sequences allow you to insert special characters in strings. Put a backslash (\) before the character you want to escape.
- We can use the Escape Sequences concept to specify actions such as tab movements in the terminal and also for the representation of non-printing characters like new line (\n) or characters that have special meaning like double quotation marks (").
- Talking about prevention, we have two methods: either use the double backslash method, which is not possible for a larger string or use the concept of raw string, i.e., adding r or R before the string.
