What is @font-face CSS?

The "@font-face" CSS rule refers to a font name that can be used in a style sheet.
The font-family property in "@font-face" is used to name the font. The rule contains an src descriptor that is associated with an external font name.
Code :
Here, the font-face 'Design Font' is applied. The font-family Splash-Regular takes effect.
Output : 1

If 'Splash-Regular' fails then the fallback option specified 'Design Font' takes its place.
Output : 2

How to Use @font-face in CSS
"@font-face" is an excellent solution for fonts that are hosted on one's servers as it helps developers to display a font on a website even if that font isn't installed on the user's computer. The rule instructs the browser to download the font from where it is hosted, then display it as specified in the CSS. This allows designers to use a variety of fonts instead of only being restricted to use web safe fonts that users have preinstalled on their computers.
Practical Level of Browser Support
The WOFF2 file format is a go-to solution as it is supported by almost all the major browsers.
Example :
Code :
HTML :
CSS :
Output :

Deepest Possible Browser Support
This method provides the deepest support possible by secifying multiple location URLs. The "@font-face" rule is added to the stylesheet before any style.
This method is used to style elements with fallback options.
Example :
Code :
HTML :
CSS :
Output :

Slightly Deeper Browser Support
The true type fonts(.ttf) act as an intermediate between practical level browser support and deepest level browser support.
Example :
Code :
HTML :
CSS :
Output :
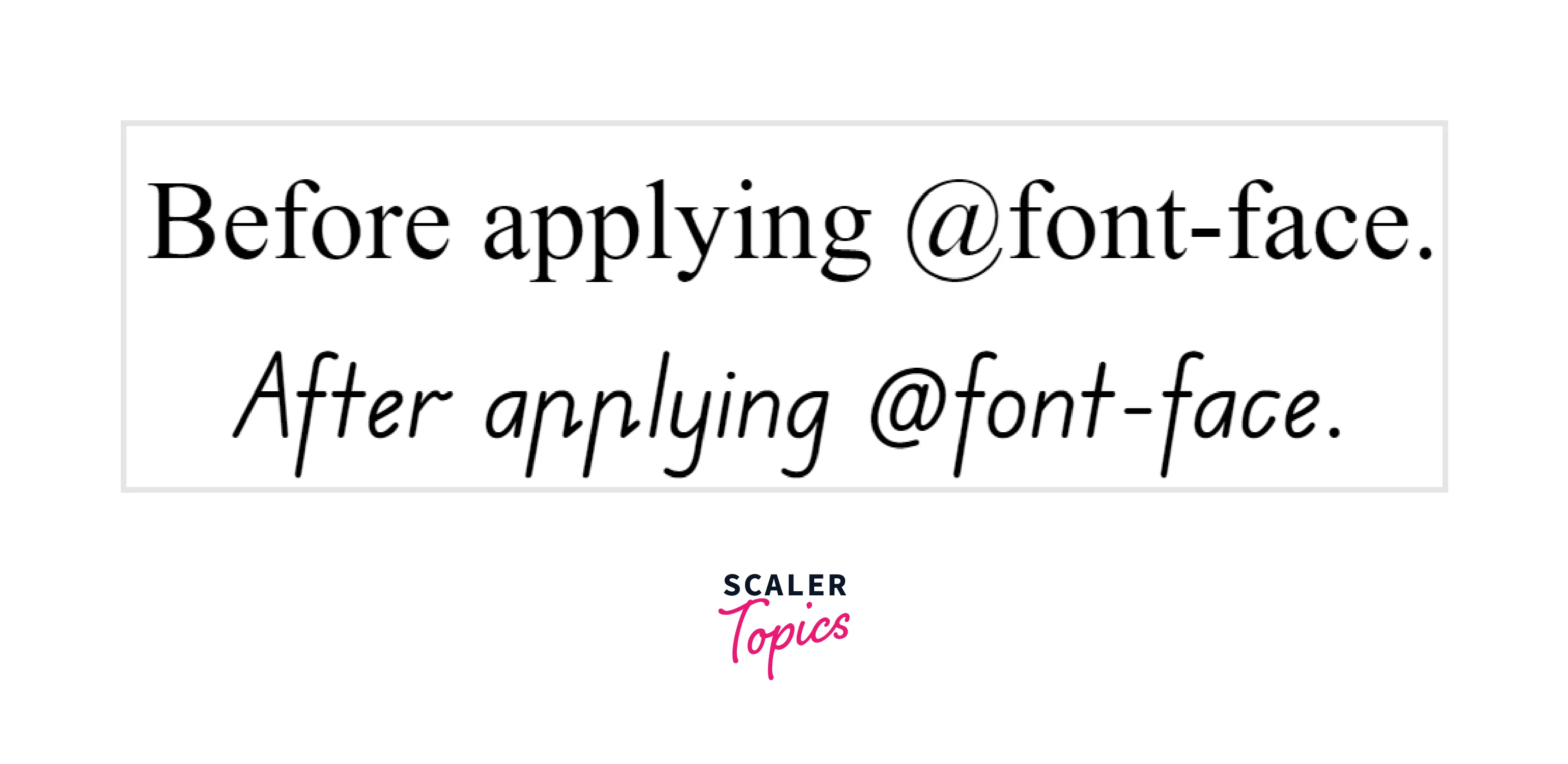
How do I Change my Font Face in CSS ?
To change the font face we can use the font-family property.
Using a hosted service helps to include all the font file variations that ensure deep cross-browser compatibility without hosting all those files ourselves.
The hosted service can be used in the following ways :
@import
Google Fonts offers users to use multiple hosted fonts. The desired font is loaded from Google fonts using @import.
Example :
<link>
The <LINK> tag helps to link the asset directly to the HTML file instead of using it through a CSS file.
Example :
What is the Syntax of Font Face CSS ?
The basic structure of the @font-face rule is straightforward. It is included at the beginning of a stylesheet, so the fonts will be loaded first.
The font-face rule consists of the font-family, src, font-strength, font-weight, and font-style parameters. The role of these descriptors is discussed below.
Syntax :
What are the Properties of Font Face ?
The properties or descriptors of @font-face are as follows :
| Property | Values | Description | Required/Optional | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| font-family | name_of_font | It specifies the font of an element. | Required | - |
| src | URL | It specifies the location or file path (URL) of the external resource. | Required | - |
| font-stretch | normal, expanded, semi-expanded, extra-expanded, ultra-expanded, condensed, ultra-condensed, extra-condensed, semi-condensed | It defines how stretched the text should be, that is wider or narrower. | Optional | normal |
| font-weight | normal, bold, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 | It defines the boldness and sets the weight or thickness of the font being used. | Optional | normal |
| font-style | normal, oblique, italic | It is used to style the given text. | Optional | normal |
Examples of Font Face in CSS
Example : 1 - Using WOFF2 Format
Code :
HTML :
CSS :
Output :

Example : 2 - Specifying a Downloaded Font
Code :
HTML :
CSS :
Output :

Example : 3 - Specifying Local Font Alternatives
Code :
HTML :
CSS :
Output :

Example : 4 - Using Icons
Code :
HTML :
CSS :
Output :

Learn About CSS Font Properties
To get in-depth knowledge on CSS Font Properties head over to CSS Font Properties
Effect on Performance
Web fonts enhance the look of a bland website. Since the custom fonts need to be downloaded before being displayed, they impact the website's performance.
Initially, the fallback fonts used to get loaded before the downloaded ones came into action.
However, the browsers hide the text until the custom font loads by default.
Browser Support
The browsers and the font format they support for the CSS "@font-face" rule are listed below :
| Browser\Font Format | TTF/OTF | WOFF | WOFF2 | SVG | EOT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Chrome | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Internet Explorer | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Firefox | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Safari | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Opera | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
Conclusion
- The CSS "@font-face" is a rule that allows defining online fonts to text on the website.
- The parameters of the "@font-face" rule are font-family, src, font-stretch, font-weight, and font-style.
- The "@font-face" rule is supported in Edge, Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Opera.
- The 5 Font formats are TTF/OTF, WOFF, WOFF2, SVG, and EOT.
