Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of AI is a realm of endless possibilities, merging the realms of science, technology, and human ingenuity. Envisioning a world where intelligent systems enhance human capabilities, the future of AI is not just about technological advancements but also about reshaping societal norms and ethics. This journey from conceptual frameworks to real-world applications signifies a pivotal shift in how we interact with technology, making the future of AI a cornerstone in the next chapter of human evolution.
Growth of AI
The journey towards the future of AI has been characterized by rapid advancements and significant milestones. This growth can be segmented into several key areas:
- Early Foundations and Theoretical Developments:
Initially, the future of AI was conceptualized through theoretical models and basic algorithms. Pioneers in the field laid the groundwork with principles of machine learning, neural networks, and computational intelligence. These early efforts set the stage for more sophisticated AI systems. - Breakthroughs in Machine Learning and Deep Learning:
A major leap in the future of AI came with the advent of advanced machine learning techniques, especially deep learning. These technologies enabled AI systems to learn from vast amounts of data, leading to breakthroughs in image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics.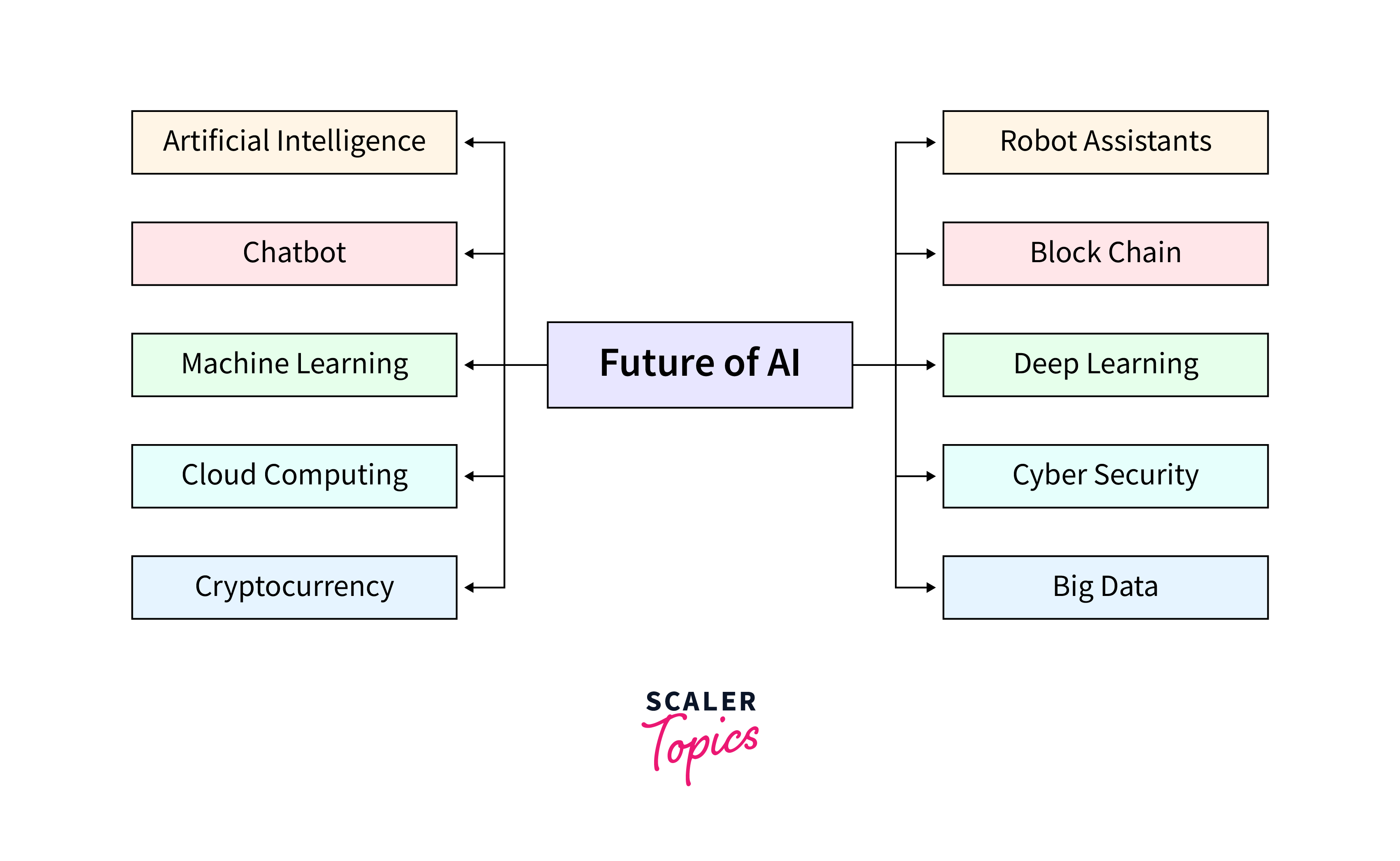
- Increase in Computational Power:
Parallel to these developments, there was a significant increase in computational power. The future of AI has been greatly influenced by the advent of powerful GPUs and cloud computing, allowing for the training of complex models and the processing of large datasets more efficiently. - Big Data Revolution:
The explosion of data, often referred to as the Big Data revolution, has been a catalyst in the growth of AI. The future of AI is closely tied to the ability to harness and interpret this data, enabling more accurate and sophisticated AI applications across various sectors. - Expansion Across Industries:
The growth of AI is not confined to tech industries alone. The future of AI encompasses a wide array of sectors including healthcare, finance, automotive, and entertainment. AI's integration into these fields has led to innovative solutions like precision medicine, algorithmic trading, autonomous vehicles, and personalized content recommendation systems. - Ethical and Regulatory Development:
As AI continues to grow, so does the discussion around its ethical implications and the need for regulatory frameworks. The future of AI is intertwined with how we address issues like privacy, bias, and accountability. Developing ethical guidelines and regulations is crucial for sustainable and responsible AI growth. - Continuous Innovation and Research:
The future of AI is sustained by ongoing research and innovation. Universities, research institutions, and tech companies are constantly pushing the boundaries of AI capabilities, exploring areas like quantum computing, AI in space exploration, and human-AI collaboration.
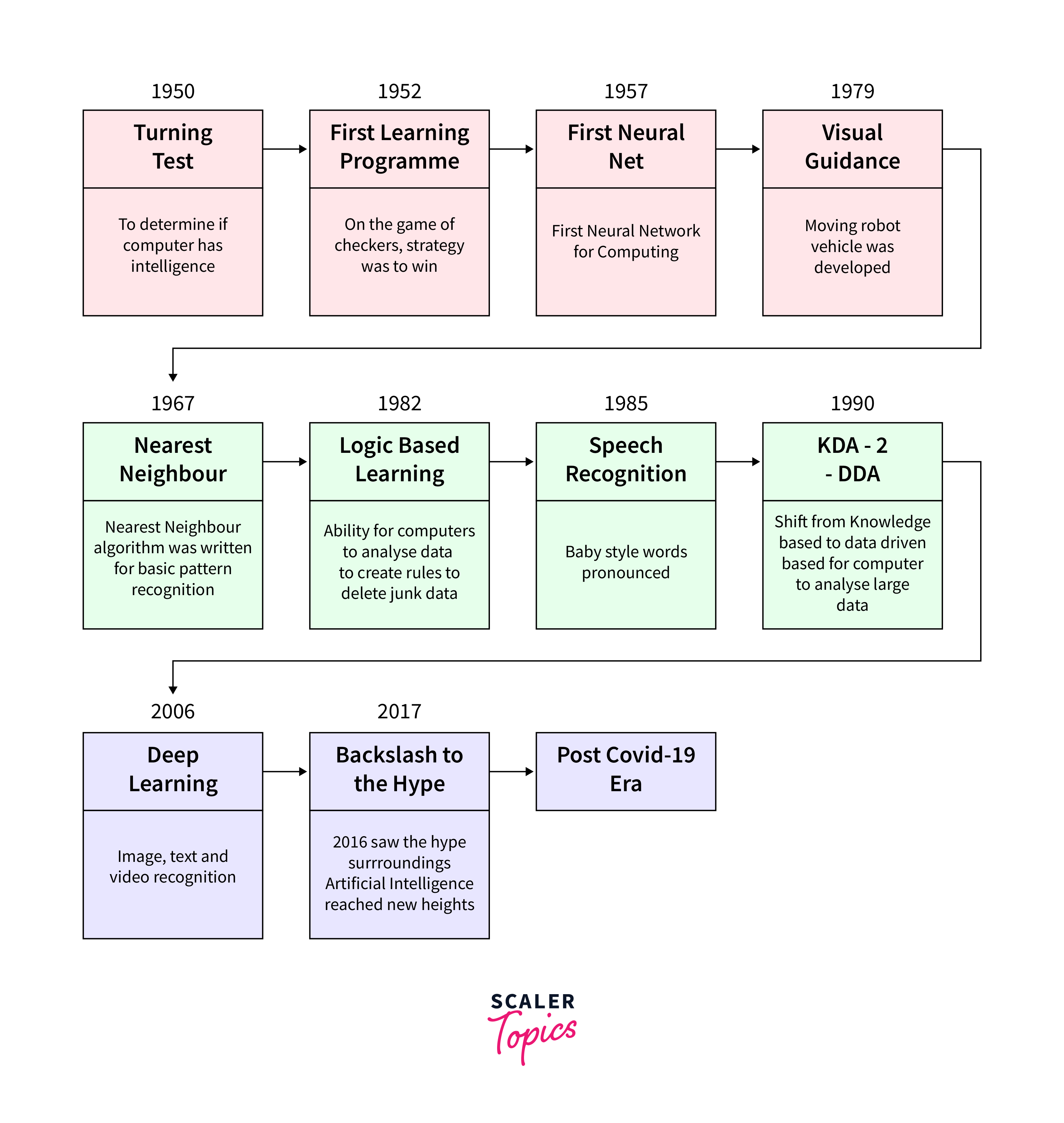
What Did the Future of AI Look Like 10 Years Ago?
Reflecting on the landscape of artificial intelligence a decade ago provides a fascinating perspective on the evolution and expectations surrounding the future of AI. Around ten years ago, the field was marked by both ambitious predictions and considerable uncertainties.
- Nascent Stage of Machine Learning and Deep Learning:
A decade ago, the future of AI was primarily envisioned through the lens of burgeoning machine learning and deep learning technologies. These fields were just beginning to make significant strides, showing promise in areas like image and speech recognition, but their full potential was yet to be realized. - Focus on Automation and Robotics:
Automation and robotics were central themes in the discussions about the future of AI. There was a strong expectation that AI would lead to the creation of highly sophisticated robots and automation systems, capable of performing tasks ranging from manufacturing to basic household chores.
- Predictions of Intelligent Personal Assistants:
The concept of AI-powered personal assistants was gaining traction. Predictions suggested that these assistants would revolutionize how we manage our daily lives, offering personalized support in managing schedules, performing online tasks, and even engaging in conversation. - Concerns Over Job Displacement:
The future of AI was also viewed through the lens of potential job displacement. There was a growing concern that AI and automation would render many traditional jobs obsolete, leading to significant shifts in the job market and necessitating new forms of workforce training and adaptation. - Speculation About Autonomous Vehicles:
Autonomous vehicles were a major topic of discussion. The future of AI was expected to bring self-driving cars to the mainstream, transforming transportation and promising significant impacts on safety, urban planning, and lifestyles. - Early Days of AI Ethics and Privacy:
Issues of ethics, privacy, and data security in relation to AI were beginning to surface, but the depth and complexity of these discussions were not as pronounced as they are today. The focus was more on the potential of AI than on its societal implications. - Limited Integration in Various Sectors:
While there was recognition of AI's potential impact across various industries, its integration was still in early stages. Industries like healthcare, finance, and entertainment were just beginning to explore how AI could be utilized effectively.
Evolution of AI
The evolution of AI can be encapsulated in several key stages, each marking a significant advancement in its capabilities and applications:
- Early AI Research and Logic-Based Models (1950s-1970s):
The inception of AI was characterized by research into problem-solving and symbolic methods. This era focused on creating systems that could mimic human problem-solving skills using logic and decision-making rules. - The Rise of Machine Learning (1980s-1990s):
AI evolved with the introduction of machine learning, shifting focus from hardcoded rules to algorithms capable of learning from data. This period saw the development of foundational algorithms that underpin many modern AI systems. - Internet and Big Data (Late 1990s-2000s):
The proliferation of the internet and the advent of big data provided a wealth of information for training AI systems. This era witnessed the transition from theoretical models to practical applications, fueled by the vast amounts of data available for analysis. - Breakthrough in Deep Learning (2010s):
A significant milestone in the evolution of AI was the emergence of deep learning. With neural networks becoming more sophisticated, AI capabilities, especially in image and speech recognition, took a quantum leap forward. - AI Integration and Specialization (Late 2010s-Present):
AI began to be integrated into various industries, leading to specialized applications. Whether it’s healthcare, finance, or entertainment, AI started to offer tailored solutions, demonstrating its versatility and adaptability.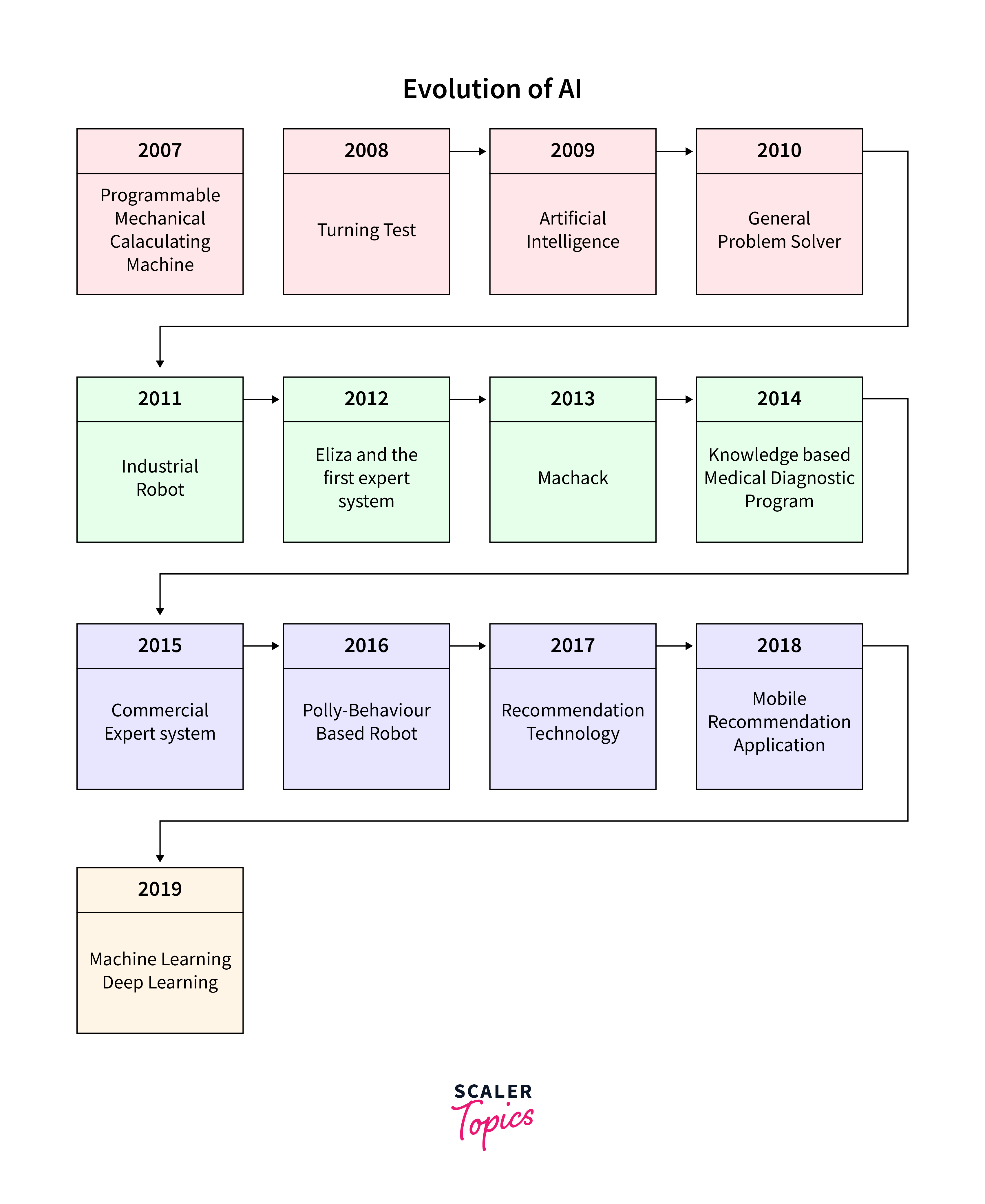
- Ethical AI and Governance (Present):
As AI systems become more prevalent, the focus has shifted towards ethical AI and governance. This involves addressing issues like bias, transparency, and accountability, ensuring AI's responsible and beneficial use. - Towards AI and Human Collaboration (Future Outlook):
The future of AI is envisaged as a collaborative effort between AI systems and humans. This involves AI augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them, leading to a harmonious integration of technology and human intelligence.
Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of AI is poised to be a transformative era, marked by significant advancements and new paradigms in technology and society. Here are some key aspects of what the future of AI might hold:
- Advanced Machine Learning Algorithms:
Future developments in AI are expected to bring even more sophisticated machine learning algorithms. These advancements will likely enable AI to learn more efficiently, make more accurate predictions, and handle complex tasks with greater autonomy. - Integration of AI in Everyday Life:
AI is set to become more integrated into our daily lives, seamlessly blending with the fabric of everyday activities. From smart homes to personalized healthcare, the future of AI promises a more interconnected and responsive world. - Ethical AI and Governance:
As AI becomes more pervasive, the emphasis on ethical AI and governance will intensify. This includes developing frameworks to address issues like privacy, bias, and accountability, ensuring that AI is used responsibly and for the benefit of society. - AI in Decision-Making and Problem-Solving:
The future of AI will likely see its increased role in decision-making processes across various sectors. AI could offer solutions to complex global challenges, such as climate change and healthcare crises, by analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying optimal strategies. - Human-AI Collaboration:
Rather than replacing human workers, the future of AI is expected to emphasize collaboration. AI systems will augment human capabilities, leading to new forms of partnership where AI assists in creative problem-solving and enhances productivity.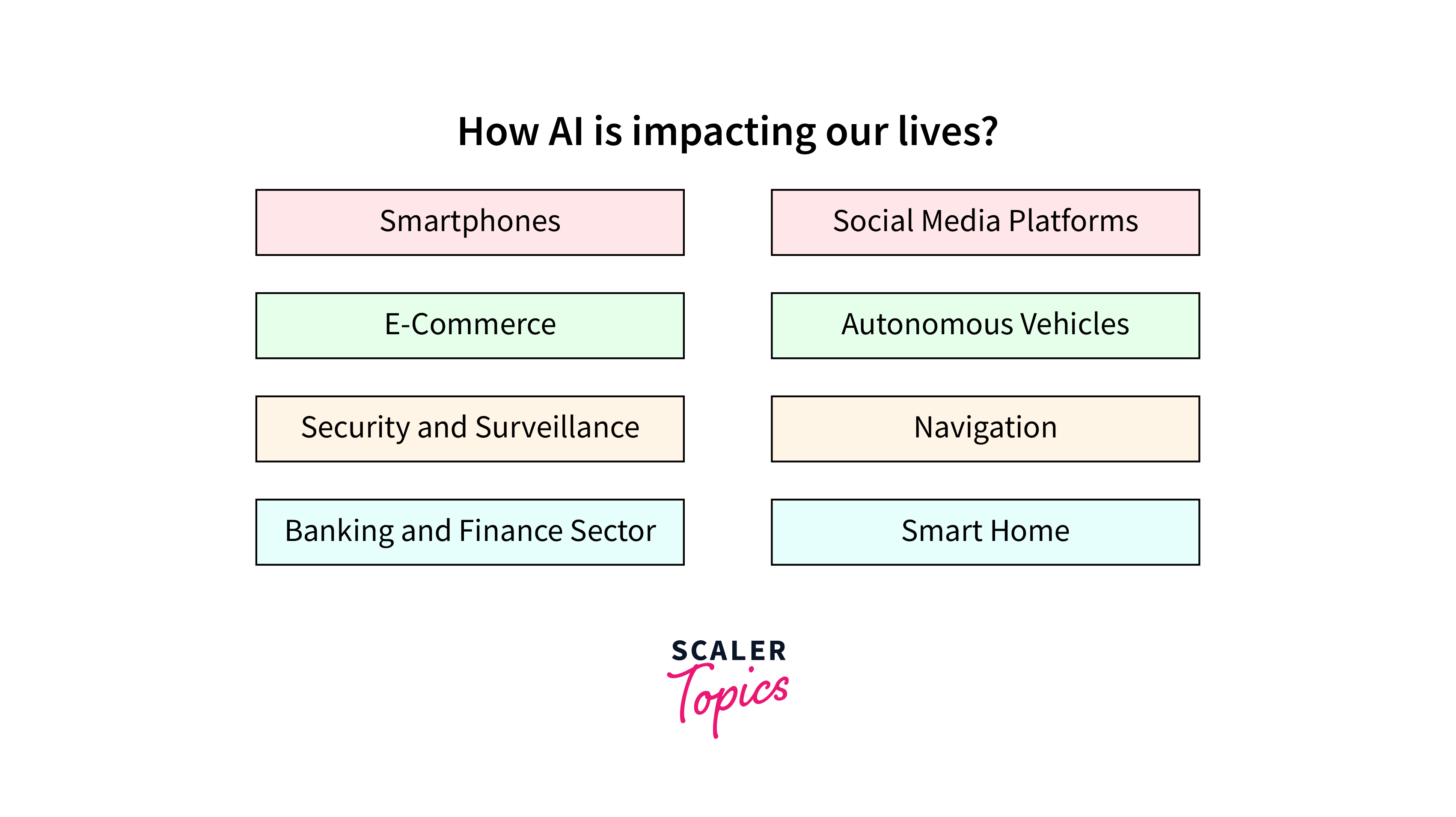
- Breakthroughs in AI Hardware:
Advancements in AI hardware, such as more powerful processors and specialized AI chips, will drive the future of AI. These technologies will support more efficient and powerful AI computations, enabling more complex and responsive AI systems. - AI and Quantum Computing:
The integration of AI with emerging technologies like quantum computing could lead to unprecedented computing capabilities. This synergy has the potential to solve problems that are currently intractable for classical computers.
Impact of AI
The impact of AI is far-reaching and multifaceted, affecting various aspects of society, economy, and daily life. Here are some key areas where AI's influence is particularly noteworthy:
- Economic Transformation:
AI is revolutionizing industries by optimizing supply chains, enhancing product design, and automating routine tasks. This leads to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and new business models, profoundly impacting the global economy. - Healthcare Advancements:
AI is playing a crucial role in healthcare, from improving diagnostic accuracy to personalizing treatment plans and aiding in drug discovery. This has the potential to greatly enhance patient outcomes and streamline healthcare services. - Environmental Solutions:
AI contributes to environmental conservation by optimizing resource use, predicting climate patterns, and enhancing renewable energy systems. It offers innovative solutions to tackle pressing environmental challenges. - Educational Enhancements:
In education, AI enables personalized learning experiences, automates administrative tasks, and provides tools for students with different learning needs, transforming the educational landscape.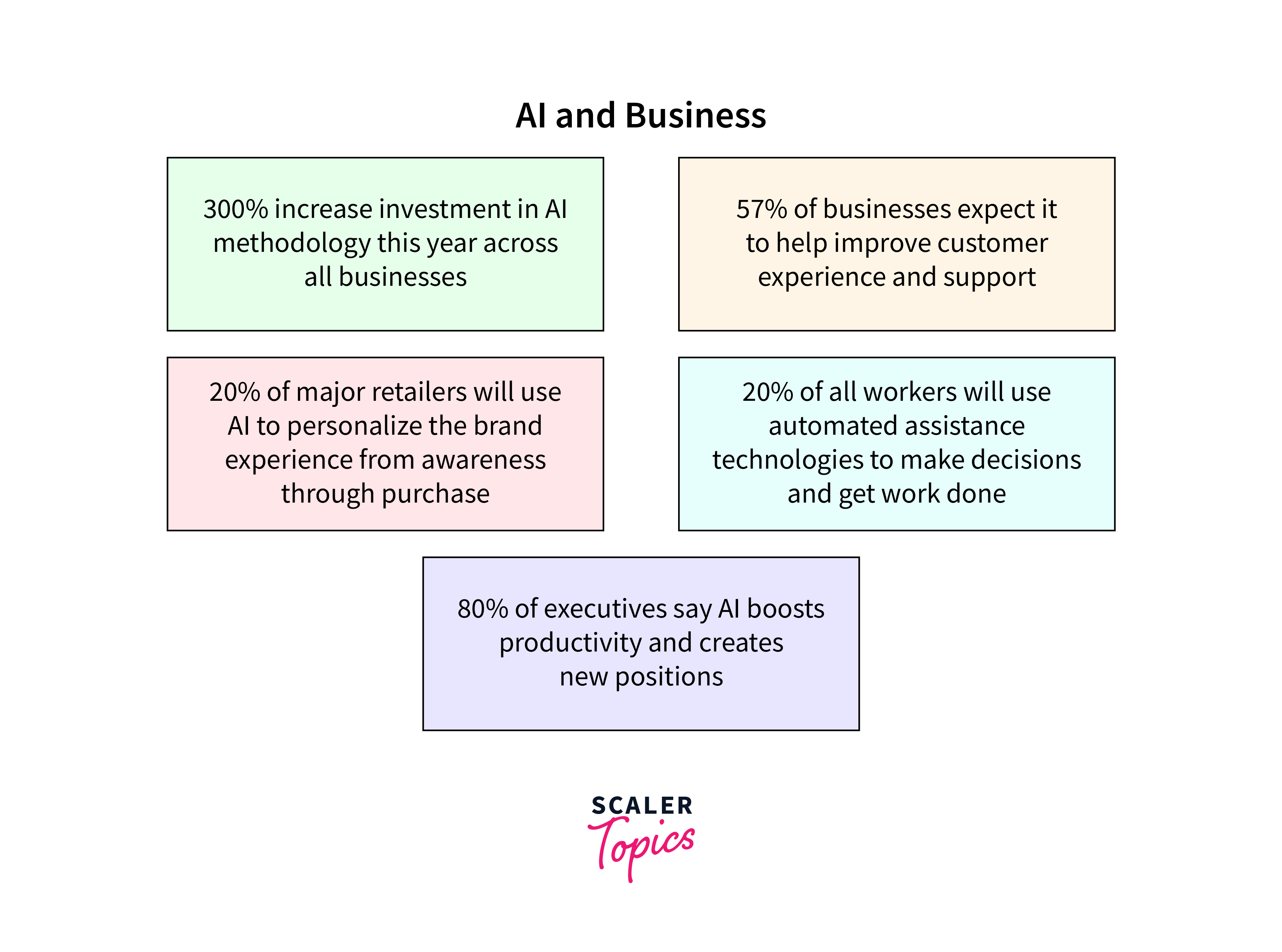
- Workforce Changes:
AI is reshaping the job market, leading to the creation of new job roles and the obsolescence of others. It necessitates a shift in workforce skills, emphasizing the need for AI literacy and adaptability. - Ethical and Societal Implications:
The rise of AI raises important ethical questions regarding privacy, bias, and decision-making. It necessitates a societal dialogue on how AI should be governed and its impacts managed. - Enhanced Consumer Experiences:
In the consumer sector, AI is improving customer experiences through personalized recommendations, advanced customer service bots, and innovative products, reshaping consumer expectations and interactions.
Myths About Advanced Artificial Intelligence
There are several misconceptions surrounding advanced AI that often distort public understanding. Here are five common myths:
- AI Can Fully Replicate Human Intelligence:
A prevalent myth is that AI can mimic all aspects of human intelligence, including emotions and consciousness. However, AI is currently limited to specific tasks and lacks the full range of human cognitive abilities. - AI Will Inevitably Lead to Job Extinction:
While AI will automate certain tasks, it's a myth that it will lead to widespread job extinction. Instead, AI is likely to create new job categories and demand for new skill sets, transforming the job market rather than eliminating it entirely. - AI Operates Without Bias:
There's a misconception that AI systems are inherently objective and unbiased. In reality, AI can inherit biases present in the data it's trained on, making it crucial to address these biases in the development process. - AI Can Surpass Human Control:
The fear that AI will become uncontrollable and surpass human oversight is a common myth. In reality, AI systems are designed with checks and controls, and their development is guided by ethical and safety standards. - AI Understands Context and Nuance Like Humans:
Another myth is that AI can understand context and nuance at a human level. While AI has made strides in interpreting complex data, it still lacks the depth of understanding and contextual awareness inherent to human cognition.
AI and the Future of Work
The intersection of AI and the future of work is a topic of significant interest and debate. The influence of AI on the workforce is multifaceted, presenting both challenges and opportunities:
- Job Transformation and Creation:
AI is expected to transform existing jobs and create new ones. While some routine tasks may be automated, new roles, particularly those requiring AI oversight and ethical management, will emerge. This shift necessitates a focus on reskilling and upskilling the workforce. - Enhancing Productivity and Efficiency:
AI tools and systems can augment human productivity, enabling workers to focus on creative and strategic tasks by automating routine processes. This can lead to increased efficiency and innovation in various industries. - Changing Skill Requirements:
The future of work will emphasize digital literacy and skills related to AI and data analysis. Soft skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, and adaptability will also become more important, as the nature of work becomes more dynamic and tech-driven. - Remote and Flexible Working Environments:
AI-driven tools facilitate remote work and flexible working environments. From virtual assistants to AI-powered communication and collaboration tools, AI is enabling a more adaptable and location-independent workforce. - Ethical and Governance Challenges:
AI in the workplace raises ethical concerns, including privacy, surveillance, and decision-making biases. Companies will need to establish clear governance structures and ethical guidelines to address these challenges. - Impact on Employment Patterns:
While there is concern about job displacement, the future of AI in the workforce is more likely to shift employment patterns rather than cause widespread unemployment. Transitioning to new kinds of work will be a key challenge for individuals and policymakers. - Creating Inclusive Work Environments:
AI has the potential to make workplaces more inclusive, by aiding differently-abled employees and providing personalized support systems. However, ensuring that AI systems are free from bias is crucial to achieving this goal.
Conclusion
- The future of AI holds transformative potential for various sectors, including healthcare, education, and industry, promising to enhance efficiency, innovation, and problem-solving capabilities.
- As AI technology advances, ethical considerations and governance will become increasingly important. Addressing issues of bias, privacy, and accountability is crucial for the responsible development and implementation of AI.
- AI is set to reshape the workforce, not by replacing humans but by transforming job roles and necessitating new skills. This evolution calls for a focus on education, training, and lifelong learning.
- AI will become more integrated into everyday life, offering personalized experiences and convenience. However, this integration must be managed carefully to balance benefits with potential privacy and security concerns.
- The future of AI will be characterized by ongoing innovation and human-AI collaboration. Embracing this collaborative approach can unlock new frontiers in technology and human potential.
