How To Become A Scrum Master?
A Scrum Master is a key role in Agile development, responsible for facilitating and optimizing the Scrum framework. They ensure the team adheres to Agile principles, remove impediments, and foster collaboration. Acting as a servant-leader, the Scrum Master supports continuous improvement, allowing teams to deliver high-quality products iteratively and efficiently.
What is Scrum?
Scrum is an agile framework for managing and organizing work, particularly in the context of software development.
Key components of Scrum include:
-
Roles:
- Product Owner:
Represents the stakeholders and is responsible for defining the product backlog, prioritizing tasks, and ensuring the team delivers value to the customer. - Scrum Master:
Facilitates the Scrum process, removes impediments, and helps the team adhere to Scrum principles. The Scrum Master is a servant-leader for the team. - Development Team:
A cross-functional group of professionals responsible for delivering the product incrementally.
- Product Owner:
-
Artifacts:
- Product Backlog:
A dynamic and prioritized list of features, enhancements, and fixes that represent the work to be done on the project. - Sprint Backlog:
A subset of the product backlog items selected for a specific iteration, known as a sprint. - Increment:
The sum of all completed product backlog items at the end of a sprint, representing a potentially shippable product.
- Product Backlog:
-
Events:
- Sprint:
A time-boxed period (usually 2-4 weeks) during which a potentially shippable product increment is created. - Sprint Planning:
A meeting at the beginning of each sprint where the team plans the work to be done and commits to delivering a specific set of product backlog items. - Daily Scrum (Stand-up):
A short daily meeting where team members discuss progress, plans for the day, and any impediments. - Sprint Review:
A meeting at the end of the sprint where the team demonstrates the completed work to stakeholders and receives feedback. - Sprint Retrospective:
A reflection meeting at the end of the sprint where the team discusses what went well, what could be improved, and how to implement those improvements in the next sprint.
- Sprint:
Who is a Scrum Master?
A Scrum Master plays a key role in the Scrum framework, serving as a facilitator, coach, and servant-leader for the Scrum team. Here are some key aspects of the Scrum Master role:
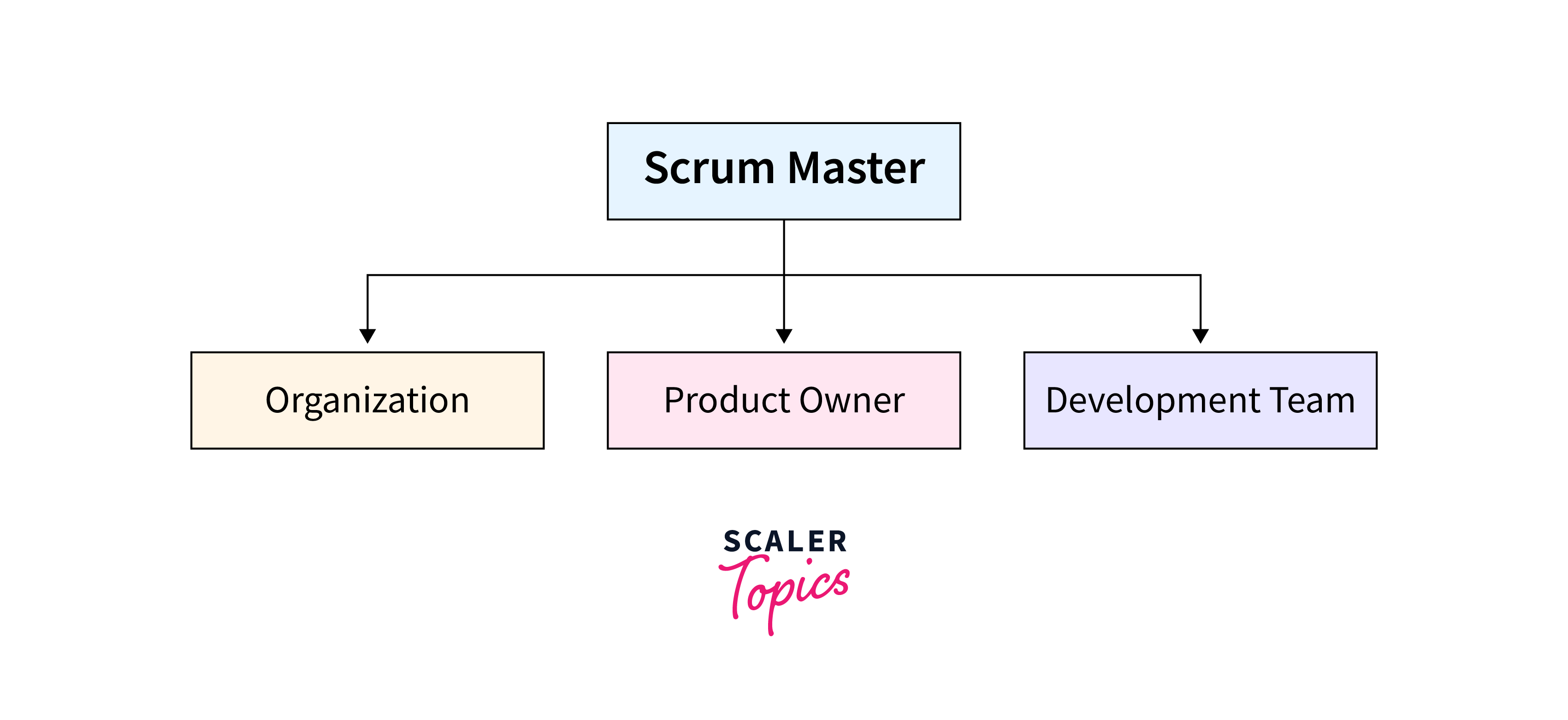
-
Servant-Leader:
The Scrum Master is a servant-leader to the team, working to support and enable them to achieve their goals. -
Facilitator:
The Scrum Master facilitates various Scrum events, such as sprint planning, daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives. -
Coach:
The Scrum Master coaches the team on Scrum practices and principles, promoting self-organization and continuous improvement. -
Barrier Remover:
The Scrum Master identifies and removes impediments or obstacles that hinder the team's progress. -
Promoter of Agile Values:
The Scrum Master advocates for agile values and principles within the organization. -
Observer and Facilitator of Team Dynamics:
The Scrum Master pays attention to team dynamics, helping to build a positive and collaborative team culture. -
Continuous Improvement:
The Scrum Master encourages and facilitates continuous improvement within the team and the overall Scrum process.
What Does a Scrum Master Do?
Scrum Master's responsibilities include:
-
Facilitating Scrum Events:
- Sprint Planning:
Helping the team plan the work for the upcoming sprint and ensuring that the sprint goal is understood. - Daily Scrum (Stand-up):
Facilitating the daily stand-up meetings to keep the team synchronized, identify potential impediments, and encourage collaboration. - Sprint Review:
Assisting in organizing and conducting the sprint review to showcase the completed work to stakeholders and gather feedback. - Sprint Retrospective:
Facilitating the retrospective meeting at the end of each sprint, where the team reflects on their performance and identifies opportunities for improvement.
- Sprint Planning:
-
Ensuring Scrum Artifacts are in Place:
- Product Backlog:
Working with the Product Owner to ensure that the product backlog is well-maintained, refined, and prioritized. - Sprint Backlog:
Assisting the team in creating and maintaining a clear and achievable sprint backlog for each iteration. - Increment:
Ensuring that the team produces a potentially shippable product increment at the end of each sprint.
- Product Backlog:
-
Removing Impediments:
- Identifying and addressing obstacles or impediments that are hindering the team's progress. This may involve working with other teams or stakeholders to resolve issues that the team cannot address on their own.
-
Coaching and Training:
- Guiding the team on Scrum principles, practices, and values.
- Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement and helping the team adapt to changing circumstances.
-
Promoting Collaboration:
- Facilitating communication and collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and other Scrum roles.
- Encouraging a culture of openness, transparency, and trust within the team.
-
Supporting Self-Organization:
- Fostering a self-organizing team by empowering team members to make decisions and take ownership of their work.
- Helping the team become more self-sufficient and less reliant on external guidance.
-
Monitoring and Reporting:
- Keeping track of key Scrum metrics and progress toward sprint goals.
- Reporting on the team's performance and progress during Scrum events or to relevant stakeholders.
-
Promoting Agile Values:
- Advocating for agile values and principles within the organization.
- Encouraging a mindset of adaptability, customer focus, and collaboration.
10 Key Skills Required to Become Scrum Master
An answer to how to become a scrum master can be fulfilled by enhancing the below-listed skills:
-
Leadership:
- As a Scrum Master, you are a leader. You should focus on serving the needs of the team, removing impediments, and facilitating their success rather than exerting authority.
-
Communication:
- Strong communication skills are crucial. You need to facilitate discussions, actively listen, and articulate ideas clearly to the team, stakeholders, and other Scrum roles.
-
Facilitation:
- The ability to facilitate Scrum events effectively, such as Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective, is vital. This involves keeping the team on track, encouraging collaboration, and ensuring that the goals of the events are met.
-
Conflict Resolution:
- Scrum Masters should be adept at resolving conflicts within the team. This involves understanding different perspectives, facilitating discussions, and helping the team find consensus.
-
Coaching and Mentoring:
- Scrum Masters need to coach and mentor team members to improve their understanding and application of Scrum principles. This involves guiding the team toward self-organization and continuous improvement.
-
Empathy:
- Understanding and empathizing with team members' concerns, challenges, and perspectives is crucial. This skill helps in building trust and fostering a positive team environment.
-
Problem Solving:
- Scrum Masters often encounter impediments that hinder the team's progress. The ability to identify problems, analyze their root causes, and collaboratively find solutions is essential.
-
Adaptability:
- Agile environments are dynamic and subject to change. Scrum Masters should be adaptable and open to change, helping the team respond effectively to evolving requirements and priorities.
-
Technical Acumen:
- While not mandatory, having a basic understanding of the technical aspects of the product being developed can be beneficial. It aids in effective communication with the development team and understanding the challenges they face.
-
Continuous Learning:
- The Agile landscape is always evolving. Scrum Masters should stay informed about the latest developments in Agile and Scrum, attend relevant training, and seek opportunities for continuous improvement.
How to Become a Scrum Master? (Step by Step)
-
Practice the Scrum Framework in Other Roles:
- Gain practical experience with Scrum by working on projects in roles such as a team member, product owner, or stakeholder. This firsthand experience will give you insights into how Scrum operates in real-world scenarios.
-
Build Your Network:
- Connect with professionals in the Agile and Scrum community. Attend meetups, conferences, and online forums to build a network of contacts who can provide advice, insights, and potential job opportunities.
-
Develop Relevant Skills:
- Focus on developing the skills mentioned earlier, such as coaching, conflict resolution, facilitation, leadership, and interpersonal skills. Gain experience in areas that complement the Scrum Master role.
-
Choose Your Scrum Certification:
- Decide on the Scrum certification that aligns with your career goals. Popular certifications include Certified ScrumMaster (CSM), Professional Scrum Master (PSM), or Scrum.org's Advanced Certified ScrumMaster (A-CSM).
-
Attend a Scrum Course:
- Enroll in a certified Scrum training course. These courses are typically led by experienced Scrum trainers and cover the principles, practices, and roles of Scrum.
-
Register for Your Exam:
- After completing the training, register for the certification exam associated with the course you attended. Check with the certifying body for specific exam registration details.
-
Study for Your Exam:
- Dedicate time to study the Scrum Guide, the foundational document for Scrum. Review the course materials, take practice exams, and ensure you have a solid understanding of Scrum principles and how they are applied.
-
Take and Pass the Exam:
- Schedule and take the certification exam. Most exams are multiple-choice and test your knowledge of Scrum concepts. Passing the exam demonstrates your understanding of Scrum and qualifies you for the certification.
-
Renew Certifications Every Two Years:
- Many Scrum certifications require renewal every two years to ensure that certified professionals stay current with the evolving practices in the field.
-
Highlight Transferable Skills:
- When applying for Scrum Master positions, emphasize transferable skills from your previous experiences, such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving.
Responsibilities of a Scrum Master
-
Responsibilities toward the Product Owner:
- Facilitation of Collaboration:
Foster collaboration between the Product Owner and the Development Team. Ensure that the team understands and works effectively with the product backlog. - Refinement Support:
Assist the Product Owner in refining and prioritizing the product backlog. Facilitate backlog grooming sessions to ensure that backlog items are well-defined and ready for implementation. - Stakeholder Communication:
Help the Product Owner in communicating with stakeholders. Ensure that stakeholders are involved appropriately in the process and provide feedback to improve the product.
- Facilitation of Collaboration:
-
Responsibilities toward the Development Team:
- Scrum Framework Adherence:
Guide and coach the Development Team on adhering to the Scrum framework. Ensure that the team follows Scrum ceremonies, roles, and artifacts to maximize efficiency. - Obstacle Removal:
Identify and remove impediments that hinder the Development Team's progress. This may involve liaising with other teams, departments, or stakeholders to address issues beyond the team's control. - Promotion of Self-Organization:
Encourage the Development Team to self-organize and make decisions collaboratively. Foster an environment where team members take ownership of their work and continuously improve their processes. - Continuous Improvement:
Facilitate retrospectives to reflect on the team's performance and identify areas for improvement. Support the team in implementing changes to enhance their effectiveness.
- Scrum Framework Adherence:
-
Responsibilities toward the Entire Organization:
- Scrum Advocacy:
Promote an understanding of Scrum principles and values throughout the organization. Advocate for the benefits of agility, collaboration, and transparency. - Collaboration with Other Scrum Masters:
Collaborate with other Scrum Masters to share best practices, resolve cross-team impediments, and ensure consistency in the application of Scrum across the organization. - Culture of Continuous Improvement:
Foster a culture of continuous improvement at the organizational level. Encourage teams and individuals to embrace change, experiment, and find better ways of working. - Conflict Resolution:
Address conflicts and challenges that arise at the organizational level. Help create an environment that supports open communication and collaboration.
- Scrum Advocacy:
Who Needs a Scrum Master?
-
Development Teams:
- Scrum Masters are crucial for development teams that follow the Scrum framework. They support and guide the team in implementing Scrum practices, ensuring that the team is effective, self-organizing, and able to deliver value to the customer.
-
Product Owners:
- While the Product Owner is responsible for the product backlog and maximizing the value of the product, the Scrum Master collaborates with the Product Owner to ensure effective communication, collaboration, and understanding between the Development Team and the Product Owner.
-
Stakeholders:
- Stakeholders, including customers and business representatives, benefit indirectly from the Scrum Master's role.
-
Entire Organization:
- Organizations adopting Scrum can benefit from having Scrum Masters at an organizational level. Scrum Masters collaborate, share best practices, and work to remove impediments that might affect multiple teams.
-
Management and Leadership:
- Leadership within the organization benefits from Scrum Masters who help create an agile culture, promote collaboration, and ensure that teams are aligned with organizational goals.
-
Project and Program Management:
- In organizations running multiple projects or large programs using Scrum, Scrum Masters play a vital role in ensuring consistency in Scrum practices, facilitating communication between teams, and addressing impediments that may span multiple projects or programs.
Benefits of Employing a Scrum Master
-
Facilitates Agile Practices:
- Scrum Masters play a crucial role in facilitating the adoption and implementation of agile practices within development teams.
-
Ensures Smooth Scrum Implementation:
- Scrum Masters guide teams through the implementation of the Scrum framework, ensuring that roles, events, and artifacts are well understood and applied effectively.
-
Promotes Collaboration:
- By fostering a collaborative environment, Scrum Masters encourage effective communication and cooperation among team members, stakeholders, and other organizational entities.
-
Removes Impediments:
- Scrum Masters actively work to identify and remove impediments or obstacles that may hinder the progress of development teams.
-
Enhances Team Productivity:
- Through coaching and mentoring, Scrum Masters contribute to improving the productivity of development teams.
Scrum Master vs Project Manager vs Product Manager
| Aspect | Scrum Master | Project Manager | Product Manager |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Facilitator, Coach, and Servant Leader | Planner, Organizer, and Task Manager | Visionary, Decision-Maker, and Value Maximizer |
| Focus Area | Team and Process | Project Scope, Schedule, and Budget | Product Vision, Strategy, and Market Requirements |
| Project Lifecycle | Agile (Scrum Framework) | Traditional/Waterfall or Agile | Entire Product Lifecycle (Conception to Sunset) |
| Planning and Execution | Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, and Retrospectives | Project Planning, Gantt Charts, and Execution | Product Roadmapping, Feature Planning, and Execution |
| Responsibilities | - Ensuring Scrum principles are followed | - Planning, organizing, and overseeing tasks | - Defining product vision and strategy |
| - Facilitating Scrum events | - Managing resources and budgets | - Prioritizing and managing product backlog | |
| - Removing impediments for the team | - Risk management and issue resolution | - Collaborating with stakeholders | |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Collaboration with the development team and stakeholders | Stakeholder communication and expectations management | Engaging with internal and external stakeholders |
| Decision Making | Facilitates team decision-making | Decision-making within the project scope | Makes decisions on product strategy and features |
| Metrics and Progress | Monitoring team progress and metrics | Tracking project milestones and KPIs | Evaluating product performance and market metrics |
| Communication | Ensuring effective communication within the team and with stakeholders | Communicating project status and updates | Communicating product vision and priorities |
| Change Management | Embraces change and helps the team adapt | Manages changes within the project scope | Adapts product strategy based on market changes |
| Role in Innovation | Fosters a culture of continuous improvement | May encourage innovation within project constraints | Drives innovation in product features and strategy |
| Customer Focus | Advocates for customer satisfaction and user experience | Ensures project meets customer requirements | Drives product success through customer value |
Why Pursue a Career as a Scrum Master?
-
Working as a Scrum Master allows you to be part of the Agile movement, emphasizing values such as collaboration, adaptability, and customer satisfaction.
-
Scrum Masters play a pivotal role in fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
-
Scrum Masters empower development teams to self-organize and make decisions collaboratively.
-
The role of a Scrum Master is dynamic and involves wearing different hats, including facilitator, coach, and servant-leader.
-
Scrum Masters focus on leadership through servant-leadership principles, guiding teams to success.
-
Real-world example of how Scrum Masters apply their skills and fulfill their responsibilities in practical scenarios.
Scenario:
An IT company is transitioning to Agile and implementing Scrum. The development team faces collaboration challenges, and the velocity is inconsistent. The Scrum Master steps in to address these issues.
Actions Taken:
-
The Scrum Master conducts regular retrospectives to gather feedback from the team on what is working well and what can be improved.
-
Actively engaging with the team to identify impediments to their progress.
-
Providing coaching sessions to team members on Agile principles and Scrum practices to ensure a common understanding.
-
Encouraging the team to self-organize and take ownership of their work.
-
Implementing changes based on retrospective feedback and tracking improvements in velocity over subsequent sprints.
Results:
The team starts collaborating more effectively. Velocity becomes more predictable and increases over time. The Scrum Master continues to support the team in refining their processes for continuous improvement.
How to Become a Certified Scrum Master?
-
Prerequisites:
- There are no specific prerequisites for taking the CSM exam. However, completing an official CSM training course from a Certified Scrum Trainer (CST) is required. The training must be taken from a Scrum Alliance-approved provider.
-
Training Course:
- To be eligible for the CSM certification, individuals must attend a two-day (16 hours) Certified ScrumMaster training course led by a Certified Scrum Trainer (CST).
-
Exam Format:
- The CSM exam is an online, multiple-choice exam. The format may include true/false and multiple-choice questions.
- The exam is typically taken after completing the training, and it is accessible through the Scrum Alliance website.
-
Exam Duration:
- The duration of the CSM exam is 60 minutes.
-
Passing Score:
- As of my last knowledge update, the passing score for the CSM exam is around 74% or higher. It is recommended to check the specific passing score requirements on the Scrum Alliance website.
-
Retakes:
- If you do not pass the CSM exam on your first attempt, you may retake the exam at no additional cost. However, there may be a waiting period before you can attempt the exam again.
-
Open Book Exam:
- The CSM exam is an open-book exam, meaning you can refer to course materials or other notes during the test.
-
Certification Validity:
- The CSM certification is valid for two years. To maintain the certification, individuals are required to earn Scrum Education Units (SEUs) and renew their certification through the Scrum Alliance.
Salary of a Scrum Master

| Region | Entry-Level | Mid-Level | Senior-Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 90,000 | 110,000 | 130,000+ |
| United Kingdom | £40,000 - £50,000 | £50,000 - £65,000 | £65,000 - £80,000+ |
| Canada | CAD 70,000 - CAD 90,000 | CAD 90,000 - CAD 110,000 | CAD 110,000 - CAD 130,000+ |
| Europe | Varies by country | Varies by country | Varies by country |
| Australia | AUD 90,000 - AUD 110,000 | AUD 110,000 - AUD 130,000 | AUD 130,000 - AUD 150,000+ |
| India | ₹6,00,000 - ₹8,00,000 per annum | ₹8,00,000 - ₹12,00,000 per annum | ₹12,00,000 and above per annum |
FAQs
Q. Can I become a Scrum Master without a technical background?
A. Yes, it's possible to become a Scrum Master without a technical background. While some technical knowledge may be helpful, the primary focus of a Scrum Master is on facilitating the Scrum process, promoting collaboration, and removing impediments.
Q. What are the roles in the Scrum framework?
A. In the Scrum framework, there are three primary roles:
- Product Owner:
Represents the stakeholders and is responsible for maximizing the value of the product. - Scrum Master:
Facilitates and supports the Scrum process, ensuring adherence to Scrum principles and removing impediments. - Development Team:
Cross-functional and self-organizing, responsible for delivering a potentially shippable product increment in each sprint.
Q. What's the difference between a Scrum Master and an Agile coach?
A. While both roles involve coaching and facilitating, a Scrum Master is specific to the Scrum framework and focuses on supporting a Scrum team.
Q. What's the typical Scrum Master career path?
A. The typical career path for a Scrum Master may involve a progression from entry-level to mid-level and senior-level positions.
Q. Is it possible to be a Scrum Master without a degree?
A. Yes, a degree is not always a requirement to become a Scrum Master. Many organizations prioritize experience, certifications (such as CSM or PSM), and skills over formal education.
Q. What is an effective Scrum Master?
A. An effective Scrum Master is someone who fosters a positive team culture, removes impediments, facilitates collaboration, and guides the team in embracing Scrum principles.
Q. How long does it take to become a Scrum Master?
A. The time to become a Scrum Master varies based on individual circumstances. Typically, it involves attending a Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) course, gaining practical experience, and passing the certification exam.
Q. Can I become a Scrum Master with no experience?
A. While having experience in a related field is beneficial, it's possible to become a Scrum Master with no prior experience. Many entry-level Scrum Masters start by taking a CSM course, obtaining certification, and gaining practical experience through internships, volunteer work, or by participating in Scrum teams.
Q. How do I start a career in Scrum Master?
A. To start a career as a Scrum Master, consider the following steps:
- Attend a Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) course.
- Obtain CSM certification.
- Acquire hands-on experience by participating in internships, volunteer roles, or becoming a part of Scrum teams.
- Develop strong interpersonal and communication skills.
- Build a network within the Agile community.
- Consider pursuing additional certifications and continuous learning.
Conclusion
- Becoming a Scrum Master involves a systematic approach and a commitment to learning and development.
- Start by gaining practical experience with the Scrum framework in various roles, such as a team member or product owner.
- Build a professional network within the Agile and Scrum community to access valuable insights and opportunities.
- Develop relevant skills, including coaching abilities, conflict resolution, leadership, and facilitation skills.
- Choose a Scrum certification that aligns with your career goals, such as Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) or Professional Scrum Master (PSM).
- Attend a certified Scrum training course led by an experienced trainer to ensure a solid foundation in Scrum principles.
- Consider additional training, certifications, and participation in the Agile community to enhance your expertise and advance in your Scrum Master career.
