How to Boot Linux from USB?
Overview
This article provides a step-by-step guide on how to boot Linux from a USB drive. It outlines the process of creating a bootable USB drive containing the Linux operating system. The article emphasizes the importance of obtaining the correct Linux ISO file using a tool named Rufus to create the bootable USB. It also highlights the need to access the computer's BIOS or UEFI settings to change the boot order and ensure the USB drive is prioritized. By following these instructions, readers will be able to boot Linux directly from a USB drive without modifying their computer's hard drive.
Introduction
Booting Linux from a USB drive can be a convenient way to explore and use the Linux operating system without making any permanent changes to your computer. Whether you want to try out different Linux distributions, troubleshoot system issues, or carry a portable Linux environment, a bootable USB drive provides the flexibility and freedom to do so. This article guides you through the process of creating a bootable USB drive and configuring your computer to boot from it. By following these instructions, you can experience the power and versatility of Linux firsthand, all from a portable USB drive. let's find out how to boot linux from usb.
What is Bootable Media?
Bootable media refers to any form of storage device that contains the necessary files and software to start up a computer and initiate its operating system. It is used to boot a computer from an external source rather than the computer's internal hard drive.
In the context of booting an operating system, bootable media can include USB drives, DVDs, CDs, or even network-based boot methods. These media contain a specific set of files called the bootloader, which is responsible for loading the operating system into the computer's memory and initiating the boot process.
Bootable media allows users to run an operating system or perform various tasks without having to install it on the computer's hard drive. This is particularly useful for trying out different operating systems, performing system diagnostics and repairs, or recovering data from a non-bootable system.
We have discussed what is bootable media, now let's delve into how to boot linux from usb.
How does a USB Drive Boot Work?
A USB drive boot works by using the computer's BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) to search for and identify bootable devices, including USB drives, during the system startup process. Here is a brief overview of how a USB drive boot works:
-
BIOS/UEFI Initialization:
When you power on or restart your computer, the BIOS/UEFI firmware is initialized. It performs a Power-On Self-Test (POST) to check the system hardware and then proceeds to the next step.
-
Boot Device Selection:
The BIOS/UEFI looks for a specified boot device according to the boot order set in its settings. It scans various devices, such as the internal hard drive, CD/DVD drive, and USB ports, in the specified order to find a bootable device. -
USB Drive Detection:
If a bootable USB drive is connected to one of the USB ports, the BIOS/UEFI detects it during the boot device selection process. It identifies the USB drive as a potential boot device. -
Bootloader Execution:
Once the BIOS/UEFI identifies the bootable USB drive, it transfers control to the bootloader stored on the USB drive. The bootloader is a small program that resides in the USB drive's boot sector and is responsible for loading the operating system. -
Operating System Load:
The bootloader reads the necessary files from the USB drive, including the kernel and initial ramdisk, and loads them into the computer's memory (RAM). It then transfers control to the loaded operating system. -
Operating System Initialization:
The loaded operating system takes control and begins the initialization process. It sets up the necessary drivers, loads additional modules, and completes the boot process.
By utilizing the boot sequence and bootloader on a bootable USB drive, the computer can bypass the internal hard drive and directly load and run an operating system from the USB drive. Now, let's find out more on how to boot linux from usb.
Get the Linux ISO
To get the Linux ISO, you can follow these steps:
-
Step - 1:
Decide which Linux distribution you want to use. Popular options include Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, Linux Mint, and many more. Consider factors such as your level of expertise, specific requirements, and personal preferences when selecting a distribution. -
Step - 2:
Go to the official website of the Linux distribution you have chosen. Most distributions provide ISO images for download on their websites.
-
Step - 3:
On the downloads page, you will typically find different versions and architectures available. Choose the version that matches your requirements, such as the latest stable release or a specific edition tailored to your needs. Also, select the appropriate architecture (32-bit or 64-bit) based on your computer's capabilities. -
Step - 4:
Once you have selected the version and architecture, click on the download link to start the download process. The ISO file is usually large, so it may take some time depending on your internet connection speed.
By following these steps, you can obtain the Linux ISO file from the official website of the chosen distribution. Remember to always download from trusted sources to ensure the integrity and security of the file.
Download Rufus
To download Rufus, a popular tool for creating bootable USB drives, follow these steps:
-
Step - 1:
Launch your preferred web browser on your computer. In the address bar of your web browser, enter the URL "https://rufus.ie/" and press Enter. This will take you to the official Rufus website. Once you're on the Rufus website, navigate to the "Downloads" section. You can usually find it in the main menu or as a prominent link on the homepage.
-
Step - 2:
In the Downloads section, you'll typically see various versions of Rufus available for download. Select the version that corresponds to your operating system. Rufus is compatible with Windows, so make sure to choose the Windows version unless you're using a different operating system.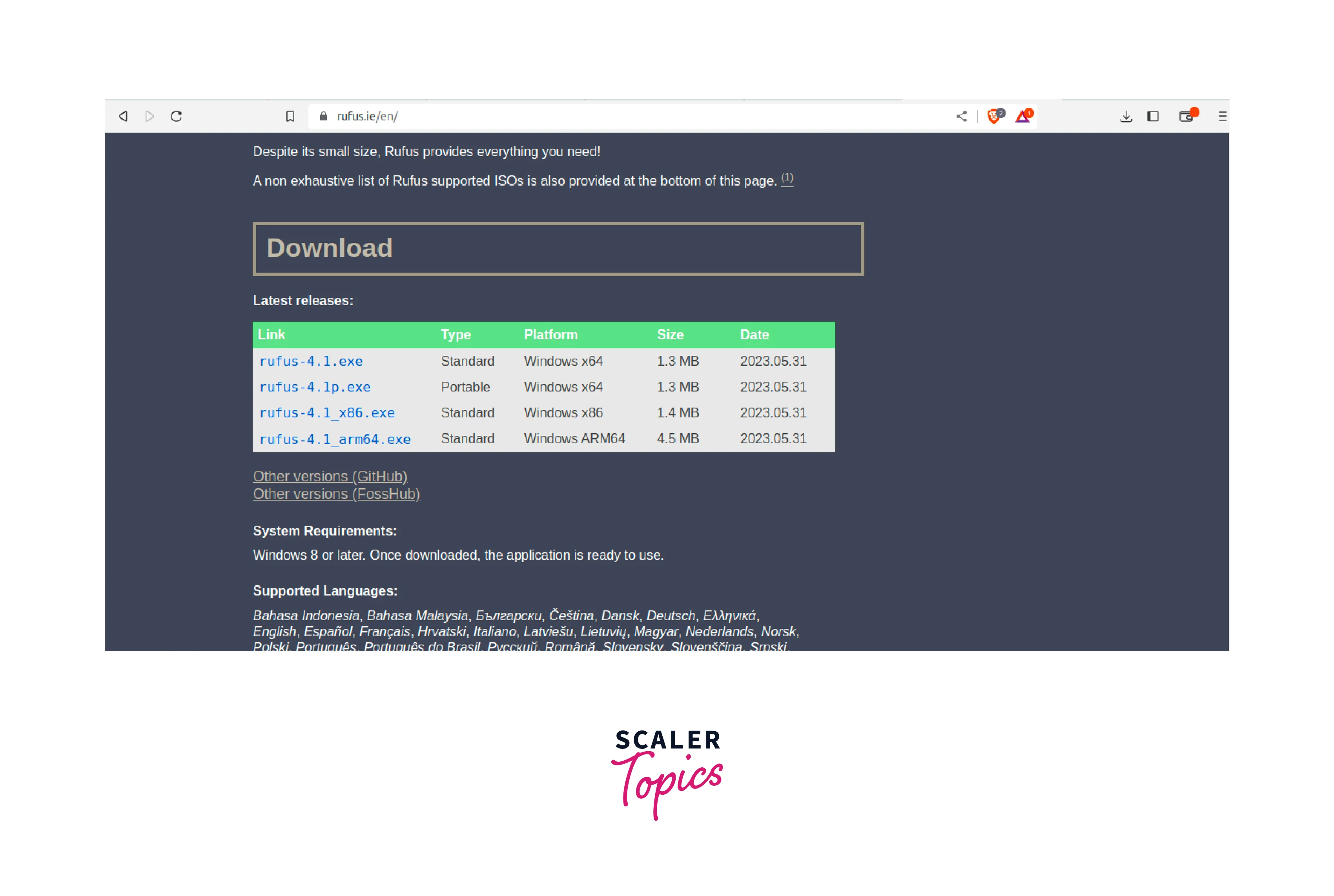
-
Step - 3:
Click on the download link for the chosen version of Rufus. Your web browser will initiate the download process, and the Rufus installer file will be saved to your computer. -
Step - 4:
Once the download is complete, locate the Rufus installer file on your computer (usually in the Downloads folder) and double-click on it to run the installer. -
Step - 5:
The Rufus installer will guide you through the installation process. Follow the on-screen prompts to install Rufus on your computer. You may need to agree to the terms of service, choose an installation location, select any additional options offered during the installation, and complete the installation.
By following these steps, you can download Rufus and install it on your computer. Rufus is a lightweight and straightforward tool that allows you to create bootable USB drives with ease.
Use Rufus to Create a Linux Bootable USB
To create a Linux bootable USB using Rufus, follow these steps:
-
Step - 1:
Connect the USB drive to your computer. Make sure it has enough capacity to accommodate the Linux distribution ISO file. Backup any important data on the USB drive, as the process will erase all existing data. -
Step - 2:
Follow the steps mentioned earlier in this article to download the Linux ISO file from the official website of your preferred Linux distribution. -
Step - 3:
Open Rufus on your computer. It should be available from your Start menu or desktop shortcut if you have installed it previously.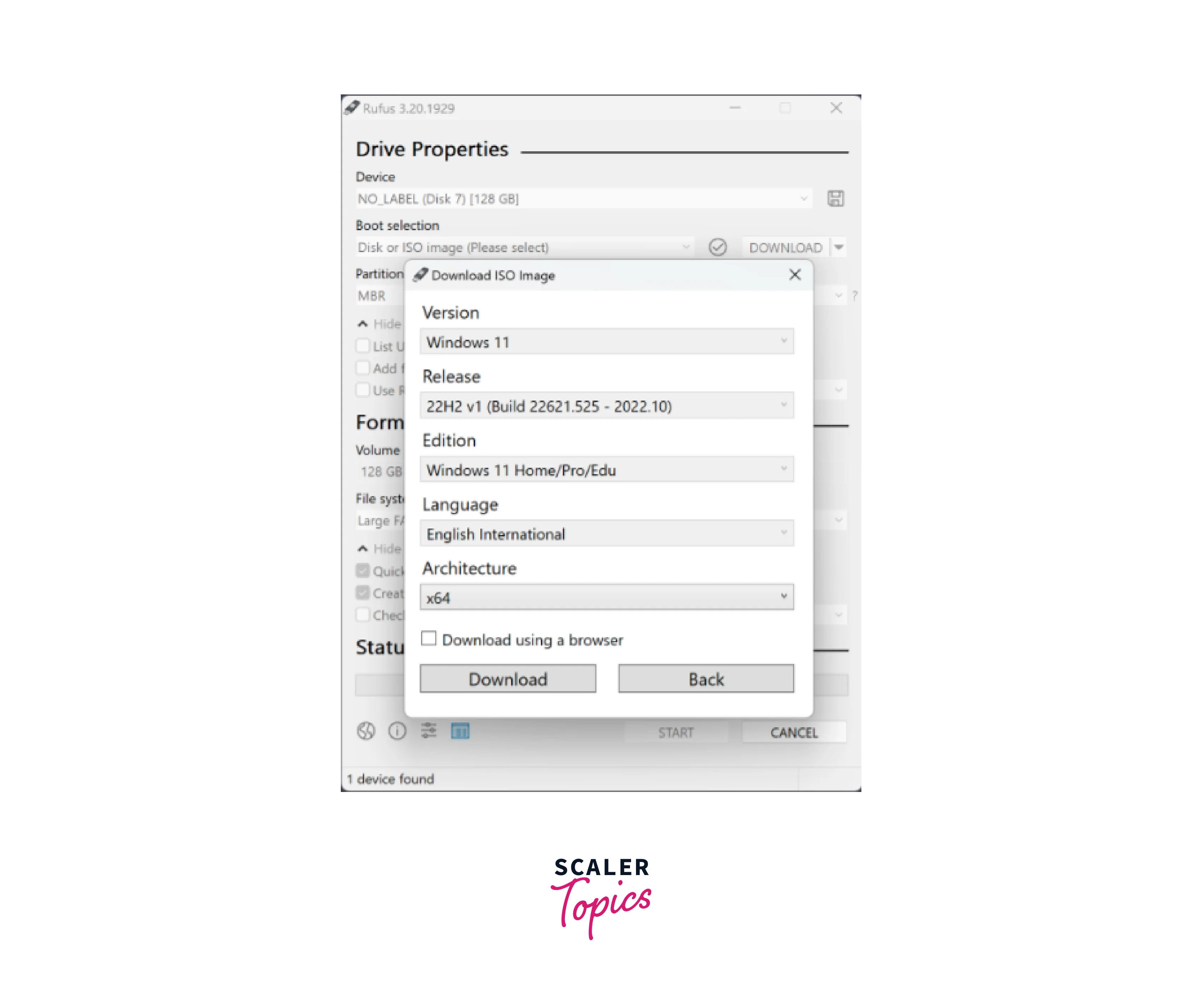
-
Step - 4:
Rufus automatically detects the connected USB drives. In the "Device" field, choose the USB drive you want to use for creating the bootable USB. -
Step - 5:
Under "Boot selection", click on the "Select" button and navigate to the location where you saved the downloaded Linux ISO file. Select the ISO file. -
Step - 6:
Leave the partition scheme as "MBR" if your computer uses BIOS, or choose "GPT" if it uses UEFI. Select the File system as "FAT32". Leave the Cluster size as the default value. -
Step - 7:
Enable the "Create a bootable disk using" option and choose "ISO Image" from the drop-down menu. Ensure that the "Quick format" and "Create extended label and icon files" options are checked. -
Step - 8:
Double-check that you have selected the correct USB drive and the Linux ISO file.Click on the "Start" button to begin the process. A warning message may appear, indicating that all data on the USB drive will be destroyed. Confirm by clicking "OK".
-
Step - 9:
Rufus will now format the USB drive, copy the Linux ISO contents, and make it bootable. This may take a few minutes, depending on the size of the ISO file and the speed of your USB drive.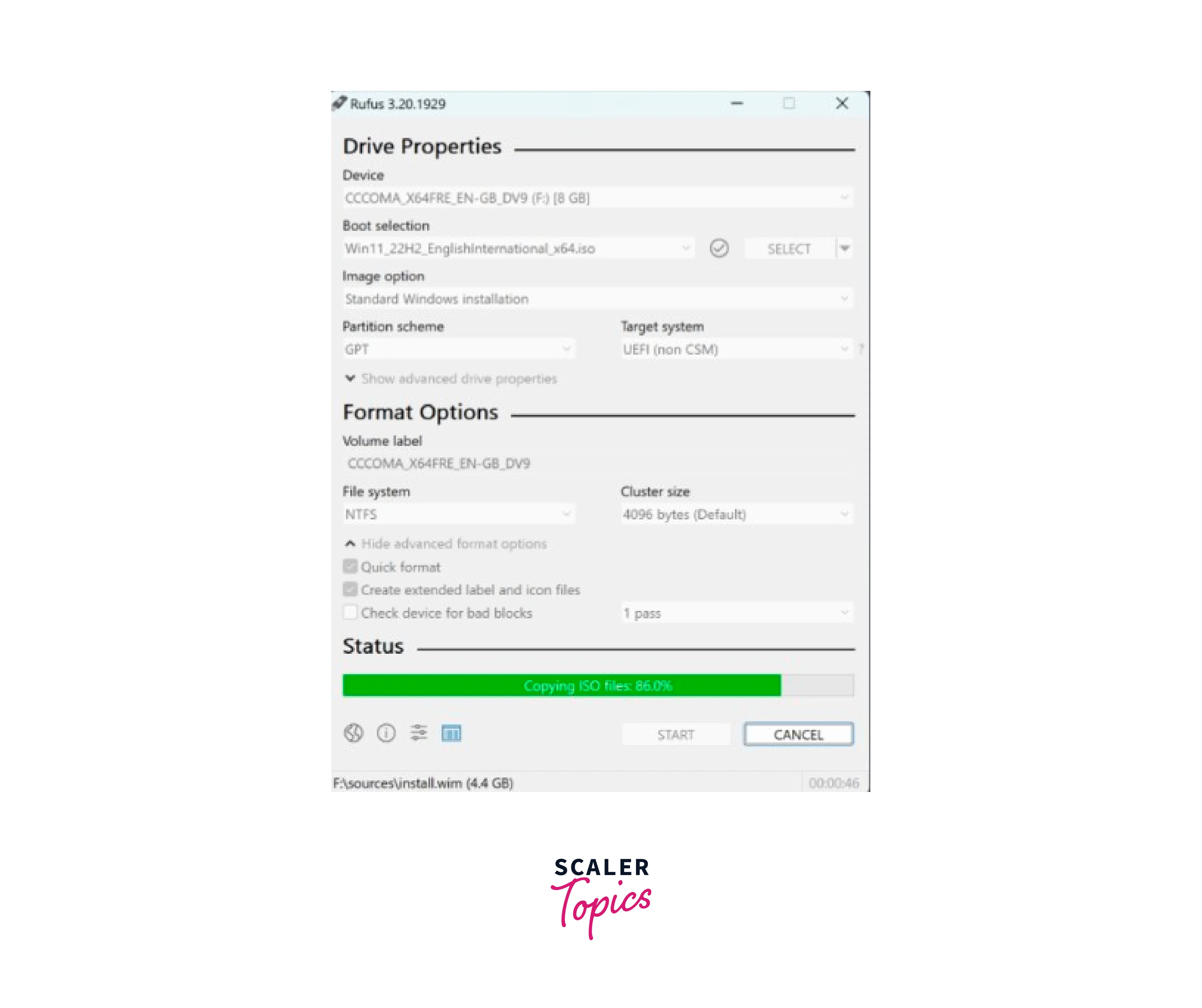
-
Step - 10:
Once Rufus finishes creating the bootable USB, you will see a "READY" message. You can now close Rufus and safely eject the USB drive from your computer.
Your Linux bootable USB is now ready to be used. You can use it to boot into the Linux distribution.
How to Boot Linux from USB?
To boot Linux from a USB drive, follow these step-by-step instructions:
-
Step - 1:
Ensure that the Linux bootable USB drive is inserted into an available USB port on your computer. Save any open files and restart your computer. Make sure to save any changes if prompted. -
Step - 2:
As your computer restarts, it will display the manufacturer's logo or a black screen with white text indicating the key to access the BIOS or UEFI settings. Common keys include F2, F10, Del, or Esc. Press the indicated key repeatedly until the BIOS or UEFI settings screen appears. -
Step - 3:
In the BIOS or UEFI settings, navigate to the "Boot" or "Boot Order" section.Locate the option that sets the boot priority or boot order. It may be named "Boot Order," "Boot Sequence," or similar. Ensure that the USB drive is set as the first boot device. If not, use the designated keys (usually +/- or F5/F6) to move the USB drive to the top of the boot order.
-
Step - 4:
Once you have set the USB drive as the first boot device, save the changes and exit the BIOS or UEFI settings. The option to save and exit is typically labeled as "Save and Exit," "Exit and Save Changes," or similar. Confirm your selection if prompted. -
Step - 5:
Your computer will restart automatically. Ensure that the USB drive remains connected during the reboot process. After the computer restarts, it will display a boot menu called GRUB (GRand Unified Bootloader). Use the arrow keys to highlight the desired Linux distribution and press Enter.
Once the Linux desktop appears, you can explore and use the Linux distribution through USB. That's it! You have successfully booted Linux from the USB drive.

If you follow the above steps as mentioned, you will get a clear picture of how to boot linux from usb.
Conclusion
-
Booting Linux from a USB drive provides a portable and non-intrusive way to experience the Linux operating system.
-
By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create a bootable USB drive and configure your computer to boot from it.
-
This allows you to explore different Linux distributions and enjoy the flexibility and customization options that Linux offers.
-
In this article, we have learned how to boot linux from usb.
