How to Stop and Disable Firewall in Linux?
Overview
Firewalls play a crucial role in enhancing the security of computer systems by monitoring and controlling network traffic. They act as a protective barrier between the internal network and external threats.
In this article, we will look at how to disable a firewall in Linux using the ufw firewall management tool. While we will primarily discuss Ubuntu 22.04 as our reference system, the concepts, and instructions can apply to other Ubuntu versions, such as Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 18.04, and their subsequent releases. Some other Linux distributions like Debian, Linux Mint, and Zorin OS also support and utilize the ufw firewall management tool.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with learning how to disable the firewall in Linux, ensure that you meet the following prerequisites:
- A system running Linux, preferably Ubuntu 22.04 or other Ubuntu versions utilizing the ufw firewall management tool.
- Log in as a user with administrative privileges (sudo).
- Access to the command-line interface.
Note: The commands mentioned in this article are specific to Ubuntu 22.04, which utilizes the ufw firewall management tool. However, it is vital to note that different Linux distributions may employ varying firewall management tools and commands. Therefore, consult the appropriate documentation or community resources specific to your Linux distribution and version for accurate instructions.
Checking the Firewall Status
Before looking into how to disable a firewall in Linux, first learn to determine the current status of the firewall on your Linux system.
Execute the following command in the terminal to check the firewall status:
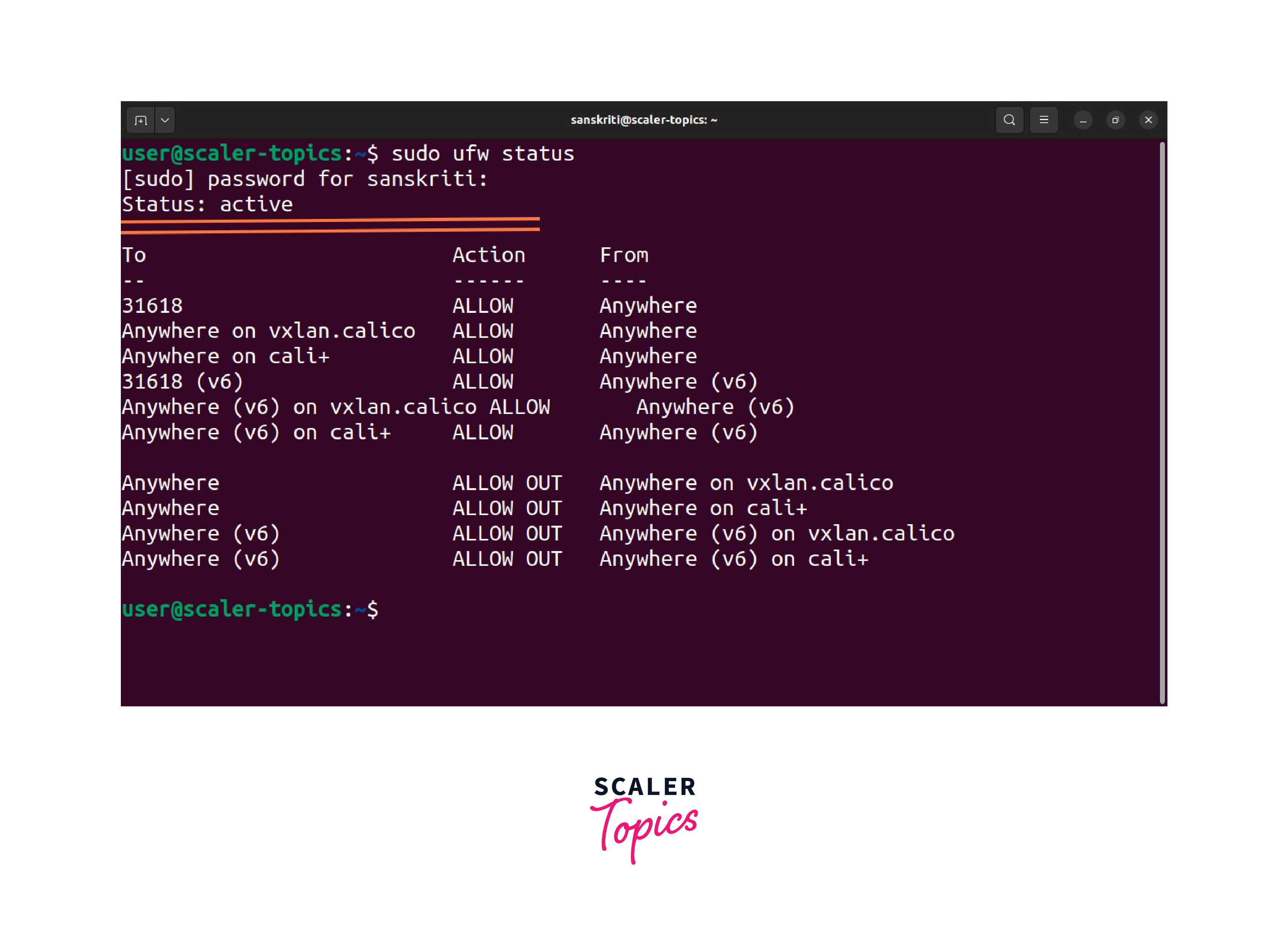
If the firewall is currently enabled, the output will indicate its status as active. If it is disabled, the terminal will display inactive as the output.
How to Stop UFW
Before disabling the firewall, you can temporarily halt the ufw service by utilizing the following command:
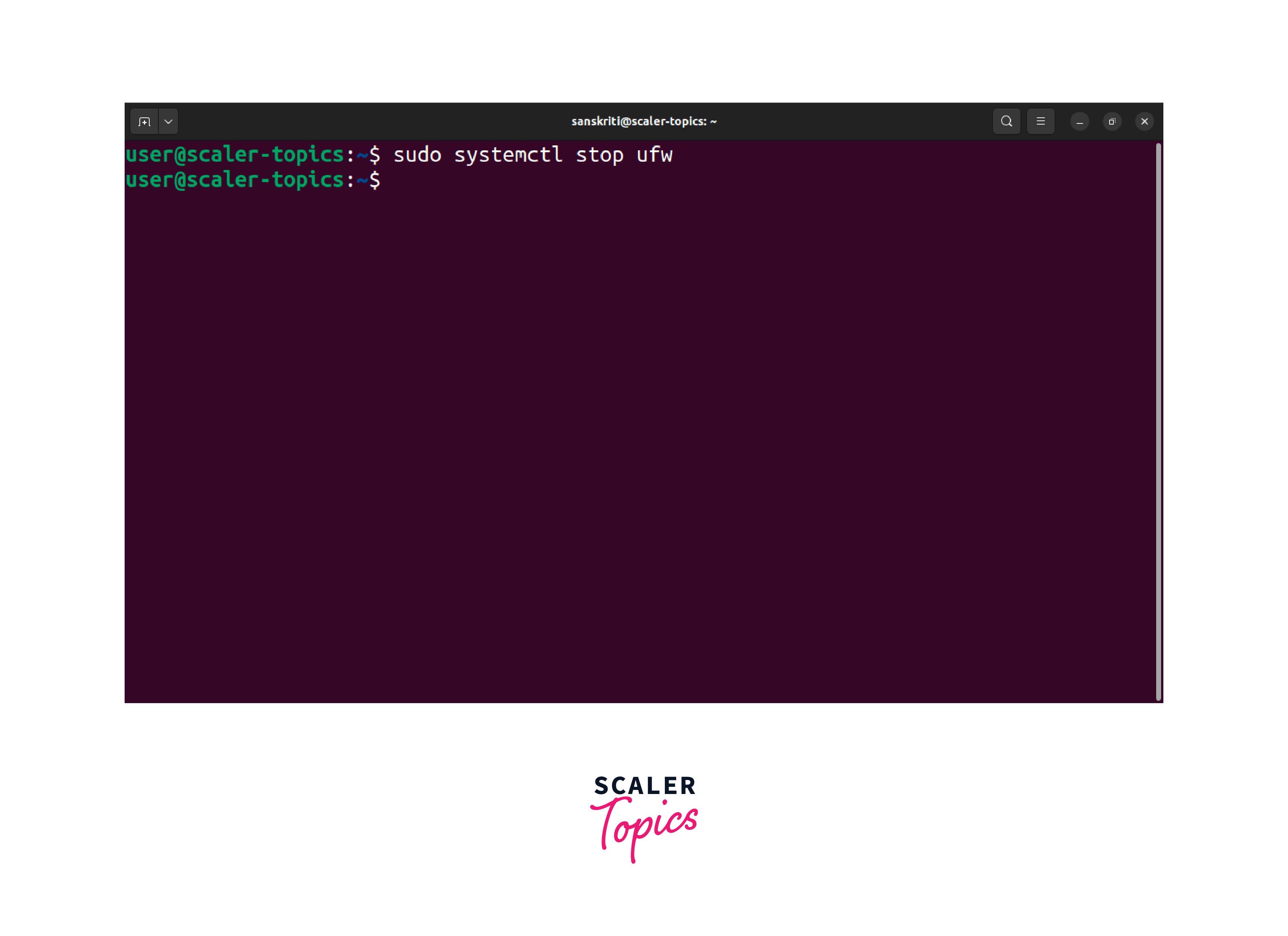
This command will immediately stop the firewall service until the next system reboot or until manually restarted.
Check the status to confirm that the new service is not active by executing the following command:
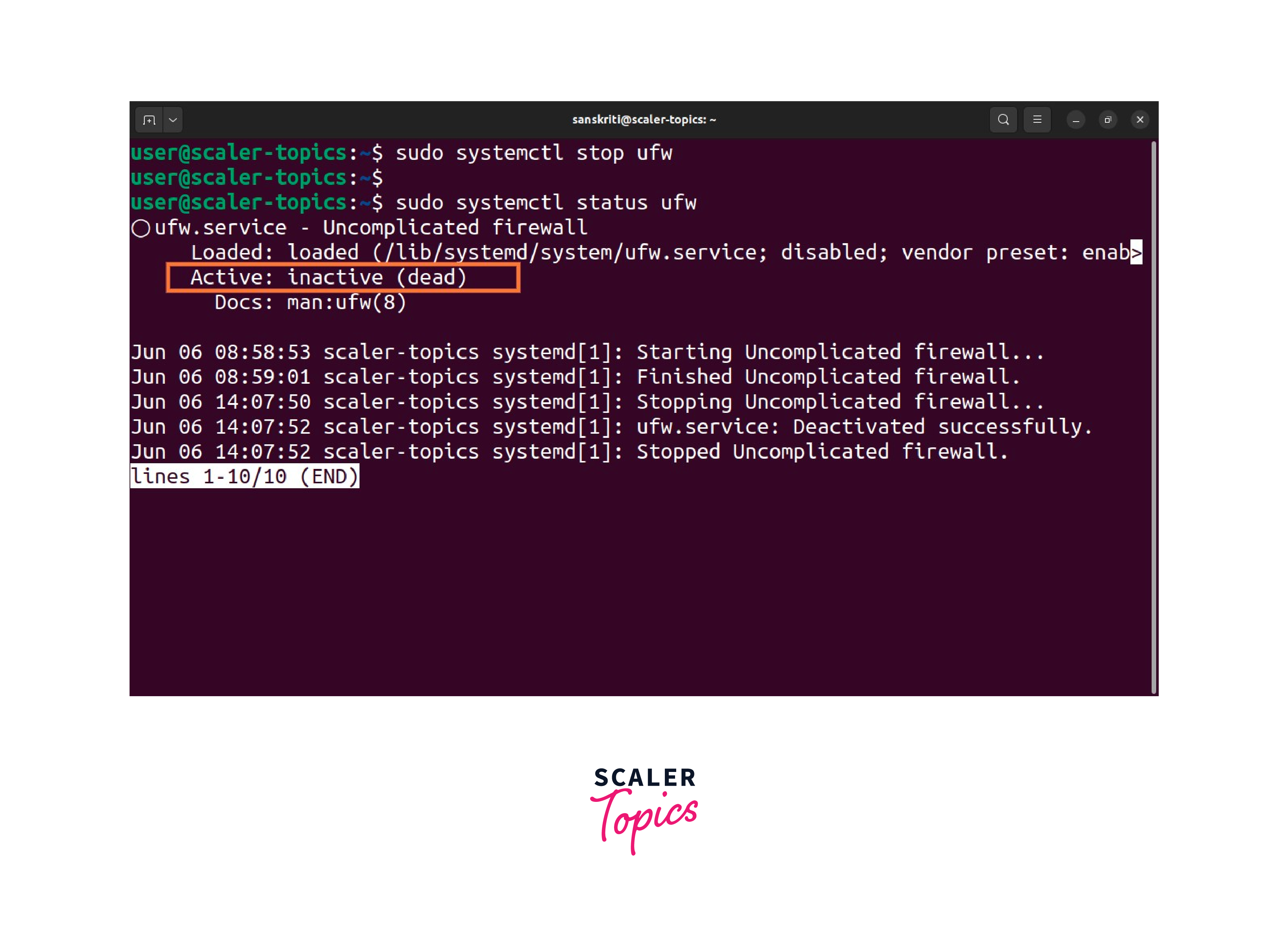
The following section provides a step-by-step guide on how to disable a firewall in Linux, enabling unrestricted network access.
Disabling UFW
Learn how to disable the ufw firewall in Linux and regain unrestricted network access by following these simple steps. By doing so, you can modify network settings and configurations as needed.
Follow the below steps and remove any firewall restrictions:
-
Open a terminal window.
-
Halt the ufw service using the following command:
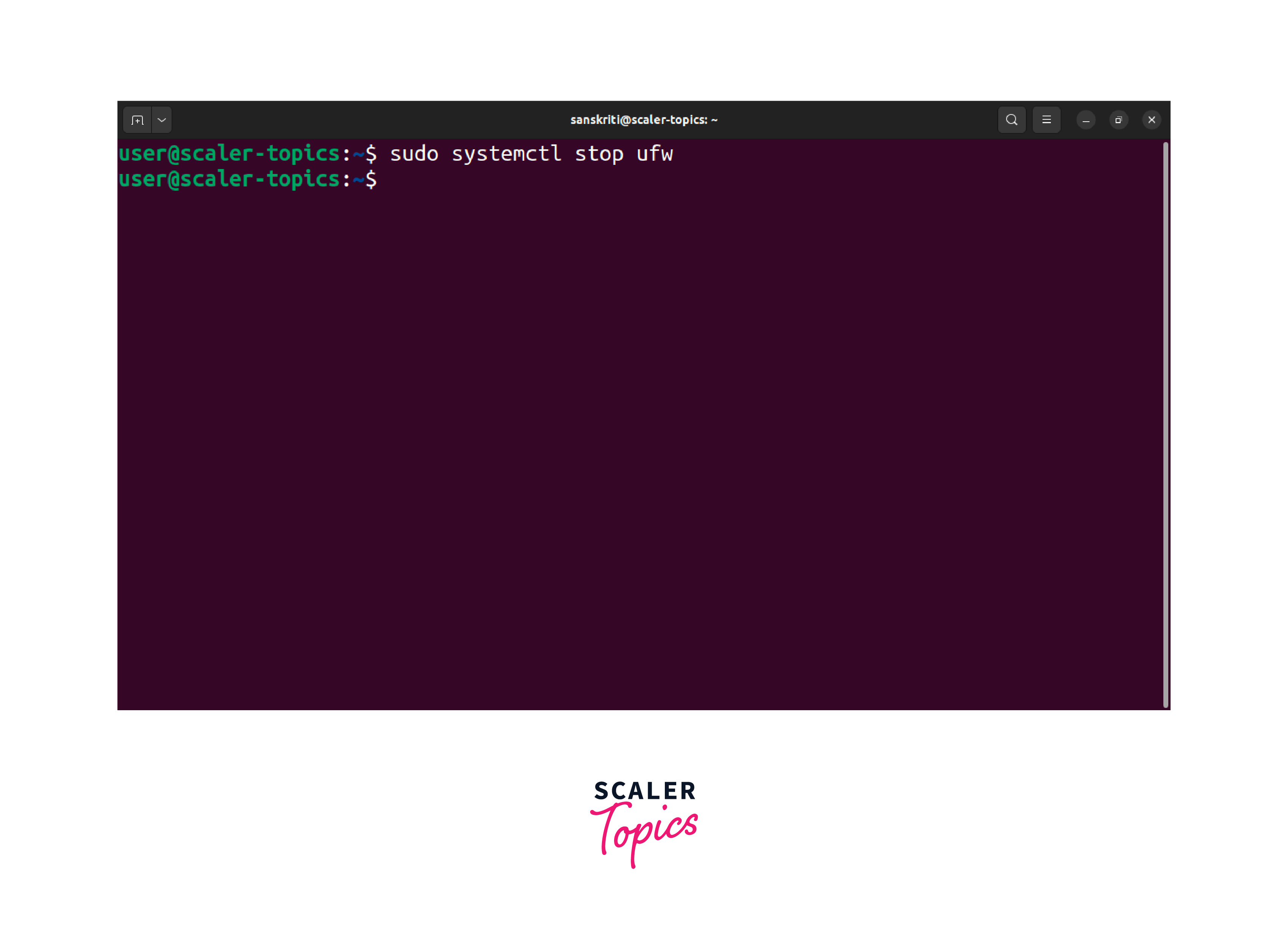
-
Disable the ufw service from starting automatically at boot:
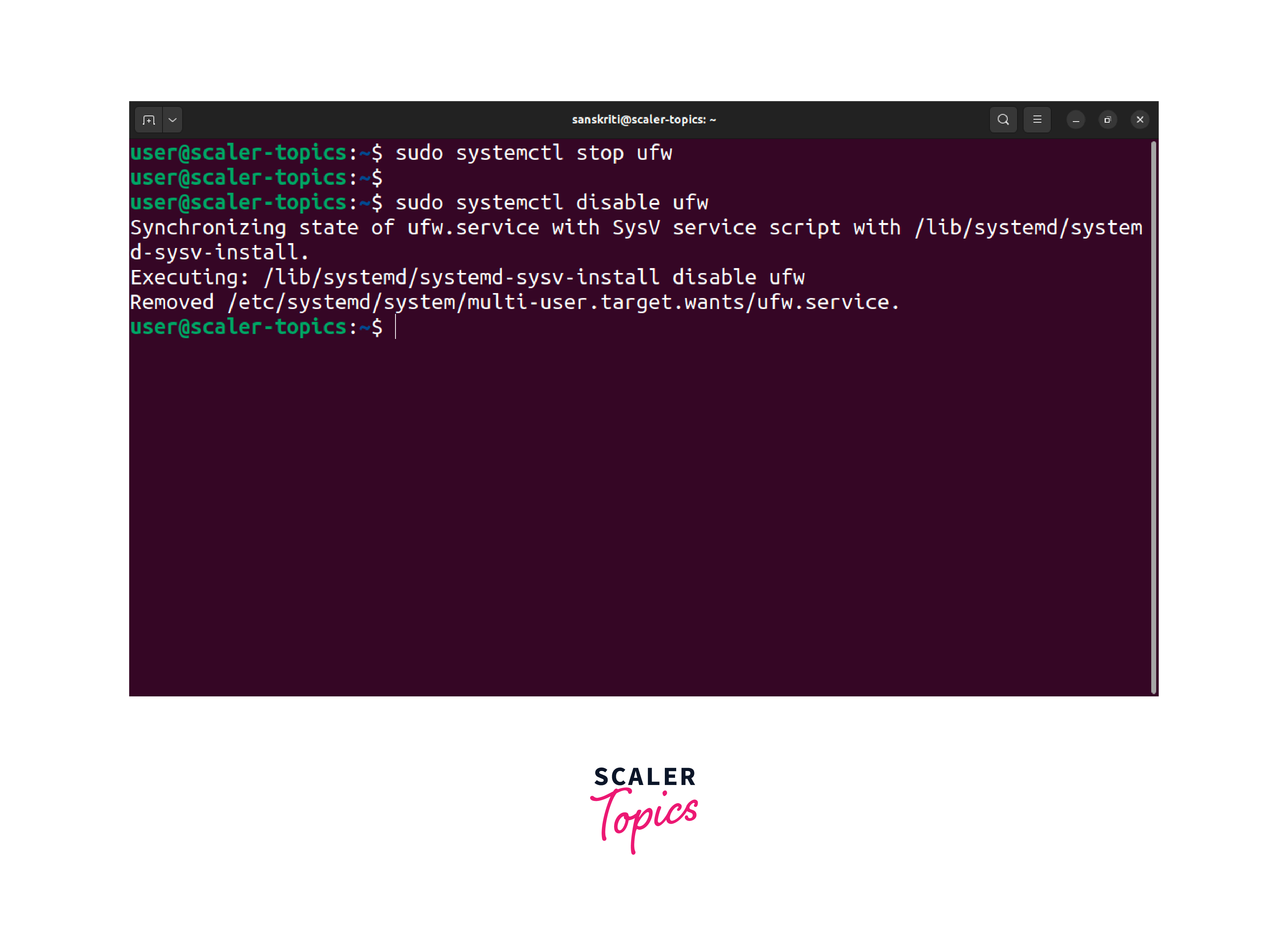
This command ensures the firewall service does not initiate automatically during system startup.
-
Finally, restart your Linux system to apply the changes.
Upon completing the mentioned steps, the ufw service will be disabled, and your Linux system will no longer have an active firewall.
FAQs
In this section, we will answer some common questions that may arise in your mind while learning how to disable a firewall in Linux. Let's look into such questions.
-
Is it recommended to disable the firewall in Linux?
Disabling the firewall should be done with caution and only in specific scenarios where it is necessary, such as for troubleshooting purposes or when implementing configurations. Keep the firewall enabled to ensure the security of your system and network.
-
How can I enable the firewall again in Linux?
Now that you know how to disable firewalls in Linux, let us also learn to enable firewalls again. To enable the firewall in Ubuntu, execute the following commands in the terminal:
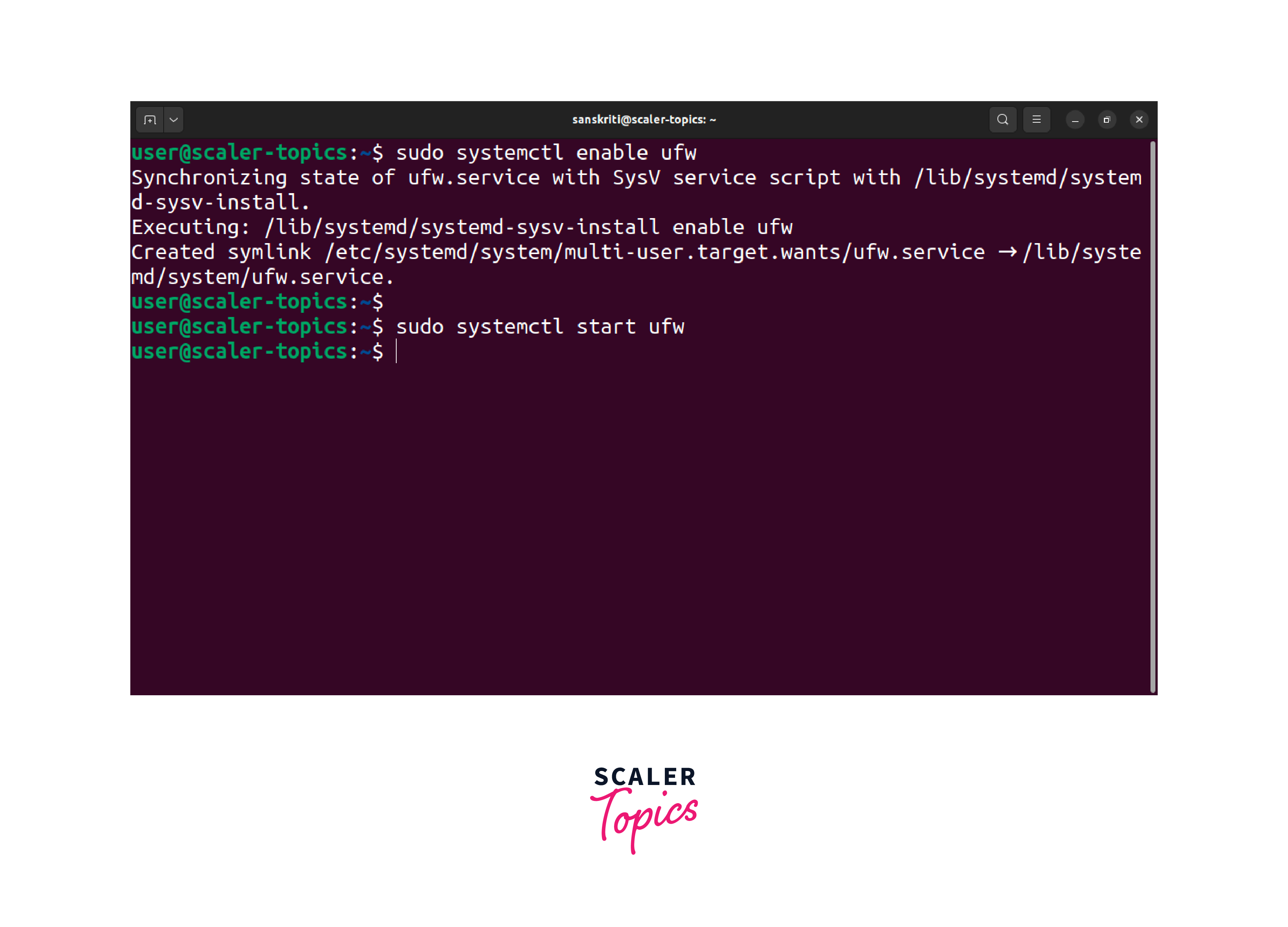
These commands will enable and start the ufw service, ensuring the firewall is active and protecting your system.
-
Are there any alternative firewall management tools available for Linux?
Yes. Linux provides various firewall management tools, including iptables, firewalld, and ufw. While ufw is a user-friendly and simplified interface for managing firewall rules in Ubuntu, iptables offers more advanced and fine-grained control. Different distributions may have varying default tools, so consult your Linux distribution documentation or community resources for more details.
-
How can I configure specific rules and exceptions in the firewall?
To set up specific rules and exceptions in the firewall, use the relevant commands or configuration files based on your chosen firewall management tool. For instance, in ufw, you can utilize the sudo ufw allow <port> command to enable incoming traffic on particular ports. For further information, consult the documentation or community resources of the firewall management tool.
-
Will disabling the firewall improve network performance?
Disabling the firewall may provide a marginal improvement in network performance in certain cases. However, a firewall protects your system from malicious network traffic and external threats. Keep the firewall enabled to ensure both security and network performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowing how to disable the firewall in Linux using the ufw firewall management tool is essential for specific situations like troubleshooting and configuration implementation. If you need to re-enable the firewall in Linux, use the appropriate commands for your Linux distribution.
Disabling the firewall may yield marginal improvements in network performance in specific cases. It is crucial to remember that the firewall serves as a defense against malicious network traffic and external threats. Therefore, keep the firewall enabled to ensure security and network performance.
