HTML <script> Tag

Overview
A tag is similar to a keyword which is used to describe how a web browser formats and displays the content. The <script> tag is known for embedding the scripts like JavaScript. The <script> tag comes with its attributes which decide behaviour of the tag. One of the example of <script> attribute is src attribute which provides the path to the external script files.
Syntax
Attributes of <script> Tag
The <script> tag has two types of attributes.
-
global attributes A global attribute is a property common to all HTML elements. It can be used on all elements, even if it has no effect on some elements.
-
event attributes When the browser reacts to a specific action by the user, event attributes are triggered. For example Form events, Mouse events, Media events, Window events.
The <script> contains the following global attributes :
| Attribute | Syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
| async | <script async> | The <script> is run asynchronously with the rest of the page when you use script async. |
| crossorign | <script crossorigin ="anonymous|use-credentials"> | enables error logging for sites that use a separate domain for static media. The value anonymous doesn't really send credentials, whereas the value use-credentials does. |
| defer | <script defer> | The script is run after the document has been parsed but before the DOMContentLoaded event has been fired. |
| src | <script src="uri\path to resource"> | Provides a URL or path for an external script. |
| type | <script type="text\javascript"> | In this attribute, we specify the type of containing script, which can be textjavascript, texthtml, textplain, applicationjson, applicationpdf, etc. |
| referrerpolicy | <script referrerpolicy="no-referrer"> | If a script is being retrieved, this attribute tells which referrer to send. It can contain values such as no-referrer, no-referrer-when-downgrade, origin, same-origin, strict-origin, etc. |
| integrity | <script integrity="sha384-oqVuAfXRKap7fdgc"> | This attribute provides a way in which a user agent can verify that a retrieved resource was not manipulated. |
| nomodule | <script nomodule> | It specifies that the script is incompatible with browsers which support ES2015 modules. |
The <script> contains the following event attributes :
- Window Events Attributes- onload, onresize, etc.
- Form Events- oninput, onchange, etc.
- Keyboard Events- onkeydown, onkeypress, etc.
- Mouse Events- onclick, onwheel, etc.
- Media Events- onabort, onerror, etc.
What is The <script> Tag Used For?
The <script> tag is a HTML element which is used to execute JavaScript into a Browser. It embeds the JavaScript code into a HTML file, it can also point to external javaScript file using it's src element. JavaScript is a scripting language basically used for form validation, image manipulation, dynamic changes and many more things.
Examples
Let's have a look at some examples for how we can use script tag in HTML.
Example 1: Basic Example of inline script inside <script> tag.
In this example, we will print something using JavaScript inside script Tag.
Code:
Output:
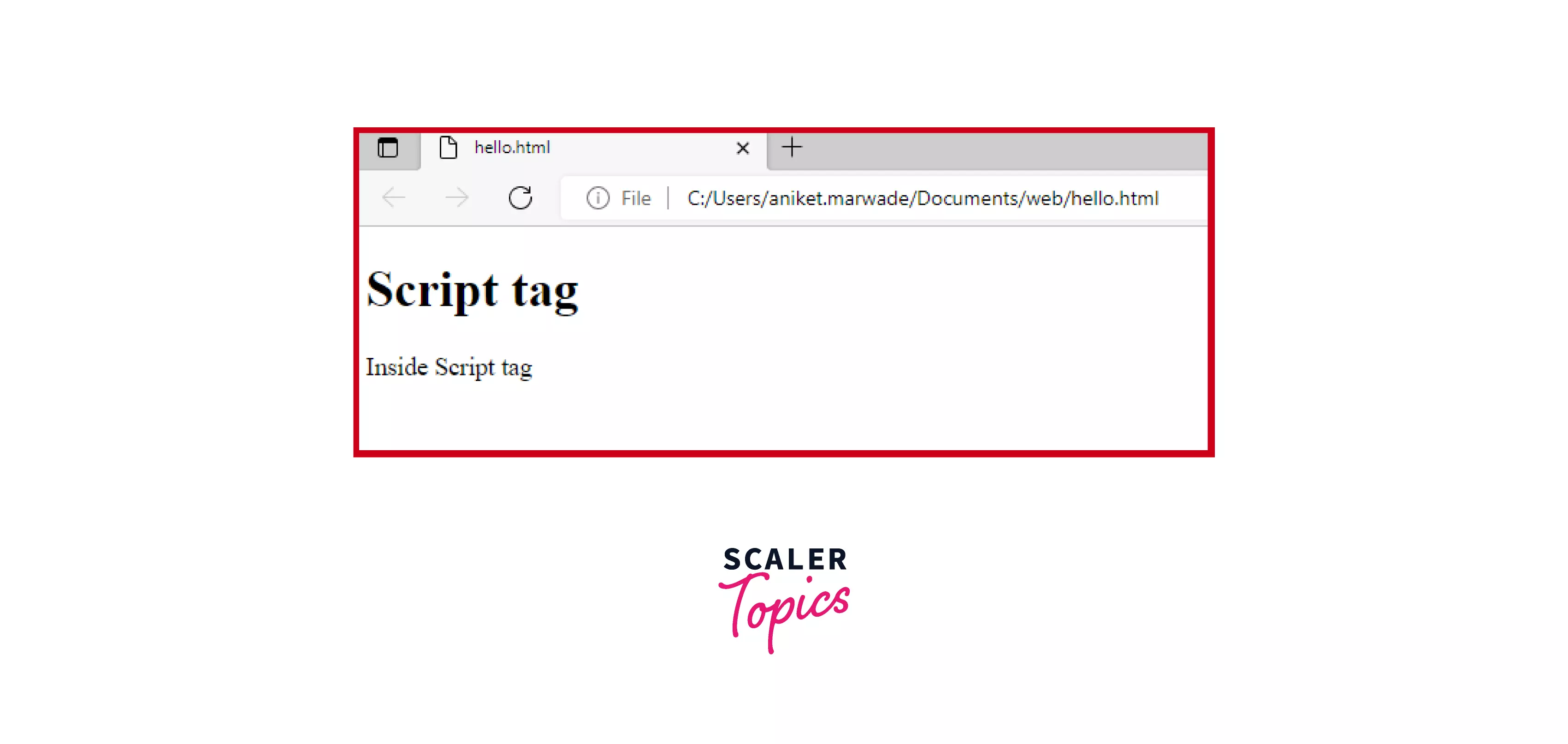
Explanation:
In the above html code we are printing "Inside Script tag" using javascript inside <script> tag using document.write('') which works as a print statement in JavaScript.
Example 2: Link script file
In this example, we will see how to include external script file inside html and print content inside it.
Code :
- Inside "hello.html" file
- Inside external_script.js file.
Output:
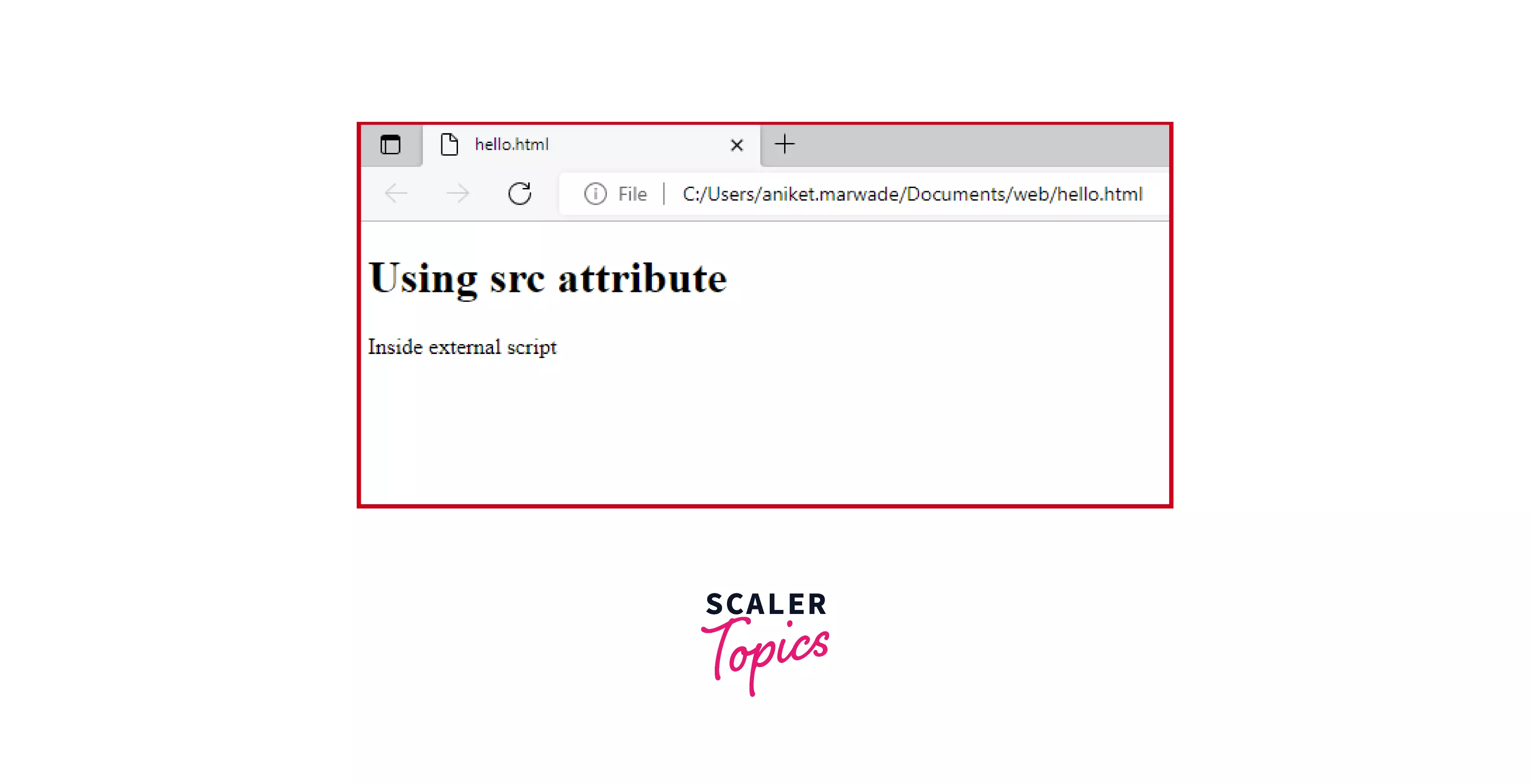
Explanation:
In the above HTML code, we are using an external script file named "external_script.js". The file is included in the HTML file using the src attribute which provides a URL or path for an external script. On including the external file the text inside it "Inside external script" can be seen in the output image.
Example 3: script outside body tag
In this example, we will see how to use script tag outside body tag in html file.
Code:
Output:
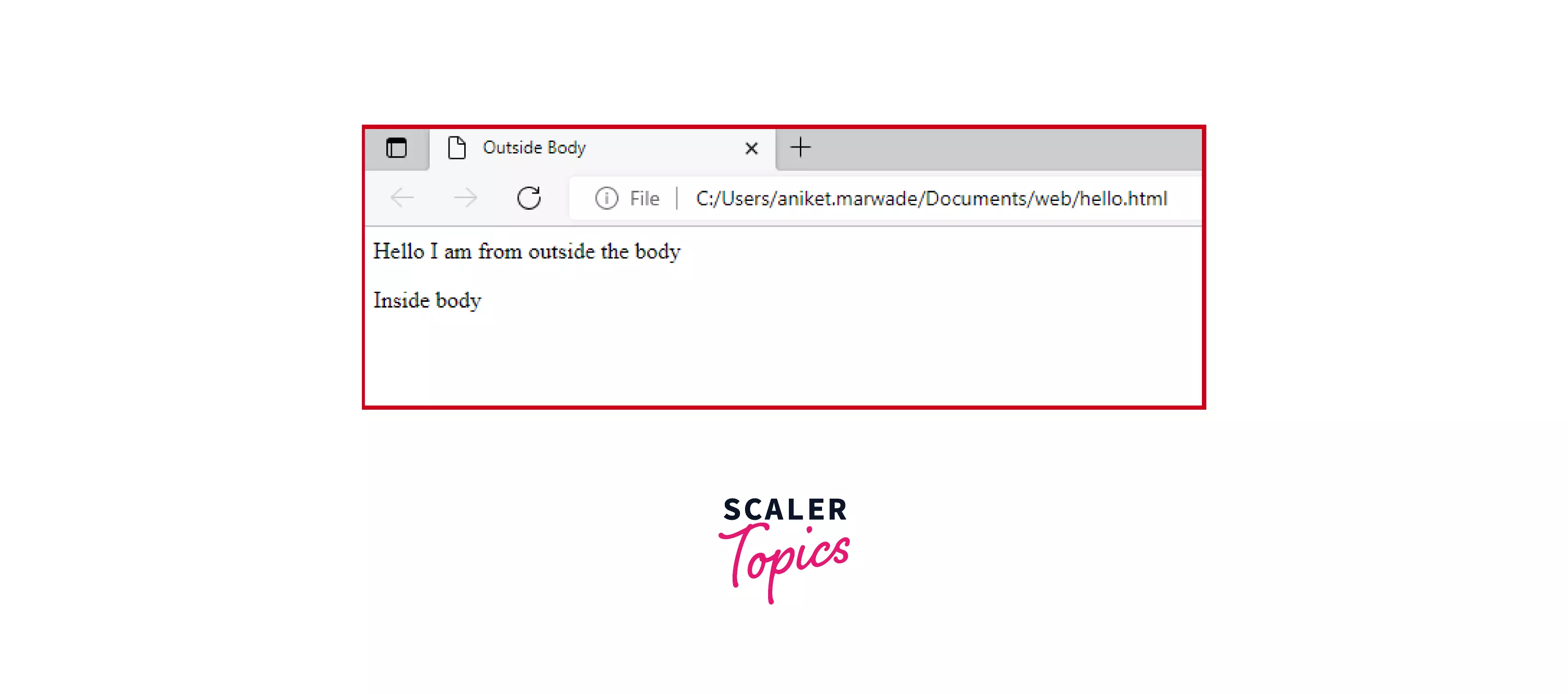
Explanation:
In the above HTML code, we are using a script tag outside the body tag. As you can see we are printing some text inside the script tag which is a present inside the head tag. It doesn't make much difference until you do use DOM manipulations.
Browser Support
The <script> tag in HTML is supported by the following browsers :
| Element | Chrome | Microsoft Edge | Firefox | Safari | Opera |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <script> | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Conclusion
- The <script> tag embeds the JavaScript code into a HTML file.
- There are two types of attributes of <script> tag global and event.
- The <script> tag is can be used inside or outside of the HTML body.
- Other than embedding, external scripts can also be used in the HTML file using src attribute.
- The <script> tag is supported by almost all the browsers.
