Iframes in HTML

HTML's <iframe> tag enables the integration of one HTML page into another, forming an inline frame. Commonly used for ads, videos, analytics, and interactive content, it creates a rectangular region for seamless interaction between the embedded webpage and the parent document, facilitated by JavaScript.
How To Use An Iframe in HTML
The purpose of iFrames is to allow content to be shared from other websites. If you wish to provide the readers with context about a certain topic, you can include an iframe tag. <iframe> tags can be used to insert an iframe element into an HTML document. In notepad, copy and paste the following code, then save the page as a .html file:
Syntax:
Example:
Elegant theme's YouTube video will be displayed by the code above.
Output:

Let's review each tag individually:
- An iFrame contains the video using the <iframe>...</iframe> tag.
- Content originating from external or internal servers is contained in the iFrame source (src). Make sure the URL contains the embedded code.
- The width and height of an iFrame determine its aspect ratio.
- As shown in the example, you can insert a fixed size of 690*470 pixels (px). Alternately, you can adjust the iFrame automatically by using a percentage-based method (10%-100%)
Attributes of Iframes in HTML
The attributes supported by <iframe> are
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| allow | allow-top-navigation, allow-forms, allow-pointer-lock, allow-popups | Determines an iframe's feature policy. Depending on where the request originates, the policy determines what features an <iframe> can access (like the microphone, camera, battery access, web-sharing API, etc |
| allowfullscreen | true,false | This value is set to true if the iframe can invoke fullscreen mode with the requestFullscreen() method. |
| allowpaymentrequest | true,false | A cross-origin <iframe> can invoke the Payment Request API if this property is set to true. |
| height | pixels | Specifies the height of the frame in CSS pixels. By default, it is 150 pixels |
| loading | eager, lazy | This tells the browser how to load the iframe content. |
| name | text | A name that can be used as a target in the embedded browsing context. |
| referrerpolicy | no-referrer, no-referrer-when-downgrade, origin, origin-when-cross-origin, same- originstrict-origin-when-cross-origin, unsafe-url | When fetching the frame's resource, specifies the referrer to use. |
| sandbox | allow-forms, allow-pointer-lock, allow-popups, allow-same-origin, allow-scripts, allow-top-navigation | Imposes additional restrictions on content in frames. A value of empty tokens for all restrictions or a list of space-separated tokens for lifting individual restrictions can be specified. |
| src | URL | Specifies the URL of the embedded page. To embed an empty page conforming to the same-origin policy, enter a value of about |
| srcdoc | HTML_Code | To embed, use inline HTML to override the src attribute. In the case where a browser does not support the srcdoc attribute, the URL in the src attribute will be used. |
| width | pixels | Indicates the width of the frame in CSS pixels. The default value is 300 pixels. |
Deprecated attributes
These attributes(<img>,<iframe> etc) are deprecated and may not be supported by all user agents. They should not be used in new content, and they should be removed from existing content.
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| align | left,right,middle,top,bottom | Aligns the element according to its surrounding context. |
| frameborder | 0,1 | Draws a border around this frame when 1 is specified (the default). The value 0 removes the border around this frame, but it is best to control the border of an iframe using the CSS property border |
| longdesc | URL | URL of a long description of the content displayed in the frame. For non-visual browsers, this is not helpful due to widespread misuse |
| marginheight | pixels | The space between the content of the frame and its top and bottom borders in pixels. |
| marginwidth | pixels | The space between the content of the frame and its left and right borders in pixels. |
| scrolling | auto, yes, no | Provides instructions for the browser when a scrollbar should be made available. |
Examples of Iframes in HTML
Iframe - Set Height and Width
Iframe sizes are specified by the height and width attributes. For the attribute values, pixels are used by default, but percentage values, such as " 80% ", can be also used.
The height and width of the HTML iframe Tag can be set by using the height and width attributes and we can specify the values we need to customize to it our needs as in the example below
Output:

Iframe - Remove Border
All iframes are framed by default with a border around them. If you want to remove the border, you must use the style attribute and CSS border property.
The border of the iframe by default can be removed by setting the style property value to none as in the example below.
Output:
Iframe - Border Style
The border of the Iframe's can be changed in size, style, and color:
We can customize the border style by using the style property as per our needs. The border styles can be solid, dotted, dashed and double.
Output:

Iframe - Links
Iframes can be used as target frames for links. A link's target attribute must refer to the iframe's name attribute.
We can set the link as the target in iframe by specifying a name to it for example as iframe_a and using the name again as a target as shown in the example below. A link will open in an iframe when the target attribute matches the iframe name
Output:

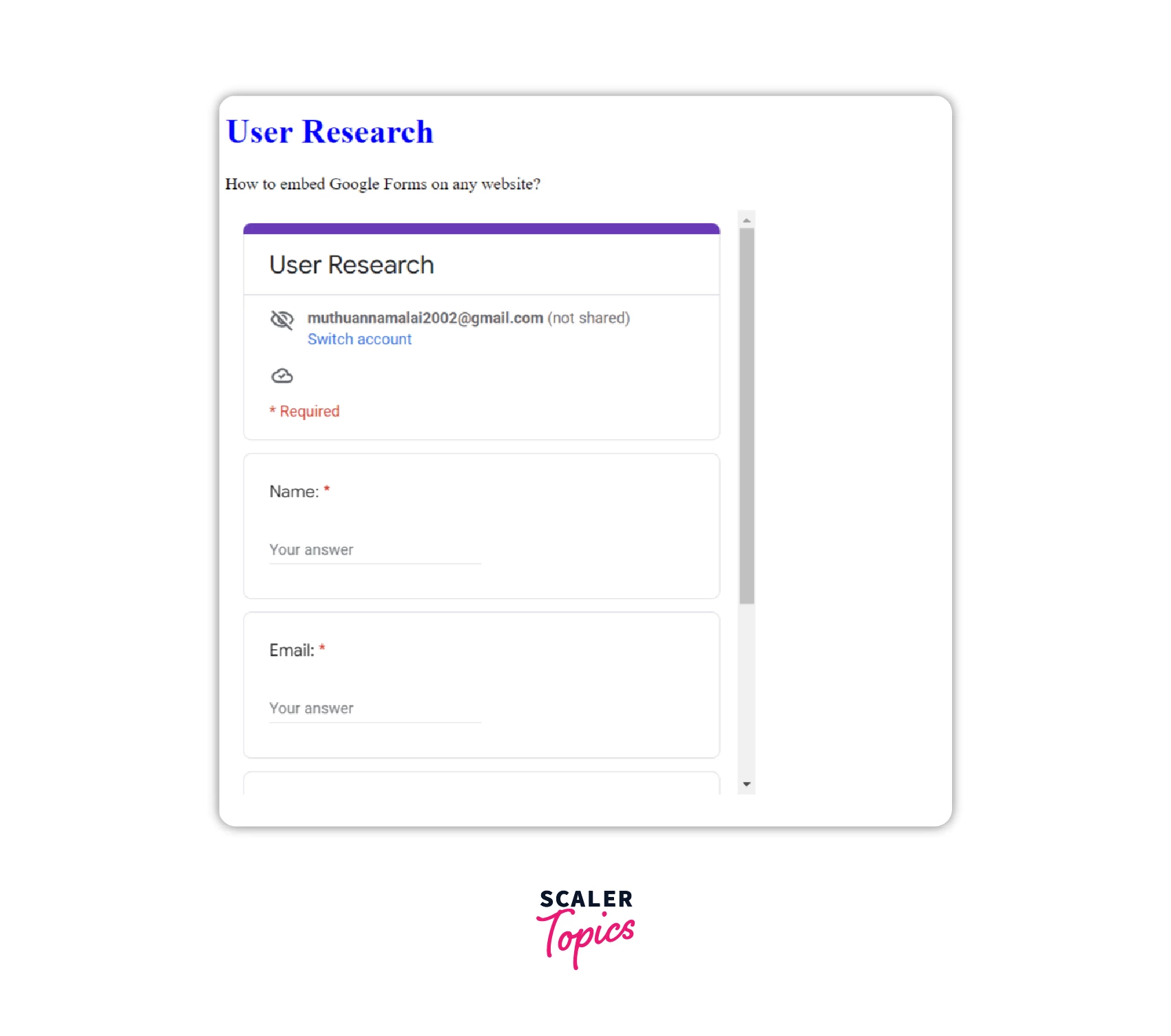
Iframe - Google Forms
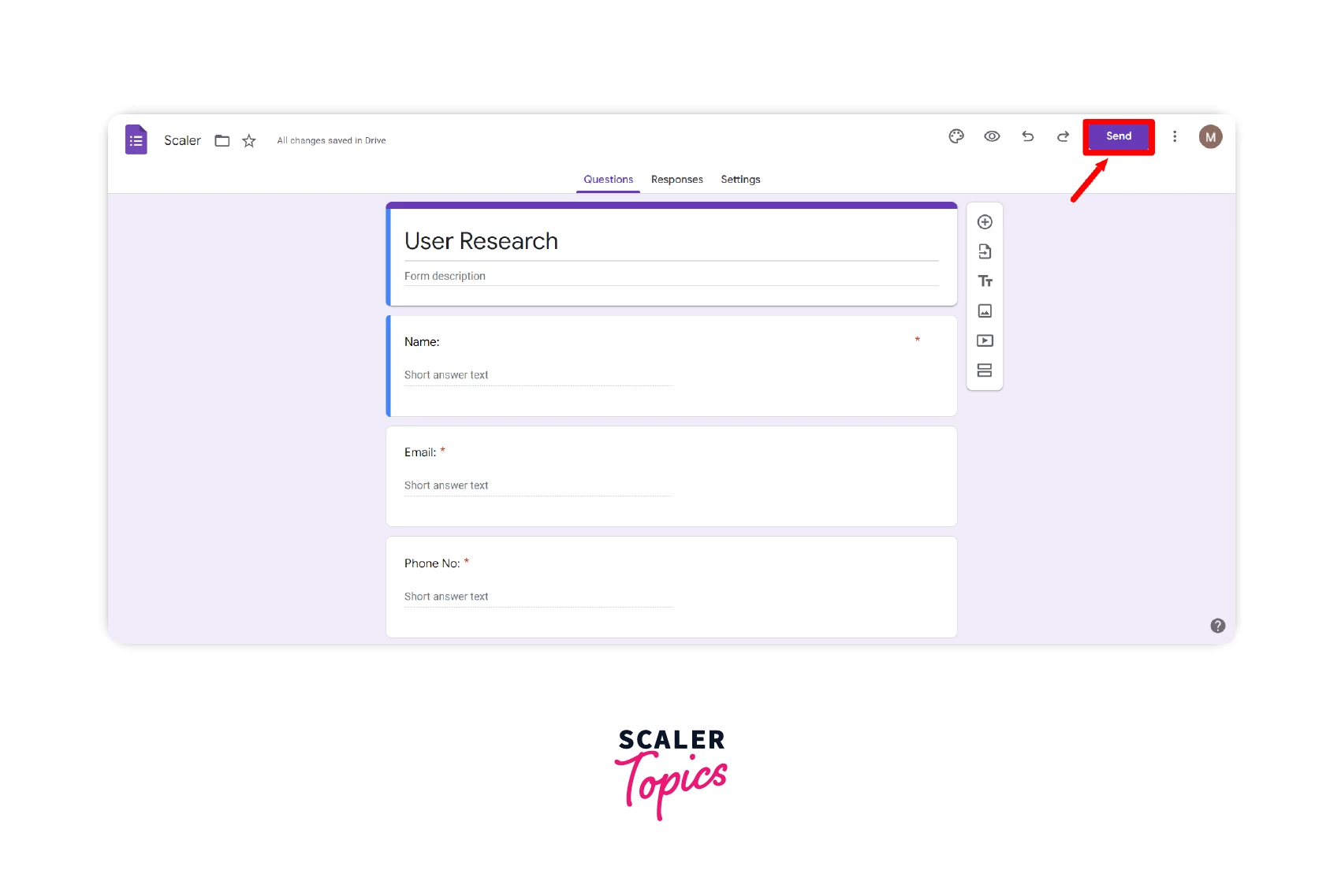
- Step 1: Create the Google Form you'd like to embed.
- Step 2: Click the Send button after you have created the form, as shown below.
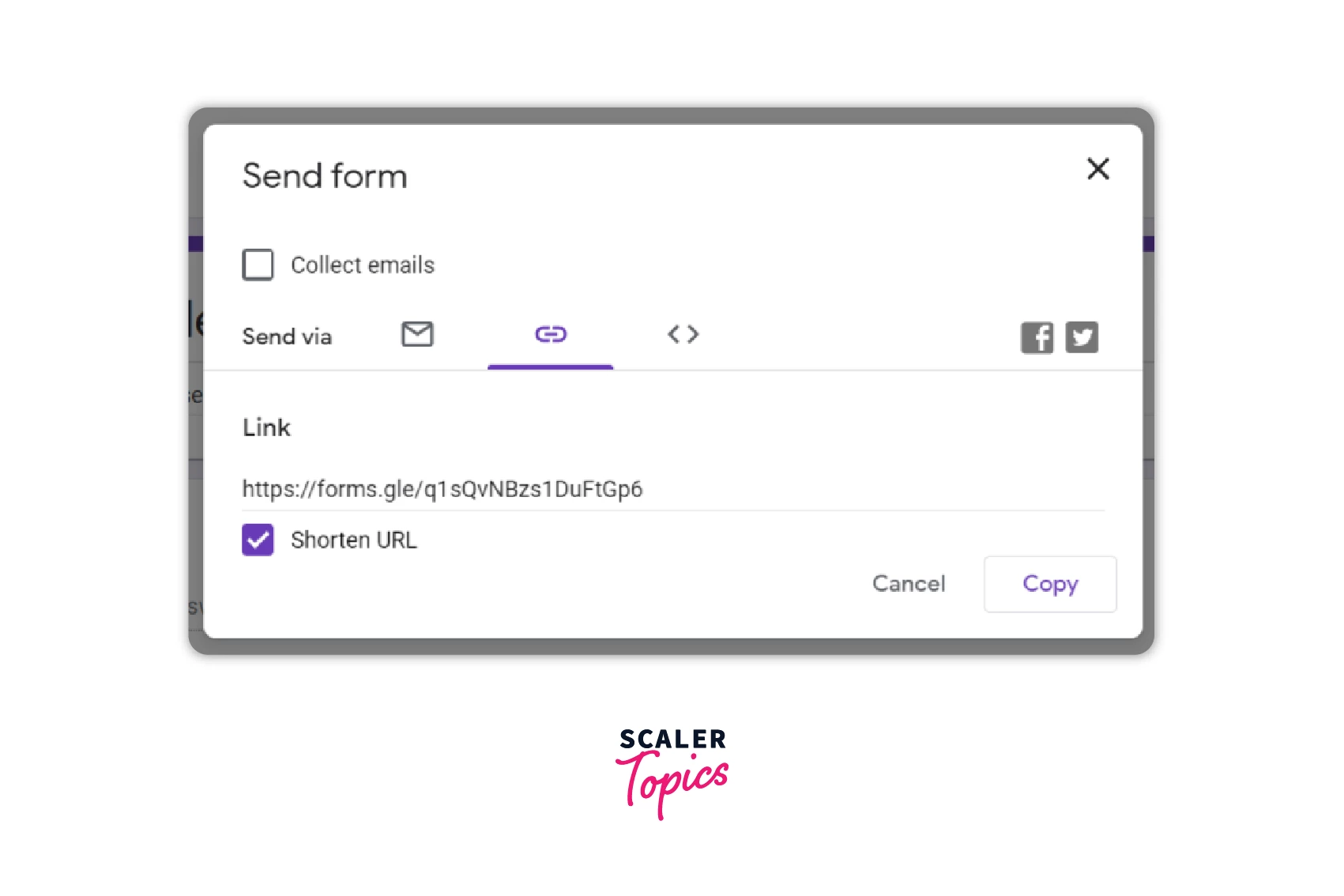
- Step 3: From the list of options for sending, select embed. A link will appear in an iframe that has to be copied.
- Step 4: Add the following <iframe> link to the HTML source code of the page where the form should be embedded. The form will automatically appear and allow the user to fill it out directly on the page.
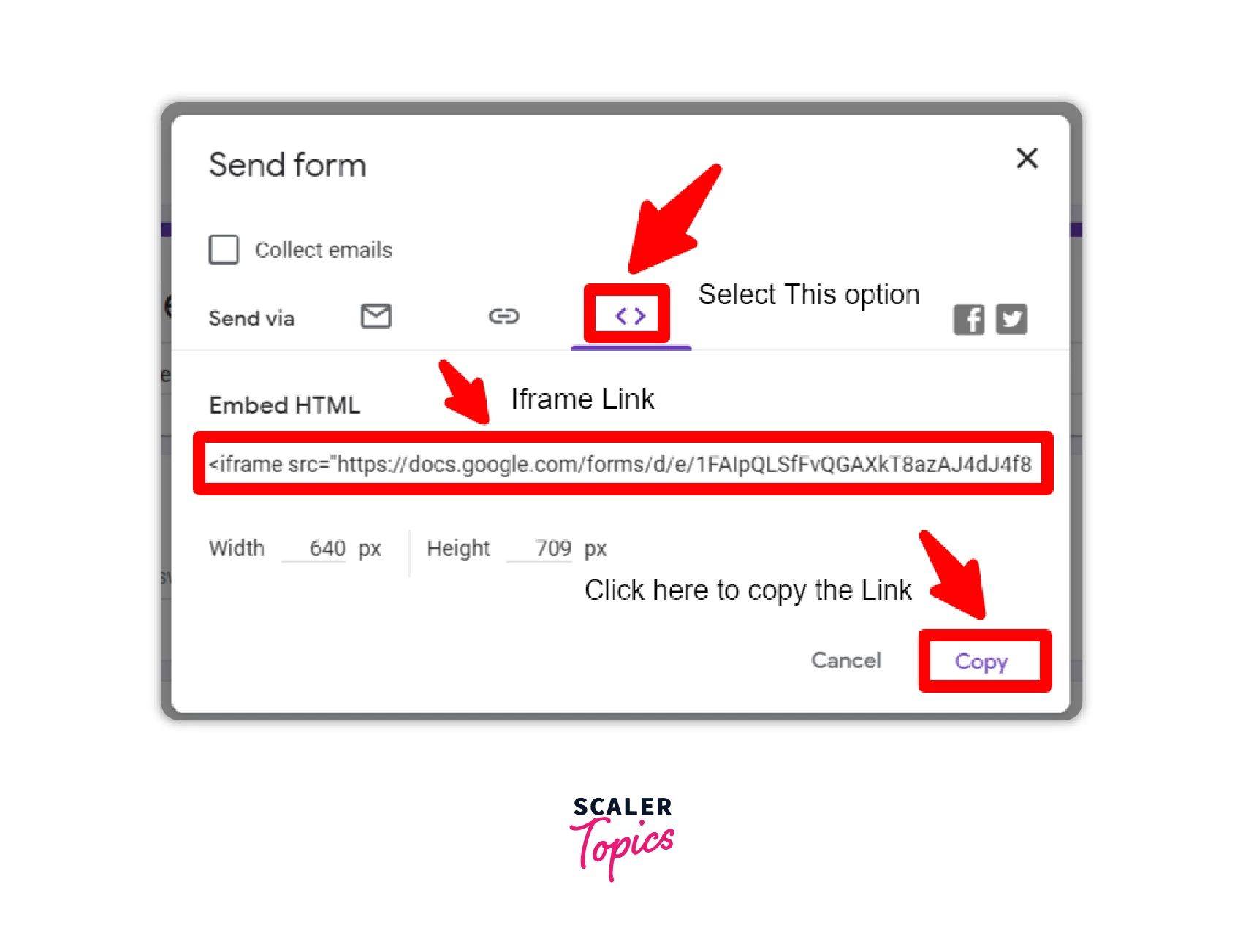
We can embed google forms by having the form link in the src attribute of iframe as shown in the example below
Output:
Supported Browsers
Here are the browsers supported by this Property:
| Browser | Compatible |
|---|---|
| Google Chrome 93.0 | Yes |
| Internet Explorer 11.0 | Yes |
| Firefox 92.0 | Yes |
| Microsoft Edge 93.0 | Yes |
| Opera 78.0 | Yes |
| Safari 14.1 | Yes |
Note: However, you shouldn't overuse <iframe>. This can slow down your site and put your site at risk of malware, especially if the content comes from a suspicious site. Iframes should be considered as components of your content, not parts of your website. If you want to stimulate your readers by including a YouTube video, you can add an iFrame element to that post.
Summary:
- The purpose of iFrames is to allow content to be shared from other websites. If you wish to provide the readers with context about a certain topic, you can include an iframe tag.
- Using iFrames will allow you to share other people's content in an ethical way, as well as display video and audio files without hosting them on your site.
- iFrames are powerful for increasing engagement with your visitors. Remember to only use content from trusted sites if you still need to use it for development purposes.
I hope that this article will help you implement and understand iFrame
