How to Calculate ln in Python

Overview
The ln in Python refers to the logarithm of a number to a given base. This base value when not mentioned is e The ln in Python can be calculated by either the Math.log() method or the Numpy.log() method.
What is the Natural Logarithm?
The natural logarithm is defined as the given number's logarithm to the base value. The base value in the case of natural logarithm is e.
Representation of Natural Logarithm:
The natural logarithm is often represented as loge(x) or ln(x). Usually, the e in loge(x) is considered implicit, thus it is represented as log(x).
- Here x is the number whose logarithm is determined to the base e.
Following are some unique attributes of natural logarithms:
- ln(1) = 0
- ln(e) = 1
Where do We use Natural Logarithms?
Natural logarithms are useful when we need to solve problems that include time events or growth events.
How to Calculate ln in Python?
So far we've learned what is the natural logarithm. In this section, we will learn how to calculate ln in Python. There are two different methods to calculate ln in Python:
Method1: Use Python math to Calculate the Natural Logarithm (ln)
To calculate the natural logarithm value of a number we can use the log() method of the math library of Python.
Syntax:
- With one argument, return the natural logarithm of x (to base e).
- With two arguments, return the logarithm of x to the given base, calculated as log(x)/log(base).
While using this method if no base value is provided, the value defaults to e, meaning that by only providing a number, you are automatically calculating the natural logarithm.
This may look like something happening not in the way we would expect it to but if we recall from the introduction that in many cases the base e is implicit, thus, many times it is omitted when referring to a log() function without a specified base.
Example
In this example, we will calculate and print the natural logarithm value for different values using the math.log() method.
Code:
Output:
Explanation of the example:
In the above example, we take the values e, 1, and 10 and pass the values to the math.log() method. The math.log() will calculate the natural logarithms for these values and store them in the variables val1, val2, val3 respectively. Thus the code outputs 1.0, 0.0 and 2.302585092994046
Method2: Use Python NumPy to Calculate the Natural Logarithm (ln)
To calculate the natural logarithm value of a number we can also use the numpy.log() method of the NumPy library of Python.
Syntax:
- Similar to the math.log method, with one argument, return the natural logarithm of x (to base e).
- With two arguments, return the logarithm of x to the given base, calculated as log(x)/log(base).
While using this method if no base value is provided, the value defaults to e, meaning that by only providing a number, you are automatically calculating the natural logarithm.
This may look like something happening not in the way we would expect it to but if we recall from the introduction that in many cases the base e is implicit, thus, many times it is omitted when referring to a log() function without a specified base.
Example
In this example, we will calculate and print the natural logarithm value for different values using the numpy.log() method.
Code:
Output:
Explanation of the example:
In the above example, we take the values e, 1, and 10 and pass the values to the n.log() method (Here, NumPy is imported as n). The n.log() will calculate the natural logarithms for these values and store them in the variables val1, val2, val3 respectively. Thus the code outputs 1.0, 0.0 and 2.302585092994046
Calculating the In of Elements of an Array in Python
So far, we have learned how to calculate the ln of a number using Python. But what if we have to calculate the ln of elements of an array?
We can use the numpy module to evaluate the ln of elements of an array in Python. The Numpy.log(arr, outArr) can be used to calculate the ln of elements of an Array in Python.
Syntax
Parameters
- arr: The arr parameter refers to the array whose ln we are supposed to evaluate.
- outArr: The outArr refers to the array where the log of the elements of the input array will be passed. This array needs to be of the same size as the input array.
Example
In this example, we will calculate the ln values of an array of numbers.
Output:
Explanation of the output:
In the above example, we are declaring a list temp and storing the numbers 10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100. Now this list is converted into an array arr using the num.array() method of the numpy library. Now, the num.log(arr) will find the ln of arr and store it in res. Thus, the output is [2.30258509 2.99573227 3.40119738 3.68887945 3.91202301 4.09434456 4.24849524 4.38202663 4.49980967 4.60517019].
How to Graph the Natural Log Function in Python
The natural log equation, being a function can be plotted on a graph. In this section, we will learn how to plot the natural log functions in Python.
In order to plot the graph for the natural log function in Python, we need to import the matplotlib library in our program.
We need to follow the following steps to plot the graph for the natural log function in Python:
- Step 1: We need to create an array of any size. In this case, we will create an array with numbers from 1 through 30.
- Step 2: We need to iterate through the array in order to create an array of the natural log.
- Step 3: Once we have got both arrays, we will plot the graph for the two arrays (the one with the original value and the one with logarithmic values) using the matplotlib library.
Code:
Output:
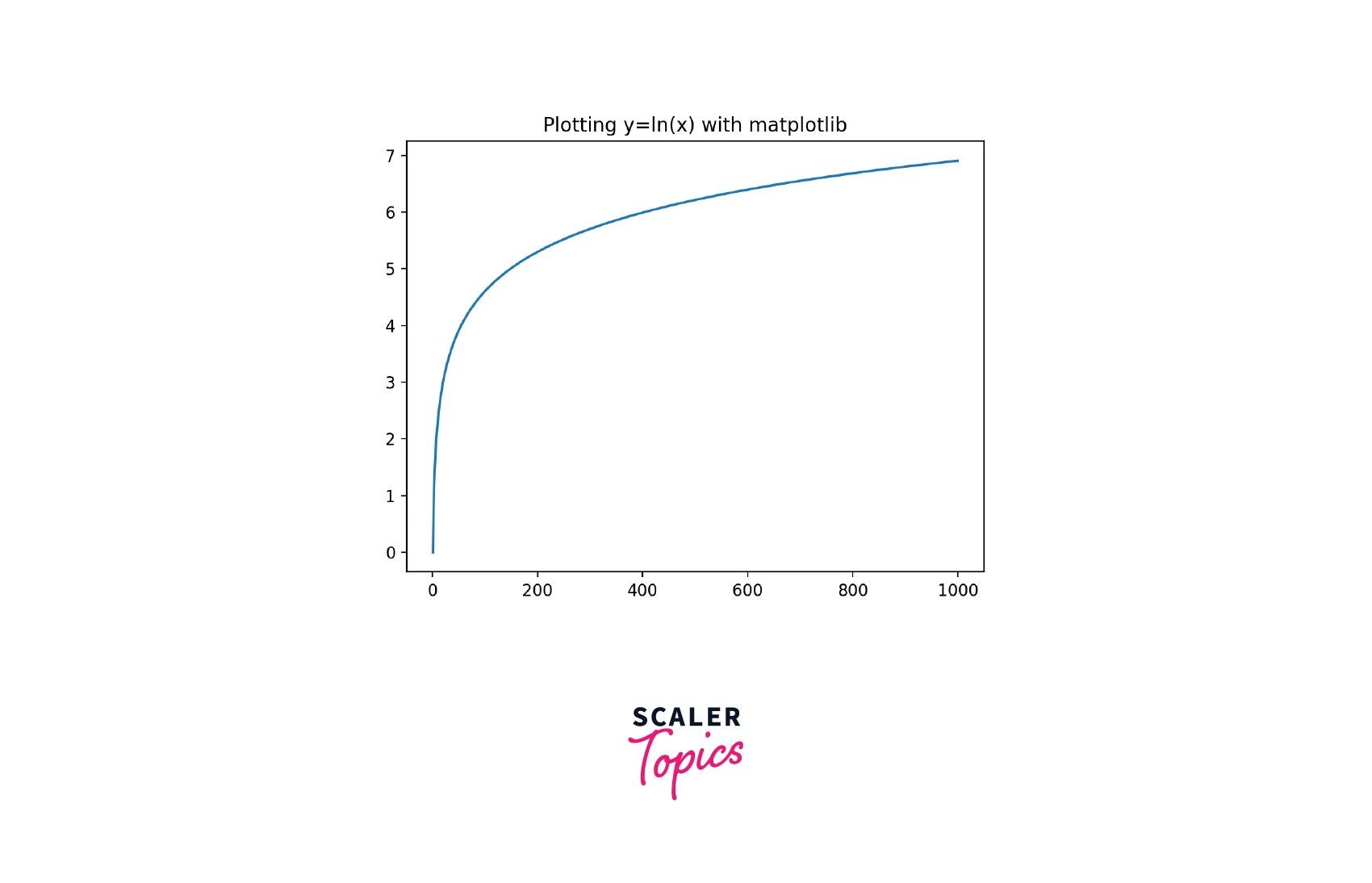
Plotting Natural Log (ln) vs Standard Log in Python
Similar to the natural log graph that we plotted in the previous section, we can also plot a standard log graph in Python. In this section, we will plot a Natural Log (ln) vs Standard Log graph in Python.
Again, in order to plot the graph for the natural log function in Python, we need to import the matplotlib library in our program.
We need to follow the following steps to plot the graph for the natural log function in Python:
- Step 1: We will make a list of integers.
- Step 2: We will convert the list to an array of integers using NumPy.
- Step 3: We will find the natural logarithm of the array and store it in another array.
- Step 4: We will find the standard logarithm of the array and store it in some other array. Now that we have got the logarithm arrays for both natural and standard logarithms, we will plot the graph.
- Step 5: We will use the graph.plot() method to plot the graph for the array (Here 'graph' is the alias used for 'matplotlib.pyplot'). We will pass the input array, the logarithmic array, and color, marker, and label parameters to set the color of the graph, line type of the graph, and the label of the graph respectively.
- Step 6: We will set the label for the axis using graph.xlabel and graph.ylabel.
- Step 7: We will set the title of the graph using graph.title().
- Step 8: We will display the graph.
Code:
Output:
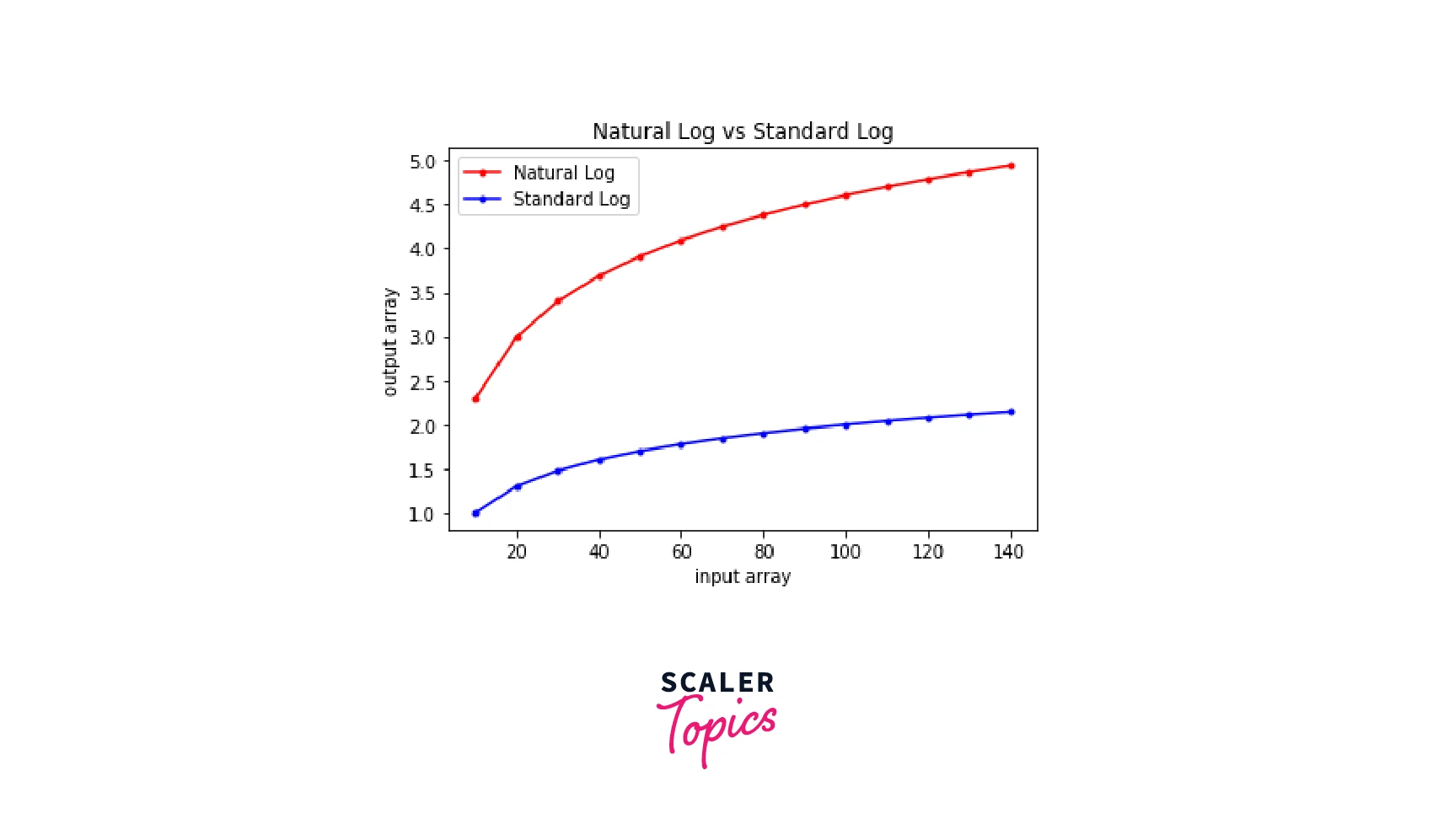
Conclusion
- The natural logarithm is defined as the given number's logarithm to the base value.
- The base value in the case of natural logarithm is e.
- The Math.log() method of math library can be used to calculate ln in Python.
- The Numpy.log() method of numpy library can be used to calculate ln in Python.
