Type Casting in Java
Type casting in Java is the process of converting one data type to another. It can be done automatically or manually. Automatic type casting occurs when a value of one data type is assigned to another compatible data type.
There are two types of casting: widening type casting and narrowing type casting.
Introduction to Type Casting in Java
First of all, let’s understand the literal meaning of Type Casting with context to programming. Type means the data type of a variable or entity and Casting means converting the data type of an entity to another data type.
Example
Let us see a quick example where we will convert a string to an integer using Integer.parseInt() method in Java.
Code:
Output:
Explanation:
- We have created a String variable s in the code above.
- Next, we have converted the string variable to an integer using Integer.parseInt() method.
What is Type Casting/Conversion in Java
Type casting, also known as type conversion, is the process of changing the data type of a variable in Java. It allows you to convert a variable from one type to another, either widening or narrowing the range of possible values.
Type casting is useful when you need to perform operations on variables of different types or when you want to assign a value of one type to a variable of another type. It can be seen in the above example, when we assigned the value of a String variable to an Integer.
Primitive Data types
There are eight types of primitive data types in Java as given below:
- byte
- short
- int
- long
- float
- double
- char
- boolean
Primitive data types in Java are like the different kinds of Lego blocks you can use to build something. Type casting is like when you need to change one Lego block into another to make it fit or work together with a different block.
Types of Casting in Java
Type Casting in Java is mainly of two types.
- Widening Type Casting
- Narrow Type Casting
Widening Type Casting in Java
Widening type casting refers to the conversion of a lower data type into a higher one. It is also known as implicit type casting or casting down. It happens on its own. It is secure since there is no possibility of data loss.
Widening Type Casting happens on the following scenarios or conditions:
- Both the data types must be compatible with each other. For example, converting a string to an integer is not possible as the string may contain alphabets that cannot be converted to digits.
- The target variable holding the type casted value must be larger than the value being type casted.
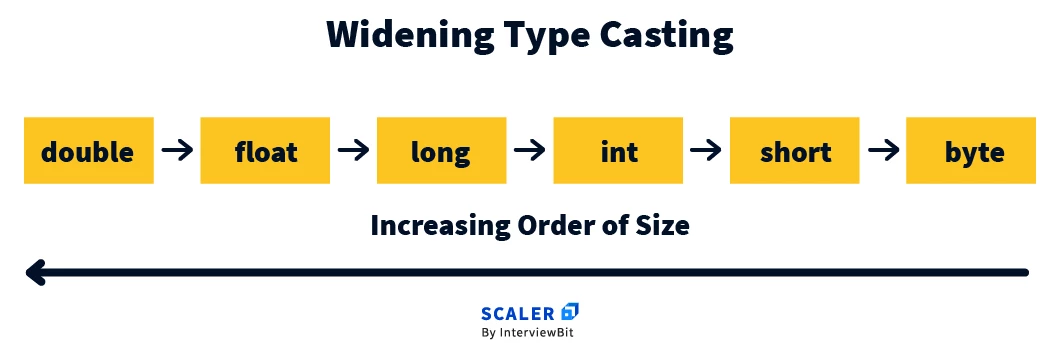
In the above image, double is larger data type than float, long, int, etc. Similarly, int is larger data type than short and byte. When converting from a lower data type to a larger data type, no loss of data occurs as the range of supported values is wider in the larger data type.
Example
Output:
Narrow Type Casting in Java (on default data types)
Narrowing Type Casting in Java refers to the conversion of a larger data type into a lower one. It is also known as explicit type casting or casting up. It does not happen on its own.
We must do it explicitly otherwise compile-time error is thrown.
Narrowing Type Casting in Java is not secure as loss of data can occur due to shorter range of supported values in lower data type.
Explicit Casting is done with the help of cast operator.
Syntax
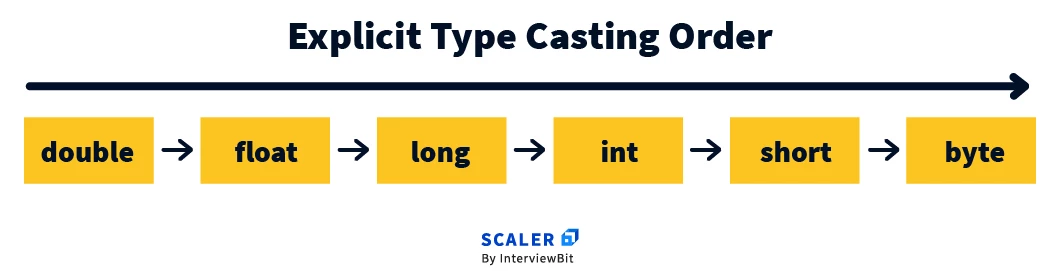
In the above image, int is a lower data type as compared to double, float, long, etc. When we convert a long to an int, it is possible that the value of the long variable is out of range of int variable.
Example 1:
Output:
Explanation:
- As it is visible in the code, there is loss of decimal digits after conversion from double to either short or int.
- We perform explicit type casting using the cast () operator and mentioning the name of target data type inside the brackets.
Lossy NarrowingType Casting in Java
Example of data loss:
Output:
Explanation:
- As you can see the output, i contains -2147483648. This is because the range of int is -2147483648 to 2147483647.
- And we are trying to store a value in i greater than its upper limit resulting in overflow situation.
Type Conversion in Java
Type conversion in Java refers to the process of converting one data type to another. It allows you to change the representation or format of a value to make it compatible with another data type.
There are two types of type conversion in Java:
Explicit Type Conversion
Explicit type conversion in Java, also known as type casting, is used when you want to convert a value of one data type to another data type that cannot be automatically done by the compiler.
Example 1: Converting an integer to a double
Example 2: Converting a double to an integer
Implicit Type Conversion
Implicit type conversion in Java, also known as automatic type promotion, occurs when the compiler automatically converts a value of one data type to another data type without requiring explicit instructions from the programmer.
Example 1: Converting an integer to a double
Example 2: Combining an integer with a long
Quick understanding of upcasting and downcasting
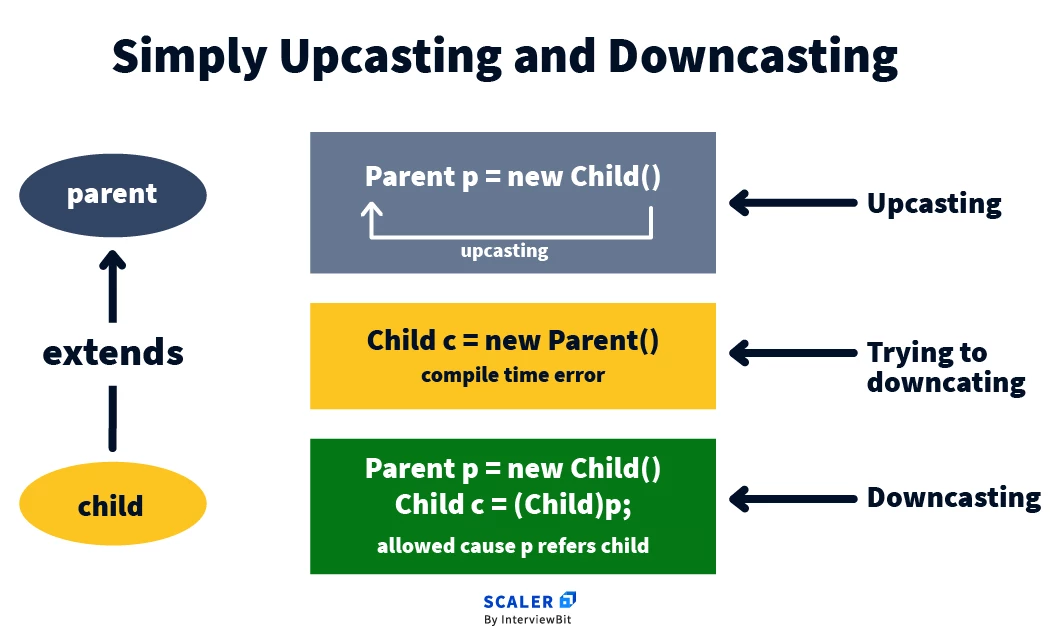
When does Automatic type conversion in Java?
Automatic type conversion occurs in Java when there is a need to convert a value from a smaller or narrower data type to a larger or wider data type.
Scenarios:
- Operations between different data types: Java automatically promotes smaller types to larger types for compatibility.
- Assignment to a larger type: Smaller values can be assigned to larger types without explicit conversion.
- Method parameter matching: Java automatically converts compatible argument types to match expected parameter types.
Advantages and Disadvantage of Explicit Type casting in Java
Advantages
- Precision Control: Explicit type casting allows precise control over data precision and range, ensuring accurate calculations or data representation.
- Data Compatibility: Explicit type casting enables seamless integration between different types, facilitating operations and assignments that require matching data types.
Disadvantages
- Data Loss: Explicit type casting can result in data loss or truncation when narrowing values from a larger type to a smaller type, potentially affecting accuracy and introducing inaccuracies.
- Potential Errors: Incorrect usage of explicit type casting can lead to runtime errors. Incompatible casting or exceeding the target type's range may cause unexpected behavior or exceptions, such as ClassCastException, resulting in program instability or crashes.
Difference Between Type Casting and Type Conversion in Java
| Type Casting | Type Conversion |
|---|---|
| Involves changing the data type of a variable. | Involves changing the representation or format of a value. |
| Performs conversion between compatible data types. | Can involve conversion between incompatible data types as well. |
| Requires explicit instructions using casting syntax. | Can be done implicitly by the Java compiler. |
| Can result in loss of data or precision if narrowing conversion is performed. | Can involve manipulation or transformation of data without necessarily changing the data type. |
| Example: (double) num converts num from an integer to a double explicitly. | Example: Integer.toString(num) converts num to a string without changing its data type. |
Conclusion
- Type Casting in Java refers to the process of converting one data type to another data type.
- The process of conversion of higher data type to lower data type is known as narrowing typecasting. It is also known as Explicit TypeCasting as it must be done explicitly.
- The process of conversion of lower data type to higher data type is known as widening typecasting. It is also called Implicit TypeCasting as it can be done implicitly by the compiler.

