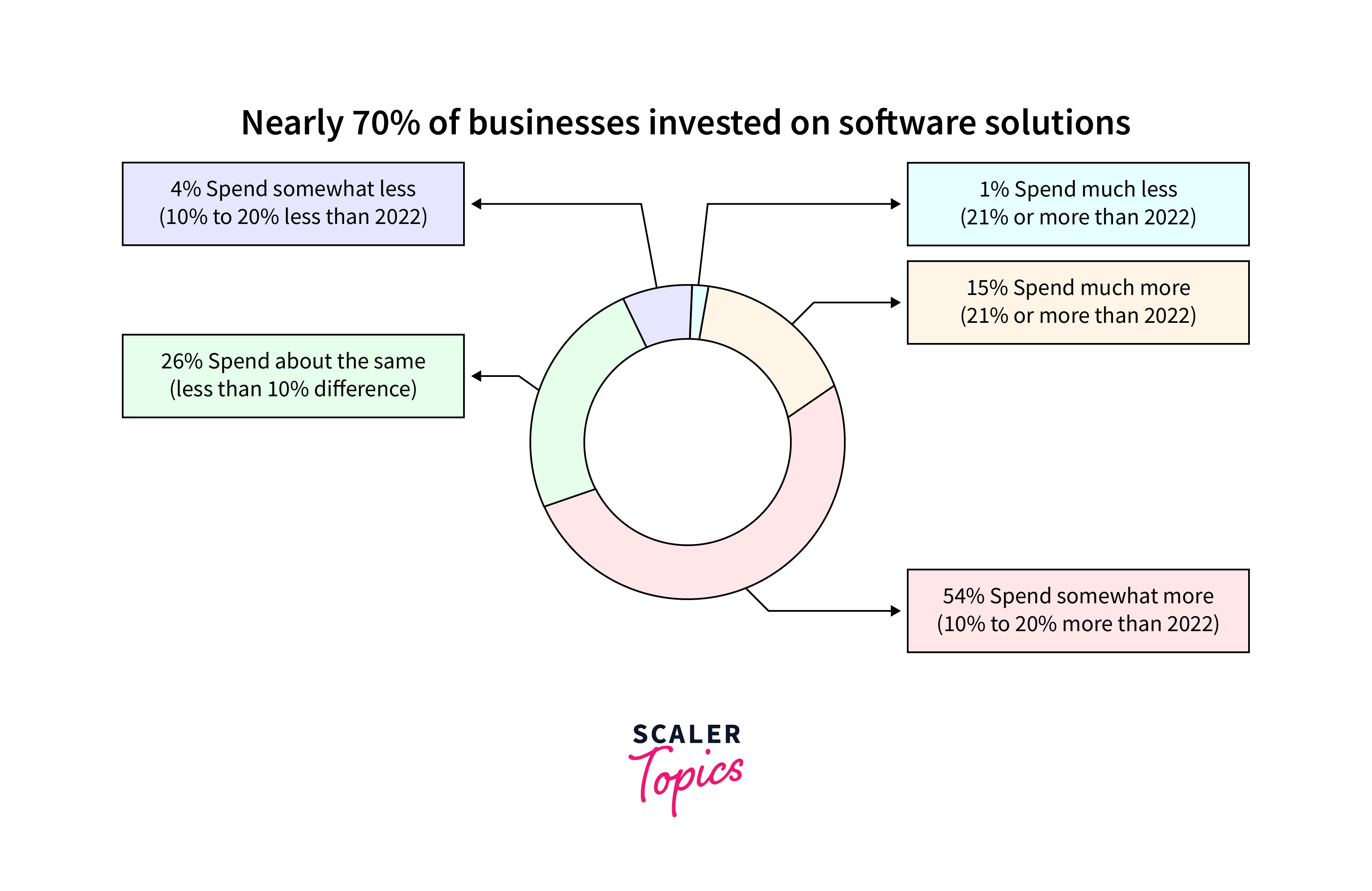
Latest Technologies in Software Industry
Several Latest technologies in the software industry are reshaping the landscape. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing data analysis and automation. Blockchain ensures secure and transparent transactions, while 5G technology enhances connectivity and speeds. DevOps methodologies streamline collaboration and deployment. Containers and Kubernetes optimize resource utilization and scalability. Microservices architecture enhances flexibility and scalability. Quantum computing promises breakthroughs in complex problem-solving. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) redefine user experiences. Edge computing minimizes latency in data processing. The rise of Low-Code/No-Code platforms empowers rapid application development. Staying abreast of these trends is crucial for professionals navigating the ever-evolving software landscape.
Generative AI
Generative AI leads in cutting-edge technology, enabling machines to create content akin to human work. This innovation sparks a revolution in industries, transforming tasks like text generation, image synthesis, and music composition.
Applications and Impact
Generative AI has diverse applications, offering opportunities in AI research, data science, and the creative industries. Mastering this tech opens doors to roles like:
Job Opportunities in Generative AI
- AI Researcher: Develop advanced generative models, pushing machine creativity boundaries.
- Data Scientist: Use generative AI for insights, driving informed decisions with vast datasets.
- Content Creator: Leverage generative AI for innovative storytelling in digital content.
- AI Ethics Consultant: Address ethical implications of AI-generated content, ensuring responsible use.
Future Prospects
Generative AI isn't just a tech trend; it's a paradigm shift in content creation. As its applications grow, mastering this tech promises a bright future, shaping industries and contributing to the evolution of AI.
Computing Power
Computing power drives the digital era, transforming every aspect of our lives. The current computing landscape, marked by data science, robotics, and IT, is dynamic and poised for continual improvement.
Current Landscape
In the digital age, nearly every device is computerized, and as we embrace 5G, anticipation for 6G grows, promising more power and interconnected devices.
Job Opportunities
Growing demand for computing power fuels tech jobs. Specialized qualifications, like Robotic Process Automation (RPA), lead to roles such as Data Scientist, AI Engineer, Robotics Researcher, AI Architect, and Robotics Designer.
Rise of RPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates business processes. While it may impact jobs, it creates opportunities for RPA developers, RPA Analysts, and RPA Architects.
Future Horizons
As cloud computing goes mainstream, Edge Computing emerges to address cloud computing limitations. It gives rise to roles like Cloud Reliability Engineer, Cloud Infrastructure Engineer, and DevOps Cloud Engineer.
Smart(er) Devices
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a driving force, going beyond simulating human behaviour to streamline and simplify our lives. In the evolving tech landscape, "Smart(er) Devices" are becoming indispensable, permeating various aspects of our lives.
AI's Role in Device Intelligence
Smarter devices leverage AI beyond automation, impacting home, work, and personal spaces. From AI-powered home robots to intelligent work devices, the influence of smart devices is set to extend well into 2024 and beyond.
Integral to Digital Transformation
In 2024, every job demands proficiency in smart software applications, making smarter devices essential in the IT industry. Roles like IT Manager, Data Scientist, Product Tester, Product Manager, Automation Engineer, and IT Researcher are increasingly sought after.
Expanding Job Landscape
As companies shift to digital spaces, the demand for professionals to understand and harness smart devices is rising, offering diverse opportunities across industries.
Skill Sets in Demand
Professionals entering this field should focus on developing IT and automation skills, crucial for navigating and optimizing smart software applications in an increasingly digitized world.
Datafication
Datafication is simply transforming everything in our lives into devices or software powered by data. So, in short, Datafication is the modification of human chores and tasks into data-driven technology. From our smartphones, industrial machines, and office applications to AI-powered appliances and everything else, data is here to stay for longer than we can ever remember! So, to keep our data stored correctly securely and safely, it has become an in-demand specialization in our economy.
Datafication leads to a higher need for IT professionals, data scientists, engineers, technicians, managers, and so much more. Even more useful is that anyone with a sound knowledge of technology can do a certification in data-related specializations to find a job in this space. Data jobs are more about skills than big-level qualifications. Let’s look at some popular data careers:
- Big Data Engineers
- Robotics Engineers
- IT Architect
- Business Intelligence Analyst
- Data Scientists
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
 In the dynamic landscape of technology, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning are pivotal players, reshaping how we engage with the world. While AI has already demonstrated its prowess in image recognition, speech processing, and personal assistants, the true potential of these technologies is just emerging.
In the dynamic landscape of technology, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning are pivotal players, reshaping how we engage with the world. While AI has already demonstrated its prowess in image recognition, speech processing, and personal assistants, the true potential of these technologies is just emerging.
As we step into 2024, AI is set to revolutionize various sectors. Beyond its current applications, AI will analyze interactions, unveil hidden patterns, and enhance decision-making processes. Predicting demand in healthcare, optimizing resource allocation, and real-time analysis of customer behaviour are just glimpses of AI's expanding role.
Complementing AI, Machine Learning empowers systems to learn from data and improve performance iteratively. The demand for skilled professionals in this field is skyrocketing, with predictions indicating that AI, Machine Learning, and automation will create 9 per cent of new U.S. jobs by 2025. For aspiring professionals, lucrative opportunities abound in the realm of AI and Machine Learning:
- AI Research Scientist: Contribute to cutting-edge AI development by creating advanced models and algorithms, pushing the boundaries of machine capabilities.
- AI Engineer: Implement AI solutions at the forefront, crafting systems that enhance efficiency and solve complex problems across diverse industries.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Specializes in developing algorithms that enable systems to learn and adapt, making them more intelligent over time.
- AI Architect: Shape the architectural foundations of AI systems, ensuring scalability, efficiency, and alignment with organizational goals.
Mastering AI and Machine Learning not only secures high-paying jobs but also positions individuals at the forefront of shaping the future of human-machine interactions. The journey into the latest technologies in the software industry is a thrilling exploration into uncharted territories of innovation, promising limitless possibilities for those ready to seize them.
Extended Reality (ER)
Extended Reality (ER) is a transformative technology encompassing various immersive experiences, including Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). In 2024, ER stands out as a significant technology trend, breaking conventional boundaries and creating digital environments that redefine how we interact with the world.
- Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in entirely artificial environments, captivating individuals in a computer-generated reality. VR finds applications in diverse sectors such as gaming, medical training, and virtual tourism.
- Augmented Reality (AR) enhances the real world by overlaying digital information onto physical environments. AR is not limited to smartphones but extends to smart glasses and other wearable devices. It plays a crucial role in fields like education, navigation, and maintenance.
- Mixed Reality (MR) combines aspects of both VR and AR, creating environments where digital and physical elements coexist and interact. This technology blurs the lines between the real and virtual worlds, offering unique experiences in industries like design, architecture, and collaborative workspaces.
In terms of career opportunities, ER presents a wealth of possibilities. Roles such as Extended Reality Architect, Front Lead Engineer, and Software Developer are in high demand. Moreover, the gaming industry benefits significantly from ER, providing opportunities for Game Designers and Pro Gamers to thrive in this dynamic landscape.
As ER continues to evolve, its impact extends beyond entertainment to revolutionize education, healthcare, and various industries. Professionals embracing ER will find themselves at the forefront of shaping how individuals perceive and engage with the digital realm.
Digital Trust
Digital Trust is a crucial trend rooted in the growing reliance on digital technologies. As of 2024, with pervasive technology integration, digital trust is paramount.
Significance:
In a world deeply intertwined with technology, maintaining digital trust assures users of a secure digital environment, allowing innovation without compromising public confidence.
Specializations:
Two key specializations fostering a safer digital space are Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking, identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring ethical use of technology.
Top Jobs:
- Cybersecurity Analyst: Cybersecurity analysts play a critical role in safeguarding an organization's computer systems and networks from cyber threats. They continuously monitor and analyze security alerts, respond to incidents, and implement security measures to protect sensitive data. Cybersecurity analysts also conduct risk assessments, identifying potential vulnerabilities and recommending solutions to enhance the overall security posture.
- Penetration Tester: Also known as ethical hackers, penetration testers simulate cyber-attacks to identify vulnerabilities in a system before malicious hackers can exploit them. They use various tools and techniques to assess the security of networks, applications, and infrastructure. Penetration testers provide valuable insights into potential weaknesses, enabling organizations to proactively address and fortify their defences against real-world threats.
- Security Engineer: Security engineers design, implement and manage security solutions for digital systems. They work closely with other IT professionals to integrate security measures into the overall infrastructure. Security engineers may be involved in configuring firewalls, implementing encryption protocols, and ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations. Their goal is to create a robust security framework that safeguards digital assets.
- Security Architect: Security architects focus on the overall design and structure of an organization's digital security. They develop and maintain security policies, standards, and guidelines. Security architects work to create a cohesive and comprehensive security infrastructure, considering factors such as access controls, encryption, and authentication methods. They collaborate with other IT professionals to ensure that security measures are seamlessly integrated across the organization.
- Security Automation Engineer: As organizations face an increasing number of cyber threats, security automation engineers play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and responsiveness. They develop and implement automated processes for tasks such as threat detection, incident response, and system monitoring. Security automation engineers leverage scripting and programming skills to create workflows that streamline security operations, allowing for faster response times and more effective mitigation of potential risks.
- Network Security Analyst: Network security analysts focus on protecting an organization's network infrastructure. They monitor network traffic, analyze security logs, and implement measures to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches. Network security analysts are responsible for configuring and maintaining firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, and other network security tools. They stay informed about emerging threats and continuously update security protocols to ensure the resilience of the organization's network against evolving cyber threats.
Educational Paths:
Interested individuals can pursue certifications in ethical hacking or obtain a diploma/master's in cybersecurity for high-salary roles. Continuous learning is crucial due to evolving cyber threats.
As digital interactions grow, establishing digital trust remains critical. Cybersecurity and ethical hacking professionals are pivotal in creating a secure digital landscape.
3D Printing
3D Printing is a transformative technology trend revolutionizing manufacturing processes, turning digital designs into tangible objects across industries in 2024.
Key Aspects:
This technology creates three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on a digital model. Now a reality, 3D printing influences healthcare, manufacturing, and design, offering possibilities for customization, rapid prototyping, and cost-effective production.
Applications:
In biomedical and industrial sectors, 3D printing excels. From prosthetics and organs to intricate industrial components, it exceeds expectations by transforming digital concepts into tangible items.
Jobs in 3D Printing:
Skilled professionals are in demand, with positions such as:
- CX Program Manager: Overseeing customer experience programs for 3D printing products.
- 3D Printer Engineer: Managing and optimizing 3D printing equipment and processes.
- Emulation Prototyping Engineer: Creating prototypes using 3D printing for emulation.
- Robotics Trainer: Integrating robots for 3D printing automation.
- AI Engineer: Using artificial intelligence with 3D printing processes.
- Operations Manager: Overseeing 3D printing facility operations.
- Organ & Prosthetic Designer: Designing organs and prosthetics using 3D printing.
Education and Skills:
Professionals need a solid understanding of AI, Machine Learning, Modeling, and 3D printing processes. Continuous learning is essential in this dynamic field.
Genomics
Genomics is a groundbreaking technology trend studying and manipulating an organism's entire genetic material, profoundly impacting healthcare in 2024.
Applications and Significance:
Genomics analyzes genes, deepening our understanding of DNA. It promises personalized medical treatments based on genetic predispositions, enhancing disease prevention and treatment. Genomics identifies genetic markers for various conditions.
Top Jobs in Genomics:
The field offers technical and non-technical roles, including:
- Bioinformatics Analyst: Analyzing genomic data for insights.
- Genome Research Analyst: Researching genome intricacies.
- Full Stack Developer: Building software for genomic data analysis.
- Software Engineer: Developing tools for genomic research.
- Bioinformatician: Applying computational techniques to biological data.
- Genetics Engineer: Manipulating genes for diverse applications.
Educational Paths:
Aspiring individuals need a blend of programming, data analysis, and biology skills. Specialized roles may require advanced degrees in bioinformatics or genetics.
Future Impact:
Genomics will revolutionize healthcare by offering targeted and personalized treatments. Professionals in genomics will be pivotal in unlocking genetic information's potential for improved patient outcomes.
New Energy Solutions
New Energy Solutions emerge as a pivotal technology trend, reflecting a global shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly energy alternatives. In 2024, this trend is reshaping the energy landscape, fostering innovation, and addressing environmental concerns.
Significance:
The world's commitment to a greener future has led to the rise of New Energy Solutions. This entails a paradigm shift in energy consumption, with a focus on minimizing carbon footprints and harnessing renewable sources. Electric vehicles, solar power, and biotechnology are among the forefronts of this transformative trend.
Top Jobs in New Energy:
The transition to New Energy Solutions has given rise to career opportunities in various fields. Notable positions include:
- Energy Specialist (Solar, Thermal, Hydro-power, etc.): Designing and implementing sustainable energy solutions.
- Solar Plant Design Energy: Creating efficient designs for solar power plants.
- Climate Strategy Specialist: Developing strategies to address climate-related challenges.
- Project Manager: Overseeing projects related to the implementation of new energy technologies.
- Chemical Energy Biotechnology Specialist: Applying biotechnology for sustainable energy solutions.
- Renewable Energy Technologist: Researching and implementing technologies for renewable energy sources.
Educational Paths:
Professionals entering the realm of New Energy Solutions often require expertise in science and social science qualifications. Specializations in renewable energy, biotechnology, and climate science pave the way for impactful careers in this dynamic and evolving field.
Future Outlook:
As the world embraces cleaner energy alternatives, the demand for skilled individuals in New Energy Solutions is set to grow, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious global energy landscape.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a transformative technology trend automating business processes, reshaping work dynamics in 2024.
Significance:
RPA uses software to automate tasks, impacting knowledge-worker jobs and creating new opportunities.
Top Jobs in RPA:
- RPA Developer: Implements automated solutions.
- RPA Analyst: Optimizes processes.
- RPA Architect: Designs overall RPA architecture.
Impact on Jobs:
Forrester Research notes threats to some jobs, but McKinsey highlights a net positive effect. Only about 5% of occupations can be entirely automated, leaving room for adaptability in roles requiring creativity.
Educational Paths:
Mastering RPA opens doors for IT professionals to high-paying roles in development, project management, business analysis, and solution architecture.
As RPA evolves, professionals with expertise are well-positioned to navigate the changing landscape, contributing to increased efficiency in various industries.
Edge Computing
Edge Computing is a pivotal technology trend diverging from traditional cloud computing. In 2024, it addresses the limitations of centralized processing by enabling data processing closer to the source.
Significance:
As the quantity of data surges, Edge Computing mitigates latency issues caused by centralized cloud computing. It processes data closer to where it's needed, fostering quicker response times and efficient real-time processing.
Top Jobs in Edge Computing:
- Cloud Reliability Engineer: Ensures reliability of edge computing solutions.
- Cloud Infrastructure Engineer: Manages and optimizes edge computing infrastructure.
- Cloud Architect and Security Architect: Designs secure and efficient edge computing architectures.
Impact on Industries:
As a response to the shortcomings of cloud computing, Edge Computing finds applications in scenarios demanding quick data processing. It's crucial for industries requiring real-time insights, such as healthcare, manufacturing, and autonomous vehicles.
Educational Paths:
Staying aligned with cloud computing trends, mastering Edge Computing opens doors to jobs at the intersection of technology and data, providing solutions for the evolving demands of decentralized processing.
Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing is a revolutionary technology trend leveraging quantum phenomena for computing power. As of 2024, it surpasses traditional computing capabilities, offering unprecedented speed and potential applications.
Significance:
Quantum Computing exploits superposition and entanglement, enabling vast computational possibilities. Its applications extend from medical research to finance, and it plays a pivotal role in addressing global challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Top Players and Innovations:
Major tech giants, including Splunk, Honeywell, Microsoft, AWS, and Google, are actively contributing to Quantum Computing advancements. Innovations in quantum algorithms, cryptography, and machine learning mark significant strides.
Jobs in Quantum Computing:
To excel in Quantum Computing, one needs expertise in quantum mechanics, linear algebra, probability, information theory, and machine learning. Jobs include quantum researcher, algorithm developer, and quantum data scientist.
Global Market Projection:
The global quantum computing market is projected to exceed $2.5 billion by 2029. Quantum Computing’s ability to query, monitor, analyze, and act on data is crucial for sectors like finance, healthcare, and high-frequency trading.
Future Impact:
Quantum Computing is not merely an evolution but a revolution in computational power. Its ability to solve complex problems and optimize processes will reshape industries, making it an indispensable technology for future scientific breakthroughs and technological innovations.
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) represent exceptional technology trends, seamlessly blending digital and physical worlds. In 2024, these immersive technologies extend beyond gaming, influencing diverse sectors.
Significance:
While primarily associated with gaming, VR and AR find applications in training, education, healthcare, marketing, and rehabilitation. The convergence of these technologies enhances experiences, offering innovative solutions.
Top Applications:
Working in tandem with other emerging technologies, AR and VR promise transformative impacts. From training doctors in surgery to providing deeper museum experiences, their potential spans training, entertainment, education, marketing, and more.
Career Opportunities:
Entering 2024, jobs in AR and VR are accessible with basic programming skills and a forward-thinking mindset. Roles include Extended Reality Architect, Front Lead Engineer, Software Developer, AR/VR Support Engineers, Game Designers, and Pro Gamers.
Future Integration:
As AR and VR become further integrated into daily life, their adoption is poised to grow. Applications in training, entertainment, education, marketing, and rehabilitation will continue to expand, making AR and VR integral components of various industries.
Evolutionary Impact:
VR and AR are at the forefront of transforming how we perceive and interact with the digital realm. As advancements continue, their combined potential will contribute to shaping the future of human-computer interaction.
Blockchain
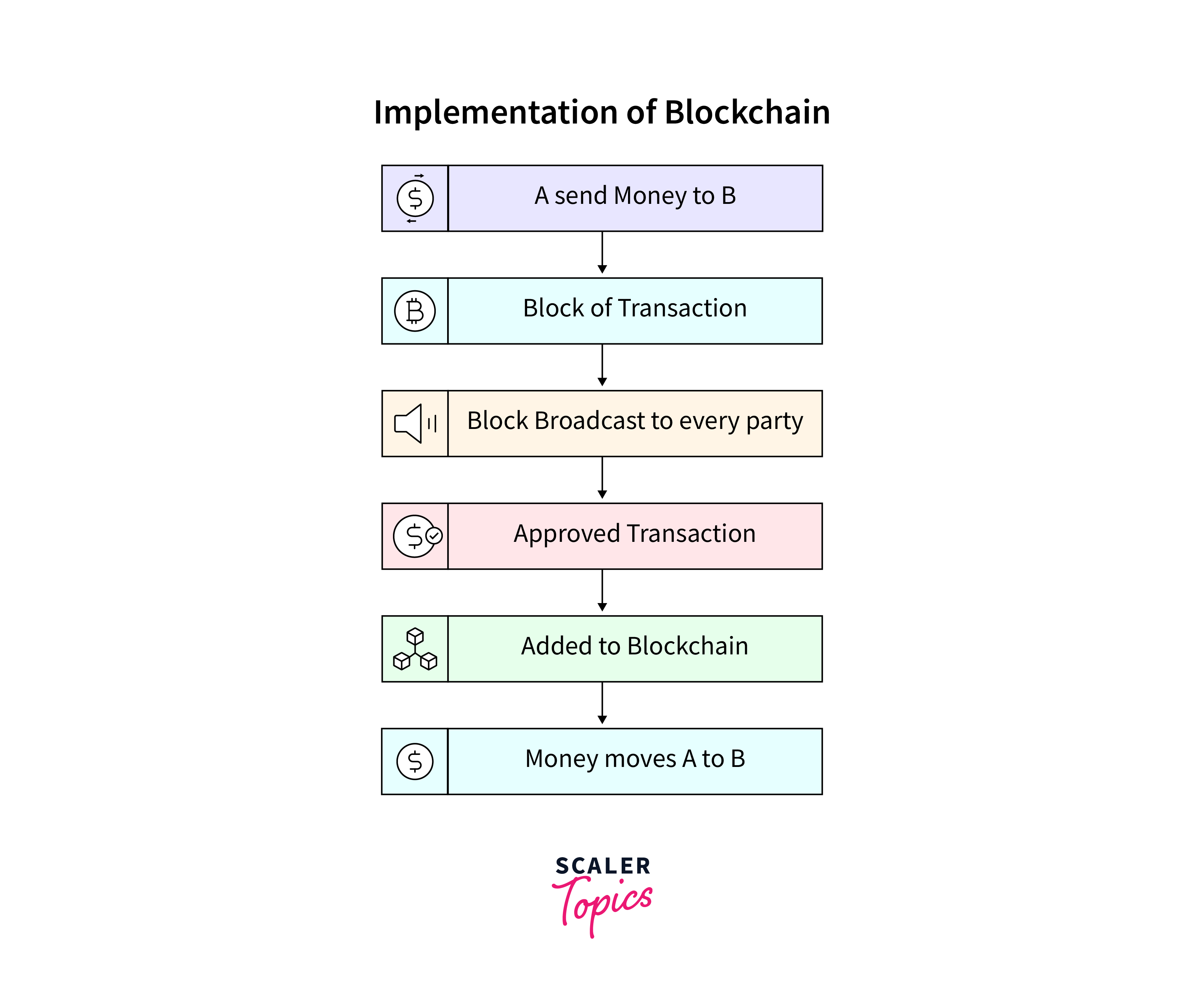
Blockchain technology goes beyond cryptocurrency, offering security with widespread implications. In 2024, its significance in industries grows, reshaping data management and transactions.
Significance:
Blockchain is a secure, transparent, and decentralized data structure, ensuring data integrity with unchangeable blocks. Initially tied to cryptocurrencies, its applications now span various sectors.
Top Players and Applications:
With security at its core, Blockchain is embraced by major industries. From financial transactions to supply chain management, it promises transparency and trust. Key players include Risk Analysts, Tech Architects, Crypto Community Managers, and Front End Engineers.
Educational Pathways:
To enter the Blockchain realm, individuals need experience in programming, databases, data structures, web app development, and networking. Mastering it opens avenues for roles at the intersection of technology and finance.
Future Outlook:
As organizations recognize the need for secure transactions, the demand for Blockchain experts rises. It will revolutionize how businesses handle transactions and data, offering a paradigm shift in secure online interactions.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a transformative technology trend, connecting devices, appliances, and systems to the internet. In 2024, it extends beyond consumer applications, revolutionizing industries with its ability to gather, analyze, and exchange data.
Significance:
In the IoT landscape, numerous "things" are equipped with Wi-Fi connectivity, enabling them to exchange data and connect to the internet. This interconnectivity spans from smart home devices to industrial machinery, ushering in a new era of efficiency and data-driven decision-making.
Consumer Impact:
IoT applications already benefit consumers by allowing remote control of devices, from smart home features to fitness trackers. However, its potential extends to predictive maintenance, improved healthcare, and enhanced customer service.
Industrial Revolution:
Businesses are leveraging IoT to enhance safety, optimize processes, and improve customer experiences. From manufacturing to healthcare, the ability to collect and analyze real-time data is reshaping industries.
Educational Paths:
To delve into the IoT realm, individuals need expertise in information security, AI and machine learning fundamentals, networking, hardware interfacing, data analytics, and automation. Proficiency in embedded systems and device design is also crucial.
Future Projection:
With an estimated 50 billion IoT devices in use globally by 2030, the IoT's impact on industries is poised to grow exponentially. Staying updated with IoT trends positions individuals for a future where connected devices play an integral role in shaping a more efficient and data-driven world.
5G
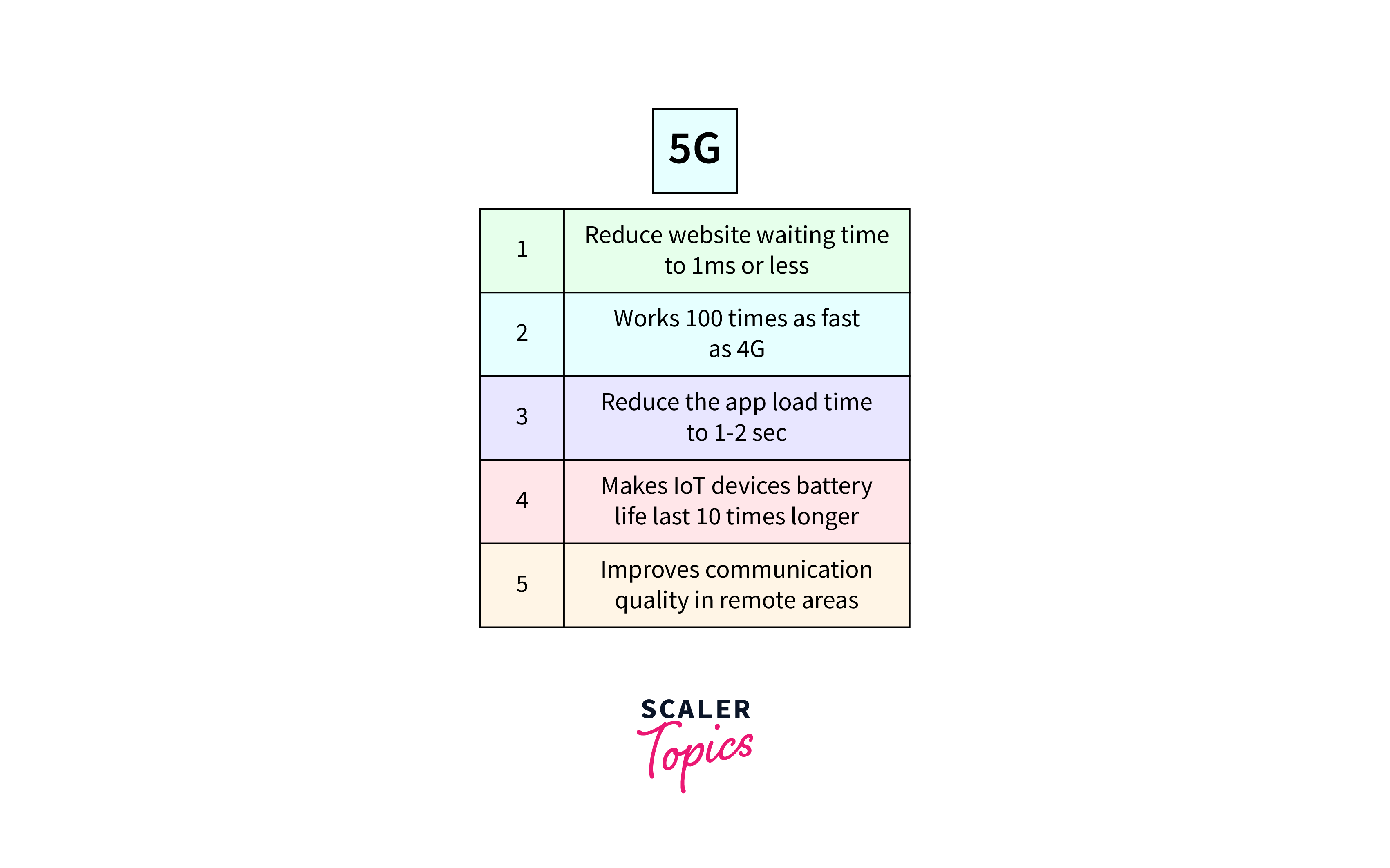 5G is the next transformative technology trend, promising to revolutionize our digital experiences. By 2024, it surpasses its predecessors, enabling advanced applications and services.
5G is the next transformative technology trend, promising to revolutionize our digital experiences. By 2024, it surpasses its predecessors, enabling advanced applications and services.
Significance:
Building on the foundations of 3G and 4G, 5G takes a quantum leap, introducing revolutionary changes. It goes beyond internet browsing, facilitating advanced technologies like AR, VR, and cloud-based gaming.
Applications:
5G services bring heightened bandwidth, supporting services reliant on AR, VR, and cloud-based gaming like Google Stadia and NVidia GeForce Now. Industries benefit from improved safety, traffic management, and smart grid control.
Global Players:
Major telecom companies such as Verizon, T-Mobile, Apple, Nokia Corp, and QualComm actively contribute to the development of 5G applications, marking it as an emerging technology trend to watch.
Future Projection:
Anticipated to reach 4.4 billion subscriptions by the end of 2027, 5G represents a pivotal technology trend. Its impact on diverse sectors, from communication to entertainment, makes it an essential focus for those seeking to stay abreast of the evolving digital landscape.
Cyber Security
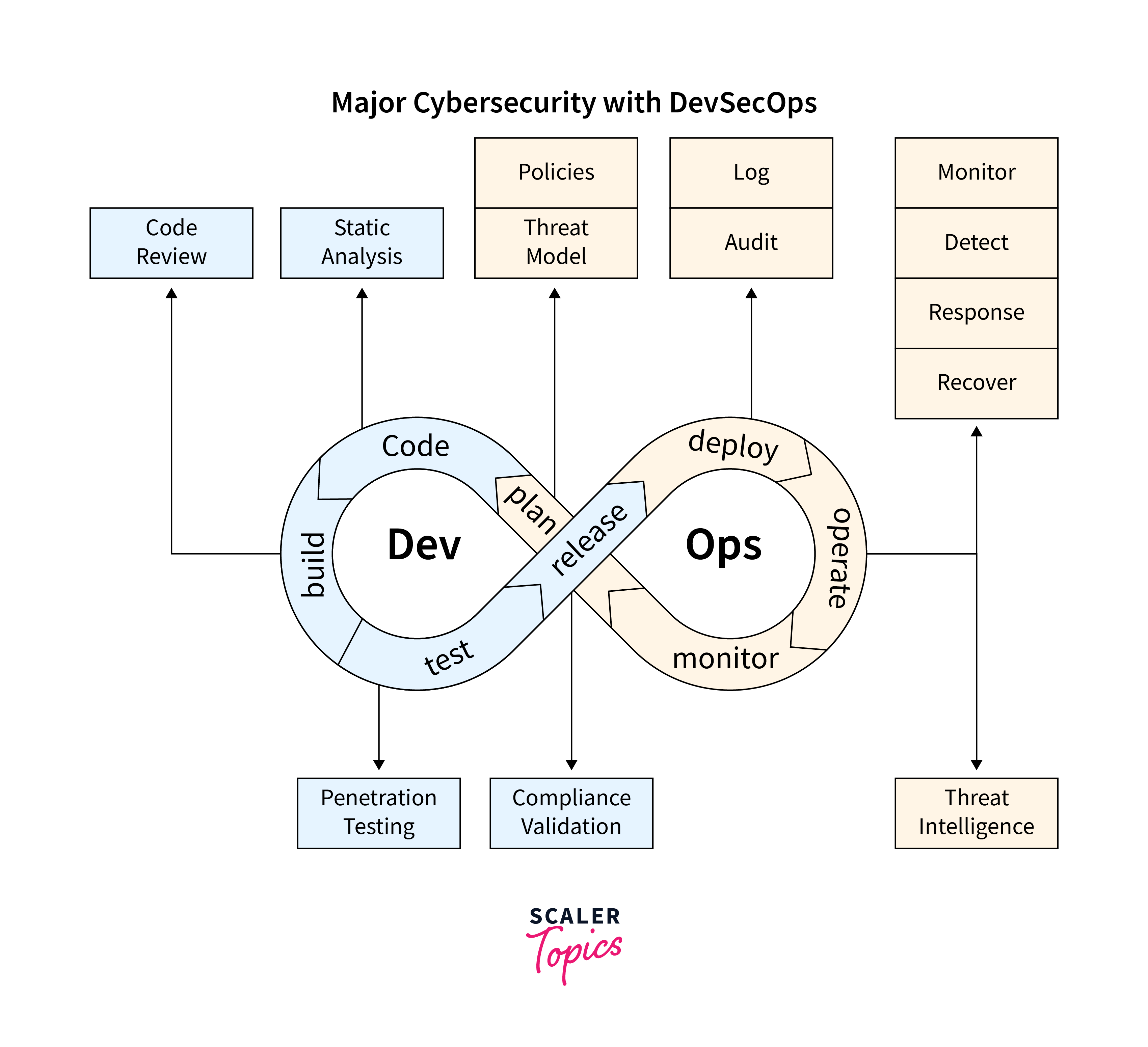 Cybersecurity, though not a new concept, remains a critical and evolving technology trend in 2024. The persistent threat from malicious hackers drives continuous innovation in safeguarding digital assets.
Cybersecurity, though not a new concept, remains a critical and evolving technology trend in 2024. The persistent threat from malicious hackers drives continuous innovation in safeguarding digital assets.
Significance:
As of 2024, cybersecurity is more crucial than ever. Organizations prioritize it as a primary determinant in third-party transactions and engagements, emphasizing its role in maintaining trust and security.
Top Roles:
Careers in cybersecurity range from Ethical Hacker to Chief Security Officer, offering lucrative six-figure incomes. Specializations like penetration testing, security engineering, and network security analysis are in high demand.
Education and Certification:
Entering the field may require professional certifications for ethical hacking and a diploma or master's qualification for broader cybersecurity roles. The industry values skills and expertise in ensuring a safe digital environment.
Evolutionary Challenge:
As threats evolve, cybersecurity remains a trending technology because of its constant adaptation. The field not only defends against cyber threats but also contributes to building a trustworthy digital world.
Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development is a versatile practice encompassing both front-end (user interface) and back-end (server-side) components of web or software applications. In 2024, it stands out as a pivotal technology trend, responding to the demand for developers proficient in the entire software stack
Versatility and Efficiency:
Full Stack Developers demonstrate proficiency in multiple programming languages and technologies, facilitating end-to-end solutions efficiently. This trend streamlines the development process, enabling faster product development and deployment.
Top Skills:
Mastering Full Stack Development involves a comprehensive skill set, including knowledge of programming languages, OOPS fundamentals, databases, data structures, web app development, and networking. Developers need a holistic understanding to create seamless user experiences.
Industry Impact:
Businesses seek Full Stack Developers for their ability to navigate both front-end and back-end development. This trend addresses the growing need for versatile developers capable of contributing to various aspects of software development.
Continuous Learning:
Staying updated with latest technologies in software industry is vital for Full Stack Developers. The dynamic nature of this trend requires individuals to engage in continuous learning and skill development to adapt to evolving industry demands.
Future Prospects:
As businesses prioritize efficiency and versatility in software development, the demand for skilled Full Stack Developers is expected to persist. This technology trend remains a solid pathway for those seeking a comprehensive role in the software development landscape.
DevOps
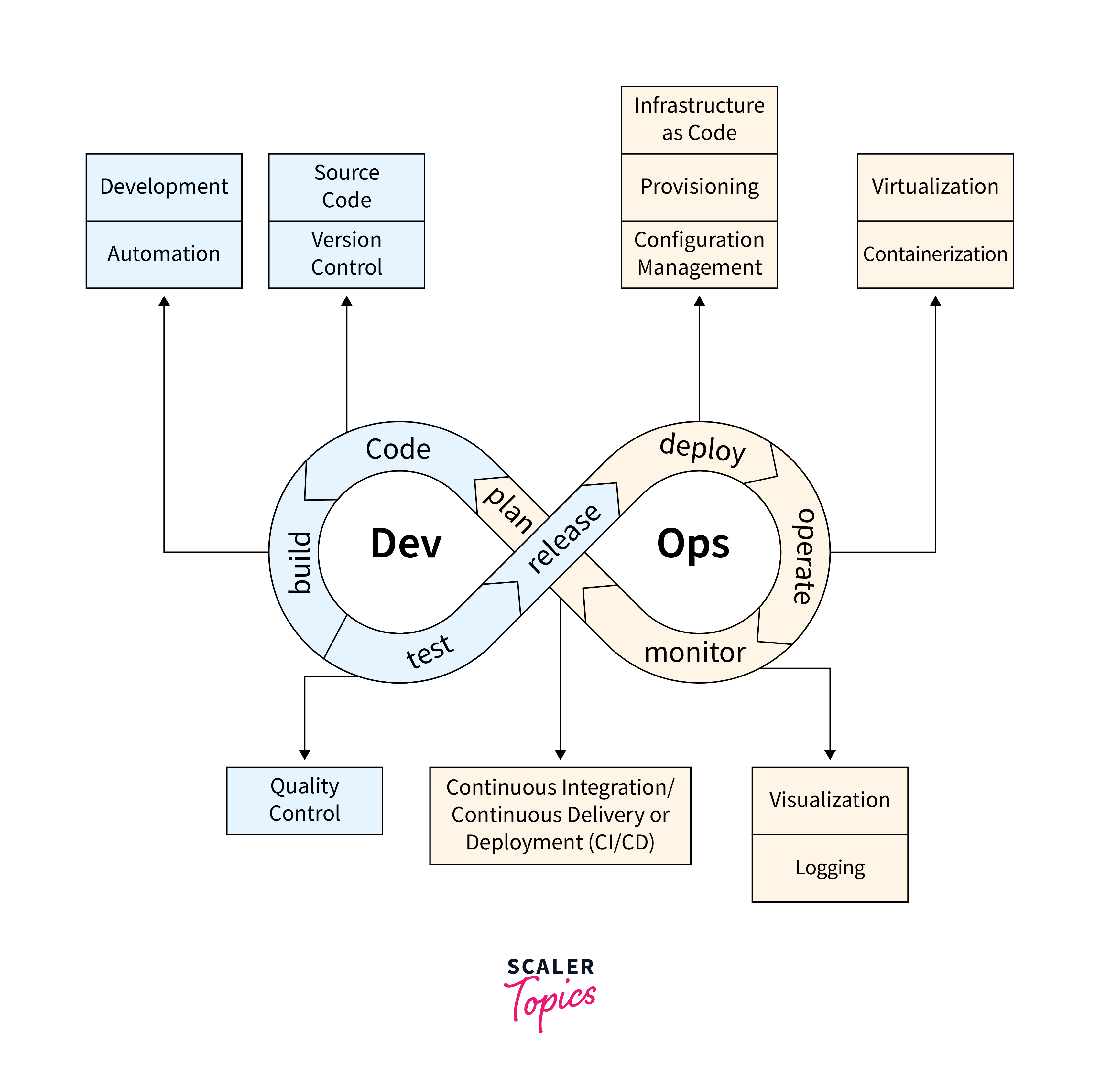 DevOps is a transformative set of practices fostering collaboration and communication between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) teams. In 2024, it continues to reshape the software development and deployment lifecycle, emphasizing automation and streamlined processes.
DevOps is a transformative set of practices fostering collaboration and communication between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) teams. In 2024, it continues to reshape the software development and deployment lifecycle, emphasizing automation and streamlined processes.
Collaborative Efficiency:
DevOps aims to break down silos between development and operations, fostering collaboration throughout the software development lifecycle. This collaborative approach leads to faster development cycles and improved software quality.
Key Practices:
Core DevOps practices include continuous integration, continuous delivery, infrastructure as code, and automated testing. These practices contribute to more frequent and reliable releases, enhancing agility in responding to changes and customer needs.
Industry Impact:
Adopting DevOps principles has a profound impact on software development. It leads to increased efficiency, reduced development cycles, and improved software quality. Businesses embracing DevOps practices can respond more effectively to dynamic market demands.
Continuous Learning:
DevOps professionals engage in continuous learning to stay abreast of emerging tools and methodologies. The ever-evolving nature of technology requires individuals in this trend to adapt and incorporate new practices for enhanced efficiency.
Future Outlook:
The adoption of DevOps principles is expected to grow as businesses recognize the benefits of collaborative and automated approaches to software development. As a technology trend, DevOps remains instrumental in achieving faster, more reliable, and efficient software development and deployment.
Metaverse
The Metaverse is a transformative technology trend, shaping a virtual, interconnected digital universe where users engage in real-time interactions with both digital environments and each other. In 2024, this emerging concept converges augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and various latest technologies in software industry to create immersive, shared experiences.
Immersive Connectivity:
The Metaverse transcends traditional virtual experiences, offering a seamless blend of AR and VR technologies. Users can interact with digital elements and other users, fostering a sense of presence in a shared digital space.
Applications Across Sectors:
Companies explore diverse applications for the Metaverse in gaming, social networking, education, healthcare, and beyond. This technology trend introduces innovative ways for individuals and businesses to connect and collaborate in digital spaces.
Future Transformations:
The Metaverse is anticipated to reshape communication, entertainment, and business collaboration. Its potential impact extends to creating new forms of online engagement, virtual economies, and interactive educational experiences.
Technology Convergence:
Achieving the vision of the Metaverse*involves the convergence of various technologies, including AR, VR, and advancements in networking. This trend underscores the integration of digital and physical worlds for a more immersive and interconnected digital experience.
Exploration and Innovation:
As businesses and individuals explore the possibilities of the Metaverse, ongoing innovation is expected. This technology trend signifies a shift toward a new era of interconnected digital spaces, offering exciting opportunities for creativity, collaboration, and digital engagement.
Digital Twins
Digital Twins are virtual replicas of physical objects, processes, or systems, created using data from sensors, IoT devices, and other sources. In 2024, this technology trend enables organizations to monitor, simulate, and analyze real-world assets and operations in a virtual environment.
Data-Driven Replicas:
Digital Twins are created by collecting and processing data from sensors and other sources. These virtual replicas offer a comprehensive understanding of physical objects, facilitating optimization and analysis.
Optimization Across Industries:
Digital Twins find applications in manufacturing, urban planning, healthcare, and more. Organizations leverage them to optimize processes, improve decision-making, and enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Real-Time Monitoring:
By offering real-time monitoring capabilities, Digital Twins empower organizations to track and analyze the performance of physical assets. This trend contributes to predictive maintenance, ensuring optimal functionality.
Integration of IoT:
The creation of Digital Twins involves integrating data from IoT devices, sensors, and various sources. This integration provides a holistic view, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and improvements.
Efficiency and Sustainability:
As a technology trend, Digital Twins align with the broader goals of efficiency and sustainability. By digitally representing physical entities, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement changes in a virtual environment before making real-world adjustments.
FAQs
Q. What are technology trends?
A. Technology trends refer to the prevailing developments, innovations, and advancements in the world of technology. These trends often shape the direction of industries, businesses, and society as a whole, influencing how we interact, work, and live. The provided text discusses various technology trends such as generative AI, computing power, smart devices, datafication, artificial intelligence, and more.
Q. Why are technology trends important?
A. Following technology trends is crucial for individuals and businesses alike because it allows them to stay competitive and relevant in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. The text emphasizes the importance of staying current with latest technologies in software industry to secure future job opportunities and thrive in a dynamic, contactless world.
Q. How do you keep up with technology trends?
A. The text suggests several ways to stay updated with technology trends, including:
- Following reputable technology news sources
- Subscribing to industry newsletters
- Attending conferences and webinars
- Participating in online communities
- Engaging in continuous learning and skill development.
These practices help individuals and professionals stay informed and adapt to the evolving tech landscape.
Q. How is technology changing the world?
A. The text discusses how technology is changing the world by introducing various trends such as generative AI, computing power, smart devices, datafication, artificial intelligence, and more. These technologies are influencing diverse sectors, from healthcare and finance to entertainment and education, reshaping how people live, work, and interact.
Q. What are the 4 ages of technology?
A. The concept of the "Four Ages of Technology" is not universally standardized, but a common framework includes:
- Pre-Mechanical Age: Early manual tools and basic machines.
- Mechanical Age: Introduction of machinery during the Industrial Revolution.
- Electromechanical Age: Integration of electrical components into mechanical systems.
- Information Age (Digital Age): Rise of digital technology, computers, and the internet.
Conclusion
- Rapid development in AI and ML technologies is reshaping automation, decision-making, and user experiences.
- Integration of Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR) is redefining digital interactions and creating immersive user experiences.
- Turning activities into data is enhancing insights, decision-making, and user personalization, emphasizing the importance of digital trust and cybersecurity.
- Advancements in computing power and exploration of quantum computing are expanding computational capabilities.
- The rollout of 5G networks and the proliferation of IoT devices are revolutionizing connectivity and fostering a highly interconnected digital ecosystem.
- Concepts like the metaverse, digital twins, and blockchain are reshaping digital interactions, offering virtual replicas, and providing decentralized solutions.
