How To Encrypt A File On Linux?
Securing the privacy and security of sensitive information is crucial in the current digital era. File encryption is a fundamental method used by Linux, a popular open-source operating system, to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorised access. For file encryption, Linux provides a variety of reliable tools and techniques, with the GNU Privacy Guard (GPG) standing out as a well-liked option. Using powerful encryption algorithms, GPG, which is based on the Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) standard, enables Linux users to encrypt data. Personal, financial, and secret information may be protected by encrypting files to stop unauthorised parties from accessing them. Users working with sensitive documents like financial data, medical information, or intellectual property need to take extra precautions to ensure their protection.
The Command-line Method of Encrypting Files
Encrypting files on Linux using the command line can be done using GNU Privacy Guard (GPG), a powerful encryption tool. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to encrypt files in linux using the command line method:
Open a Terminal Window and Generate a GPG Key

- Launch the terminal application on your Linux system. You can typically find it in the applications menu or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+T.
- Generate a GPG key pair by entering the command gpg --full-generate-key in the terminal. This will initiate the key generation process.
- You will be prompted to choose the key type. Select option 1 for RSA and RSA.
- Next, specify the key size. Enter the desired key size, such as 4096 for a strong key.
- Set the key validity period by entering the duration for which the key should remain valid. For example, you can enter 0 for no expiration.
- Provide your details, including your name and email address associated with the key.
- Finally, set a strong passphrase to protect your private key. Make sure to remember this passphrase as it will be required for decryption.
Change into the Directory Housing the File
Navigate to the directory where the file you want to encrypt is located. Use the cd command followed by the directory path. For example,
Encrypt the File
- Once you are in the correct directory, use the command gpg --encrypt --recipient <recipient> <filename> or gpg --e --r <recipient> <filename> to encrypt the file. Replace <recipient> with the intended recipient's key ID or email address, and <filename> with the name of the file you wish to encrypt. For Example:
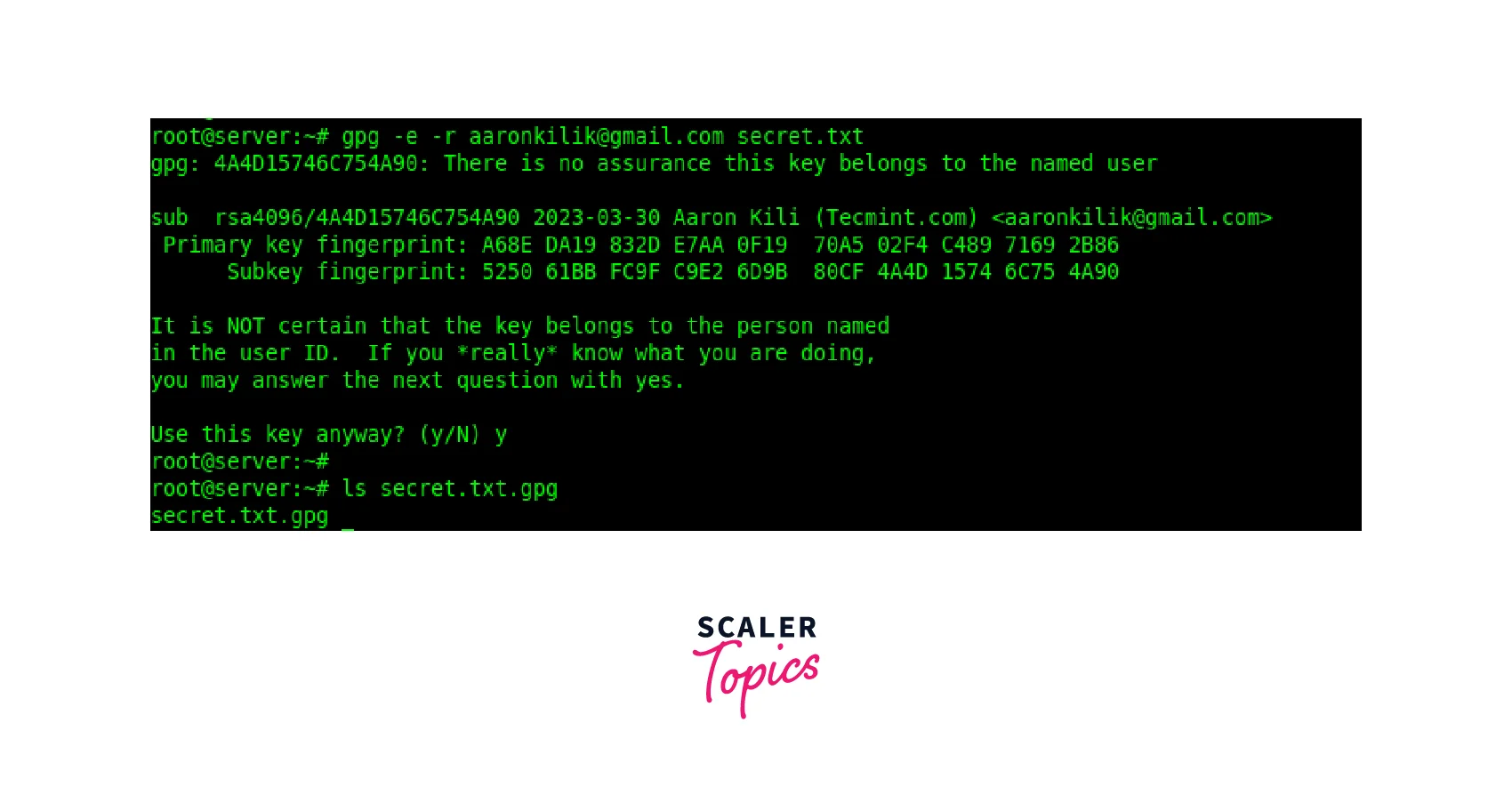
- If the recipient's public key is not in your keyring, import it using the command gpg --import <recipient_public_key_file>.
- GPG will create an encrypted version of the file with the .gpg extension while keeping the original file intact.
Configure the Password Cache Agent
By default, GPG will prompt you for the passphrase every time you encrypt or decrypt a file. However, you can configure a password cache agent to temporarily store the passphrase, saving you from entering it repeatedly.
- Open your GPG configuration file by entering the command nano ~/.gnupg/gpg-agent.conf in the terminal. If the file doesn't exist, create it.
- Add the following line to the configuration file: default-cache-ttl 3600. This sets the cache timeout to 3600 seconds (1 hour). You can adjust the value as per your preference.
- Save the changes and exit the text editor.
- Restart the GPG agent by entering the command gpg-connect-agent reloadagent /bye in the terminal.
With the password cache agent configured, the passphrase will be temporarily stored, and you won't be prompted to enter it every time you encrypt the file in linux within the specified timeout period.
Remember to keep your private key secure and regularly back it up to prevent data loss. Additionally, ensure you share the encrypted file securely with the intended recipient.
GUI Method of Encrypting Files
Encrypting files on Linux can also be accomplished using a Graphical User Interface (GUI) approach. The following steps outline how to encrypt files using the GUI method:
Install the Required Software
- Open a terminal window and execute the command sudo apt-get install seahorse. This will install the Seahorse application, which provides a user-friendly interface for managing encryption keys.
- Follow the prompts to complete the installation. Once installed, you will have access to Seahorse for encryption and decryption tasks.
Open the Nautilus File Manager
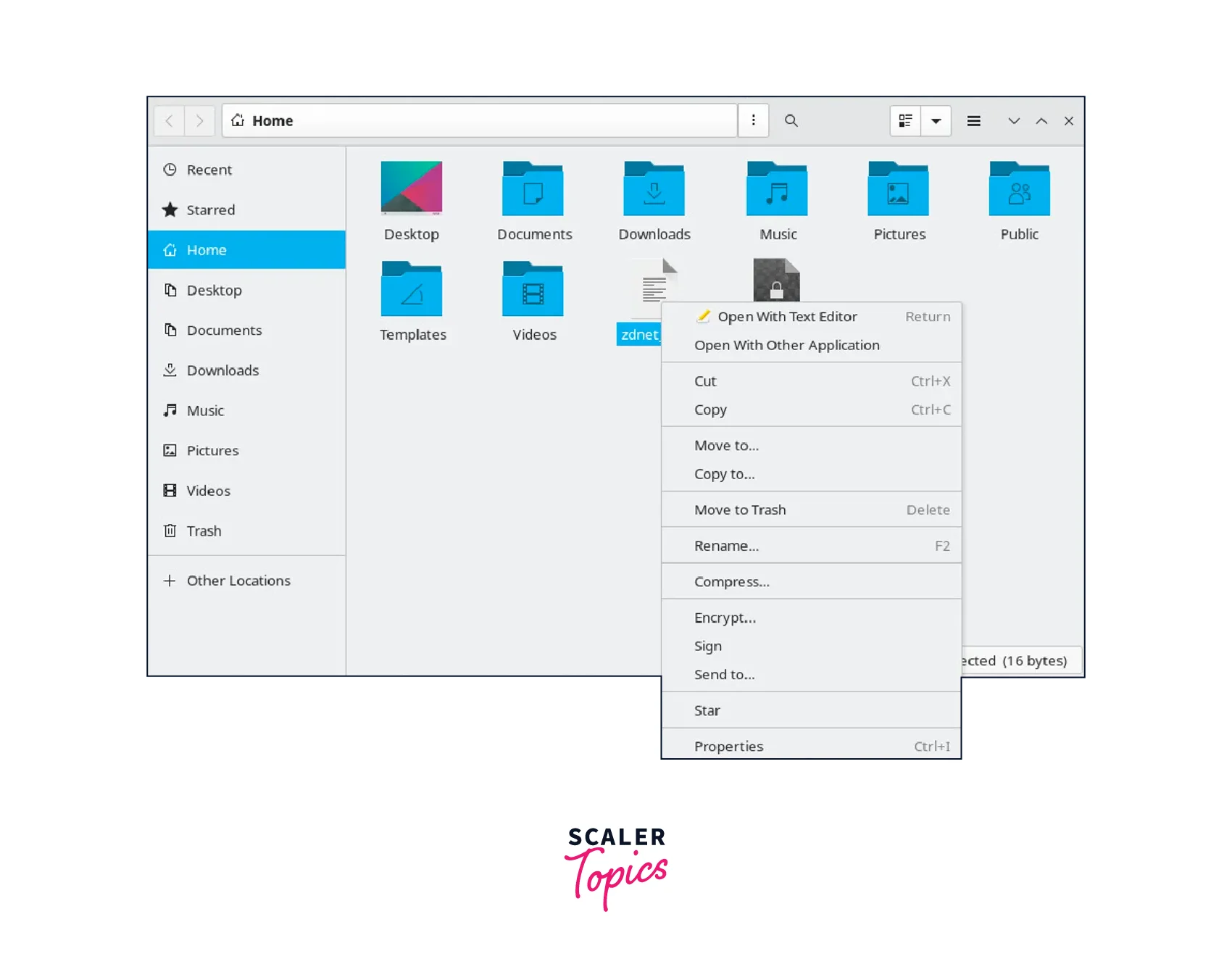
- Open the Nautilus file manager by clicking on the Files icon on your desktop or accessing it from the applications menu.
- Navigate to the directory containing the file you want to encrypt.
Select Your Encryption Method

- Right-click on the file you wish to encrypt and select Encrypt from the context menu. This action will open the Seahorse application.
- In the Seahorse window, you will see a list of your encryption keys. If you haven't created any keys yet, you can generate a new one by clicking on the + icon and following the prompts.
- Once you have selected or created a key, click on the Encrypt button in the Seahorse window.
- A dialog box will appear, prompting you to enter a passphrase. Choose a strong passphrase and confirm it. This passphrase will be required to decrypt the file later.
- After entering the passphrase, click on the OK button to initiate the encryption process. Seahorse will encrypt the selected file using the chosen key and passphrase.
- Once the encryption process is complete, you will notice a new file with the ".pgp" or ".gpg" extension created in the same directory. This file represents the encrypted version of your original file.
Decrypt the File
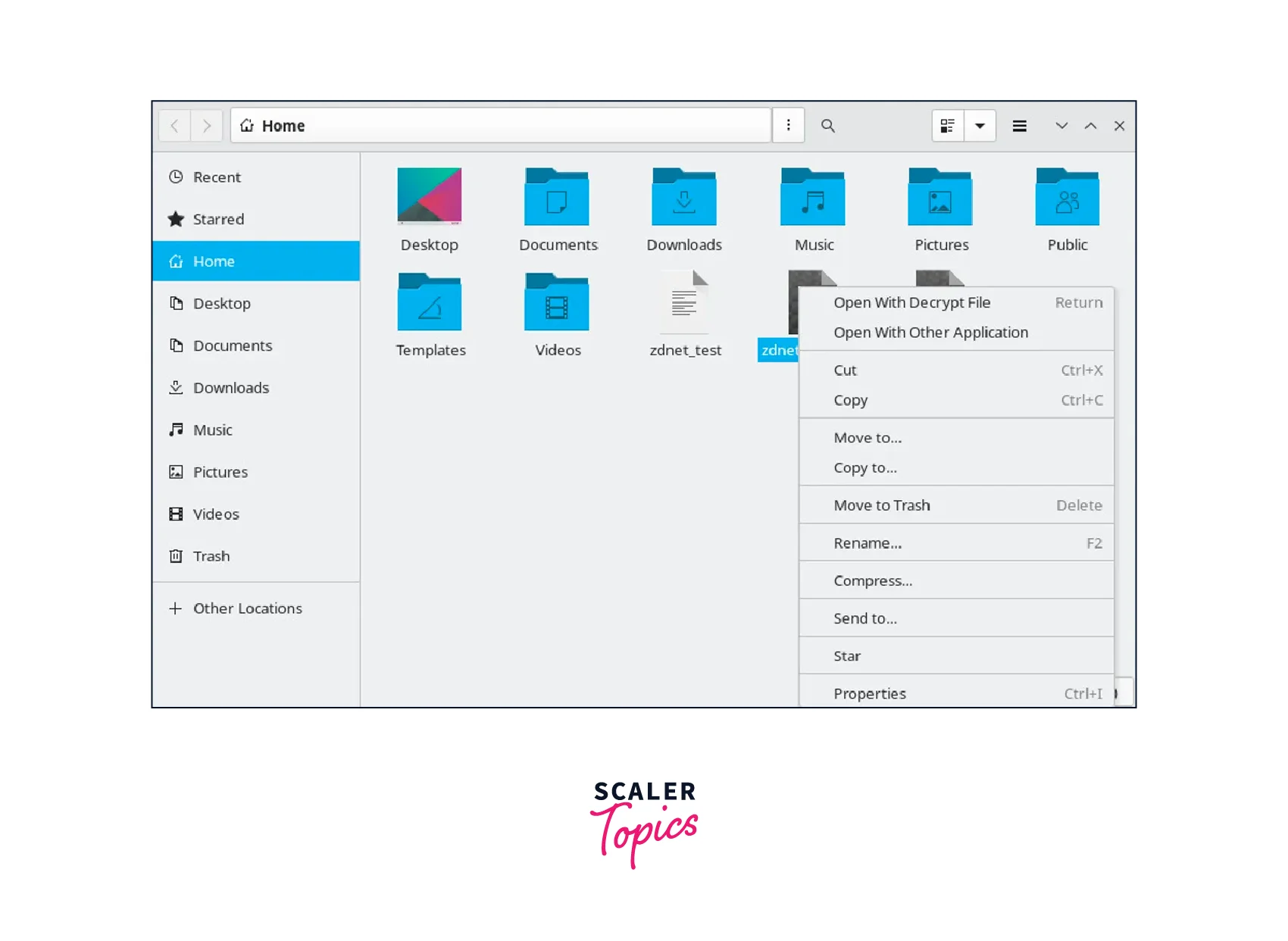
- To decrypt the encrypted file, double-click on it in the Nautilus file manager. Seahorse will automatically launch and prompt you to enter the passphrase associated with the encryption key.
- Enter the correct passphrase and click on the OK button. Seahorse will decrypt the file and restore it to its original format.
- By following these steps, you can conveniently encrypt and decrypt files using the GUI method of encrypting files in Linux. Seahorse provides an intuitive interface for managing encryption keys and securing sensitive data.
Remember to keep your encryption keys and passphrases secure. It is also advisable to create backups to prevent data loss. Properly managing your encrypted files will help ensure the confidentiality of your information.
Conclusion
- Encryption adds an extra layer of security to your files by converting them into unreadable formats that can only be accessed with the appropriate decryption key or passphrase.
- GNU Privacy Guard (GPG) is a powerful encryption tool widely used on Linux systems for encrypting files in linux.
- The command line method of file encryption involves generating a GPG key pair, changing into the directory housing the file, encrypting the file using the recipient's key, and verifying the encryption.
- The GUI method of file encryption involves installing the Seahorse application, opening the Nautilus file manager, selecting the file to encrypt, choosing the encryption method and key, and decrypting the file when needed.
- When generating a GPG key pair, choose a strong key size and a passphrase that is not easily guessable.
- Keep your private key secure and back up your keys regularly to prevent data loss.
- When encrypting files using GPG, make sure to import the recipient's public key if it's not already in your keyring.
- Use the appropriate commands (gpg --encrypt or right-click and select Encrypt) to encrypt the files in linux, and check for the ".gpg" or ".pgp" extension on the encrypted files.
- When decrypting files, provide the correct passphrase or key to successfully access the original content.
- Consider configuring a password cache agent like GPG Agent to temporarily store the passphrase and avoid frequent entry.
- Ensure secure sharing of encrypted files with the intended recipient, taking necessary precautions to protect the keys and passphrases during transmission.
- The GUI method offers a user-friendly interface for managing encryption keys and simplifies the encryption and decryption process.
- Regularly update your encryption software and system to benefit from the latest security features and bug fixes.
- Encryption is an effective way to protect sensitive files and maintain confidentiality, especially when sharing files over insecure networks or storing them on external devices.
- Understanding and implementing proper encryption practices is crucial for maintaining data security and privacy in today's digital landscape.
