How to Add a Matplotlib Grid on a Figure
Overview
- Matplotlib is a robust and dynamic Python library that helps users create meaningful and interactive plots.
- Plots and other visualizations in Python increase the chances of understanding complex datasets. Hence we can derive meaningful inferences from them.
- A grid is a collection of straight lines that help us show our plots' divisions. It makes something like finding the slope of a graph easy.
Grid in Matplotlib
- A grid is a collection of straight lines that help us show our plots' divisions.
- Grids help us visualize our plots a lot better, and it also helps us calculate plots' slopes and gradients.
- The syntax of grid is:
x: horizontal grids y: vertical grids color: color of the grid
How to Add a Grid to a Plot?
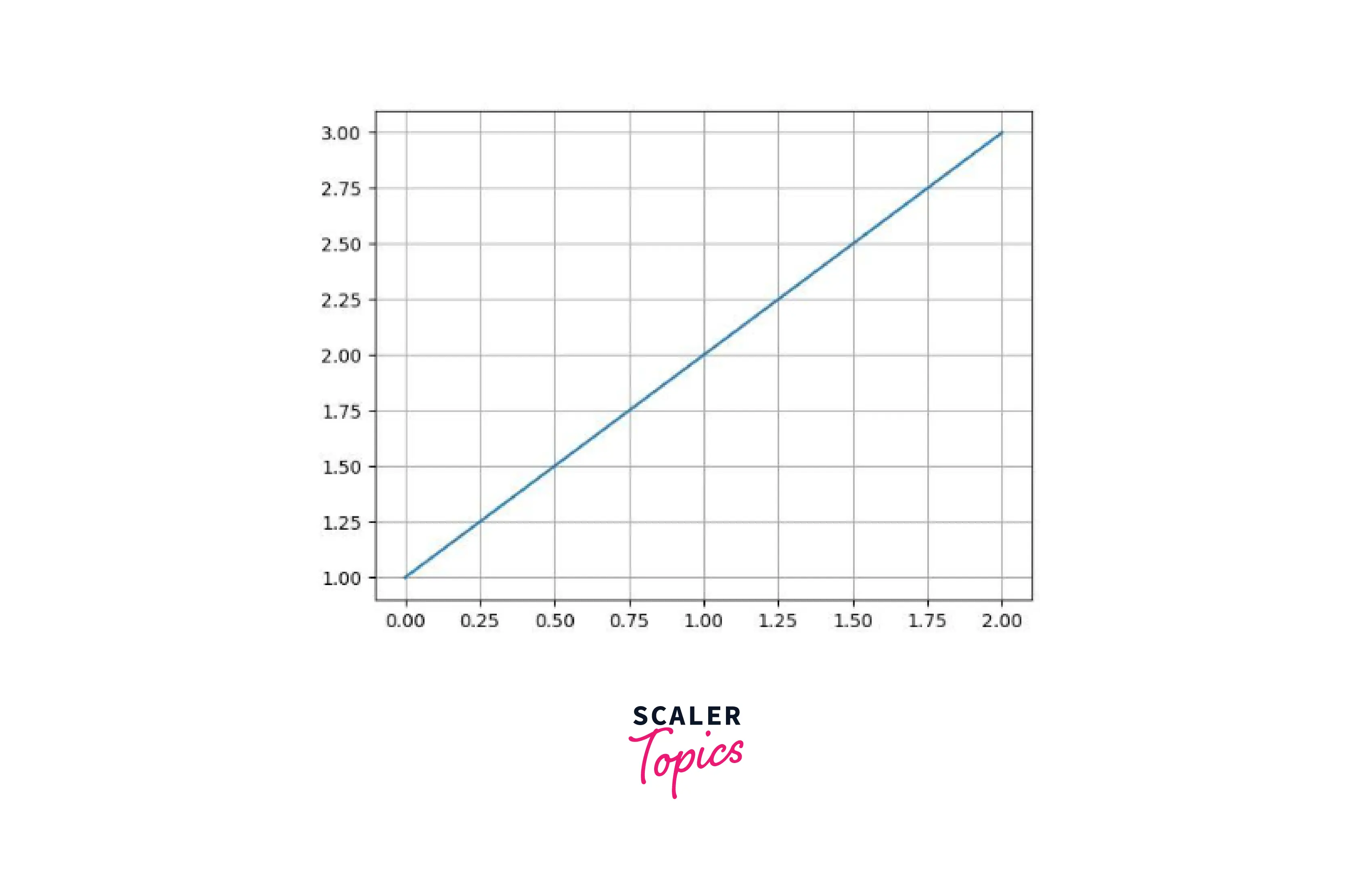
a) In this example, we will try to make grids on our strictly increasing plot:
b) Here, we create a strictly increasing graph (the slope will constantly increase).
- We use a scatter plot to display our data points.
- The .gca() function is used to get the current polar axes of our plot.
- We use the .grid() function to represent grids in our plots.
- Here's the output of the above code:
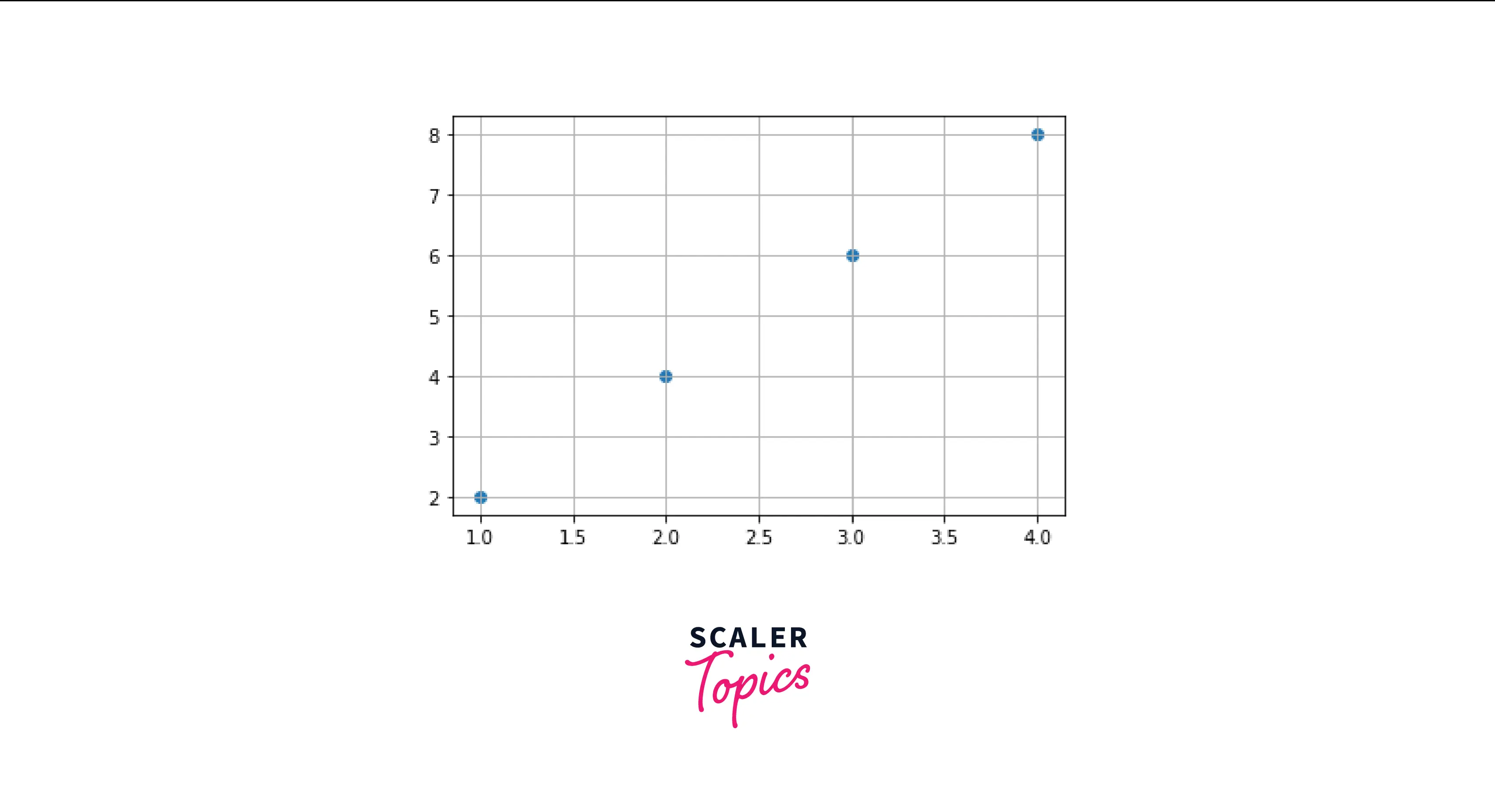
Note: There are many other ways to add grids to your plots, but this will ensure your code's scalability and readability.
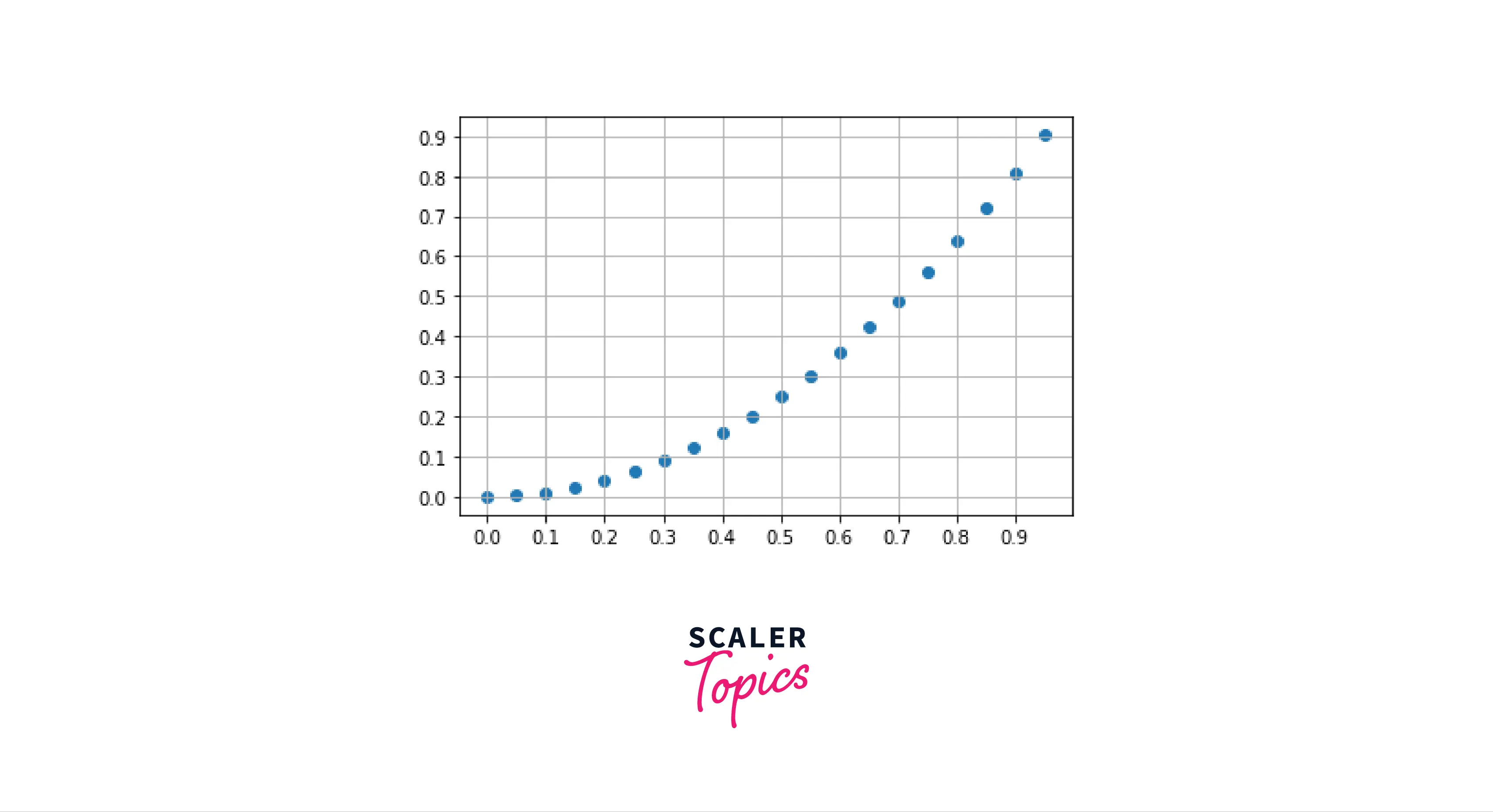
c) Let's talk about a very efficient type of grid, the logarithmic grid
-
Logarithmic grids help us to analyse data more efficiently, as the spaces in the grid are logarithmic-spaced.
-
For a logarithmic grid, we must add the which and axis parameters to our grid function.
-
Syntax:
- Logarithmic grids will look something like this:
What is Background Grid in Matplotlib?
- A background grid in Matplotlib is when we try to superimpose a rectangular grid in the background of a plot.
- The normal grid consists of straight lines intersecting at specific points. However, regarding background grids, the shape and density of the grid can be varied according to our needs.
- We can specify parameters if we want our grids to be dotted or have breaks.
Output:
How to Customize a Grid in Matplotlib?
- Customizing grids in matplotlib is one of the most salient features in matplotlib. It has many use cases.
- Suppose your client wants you to sort women's clothing by red and men's clothing by blue. You would have to create a grid in such a way that it differentiates between red and blue clothes.
- There are a lot of functions in Matplotlib to customize grids. A few of them are:
- set_facecolor()
where: color: hex-code of any colour.
- Example****Example:
Output:
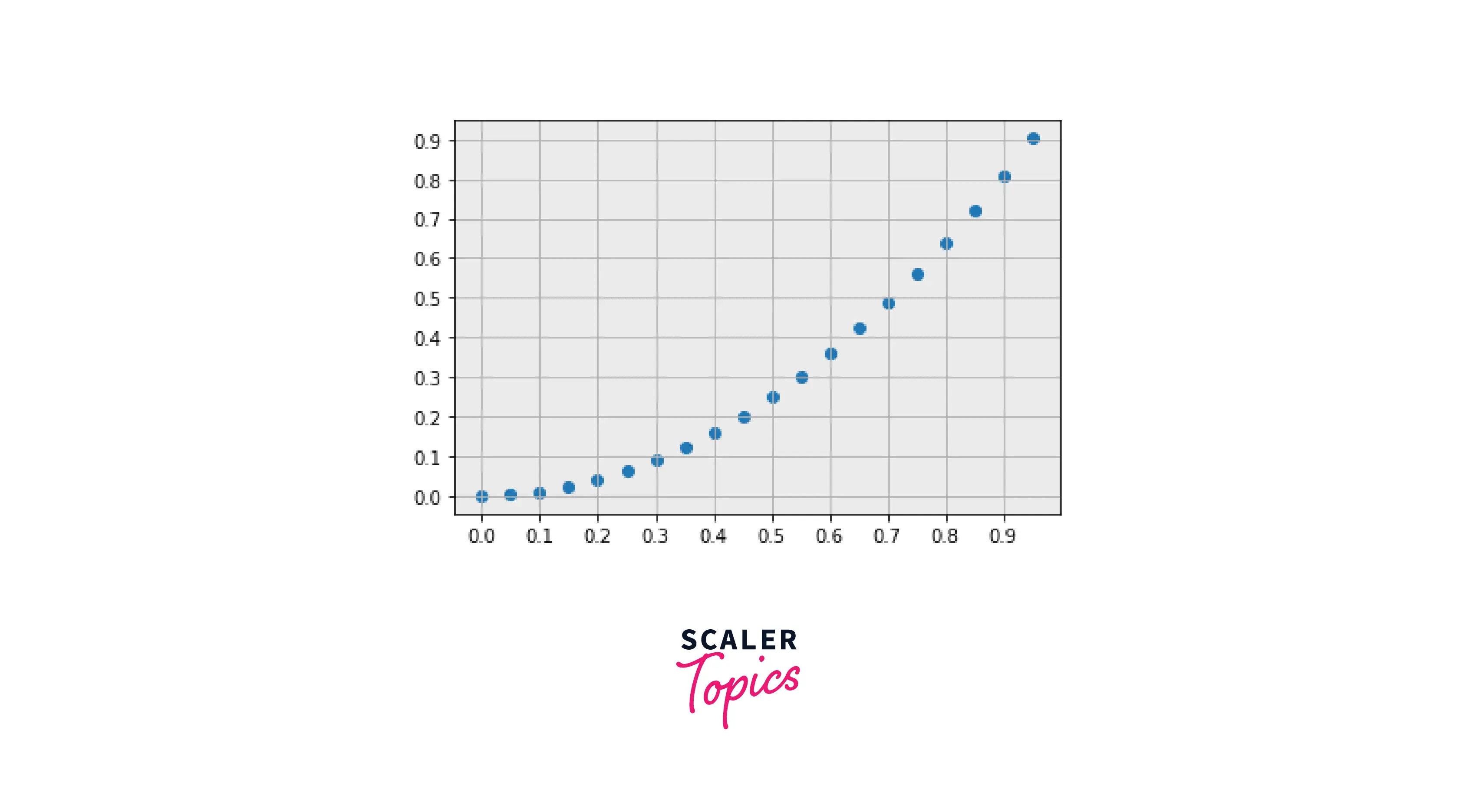
- Removing borders around our plots:
- For removing borders around our plots, we need to use the .spines function, and change the set_visible() to False.
Output:
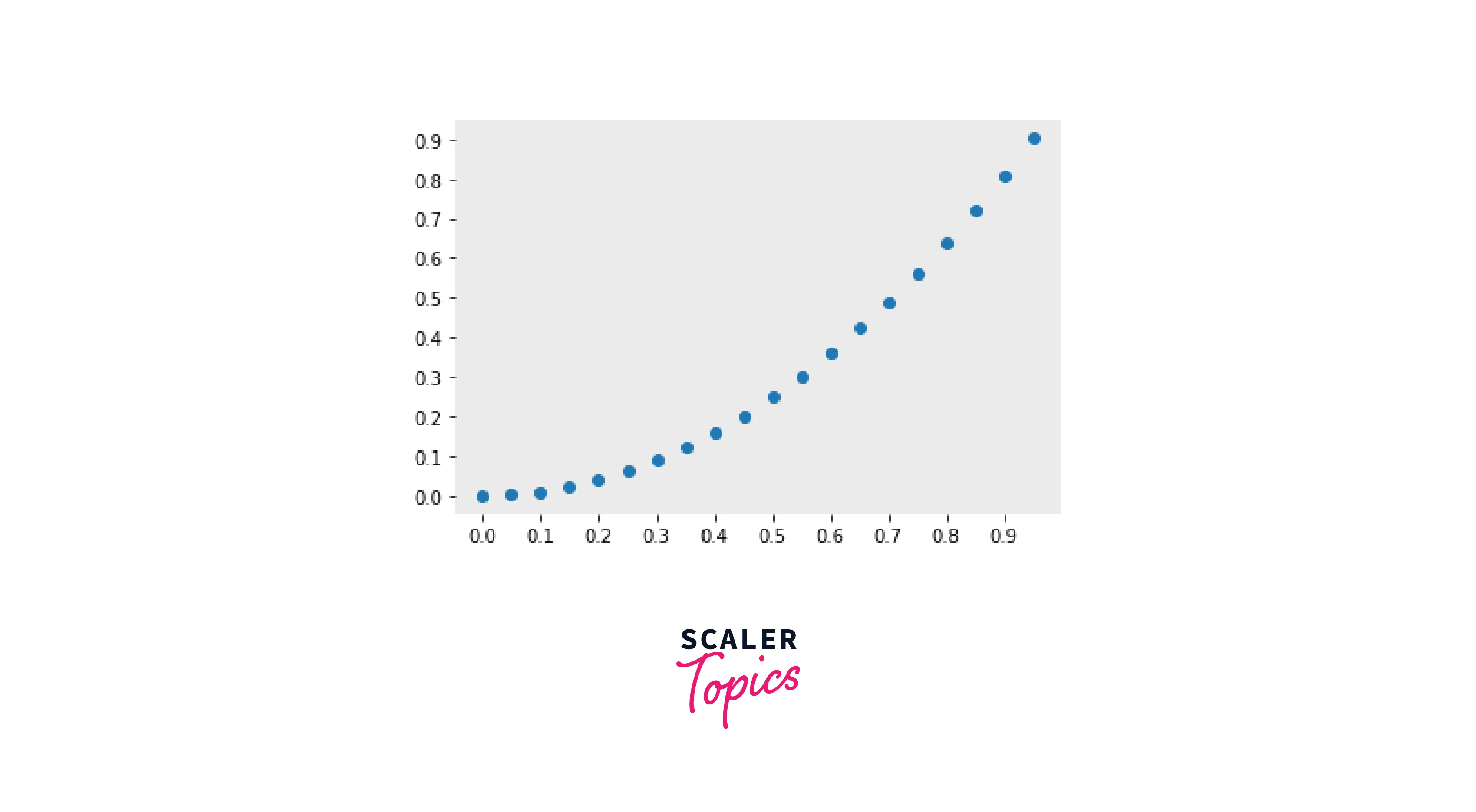
- Showing minorticks
- Minorticks can be switched on/off using the minorticks_on() function.
Output:
How to Add a Grid When the Ticks are Off?
- The values used to display certain positions on the coordinate axis are called ticks. It might be a string or a number.
- The axes automatically change and take the default ticks whenever we plot a graph.
- To demonstrate this, we will take the "GDP-2014" dataset.
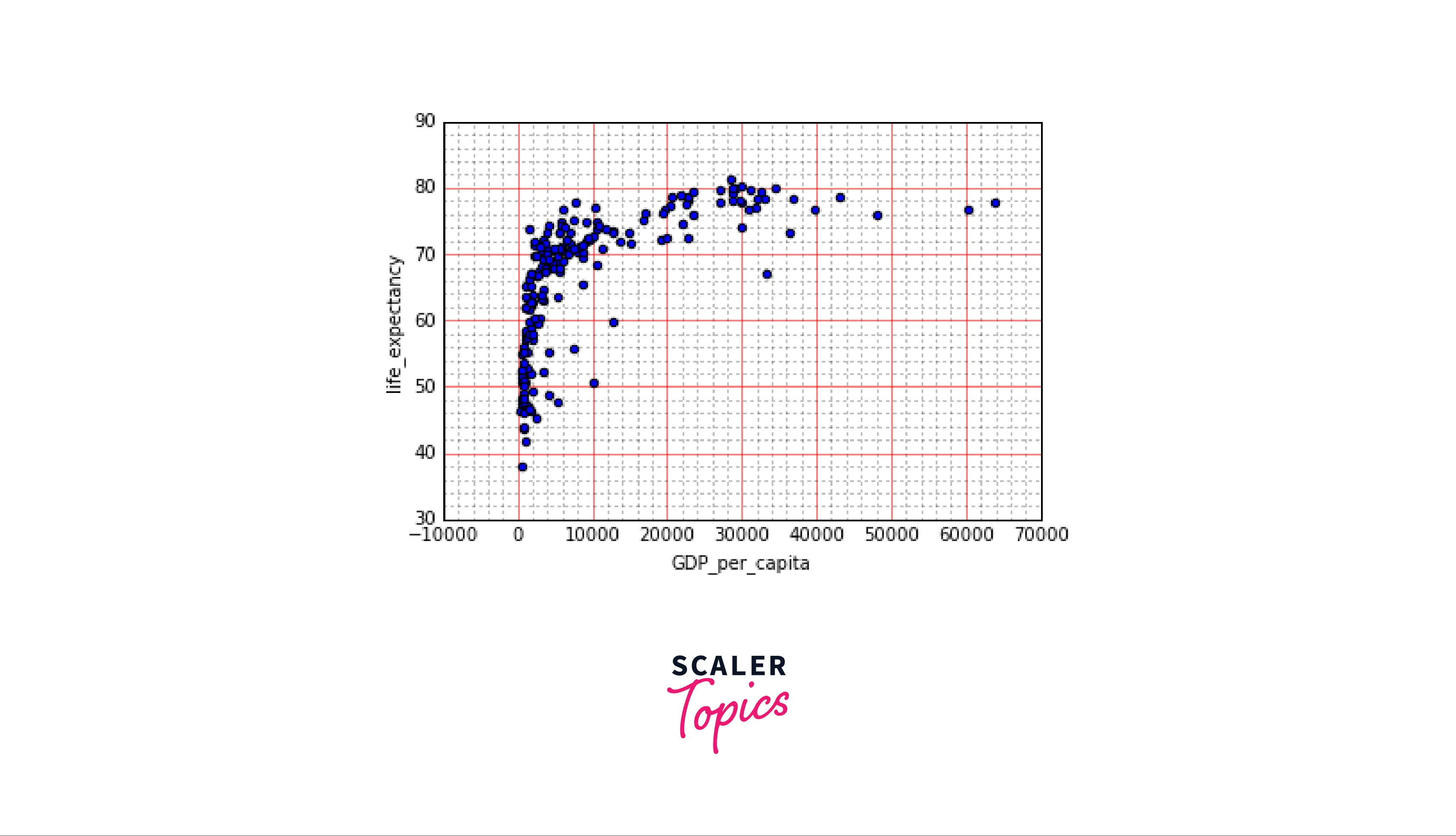
- To turn off all the ticks, we will use the .tick_params() function, and we will set every tick to "off".
Output:
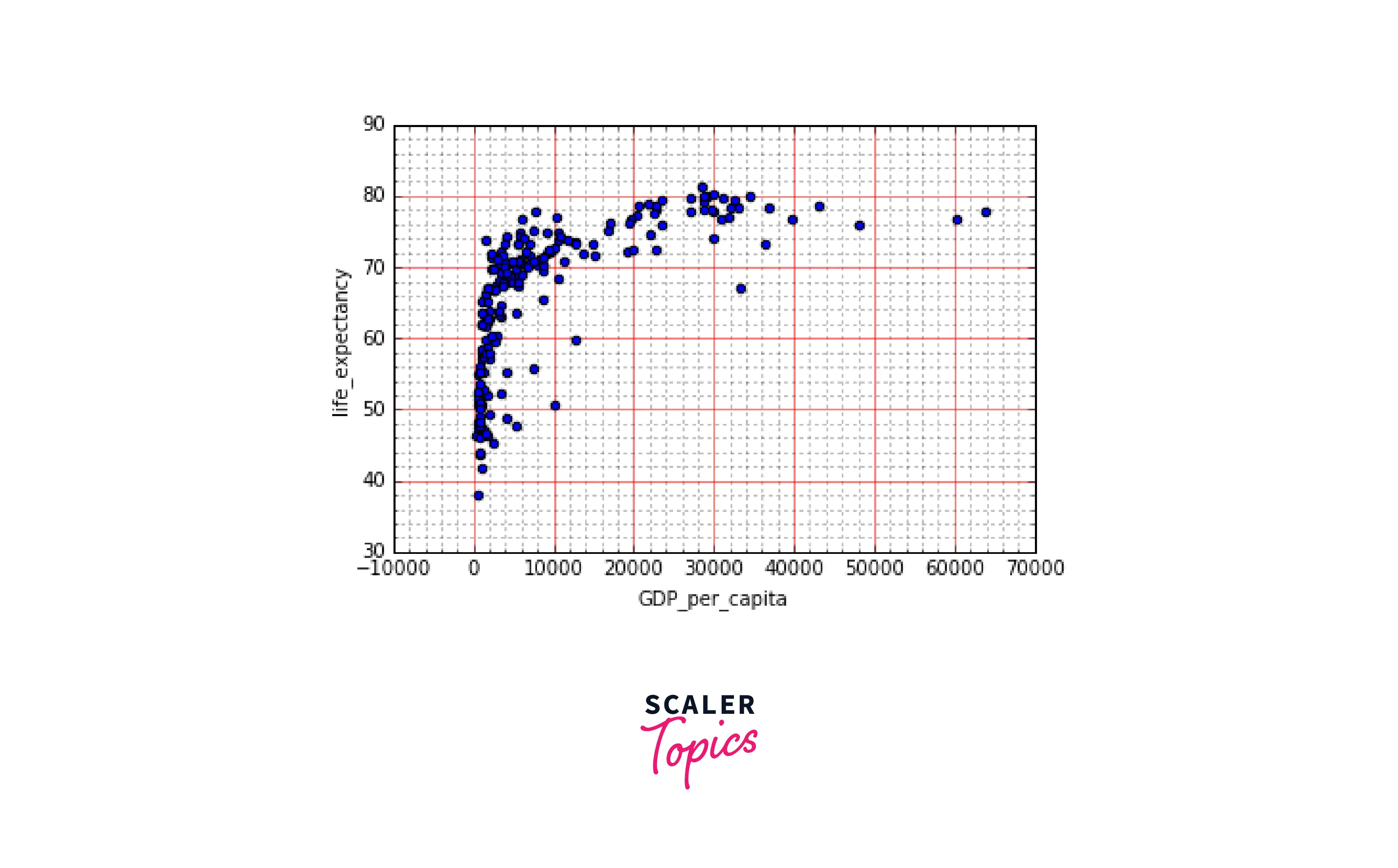
More Grid Examples
-
Here are some grid examples that will help you understand the concept and meaning of grids in a better way.
-
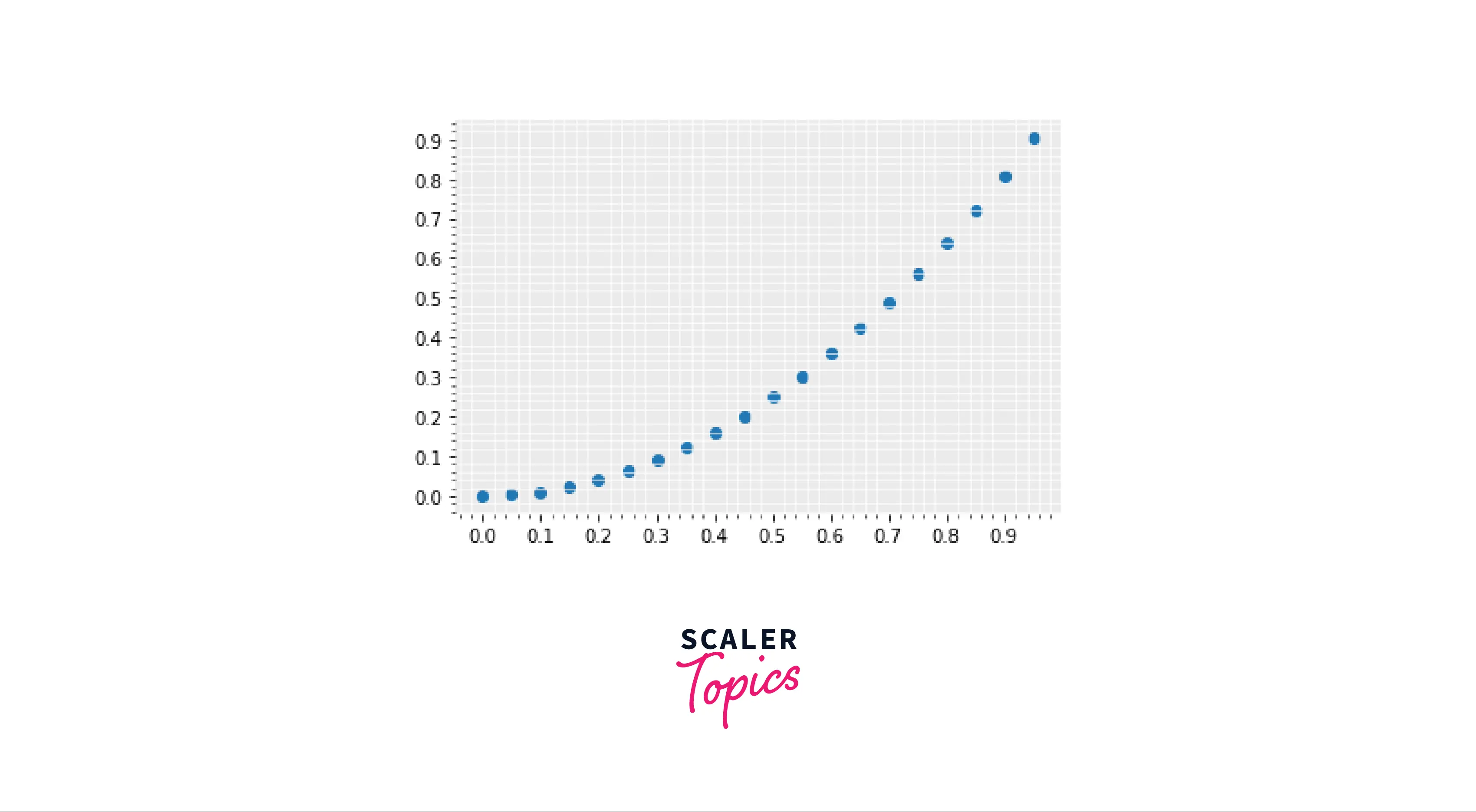
In this example, we will try to create a simple and comprehensive grid for a plot.
Output:
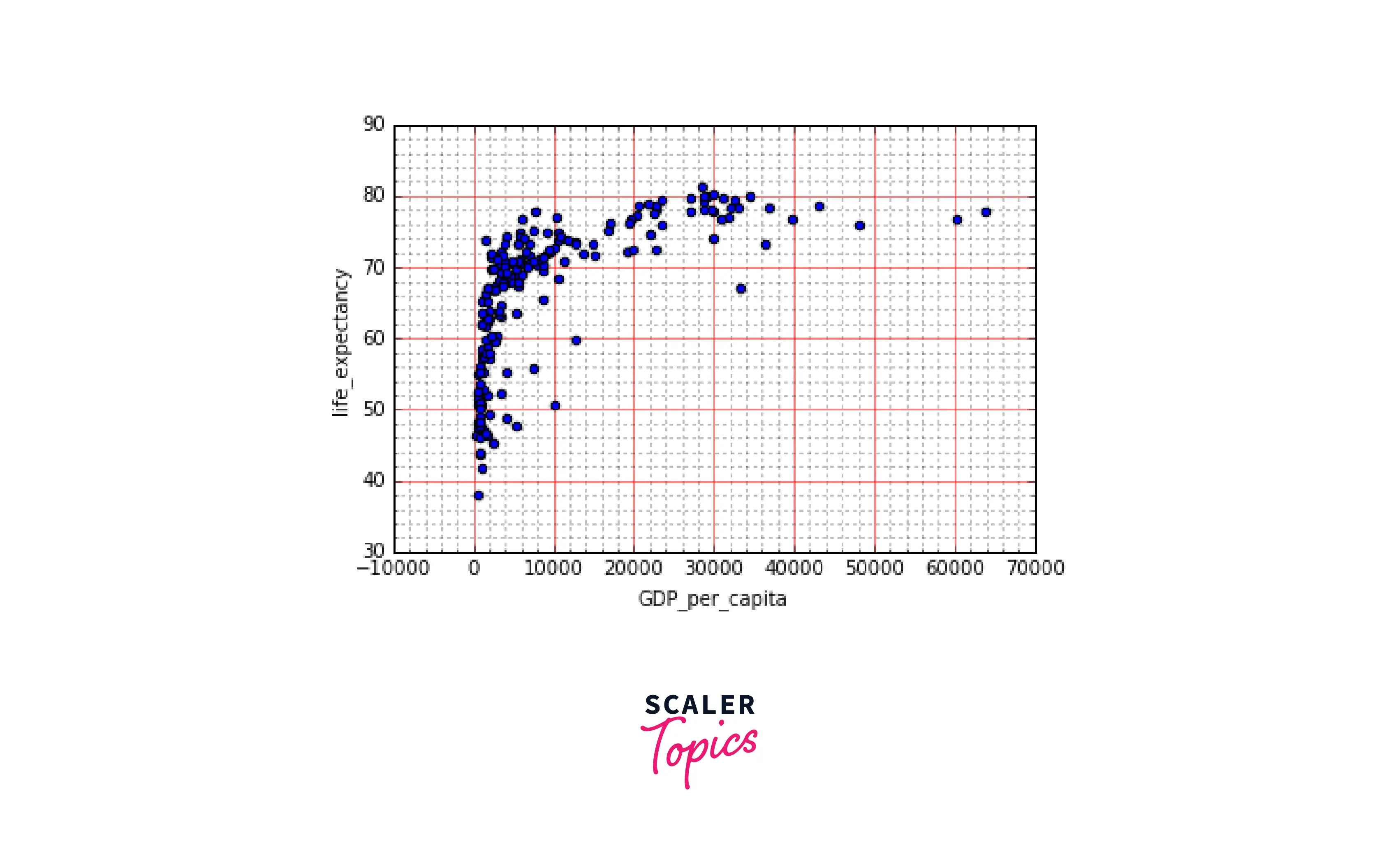
-
In this example, we will try to render a major and minor grid.
-
Rendering a major grid on a minor grid means that we would have our smaller/minor grids inside our major grids.
Output:
Conclusion
- In this article, we covered what grids in matplotlib are.
- We went through the process of adding a grid to our plot.
- Apart from this, we also covered logarithmic grids that enhance our visualizations.
- Customizing grids according to our own needs was also covered in depth.
- We learned how to add a grid when the ticks are off in a plot.
