Build Microservices with Nodejs
Overview
Microservices architecture is a way of organizing software services. It is a small self-contained application, which can be used to perform a specific function. A lot of services combine to make a large application. In Node.js, it's possible to build microservices using various JavaScript libraries. There are lots of advantages to using microservices in Nodejs like high performance, scalability, and robustness.
Prerequisites
- Basic understanding of Node.js.
- Basic understanding of application development using Node.js.
- Basic understanding of APIs.
- Basic understanding of application development processes like deployment, testing, etc.
What is a Microservice?
A Microservice is a type of application architecture. It is a method to lay out web services in distributed systems that can scale on demand. To get a better understanding of Node.js Microservices, let us first discuss the need for Microservices.
Back in the day, around the 1990s, companies offering internet services would run a large Monolithic Application on an in-house server. A Monolithic Standard meant that all the components of the application were part of a single unit of code. For Eg, if it was a Library Management System then all services like User Authentication and Authorization, Inventory Management, Books list, Book issue data, etc. were part of the same codebase.
A Monolithic application was developed and scaled as one unit. It was the gold standard for application development but the developers soon realized a few key drawbacks:
- A bug in one service would affect the whole application as the environment would need to be brought down as a whole, then the bug would be fixed then the application needed to be re-deployed as one unit. Imagine taking down an entire e-commerce application from production because the discount service was not working. This is detrimental to a business.
- If there were multiple teams, each working on a specific part of the application, then they must ensure that all the code works well together. One team's buggy code could easily affect the code of another team. This increased development time and took focus away from specific solutions.
- Updating the application would again require a complete re-deployment. There is no continuous integration.
- A single language is used to make a monolithic application so all the services use the same programming language and the same tech stack. A monolithic application doesn't benefit from a service with a different tech stack.
- To scale these applications, a new server was added to the old one to increase load handling. Soon, this became economically infeasible for the business.
- Even for a small change, the entire application needed to be tested.
- A single large code base quickly became far too complex and debugging became a developer's nightmare.
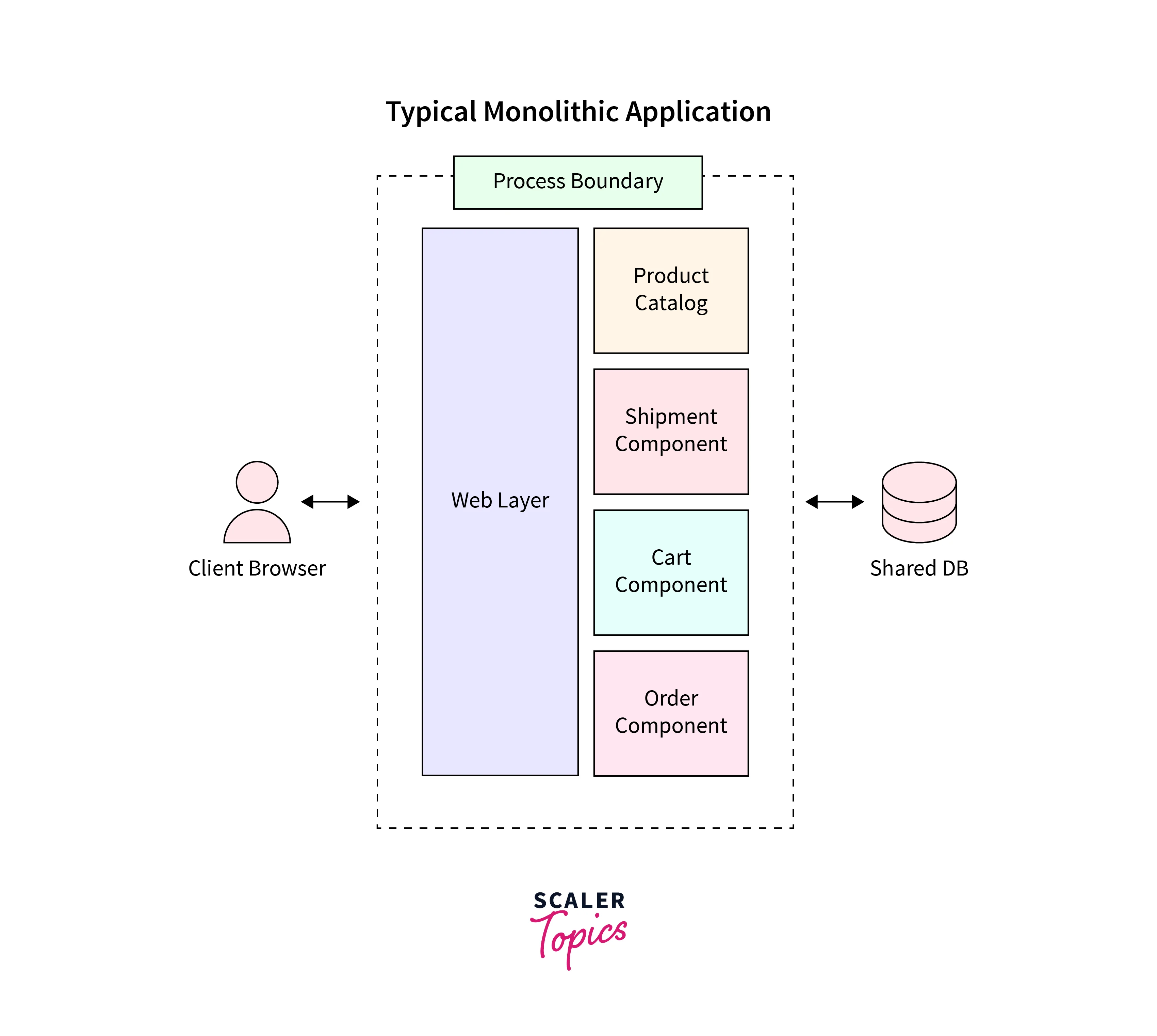
The Monolithic application architecture was not ready to handle the large number of user demands which were going to come with the spread of fast and cheap internet. The solution? Microservices!
A Microservices-based architecture is one where the application is broken down into small and independent services which are then combined to become one large application. Imagine multiple small applications, each with only one service, combined to make one large application. Microservices offer increased modularity, specific and cost-effective scalability, and a much better developer experience. When these services are created or implemented using Node.js runtime environment, then we call them Node.js Microservices. Let us look into this node.js microservices architecture in detail.
Microservices Architecture and How They Work?
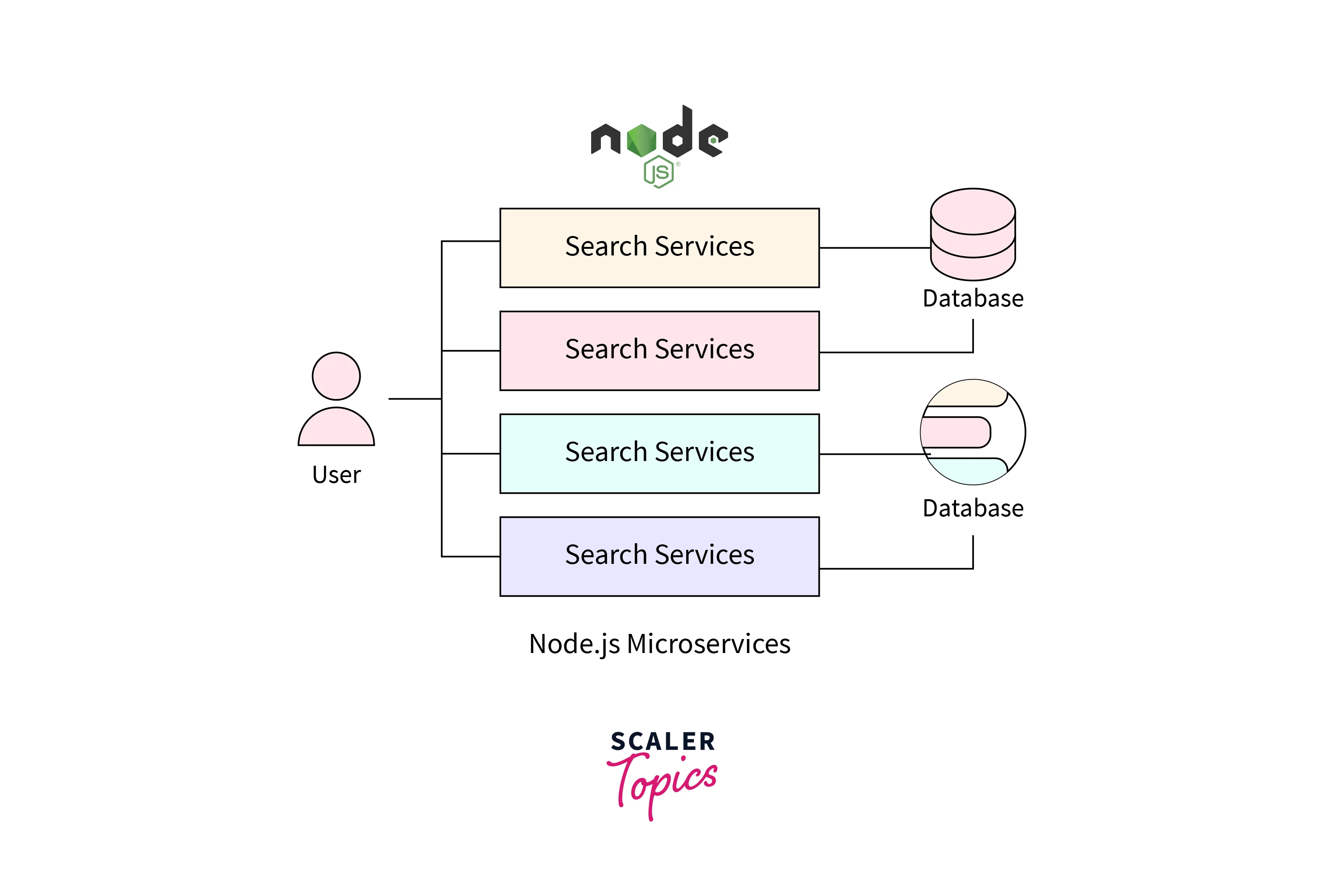
Microservices is a style of architecture of application development where the application is broken down into small components. These components are the microservices since each of them serves only a single purpose. Usually, the application is split according to business logic. For eg, a banking application would have business features like Accounts, Users, Loans, Deposits, transfers, etc. If this banking application is built using the Microservices Architecture, then all the tasks would be split into individual services. One service would handle only one task like transfer or user authentication.
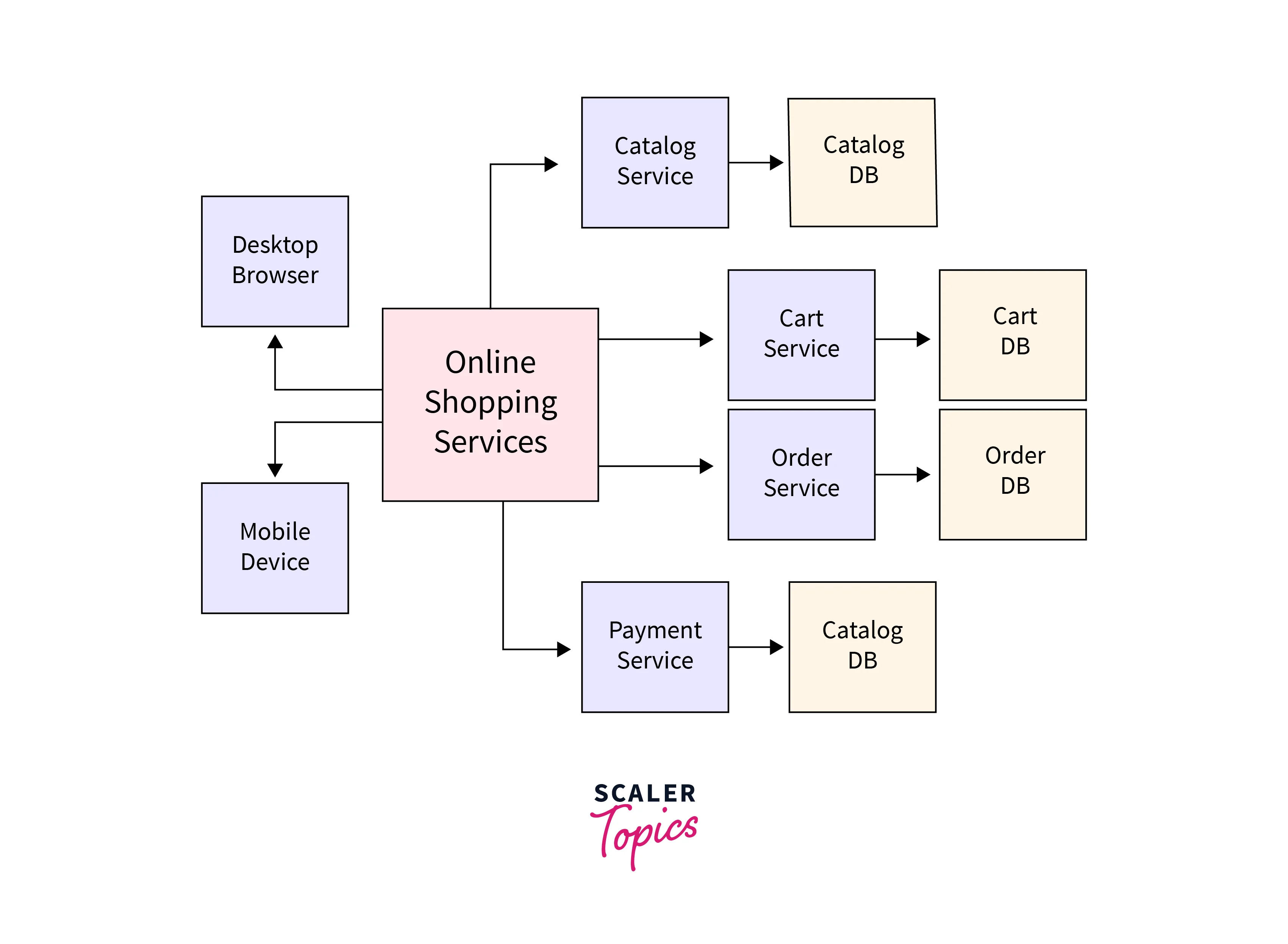
Node.js Microservices are self-contained and independent of each other. This means that every service is developed, deployed, and scaled as a separate and standalone unit. They do not have any dependency on other services even though these services combine to form the application. This is called as loose-coupling. If there is an update to one of the services, then only that microservice needs to be tested and deployed without affecting the whole application. Every microservice in an application has its version.
Node.js Microservices allow for scalability of only a part of the application which is under major load. There is no need for scaling the whole application. Virtualization of operating systems helps the microservice-based architecture. A single server can host many virtualized operating system instances and each of these instances can run a microservice. This means multiple microservices on the same server! This also increased the overload because companies had to manage applications as well as virtualization hardware.
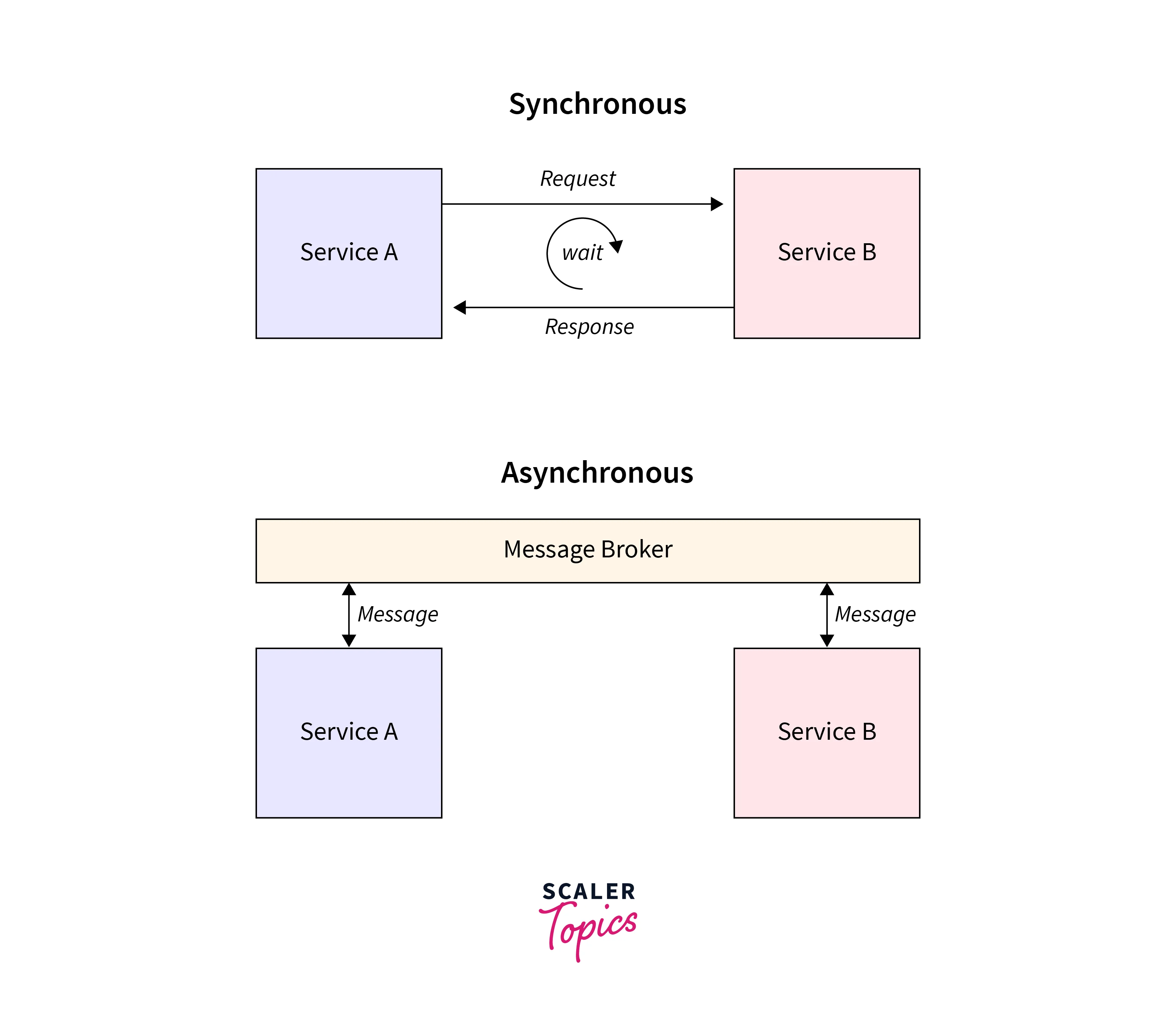
Communication Between Microservices
Since all the node.js microservices are essentially stand-alone and independent applications, the communication between them happens via API calls. Each service has its own set of APIs. One service can communicate with the other by sending an HTTP request to an API endpoint. This communication can be both synchronous and asynchronous depending on the business requirement. Modern applications are also using a dedicated service layer to delegate communication between services. This is known as a service mesh.
Why is Node.js an Outstanding Choice for Microservice?
- Event-based: Helps to make event-oriented applications as Node.js objects can emit events and listen to events as well. An event could be like a click or message.
- Asynchronous and Single-threaded: Node.js is asynchronous due to the event loop. The code execution is non-blocking. The execution doesn't wait for the current request's response and moves on to the next one.
- High Performance: Node.js is built on top of Chrome's V8 Engine which is very fast making it capable of supporting multiple thousands of requests each second.
- Real-Time Applications: Since the execution is non-blocking, Node.js is ideal for real-time applications and better user experience.
- Scalability: Due to its speed and ability to handle a large volume of requests, Node.js is highly scalable for very large applications with millions of users.
- Shareability: Node.js has a very good modules system and sharing code for distributed systems is very easy. Thus, multiple developers can together work on node.js microservices.
- Extensive Library Support: NPM or Node Package Manager hosts hundreds of thousands of Node.js libraries which can be imported using CLI commands and used in our applications for free.
- Cost Effectiveness: Node.js is open source and has huge community support both in terms of libraries and the environment itself.
- Easy Integration with Front-End Systems: Since Node.js uses JavaScript, it has much easier integration with front-end libraries and frameworks like React and VueJs. The same language can be used in the frontend as well as the backend which reduces complexity.
Benefits
- Selective Scalability: Node.js Microservices allow us to only scale the required components. This saves costs as the business only needs to spend on the specific infrastructure and development time. Microservices also enable easy scaling down of applications. If there are components that do not require as many resources as they are consuming then they can be selectively scaled down to save costs. Many cloud services thus offer a Pay-as-you-go service where the cost is mapped to the resources being used at all times dynamically. There is no need to buy more or less than required.
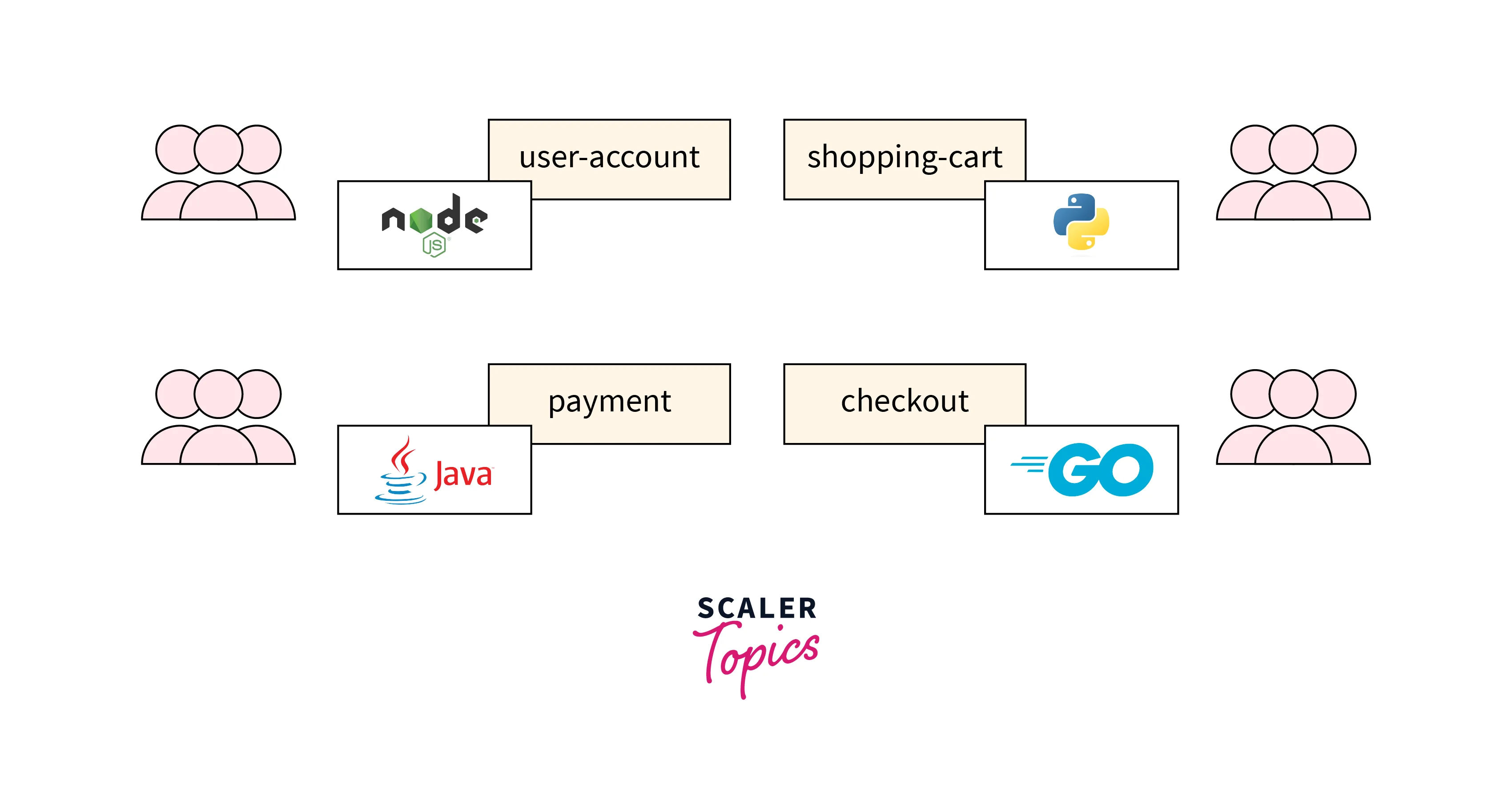
- Tech-Stack Agnostic: Node.js Microservices are independent and stand-alone. Microservices developed using different tech stacks can be used together to make one application. The languages can also be different for the services. This also enables faster shipping of production-grade software since 3rd party services can be used for common tasks like Authentication, Payments, etc.
- Debugging: If one component of the application fails, then only that service can be taken down, fixed, and deployed. There is no need to shut down the entire application which stops the business.
- Modularity and Testing: Increased modularity gives way to easy software sharing and maintainability. Unit Testing of components becomes easier as the whole application doesn't need to be tested. Outsourcing development, testing, deployment, etc. have never been easier.
- Improved Security: As node.js microservices are isolated, all of them can have their security layer rather than one security layer at the application level.
- Multiple instances: There can be multiple instances of the same service which provided re-usability and increased efficiency.
Drawbacks
- Increased Complexity: Having a large number of node.js microservices increases the layers of our application as every service becomes a separate component. It takes careful design, planning, and development to ensure proper communication between the node.js microservices.
- Monitoring and Orchestration: Increase in the number of Microservices makes it hard to monitor all of them from a high level. Good orchestration ensures that services work well together between individual services and the various instances of each service. This process is quite complex.
- Integration Testing: While unit testing becomes easier, integration testing becomes harder as multiple node.js microservices need to be tested with each other.
- Error Tracing: If the communication between node.js microservices is not set up properly then it becomes extremely hard to trace the origins of an error or a bug.
- Fragmentation: In some situations, the system becomes needlessly distributed. In such cases, the coupling is very loose and this results in very fragmented code which makes orchestration harder.
Building Microservices With Node.js
To demonstrate the power of Service Oriented Architecture using Node.js Microservices, we will create a back-end Node.js application that will send requests to 3 different Microservices using API calls and we will display this data.
First of all, we need to check if our system has node.js and npm installed or not.
Fire up the terminal and run the following commands:
node -v
npm -v
The output should be the versions for both:

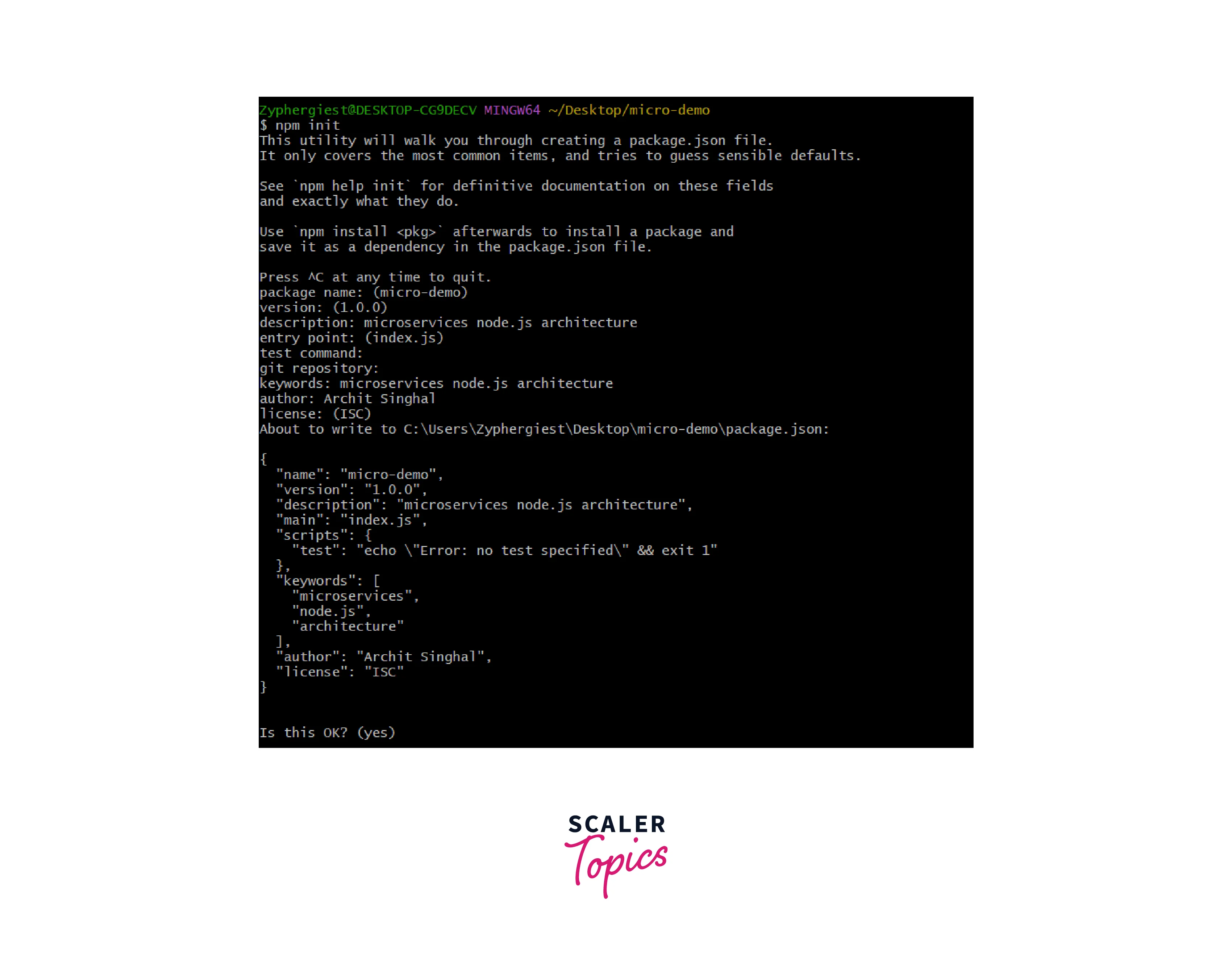
If they are not installed, we should visit the Node.js website to download and install them. Now we will initialize our Node Application. Run the following command and go through the terminal prompts
npm init
Here is the final output after all Terminal prompts:
Now we will install all the required dependencies. For this application, we need an ExpressJS server and axios.
For this demonstration, we are going to use the following 3 Microservices.
- Bored - API for random activity suggestions.
- Cocktail Database - API for all details on all drinks.
- WeatherDB - API for simple weather forecasts based on location.
We will code a simple Node.js back end using ExpressJS and try to get data from all three of the above Microservices and log it to the console. Here is the code for that:
Here is the output when we run the above server:
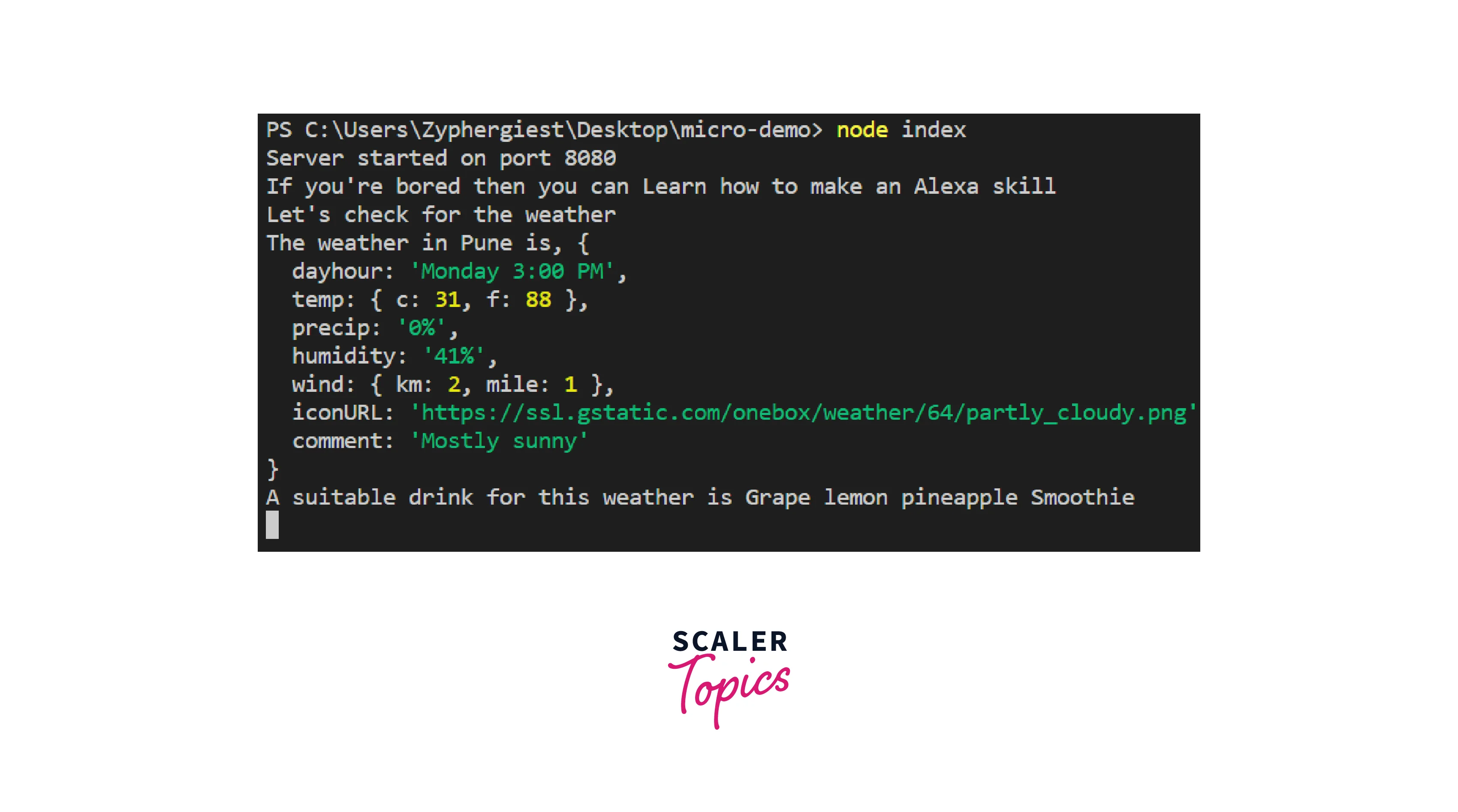
Thus we have used three separately hosted Node.js Microservices running on their servers to get data for our back-end server application. This data can now be used anywhere in our application. This is only possible because of Node.js Microservices architecture. We don't need to worry about the implementation of external services and only focus on our applications. These services extend API which we simply call and our application is ready in no time. Now, this is called fast-paced development!
Unlock the Power of Full-Stack Development With Our Full Stack Development Course and Seamlessly Integrate JavaScript Across the Stack.
Conclusion
- Node.js Microservices architecture splits the application into independent and stand-alone units that work together to form a large application.
- One service only takes care of one specific task like authentication or authorization.
- They are loosely coupled and communicate with each other through APIs.
- Each service can be developed using its tech stack and runs on its separate server.
- Node.js Microservices were created to counter the drawbacks of Monolithic architecture.
- They offer easy scalability, and better security and make the code easier to debug.
- Node.js is an extremely good option to build microservices. Node.js Microservices are fast, scalable, asynchronous and event-driven.
- Node.js allows us to build microservices in JavaScript and integrate these services with third-party services as well.
- Drawbacks of Node.js Microservices include increased complexity, difficulty in monitoring and orchestration, etc.
