What is a Bootloader in Operating System (OS)?
Overview
Bootloader stands for Bootstrap Loader which is the compact software which is responsible to load the operating system into the memory of the computer. The bootloader will always run whenever the computer system is started or restarted.
What is a Bootloader?
When you start your computer, the operating system gets loaded and after that, you are able to login into the system and use the system, but who loads the operating system into the memory of your computer? It’s called Bootstrap Loader which loads the operating system into the memory.
So, when we start out the system, all the hardware components receive the power signal and get initialized. Now BIOS which is a basic input-output system will read the instructions and based on the instructions BIOS will look for a bootable device.
Once the bootable device is found, the BIOS loads the bootloader. Bootloader will load the operating system into memory. This entire process is called booting. Any kind of hardware device which contains the bootloader is called Bootable Device.
How does a Bootloader Work?
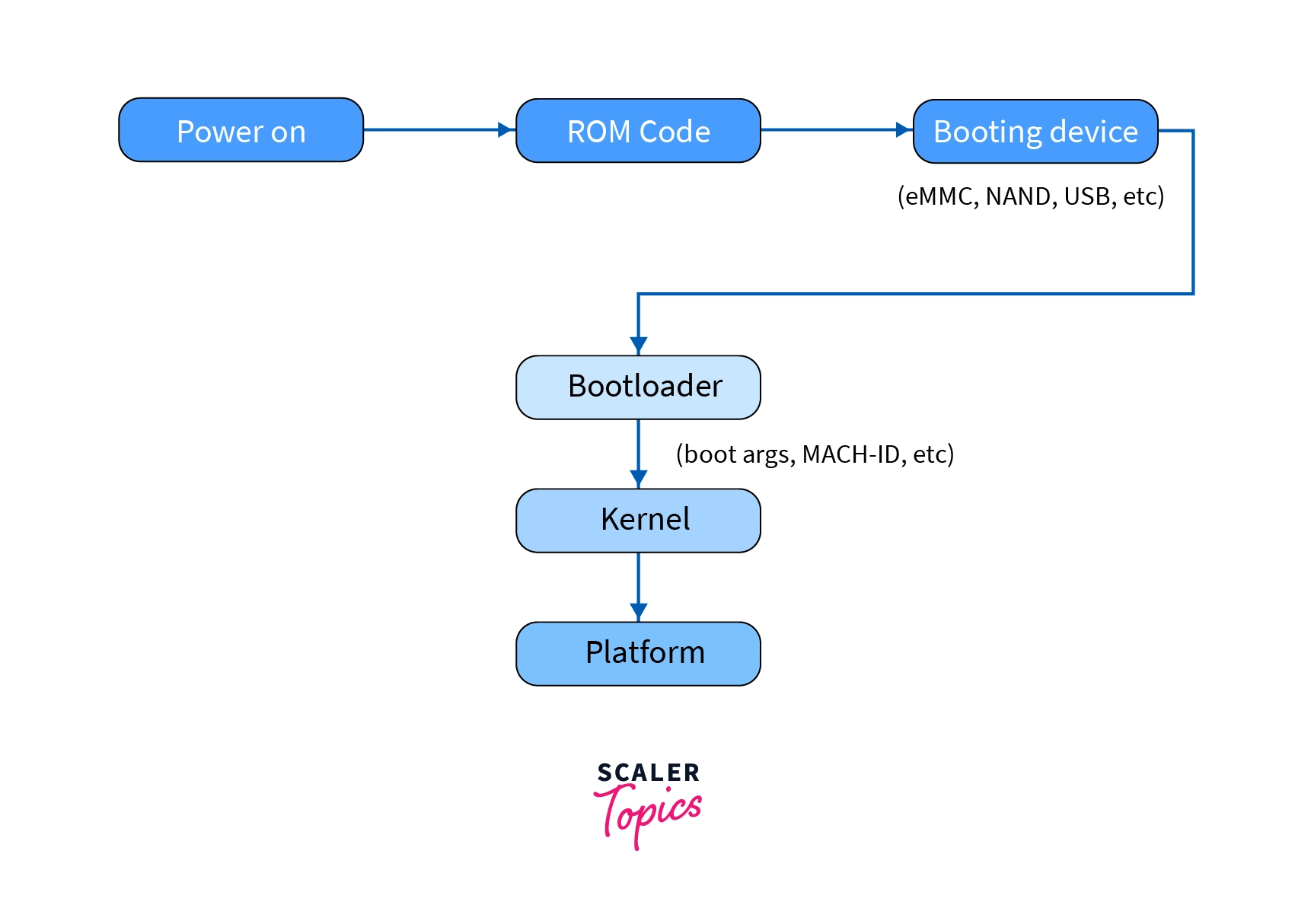
- When we press the power button of our system, the hardware components get initialized and we see the different pieces of information about the hardware of the system.
- As the main memory of the system is volatile it won’t have any content present in it. In order to start the execution, the initial instructions are fetched from non-volatile memory called ROM(Read Only Memory), and this initial set of instructions is called BIOS.
- BIOS is a compact program that will find the bootable device present in the system, eg. Floppy disk, Hard disk, CD etc.
- Once the bootable device is found, BIOS search for Master Boot Record (MBR) which contains the bootloader.
- If the MBR is found, BIOS will load the bootloader present in it.
- From here on, the bootloader takes the control of CPU and loads the operating system into the main memory of our system.
- Once the operating system is loaded into the main memory it takes the control of the entire system.
Note: Non-Volatile Memory is the memory that can hold the information even if we restart the device. eg. ROM (Read Only Memory) Whereas, Volatile Memory is the memory that gets erased if we restart the device. eg. RAM (Random Access Memory)
If BIOS fails to find MBR in any of the bootable devices it will return an error message.
Where Exactly are Bootloaders Stored?
Bootloaders are generally stored in the first sector of a bootable device called Master Boot Record. So, whenever the BIOS finds the bootable device, BIOS simply reads the data present in the first sector.
We can keep some data that is not related to the loading of the Operating System into the first sector of the bootable device detected by BIOS. Many gaming vendors keep the code responsible to start the game in the first sector of the bootable device as a result when we start the system, BIOS looks for the bootable device, and as the bootable device now contains the code which can start the game so rather than loading the operating system bootloader will execute the instructions responsible to start the game.
There is a second way in which the bootloader is stored. With the advancement of technology in many systems, the bootloader is present in specific partition of the bootable medium and BIOS are smart enough to identify in which sector the bootloader is present.
It is possible that we can have more than one bootloader. There are systems that have a primary bootloader that is very small in size and whose only work is to load the secondary bootloader. Once the secondary bootloader is loaded it will be responsible to load the operating system.
Let’s quickly summarize the functions of bootloaders.
A Summary of a Bootloader’s Functions
- The main function of the bootloader is to load the operating system.
- If there is more than one bootloader, the primary bootloader has to load the secondary bootloader.
- Bootloaders are also used to launch the application programs. (e.g., games)
- Bootloaders are also used to expand or add the missing function's firmware.
- Bootloaders are used to load the alternative firmware.
We will be seeing different well-known bootloaders available currently in the market.
What well-known Bootloaders are there?
- Extensible Firmware Interface(EFI) bootloader – Bootloader used in current windows machines
- Bootmgr – Bootloader used in windows vista
- NT Loader (NTLDR) – Bootloader used in windows XP
- BootX – Bootloader used in MAC machines.
- Grand Unified Bootloader (GRUB) – Bootloader which is used in Unix-like machines. E.g., Linux
- AndroidBoot (Aboot) – Bootloader which is used in android.
- iBoot – Bootloader which is used in iPhones. Let’s conclude the learning we had so far.
Conclusion
- Bootloader is a compact software which Is responsible for loading the operating system.
- BIOS detects the bootable device and if it finds the bootable device, it will load the bootloader which will eventually load the operating system.
- Bootloaders are used to load other bootloaders, load firmware, launch gaming applications, and add or expand missing functions in firmware.
- There can be multiple bootloaders present in the system: primary bootloader and secondary bootloader.
- Bootloader is generally present in the first sector of the bootable device or in the specific sector of the bootable device.
- GRUB, Bootx, Aboot, iBoot, EFI bootloader are a few examples of well-known bootloaders.
