Power BI vs Tableau: Differences and Comparison
Overview
Power BI and Tableau are two leading business intelligence (BI) tools designed to help organizations transform raw data into actionable insights. Understanding the strengths and differences of each platform is vital for organizations seeking the most suitable BI solution to meet their needs and drive data-informed decision-making. This article will compare the two prominent tools for BI: Power BI vs. Tableau.
What is Power BI?
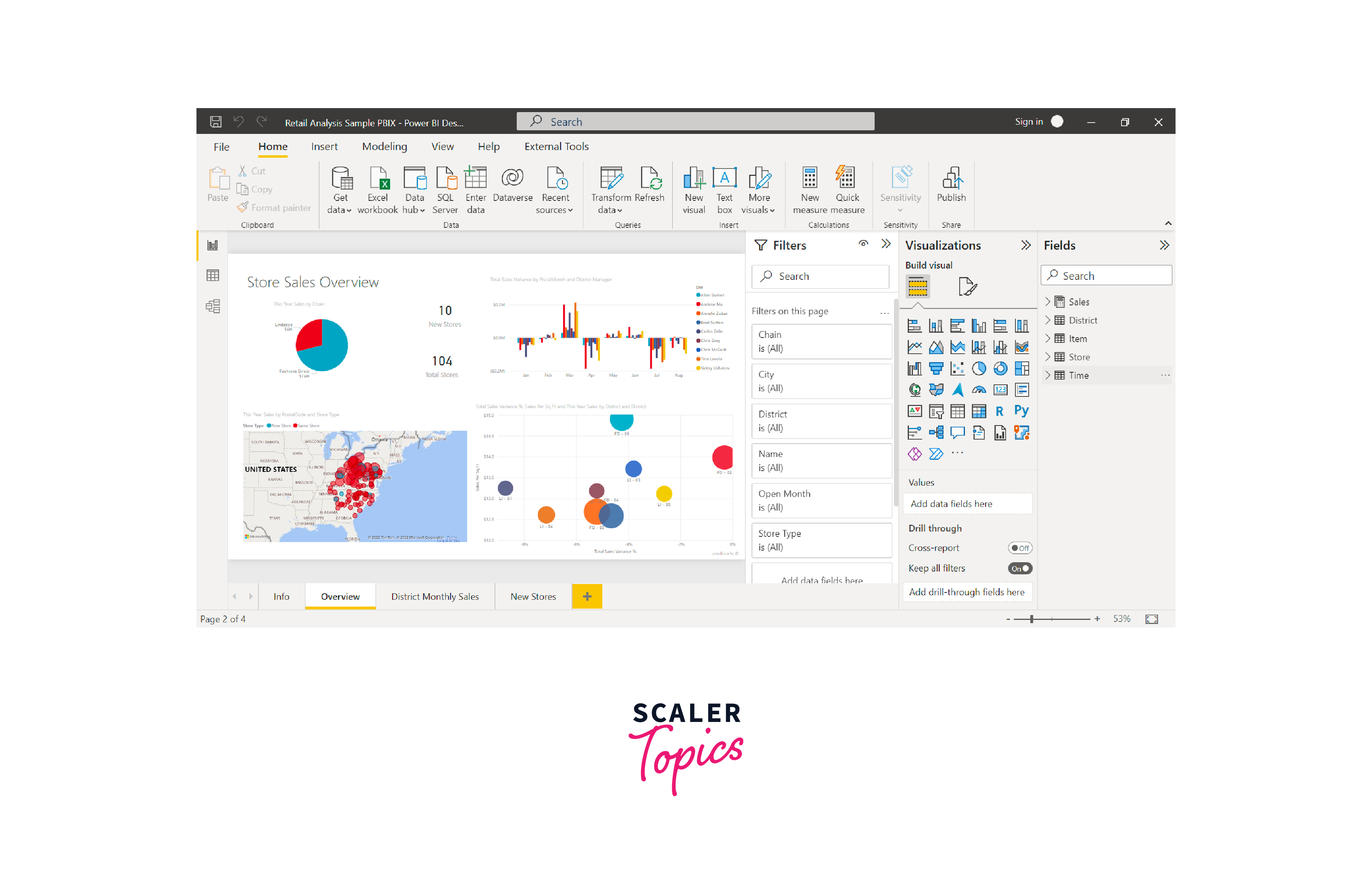
- Power BI is a powerful business intelligence and data visualization tool developed by Microsoft. It empowers users to connect to various data sources, including databases, cloud services, and Excel files, to gather and transform raw data into insightful reports and interactive dashboards.
- With its user-friendly interface and drag-and-drop functionality, Power BI enables even non-technical users to create compelling visualizations and conduct data analysis effortlessly.
- Power BI can be accessed from various platforms, such as desktop applications, web browsers, mobile devices, etc.
- Additionally, its seamless integration with other Microsoft products, such as Excel and Azure, enhances collaboration and provides a comprehensive suite of data-driven solutions for organizations of all sizes.
What is Tableau?
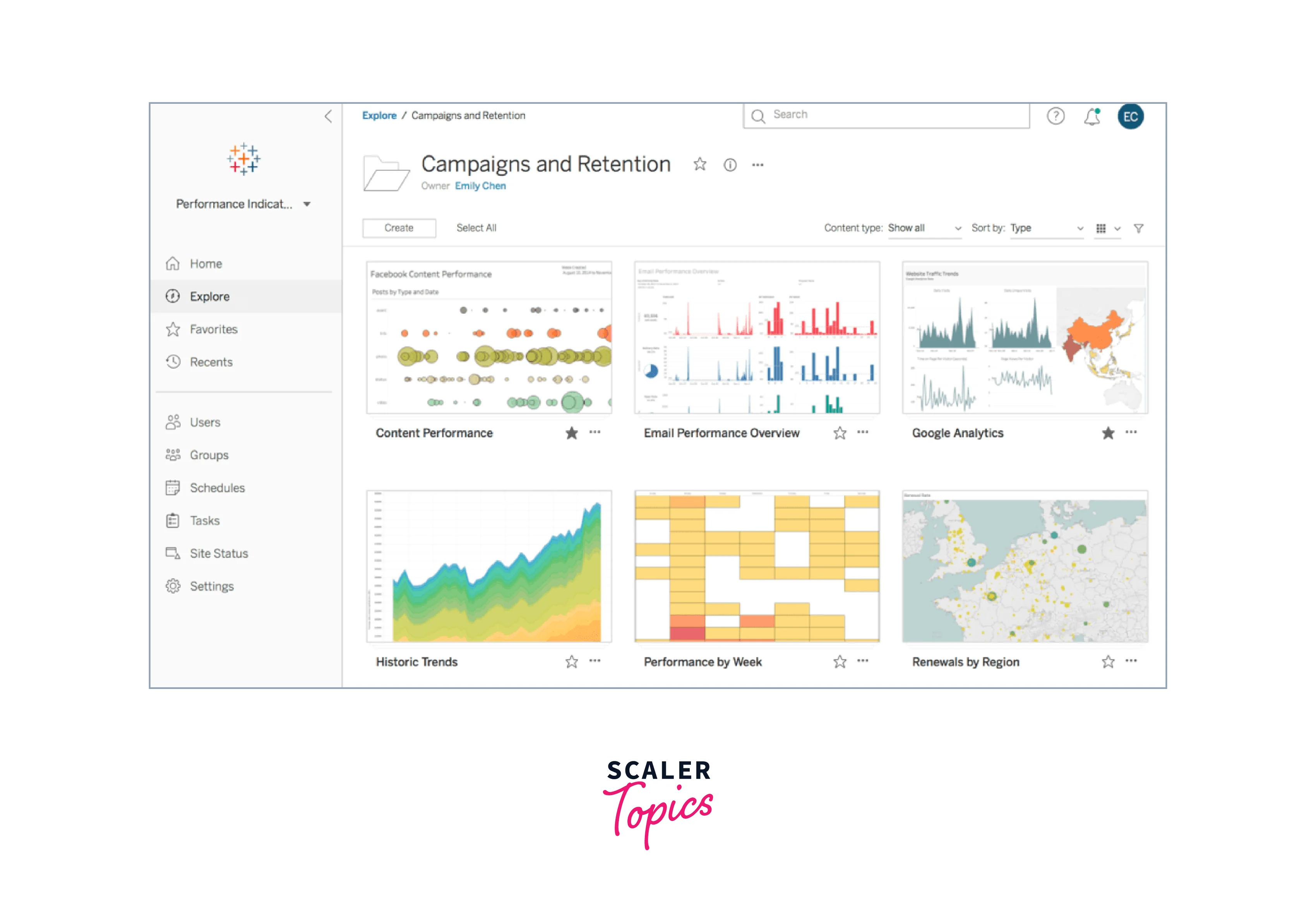
- Tableau is a leading data visualization and business intelligence software acquired by Salesforce. It allows users to connect to various data sources, from spreadsheets to databases, and transform raw data into interactive, visually engaging dashboards, reports, and charts.
- Tableau's intuitive drag-and-drop interface makes it easy for both technical and non-technical users to quickly analyze and explore large and complex datasets, perform ad-hoc analysis, and gain valuable insights without the need for complex coding or programming skills.
- Its versatility, vast library of visualization options, and powerful data manipulation capabilities have made Tableau a popular choice for organizations seeking to unlock the full potential of their data and make data-informed decisions across different business departments.
Features of Power BI
Here are a few of the top features of Power BI:
- Interactive Data Visualizations:
Power BI offers a wide range of customizable and interactive data visualizations, including charts, graphs, maps, and tables. Users can easily explore and analyze data by simply interacting with the visuals, helping to uncover valuable insights quickly. - Data Connectivity:
Power BI allows seamless integration with various data sources, such as Excel, SQL databases, cloud services like Azure, and popular online platforms like Google Analytics. This extensive connectivity enables users to consolidate data from multiple sources for comprehensive analysis. - Power Query and Data Transformation:
With Power Query, users can clean, transform, and shape their data, ensuring data accuracy and consistency. This feature simplifies the data preparation process and enhances the quality of analysis and reporting. - Natural Language Query:
Power BI supports natural language queries, allowing users to ask questions in plain English to obtain relevant visualizations and insights. This intuitive feature makes it friendly and accessible for both technical and non-technical users. - Cloud-Based Collaboration:
Using Power BI facilitates seamless collaboration among team members as a cloud-based tool. Users can share reports and dashboards with colleagues, making it easier to collaborate on data-driven projects and make collective data-driven decisions. - Real-Time Data Streaming:
Power BI enables real-time data streaming, ensuring that reports and dashboards reflect the most up-to-date information. This feature is particularly valuable for monitoring critical business metrics and responding to changes swiftly.
Features of Tableau
Here are a few of the top features of Tableau:
- Robust Data Visualization:
Tableau offers a vast array of powerful data visualization options, from basic charts to advanced visuals like heat maps, tree maps, and bubble charts. Users can create compelling, interactive visualizations to gain deeper insights into their data. - Data Connectivity and Integration:
Tableau seamlessly connects to various data sources, including spreadsheets, databases, cloud platforms, and web data connectors. - Drag-and-Drop Interface:
Tableau's user-friendly drag-and-drop interface makes it easy for both technical and non-technical users to create dynamic dashboards and reports. Users can quickly build visualizations without extensive coding or scripting. - Ad-Hoc Analysis:
Tableau excels in ad-hoc analysis, enabling users to explore data in real-time to uncover trends and patterns instantly. This iterative and exploratory approach supports data discovery and drives data-driven decision-making. - Advanced Calculations and Expressions:
Tableau provides a wide range of powerful calculations and expressions, such as table calculations, LOD (Level of Detail) expressions, and custom calculations. These advanced features allow users to perform complex data manipulations and create sophisticated analytics. - Storytelling and Dashboard Interactivity:
Tableau allows users to create interactive dashboards and stories that present data in a compelling narrative format. With dashboard interactivity, users can drill down into details, filter data, and gain deeper insights directly from the visualizations.
Key Difference Between Power BI and Tableau
Here are the key differences between Power BI vs. Tableau in tabular format:
| Factor | Power BI | Tableau |
| Developer | Developed by Microsoft | Developed by Tableau (acquired by Salesforce) |
| Data Visualization | Rich set of interactive visualizations | A vast array of powerful and advanced data visualization options |
| Data Connectivity | Seamless integration with Microsoft products (Excel, Azure, etc.) and various other data sources | Connects to various data sources, including spreadsheets, databases, and cloud platforms |
| Drag and Drop Feature | Supports | Supports |
| Natural Language Query | Supports natural language queries for data exploration | Lacks natural language query capabilities |
| Ad-hoc Analysis | Good for ad-hoc analysis and data exploration | Excels in ad-hoc analysis and iterative data discovery |
| Strengths | Strong integration with Microsoft ecosystem, natural language query, cloud-based collaboration | Ad-hoc analysis, powerful data visualization options, and storytelling capabilities |
| Learning Curve | Relatively easy to learn for users familiar with Microsoft products | Slightly steeper learning curve, especially for complex data manipulation and calculations |
| Cost | Offers various pricing plans, including free and premium versions | Generally considered more expensive, but offers a free Tableau Public version for sharing visualizations |
| Community Support | Large community with extensive resources and an active user base | Well-established community with a vast repository of tutorials and forums |
Advantages of Power BI and Tableau
Advantages of Power BI
- Seamless Integration:
Power BI seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft products like Excel, SharePoint, and Azure, creating a cohesive data analysis and reporting ecosystem. - User-Friendly Interface:
Its intuitive drag-and-drop interface and natural language query support make its UI user-friendly, reducing the learning curve. - Cost-Effective Solution:
Power BI's flexible subscription-based pricing allows organizations to scale their usage according to their needs, making it a cost-effective option. - Robust Data Connectivity:
With a wide range of data connectors, Power BI can connect to various data sources, enabling comprehensive data analysis from different systems. - Cloud and On-Premises Deployment:
Power BI offers both cloud-based and on-premises deployment options, providing flexibility for organizations with different data hosting preferences.
Advantages of Tableau
- Extensive Data Visualization:
Tableau provides an extensive library of data visualizations, enabling users to create compelling and interactive dashboards easily. - Advanced Analytics and Calculations:
Its support for advanced calculations, Level of Detail (LOD) expressions, and powerful data manipulation capabilities cater to complex data analysis needs. - Data Exploration and Ad-Hoc Analysis:
Tableau's ad-hoc analysis capabilities allow users to explore data on the fly and uncover insights in real time. - Flexibility and Customization:
Tableau offers a high level of customization, giving users more control over the appearance and functionality of their visualizations and reports. - Community and Resources:
With a vibrant user community, Tableau provides access to a vast array of resources, including tutorials, forums, and templates, enhancing user support and knowledge sharing.
Disadvantages of Power BI and Tableau
Disadvantages of Power BI
- Limited Offline Access:
Power BI heavily relies on cloud-based services, which can be a limitation for users who require frequent offline access to their reports and dashboards. - Complex Data Modeling:
Power BI is user-friendly for basic operations. However, creating complex data models and relationships may require a deeper understanding of DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) and data modeling concepts. - Data Refresh Limitations:
Power BI imposes restrictions on data refresh rates, particularly in lower-tier plans, which can be a challenge for real-time data analysis. - Limited Advanced Analytics:
Although Power BI has advanced capabilities, it may not match Tableau regarding sophisticated statistical analysis and predictive modeling. - Customization Complexity:
Customizing visualizations beyond the built-in options may require more technical expertise, making it less accessible for users without coding knowledge.
Disadvantages of Tableau
- Costly Licensing:
Tableau's licensing model can be expensive, especially for large organizations or those requiring a significant number of users and server deployments. - Learning Curve:
While Tableau's drag-and-drop interface is intuitive, mastering its more advanced features and calculations may have a steeper learning curve, especially for non-technical users. - Data Preparation Challenges:
Unlike Power BI, Tableau does not offer robust data preparation capabilities, so users may need external tools for extensive data cleansing and transformations. - Limited Natural Language Processing:
Unlike Power BI, Tableau lacks native support for natural language queries, which may limit its accessibility for non-technical users who prefer a more conversational approach to data exploration. - Cloud Limitations:
While Tableau does offer cloud deployment options, it may not have the same level of native cloud integration as Power BI, potentially impacting collaboration and data sharing in cloud-based environments.
Tableau Products
Tableau provides a range of data analysis and visualization products. Let's explore some of their main products:
- Tableau Desktop:
Tableau Desktop is the core product that allows users to create interactive data visualizations and dashboards, perform advanced data analysis, and build insightful reports. It offers a user-friendly drag-and-drop interface and is ideal for data analysts and business users seeking to gain valuable insights from their data. - Tableau Prep:
Tableau Prep is a data preparation tool that enables users to clean, shape, and combine data from multiple sources before analysis. It simplifies the data preparation, helping users ensure data quality and consistency for more accurate and impactful visualizations. - Tableau Online:
Tableau Online is a cloud-based platform allowing users to publish, share, and collaborate securely on Tableau dashboards and reports. It enables real-time data sharing and collaboration among team members, making it easier to access insights from anywhere with an internet connection. - Tableau Mobile:
Tableau Mobile is a companion app that extends Tableau's capabilities to mobile devices. It empowers users to access and interact with Tableau dashboards on the go, ensuring they have data insights at their fingertips. - Tableau Public:
Tableau Public is a free version of Tableau that allows users to create and share interactive visualizations with the public. Data and dashboards created using Tableau Public are openly accessible online, making it an excellent choice for data enthusiasts and organizations that want to promote data transparency.
Power BI Products
Power BI, developed by Microsoft, encompasses various key products to cater to diverse data needs. Let's explore some of the primary offerings of Power BI:
- Power BI Desktop:
Power BI Desktop is a powerful application for creating data models, visualizations, and reports. It empowers users to connect to various data sources and design compelling insights. - Power BI Service (Power BI Pro and Power BI Premium):
Power BI Service is a cloud-based platform for sharing, collaborating, and publishing Power BI reports and dashboards. It offers both Pro and Premium licensing options to cater to different organizational needs. - Power BI Mobile:
Power BI Mobile is a mobile app that allows users to access and interact with their Power BI reports and dashboards on smartphones and tablets, ensuring data insights on the go. - Power BI Report Server:
Power BI Report Server enables organizations to host and manage Power BI reports and dashboards on their premises, offering enhanced security and control over data. - Power BI Embedded:
Power BI Embedded allows organizations to integrate Power BI reports and dashboards directly into their websites and business applications, delivering data analytics capabilities seamlessly to end-users. - Power BI Dataflow:
Power BI Dataflow simplifies data preparation and transformation by enabling users to build reusable data entities, promoting data consistency across reports and dashboards.
History of Power BI and Tableau
Power BI's journey began in 2011 as an add-on for Microsoft Excel called Power Pivot. Over time, Microsoft continued to expand its capabilities, introducing Power Query in 2013 and Power View in 2014. In 2015, Power BI was officially launched as a cloud-based business intelligence service. Since then, it has evolved with regular updates and enhancements, becoming one of the leading BI tools in the market.
Tableau was founded in 2003 by Chris Stolte, Pat Hanrahan, and Christian Chabot. The company aimed to simplify data visualization and analytics for non-technical users. In 2005, the first version of Tableau Desktop was released, and it gained popularity for its user-friendly interface and powerful capabilities. The company went public in 2013 and was acquired by Salesforce in 2019.
Cost of Power BI and Tableau
Let's delve into the pricing details of both Power BI and Tableau, where we can observe significant differences between these two business intelligence tools.
Power BI
- Power BI Desktop: Free:
Designed for individual users, this free version allows you to use Power BI on your desktop. - Power BI Pro: $10 per user/month:
With a single license, this plan offers self-service analytics, enabling data visualization with live dashboards and reports. It is also included for free with Microsoft 365 E5. - Power BI Premium: $20 per user/month:
Geared towards enterprise-level needs, this option provides big data analytics tools and simplified data management. - Power BI Premium (Capacity Node): $4995 per capacity/month:
Ideal for entire organizations.
Tableau
- Tableau Public: Free:
Aimed at at-home users, this free version allows you to create visualizations connected to Excel, CSV, and JSON files. However, all visualizations are publicly viewable. - Tableau Creator: $70 per month/user:
Intended for individuals and team members, this plan grants access to Tableau Desktop, Tableau Prep Builder, and one Creator license for Tableau Server or Tableau Cloud, providing comprehensive visualization and analytics tools. - Tableau Explorer: $42 per month/user:
This option facilitates data exploration with self-serve analytics and includes one Tableau Cloud Explorer license. - Tableau Viewer: $15 per month/user:
With this plan, users can only view existing Tableau dashboards and visualizations, and it comes with one Tableau Cloud Viewer license.
Performance of Power BI and Tableau
Power BI is known for its user-friendly interface and ease of use, making it an excellent choice for quick and straightforward data analysis. It performs well when dealing with smaller datasets but may experience slower performance when handling large volumes of data.
On the other hand, Tableau excels in handling large datasets swiftly, providing extensive data visualization features without limiting the number of data points or enforcing row or size restrictions. Its capability to handle vast amounts of data efficiently offers users a comprehensive 360-degree view of their data, making it a preferred option for data-intensive tasks.
User Interface of Power BI and Tableau
Regarding the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX), the experience of Power BI vs. Tableau is more or less the same, with minimal differences to set them apart. Both platforms are designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, allowing users to explore their data familiarly and effortlessly.
Data Sources in Power BI and Tableau
Both Power BI and Tableau offer robust support for a wide range of data sources. Power BI allows seamless connectivity to various data sources, including Excel, Text/CSV, Folders, MS SQL Server, Access DB, Oracle Database, IBM DB2, MySQL database, PostgreSQL database, cloud services like Azure, and popular online platforms like Google Analytics.
Similarly, Tableau supports connectivity to spreadsheets, databases, cloud platforms, and web data connectors, such as Excel, Text File, PDF, JSON, Amazon Redshift, Cloudera Hadoop, Google Analytics, dropbox, Google Sheets, etc., enabling users to access and analyze data from diverse sources.
Ease of Using Power BI and Tableau
Regarding ease of use, Power BI and Tableau are both known for their user-friendly interfaces, making them accessible to a wide range of users. Power BI's seamless integration with other Microsoft products and drag-and-drop functionality make it intuitive for those familiar with the Microsoft ecosystem. Tableau's drag-and-drop interface and powerful data exploration features provide a smooth experience for technical and non-technical users alike.
Finally, Power BI holds an advantage here, stemming from its integration with Microsoft Office 365. This familiarity with the Microsoft ecosystem makes it easier for end-users, who are already accustomed to Office 365 applications, to adapt and utilize Power BI seamlessly.
Programming Support for Power BI and Tableau
Power BI provides support for Data Analysis Expression (DAX) language, enabling users to manipulate and model data effectively. Additionally, Power BI can connect to the R programming language, but this functionality is restricted to enterprise-level users.
On the other hand, Tableau surpasses Power BI in its integration with the R language. The Tableau SDK also allows developers to utilize four programming languages: C, C++, Java, and Python. By connecting to these programming languages, users can create even more powerful and advanced visualizations, giving Tableau an edge in terms of programming support.
Data Visualization in Power BI and Tableau
Both Power BI and Tableau excel in data visualization, offering impressive features for creating engaging and meaningful reports and dashboards. Power BI provides an intuitive drag-and-drop functionality, making it easy to build visualizations without prior knowledge. It offers various attractive and detailed visualizations to create visually appealing reports and dashboards. The Power BI service allows users to ask questions about their data, generating meaningful insights on the fly.
Tableau enables users to customize dashboards for specific devices, ensuring a seamless user experience across various platforms. It delivers interactive visuals that support real-time insights, allowing users to spot trends and identify opportunities. Tableau's query-to-visualization capabilities make data exploration effortless, and its built-in table calculations simplify building reports and dashboards. Users can easily leverage Tableau's powerful visualization tools to create impactful data presentations regardless of prior knowledge.
Machine Learning in Power BI and Tableau
Both Power BI vs. Tableau offers machine learning capabilities but with some distinctions. Power BI supports the integration of Azure Machine Learning, enabling users to leverage pre-built machine learning models for predictive analytics. Tableau, on the other hand, provides support for integrating with R and Python, allowing users to build and execute custom machine-learning algorithms directly within Tableau.
Customer Support in Power BI and Tableau
In terms of customer support, the features of Power BI vs. Tableau provide are good, catering to the needs of their users. Power BI offers support through its comprehensive online documentation, community forums, and official user community. On the other hand, Tableau has a well-established and extensive customer support network, boasting over 160,000 active users engaged in more than 500 global user groups and over 150,000 active customers actively participating in its online community.
Google Trends
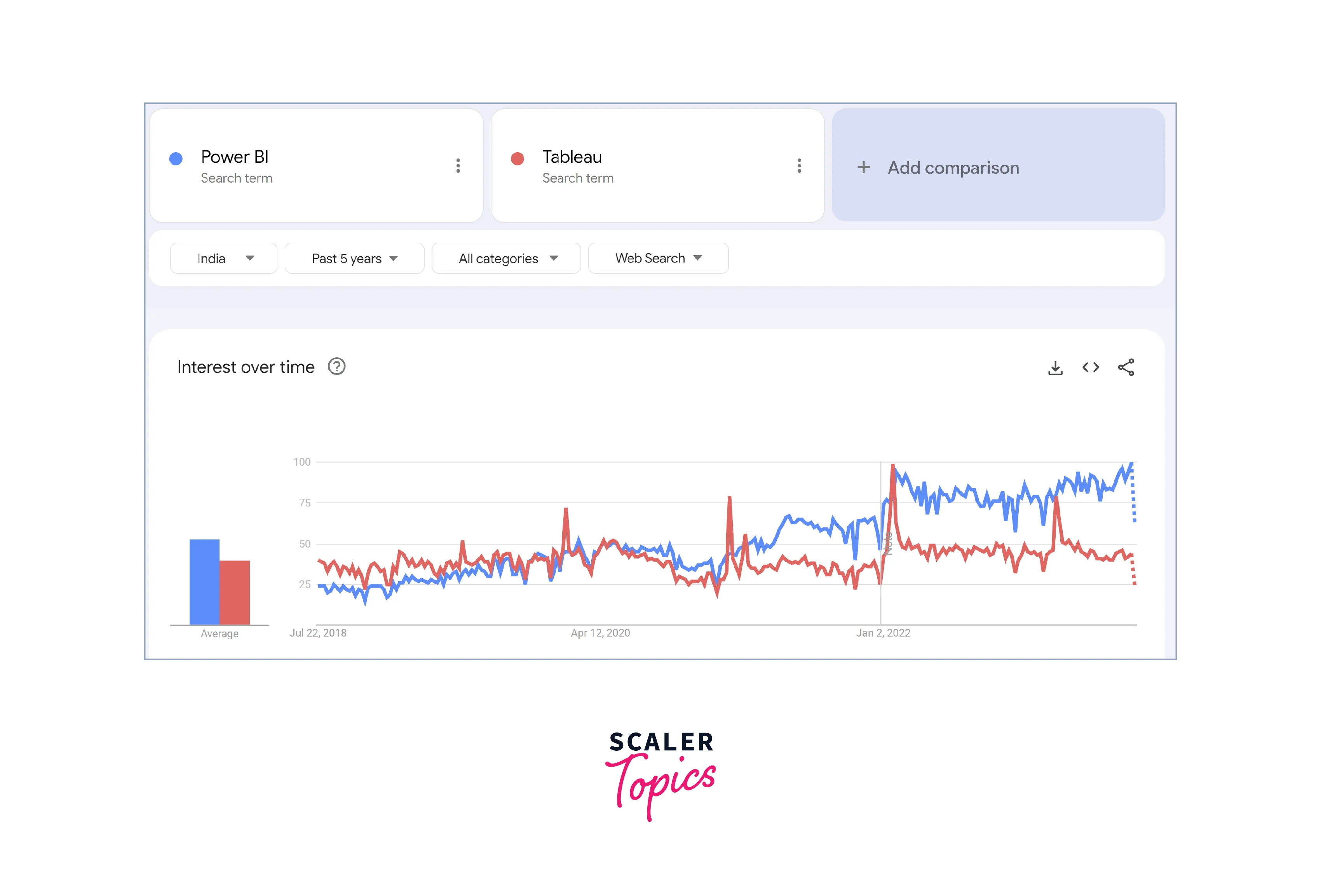
Over the past five years, Google Trends data for Power BI vs. Tableau for India indicates that Tableau used to outperform Power BI regarding search interest. However, since around mid-2020, the trend has shifted for Google Trends data for Power BI vs. Tableau, and Power BI's popularity has been consistently surpassing Tableau. The gap between the two tools has significantly widened, making Power BI the clear winner in terms of search interest in India.
Power BI vs. Tableau: What is Better?
Determining Power BI vs. Tableau depends on specific organizational needs and preferences. Power BI is advantageous for businesses deeply integrated with the Microsoft ecosystem, offering user-friendliness and seamless collaboration. On the other hand, Tableau excels in handling larger datasets and providing advanced data visualization options, making it a preferred choice for data analysts and users seeking extensive data exploration capabilities.
FAQs
Q: How is Tableau different from Power BI?
A: Tableau differs from Power BI in terms of data handling, integration with programming languages, and pricing models. Tableau is known for better performance with large datasets and offers more extensive programming support, while Power BI seamlessly integrates with Microsoft products and offers cost-effective licensing options.
Q: What is better, Tableau or Power BI?
A: Determining which is better, Tableau or Power BI, depends on specific needs and preferences. Tableau excels in handling large datasets and providing advanced data visualization options, making it preferred for data analysts. On the other hand, Power BI seamlessly integrates with Microsoft products and offers user-friendliness, making it suitable for organizations within the Microsoft ecosystem. Ultimately, the choice depends on factors like budget, data volume, and existing infrastructure.
Q: Can Power BI connect to Tableau?
A: Yes, Tableau can now consume data models generated in Power BI. This means that the data models created in Power BI are accessible and usable within Tableau.
Q: Which is easier to use, PowerBI or Tableau?
A: Power BI is deemed more user-friendly, particularly for non-data analysts and new users, while Tableau is popular most among experienced data analysts/scientists due to its slightly steeper learning curve.
Q: Does Tableau require coding?
A: While Tableau offers scripting options through its Calculation Editor and Script Editor features, coding is not required to create basic visualizations. Tableau provides connectors to various data sources, allowing users to extract, transform, and load data without the need to write any code, making it accessible to users without programming knowledge.
Q: Do more people use Tableau or Power BI?
A: Tableau and Power BI are both popular tools, but Power BI has a larger user base due to its seamless integration with Microsoft products and accessibility for users within the Microsoft ecosystem.
Q: Should I learn Excel before Tableau?
A: Learning Excel before Tableau can be beneficial, but it is not a strict requirement as Tableau's user-friendly interface allows beginners to get started directly with data visualization and analysis.
Q: Is Tableau still in demand in 2023?
A: Tableau is a popular data visualization tool, and its demand is expected to continue in 2023 and beyond. Its user-friendly interface, powerful capabilities, and continuous updates make it a preferred choice for businesses for their BI tools.
Q: Why is Power BI better than other visualization tools?
A: Power BI stands out as a top visualization tool due to its seamless integration with Microsoft products, user-friendly interface, and extensive range of data connectors, making it highly accessible for users within the Microsoft ecosystem. Its flexible pricing options, powerful data modeling capabilities, and cloud-based collaboration features further solidify its position as a preferred choice for data analysis and visualization.
Q: Which has a better job market, Tableau or Power BI?
A: The job market for both Tableau and Power BI is robust, but Power BI's demand has witnessed significant growth in recent years, primarily because of its integration with the Microsoft ecosystem. This integration has made Power BI a valuable tool for businesses already leveraging Microsoft products, further enhancing its appeal in the job market.
Q: What are the pros and cons of Power BI vs Tableau?
A: For Power BI, the pros are seamless integration with Microsoft products and a user-friendly interface for non-technical users, and the cons are limited offline access and complex data modeling for advanced users. For Tableau, the pros are excellent performance with large datasets and extensive data visualization options, and the cons are relatively higher cost and a steeper learning curve for beginners.
Q: Among Tableau and Power BI, which is easier to learn, and which among both is more effective in visualization?
A: Power BI is generally considered easier to learn, while Tableau is often regarded as more effective in data visualization with its extensive range of visual options.
Q: What can Tableau do that Power BI cannot, and vice versa?
A: Tableau can handle larger datasets more efficiently, while Power BI offers seamless integration with Microsoft products and services.
Conclusion
- Both Power BI and Tableau are popular and powerful business intelligence tools with unique strengths.
- Power BI's seamless integration with Microsoft products, user-friendliness, and cost-effective pricing make it an excellent choice for organizations within the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Tableau's ability to handle large datasets efficiently, extensive data visualization options, and strong programming support make it a preferred tool for data analysts and advanced users.
- The choice between Power BI and Tableau ultimately depends on specific organizational needs, existing infrastructure, and user preferences, ensuring that organizations can find the right fit for their data analysis and visualization requirements.
