Relationship in DBMS

A database is a collection of data that contains multiple tables in which the data is stored in the form of rows and columns. The process by which these databases are managed and controlled is known as the database management system (DBMS). Basically, it is software that is used for performing various operations on the data. An example of a database management system can be MySQL, Oracle, etc.
Relationships correspond to connections between things, people, etc. These relationships in DBMS are actually created between entities. These entities are real-life objects that are distinguishable from other objects and have some attributes associated with them.
You can refer to the Entity in DBMS for more information.
What is a relationship in DBMS?
An entity in a database management system is a real-life object distinguishable from other objects. These entities have an attribute that defines the properties and characteristics of the entity.
Examples of an entity can be a student, a car, animals, etc. All these are real-life entities whose data can be stored in a database. A student's attributes can be his ID, course, or semester which can describe a student entity.
Any association between two entities is known as a relationship between those two entities. This relationship in DBMS is represented using a diamond shape in the entity-relationship diagram. An entity-relationship diagram is a graphical representation of entities and the relationships that exist between them.
For example:-
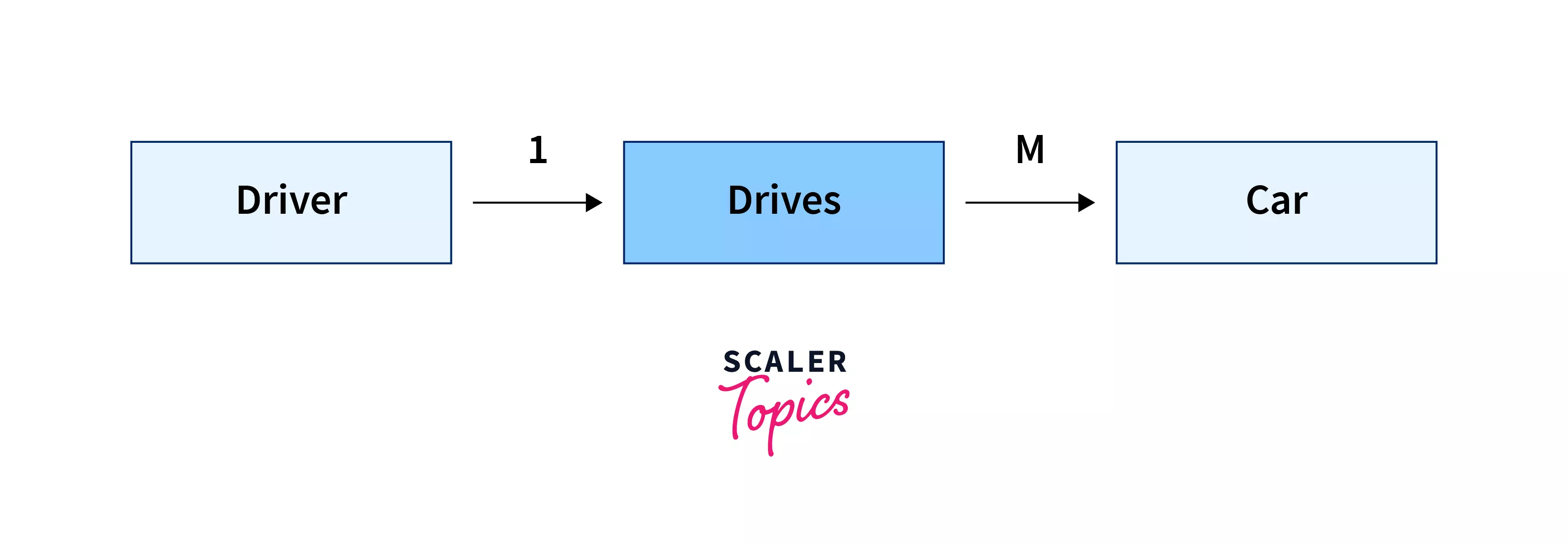
The driver drives a car.
In the above example, the driver and the car are entities whereas the word drives is a relationship between those entities. Moreover, the attributes of the driver entity can be that it is a person, and the car entity can be that it is a vehicle.
Similarly, another example of the relationship in DBMS is-
Rohit plays football.
Therefore, here Rohit and football are entities, and plays are the relationship between them. However, the attribute associated with the Rohit entity is that it is a person's name and the football entity belongs to a sport.
Types of Relationships in DBMS
Three types of relationships can exist between two entities of tables, which are given below and discussed with examples.
- One-to-One relationship
- One-to-Many relationship or Many-to-One relationship
- Many-to-Many relationship
One-to-One Relationship
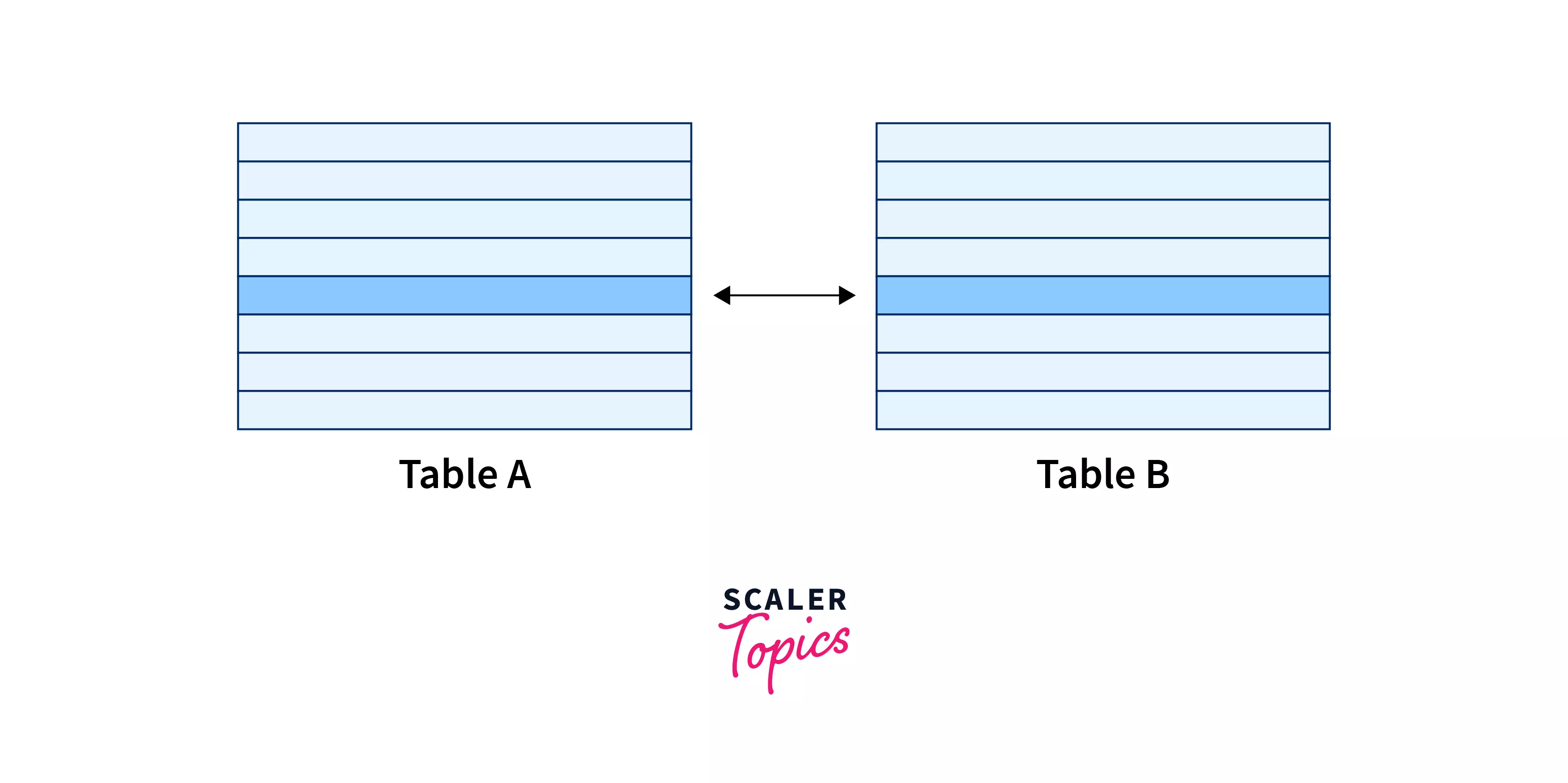
A One-to-one relationship means a single record in Table A is related to a single record in Table B and vice-versa.
For example, If there are two entities, 'Person'(Name, age, address, contact no.) and 'Aadhar card' (Name, Aadhar no.). So each person can have only one Aadhar card, and the single Aadhar card belongs to only one person.
You can visualize the one-to-one relationship in DBMS like this:
This type of relationship is used for security purposes. In the above example, we can store the Aadhar card number in the same entity, 'Person', but we created another table for the 'Aadhar card' because the Aadhar card number may be sensitive data and should be hidden from others. Let's take another example with the databases.
Example:
Consider a table of Employees as shown below:
Table A:
| emp_id | emp_name | emp_address |
|---|---|---|
| 001 | Claira Anderson | 113, Zaraiah Road, TX 77001 |
| 003 | Marc Doe | 34343, Palm Jumeirah Road, Dubai 990039 |
| 005 | Bruce Quilt | 23, Santa Cruiz Road, NY 44303 |
Now, you can place the employee address in a separate table as shown below:
Employee:
| emp_id | emp_name | emp_address_id |
|---|---|---|
| 001 | Claira Anderson | 901 |
| 003 | Marc Doe | 903 |
| 005 | Bruce Quilt | 905 |
Employee Address:
| emp_address_id | emp_address |
|---|---|
| 901 | 113, Zaraiah Road, TX 77001 |
| 903 | 34343, Palm Jumeriah Road, Dubai 990039 |
| 905 | 23, Santa Cruiz Road, NY 44303 |
Now, the relationship between the Employees table and Employee Address can be created. In the above example, one emp_address_id belongs to only one emp_address; that is, the relationship is a one-to-one relationship. This type of relationship is not very common as the employee's address can also be included in the Employee table as shown in Table A, and this would work too.
One-to-Many Relationship
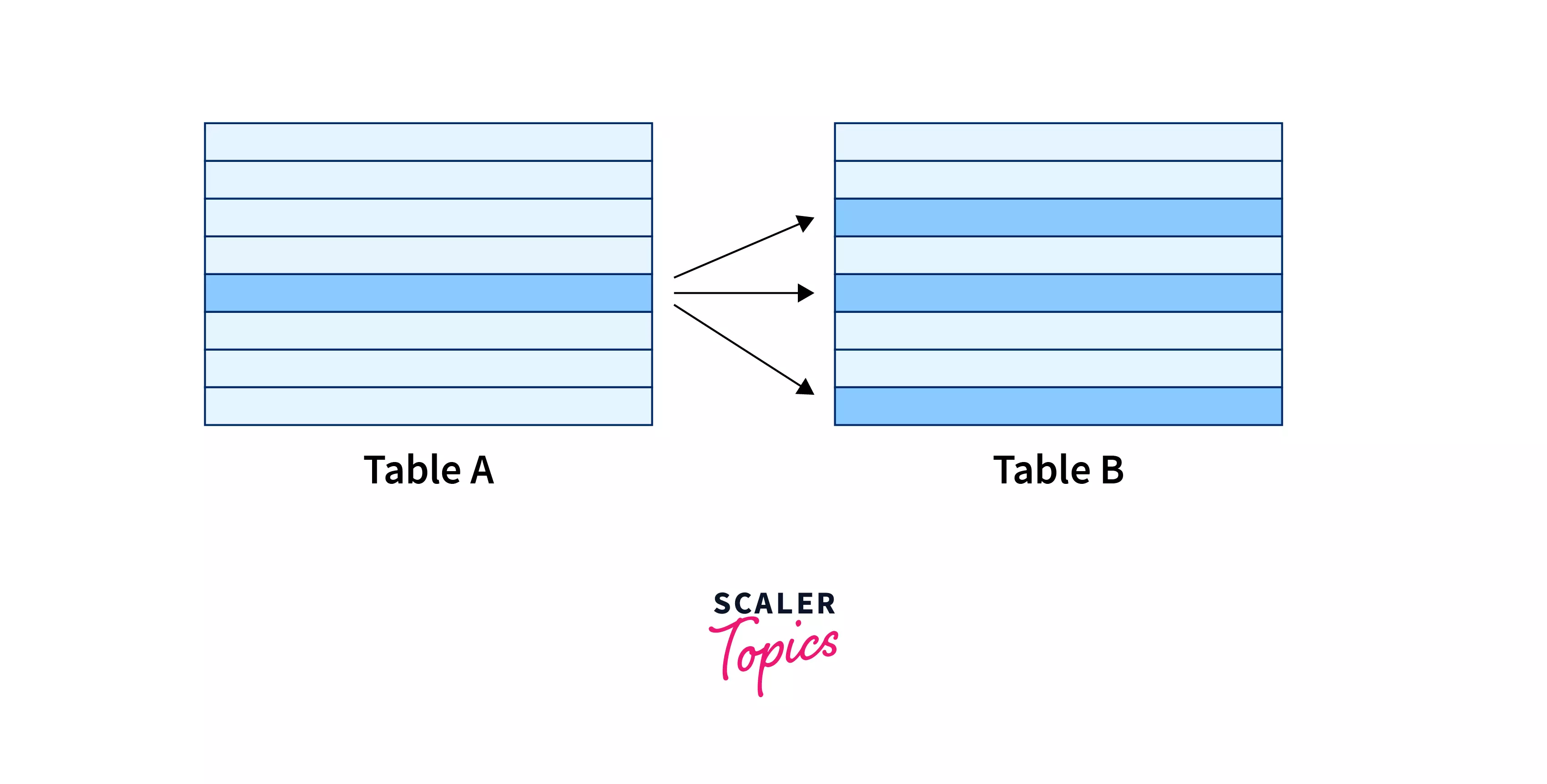
Such a relationship exists when each record of table A can be related to one or more records of another table, i.e., table B. However, a single record in table B will have a link to a single record in table A. This is the most common relationship you will find that is widely used. A one-to-many relationship in DBMS can also be named a many-to-one relationship, depending on how we view it.
The one-to-many relationship in DBMS exists between the pair of tables if a single record in one table is related to one or more records of the other table. For example, if there are two entities, 'Customer' and 'Account', then each customer can have more than one account, and each account is owned by one customer only.
You can visualize the one-to-many relationship in DBMS like this:
Example:
Consider a table of Customers and Orders as shown below:
Customers:
| customer_id | customer_name | customer_no |
|---|---|---|
| 111 | Maria Danzie | 1199229921 |
| 222 | Alex Brat | 3939637382 |
| 333 | Sania Martini | 82492835634 |
Orders:
| order_id | order_amount | customer_id |
|---|---|---|
| 10001 | 1200 | 222 |
| 10002 | 2000 | 333 |
| 10003 | 4500 | 222 |
| 10004 | 1220 | 111 |
| 10005 | 3550 | 222 |
The relationship between the above two tables can be visualized like this:
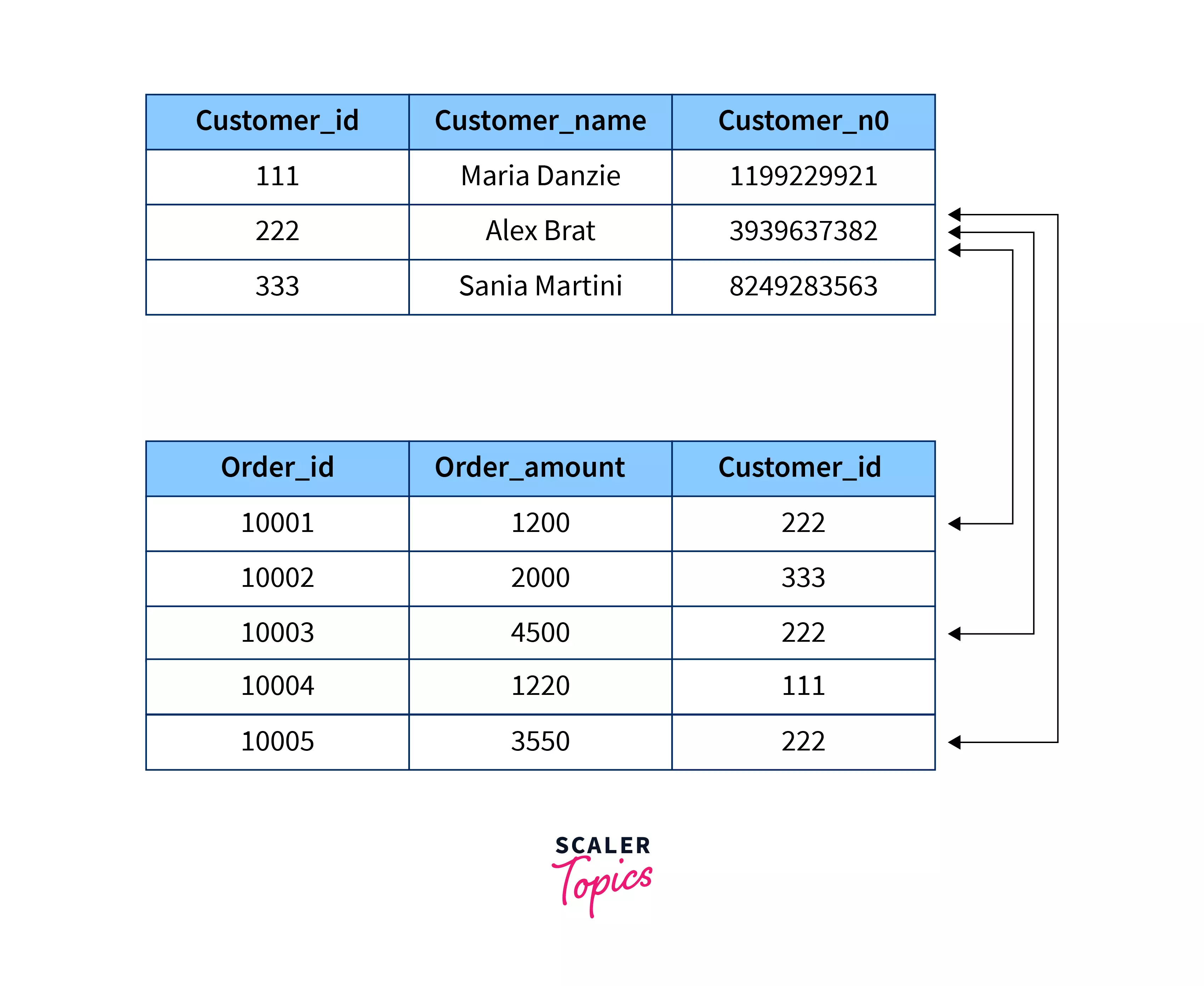
In this example, there is a one-to-many relationship if looked at from the perspective of the Customers. As shown above, the customer_id - 222 is related to the three different order_id. Similarly, there is a many-to-one relationship between the tables if looked at from the perspective of the Orders table.
Many-to-Many Relationship
A many-to-many relationship exists between the tables if a single record of the first table is related to one or more records of the second table and a single record in the second table is related to one or more records of the first table. Consider the tables A and B. In a many-to-many relationship, each record in table A can be linked to one or more records in table B and vice-versa. It is also represented as an N: N relationship.
For example, consider the two tables, i.e., a student table and a courses table. A particular student may enroll himself in one or more than one course, while a course also may have one or more students. Hence, this is a great example of many-to-many relationships.
You can visualize the many-to-many relationship in DBMS like this:
A many-to-many relationship from the perspective of table A.
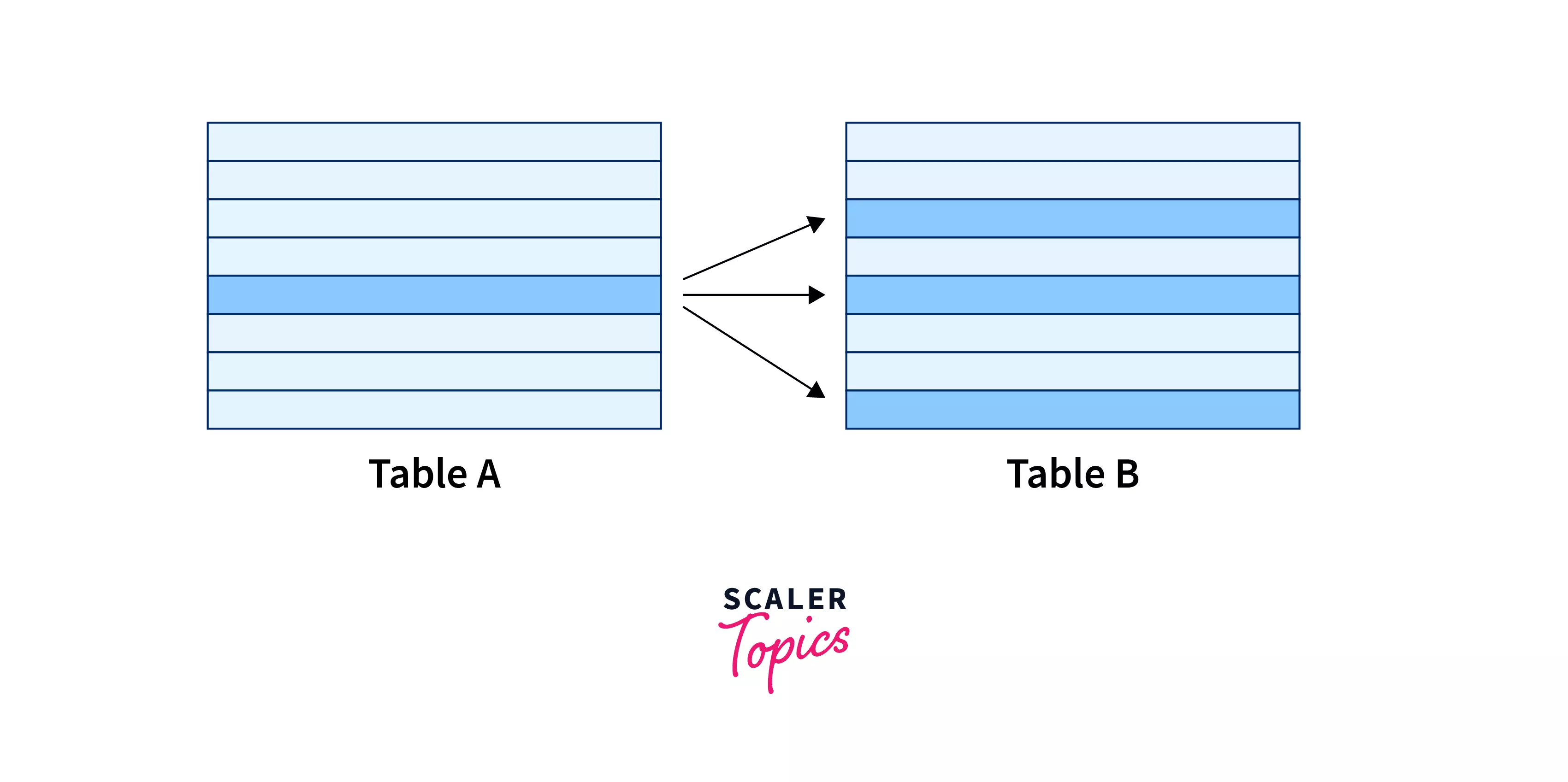
A many-to-many relationship from the perspective of table B.
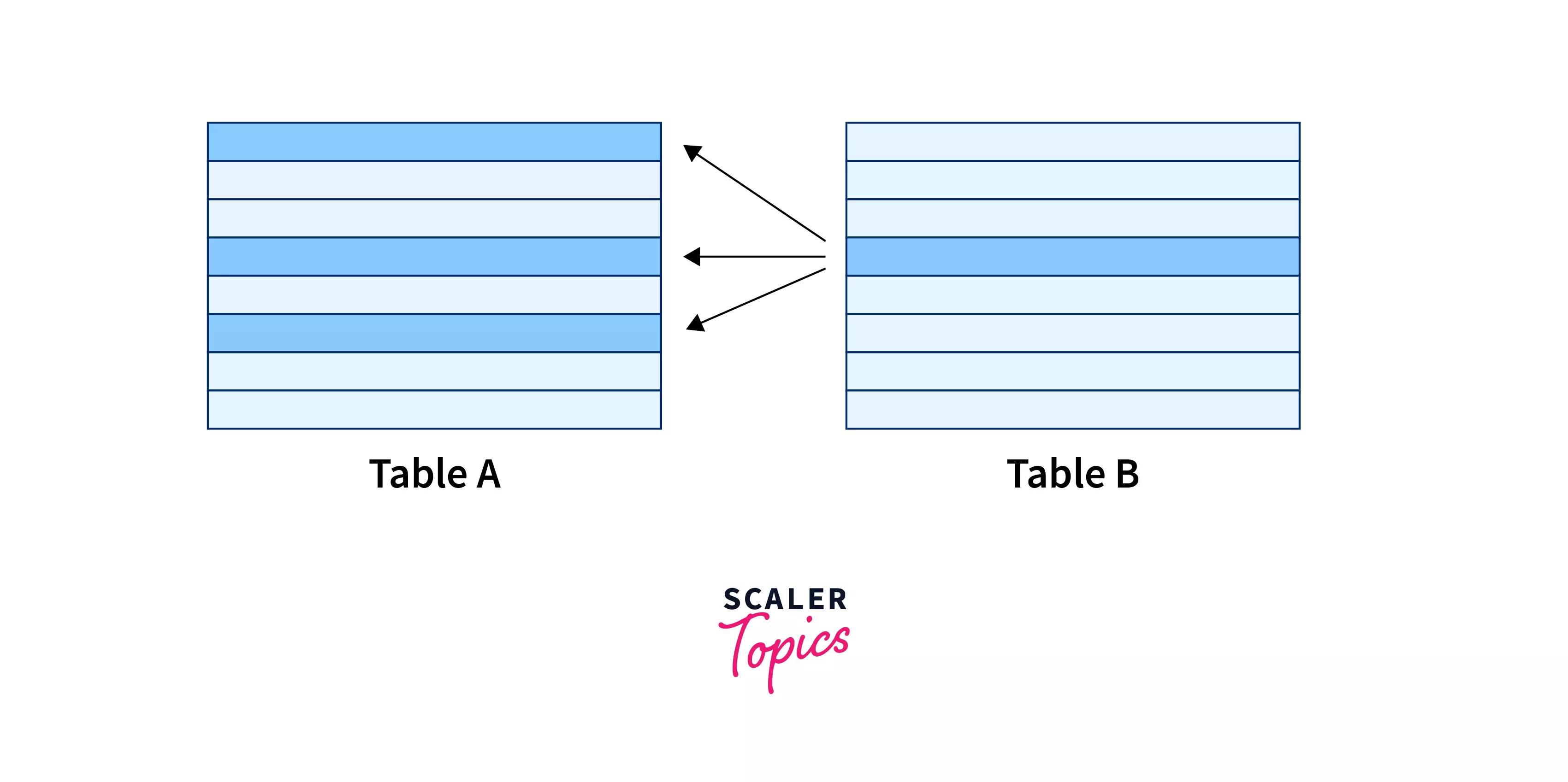
Example:
Consider the tables of Orders, Items, and Items Orders as shown below:
Orders:
| order_id | order_amount | customer_id |
|---|---|---|
| 10001 | 1200 | 222 |
| 10002 | 2000 | 333 |
| 10003 | 4500 | 222 |
| 10004 | 1220 | 111 |
| 10005 | 3550 | 222 |
Items:
| item_id | item_name |
|---|---|
| 1201 | Maggi |
| 1202 | Pizza |
| 1203 | Kurtossh |
Items Orders:
| order_id | item_id |
|---|---|
| 10001 | 1201 |
| 10001 | 1203 |
| 10004 | 1202 |
| 10004 | 1203 |
| 10005 | 1201 |
| 10003 | 1201 |
The relationship between the above two tables can be visualized like this:
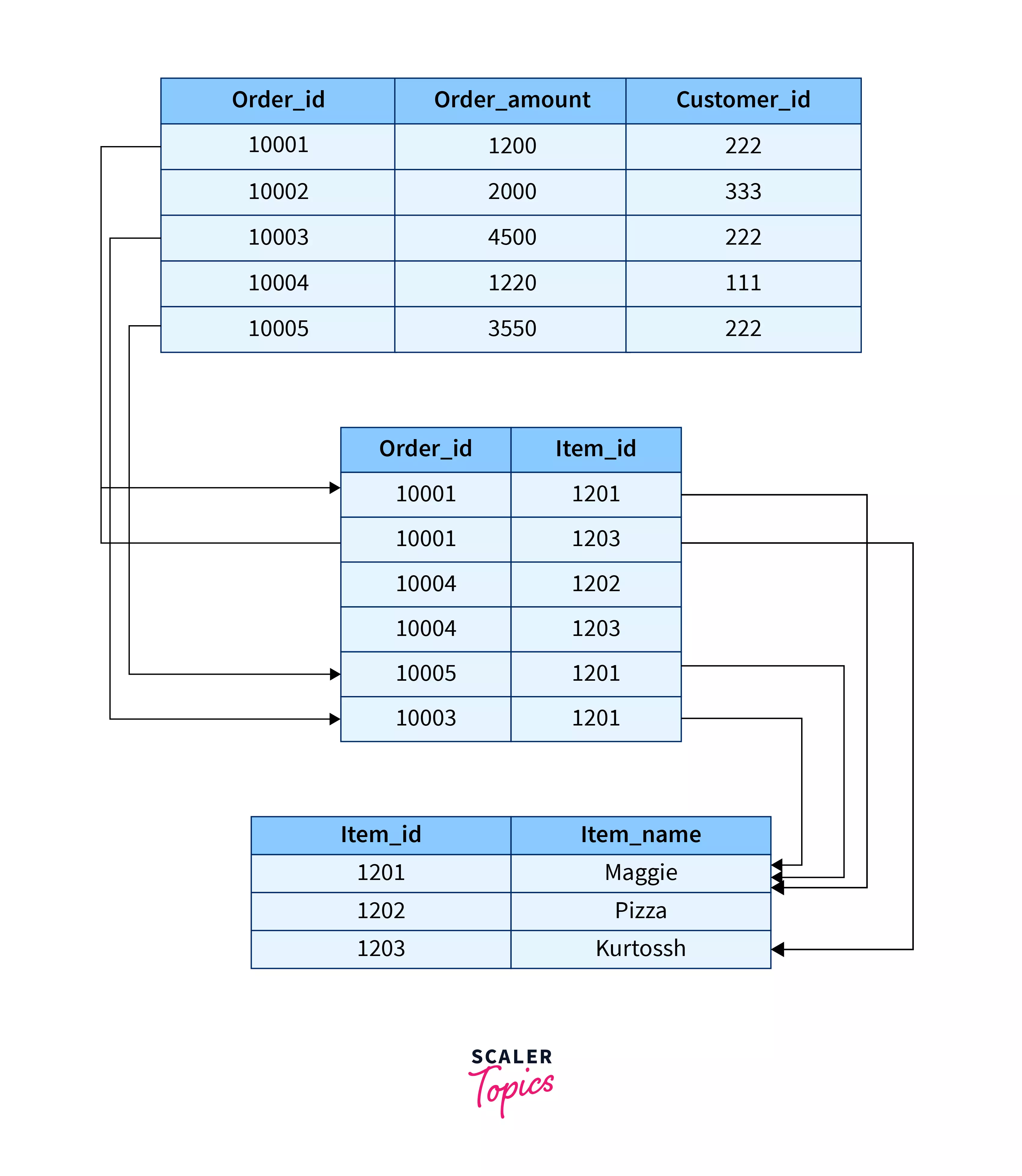
As shown in the above example, the table Items Orders has only one purpose: to create many-to-many relationships between the items.
| Type of relationship | Description |
|---|---|
| One-to-one | This type of relationship holds when a record of one table is related to only one record of another table. An example of such a relationship can be the records of people all over India, where each person can have only one Aadhaar card. |
| One-to-many | This type of relationship holds when one record of a table is related to many records of another table. An example of such a relationship can be an employee and a project database in which a single employee works on multiple projects simultaneously. |
| Many-to-Many | This type of relationship holds when many records of one table are related to many records of another table. An example of such a relationship can be a Course database in which more than one teacher can teach multiple courses. |

Importance of Relationships in DBMS
- These relationships help establish a smooth workflow in a database management system. When we require such queries that fetch data from disparate tables, our query would fail and return a null value in the absence of such relationships.
- These relationships help in minimizing the redundancy of data by combining some cells together. While establishing these relationships between tables, some changes would be applied to the table structure that would remove the irrelevant data from the table.
- A well-defined relationship provides referential integrity to the table structure, making the database management system more efficient.
- These relationships make collaboration among multiple users using the database much easier.
Conclusion
- A relationship is an association between entities in a table.
- Entities are real-life objects that are distinguishable from the other objects and have an attribute associated with them.
- These attributes are properties or characteristics of the entities.
- These entities can be related in any of the following relationships: ' one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many`.
- These relationships help `minimize data redundancy' in a table.
