Reverse Doubly Linked List

Problem Statement
You are given a pointer or reference to the doubly linked list's head node and the task is to reverse a doubly linked list (the order should be reversed). After changing the order, you need to return the pointer or reference to the head node of the reversed doubly linked list.
Refer to the example and explanation section for more details and the approach section to understand how to reverse a doubly linked list.
Example
The given input doubly linked list is :
The user needs to reverse the doubly linked list.
After the reversal, the reverse doubly linked list is the output :
Example Explanation
Before getting into the explanation of the example and how to reverse a doubly linked list, let us first get a brief introduction about the doubly linked lists.
The doubly linked list is a sequential collection of data elements connected via links. The data element of a doubly linked list node contains three parts namely - the data part and two-pointers.
The data part contains the actual data. One of the pointers points to the next element of the doubly linked list and the other pointer points to the previous element of the doubly linked list.
Note :
The previous pointer of the head node of a doubly-linked list points to NULL similarly to the next pointer of the last node of a doubly-linked list points.
Example :
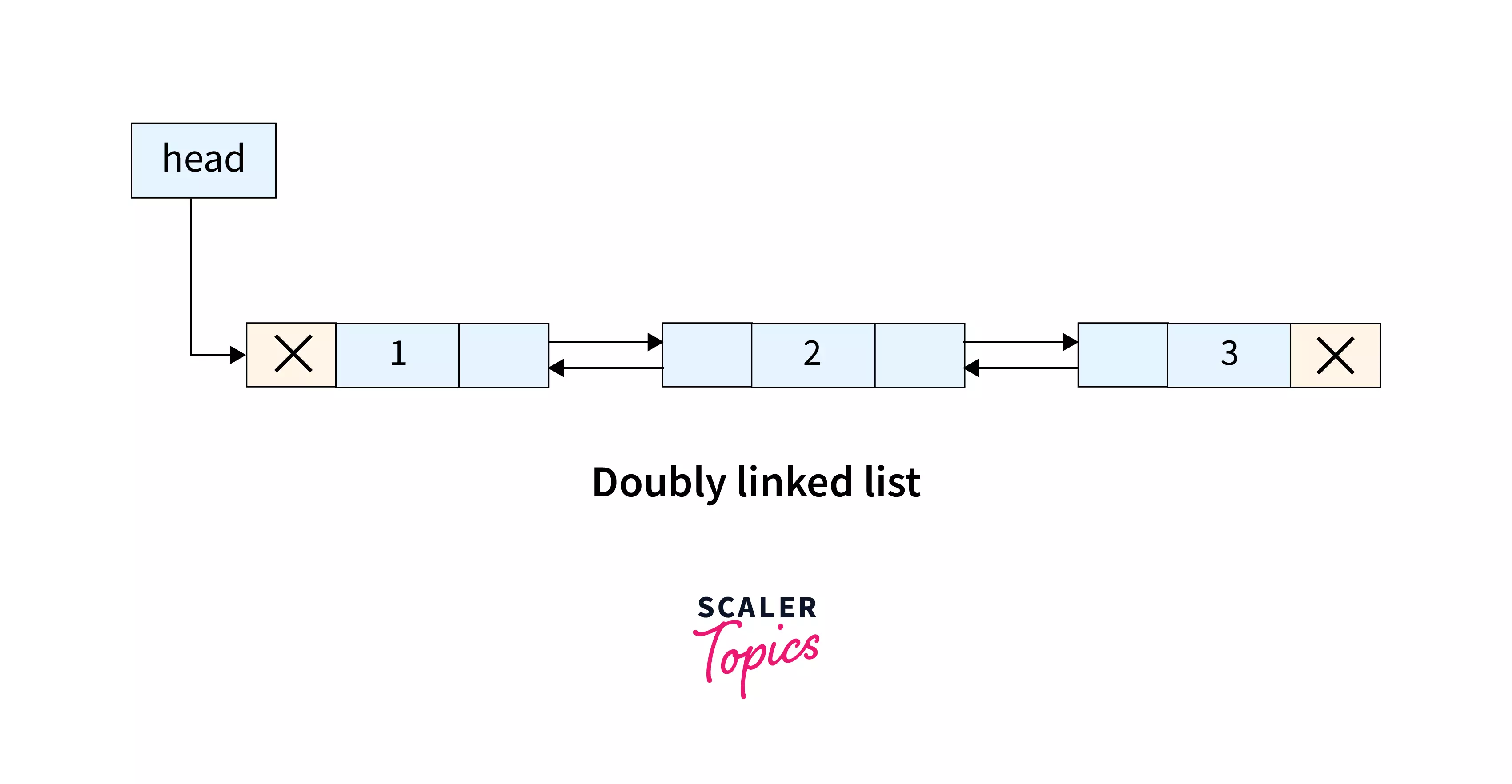
Now, let us take the same example as above and learn how to reverse a doubly linked list. We have drawn the links (pointed by pointers) so that the actual doubly linked list can be visualized easily.
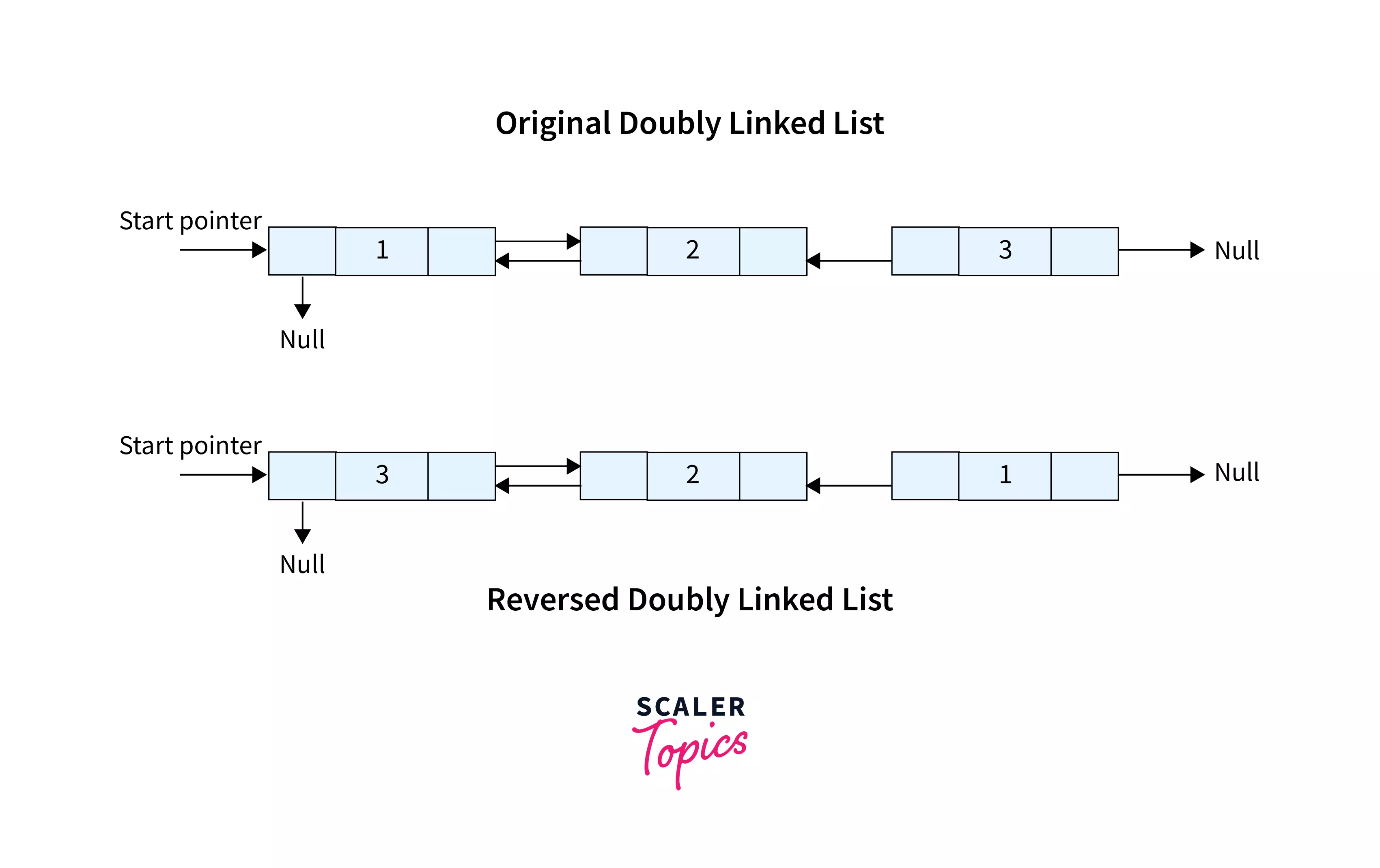
Initially, the first node is 1, and its next pointer points to node-2. The pointer of node-2 points to node-3 and finally, the pointer of node-3 points to NULL. So after the reversal, the last node becomes the first node, the second last node becomes the second node, and so on. Hence after continuing this procedure,
The final output becomes :
So, we need to return the head pointer which is now pointing to the node-3.
Constraints
- The first input is the number of elements present in the doubly linked list i.e. n.
- The second input is the sequential set of elements of the doubly linked list.
In some problems, you may find the number of test cases represented by t. So, we only need to call the reverse function t-times.
Approach - 1 : Simple Method
Let us learn the most basic approach to reverse a doubly linked list. One of the most basic or brute force solutions can be swapping the previous and next pointer of each node and finally changing the head pointer to the end of the doubly linked list.
Pseudo code can be :
C++ Code :
Java Code :
Python Code :
Output :
Complexity Analysis
In this brute force approach to reverse a doubly linked list, we are traversing the doubly linked list once. Apart from that, we are not using any extra space rather than two-pointers or references namely - first and second.
Time Complexity :
The time complexity of the above approach is , where n is the number of nodes in the doubly linked list.
Space Complexity :
The space complexity of the above approach is :
Approach - 2 : Using Stack
Another basic approach to reverse doubly linked lists can be using a stack data structure. As we know, the stack has a property that the element which is inserted first gets removed last. So, we can use this property and keep on inserting all the elements of the Doubly Linked List sequentially into the stack, and at the end, we start popping out the elements from the stack to get the reversed order.
Pseudo code can be :
C++ Code :
Java Code :
Python Code :
Output :
Complexity Analysis
In this stack-based approach to reverse a doubly linked list, we are traversing the doubly linked list once. Apart from that, we are using extra space in the form of a stack.
Time Complexity :
The time complexity of the above approach is , where n is the number of nodes in the doubly linked list.
Space Complexity :
The space complexity of the above approach is , where n is the size of the stack.
Approach - 3 : Recursive Solution
In the recursive approach to reverse the doubly linked list, we will change the previous and next pointer of the current node and pass the rest of the doubly linked list to the recursive function. So, at each recursive call, one of the doubly linked lists is interchanged and we get our desired result.
Pseudo code can be :
C++ Code :
Java Code :
Python Code :
Output :
Complexity Analysis
In this recursive approach to reverse a doubly linked list, we are traversing the doubly linked list once. Apart from that, we are using extra space in the form of a stack.
Time Complexity :
The time complexity of the above approach is , where n is the number of nodes in the doubly linked list.
Space Complexity :
The space complexity of the above approach is because the recursive solution is using a recursive stack of size n.
Approach - 4 : Iterative Solution
The iterative approach to reverse doubly linked list is similar to the brute force approach . We need to use two pointers to swap the previous and next pointers of each node of the doubly linked list.
Pseudo code can be :
C++ Code :
Java Code :
Python Code :
Output :
Complexity Analysis
In this iterative approach to reverse a doubly linked list, we are traversing the doubly linked list once. Apart from that, we are not using any extra space rather than two-pointers or references namely - first and second.
Time Complexity :
The time complexity of the above approach is , where n is the number of nodes in the doubly linked list.
Space Complexity :
The space complexity of the above approach is .
Conclusion
-
The doubly linked list is a sequential collection of data elements connected via links.
-
The data element of a doubly linked list (node) contains three parts namely
-
the data part and two-pointers. The data part contains the actual data.
-
One of the pointers points to the next element of the doubly linked list and the other pointer points to the previous element of the doubly linked list.
-
One of the most basic approaches to reverse a doubly linked list is swapping the previous and next pointer of each node and finally changing the head pointer to the end of the doubly linked list.
-
Another approach to reverse a doubly linked list is using a stack. We keep on inserting all the elements of the Doubly Linked List sequentially into the stack and at the end, we start popping out the elements from the stack to get the reversed order.
-
In the recursive approach to reverse a doubly linked list, we change the previous and next pointer of the current node and pass the rest of the doubly linked list to the recursive function.
