Cyber Security Architect Career Paths, Roles & Salary
Cyber Security Architects play a major role in guarding digital integrity and designing and implementing defense measures against cyber threats. Their role is important in safeguarding organizations' IT infrastructure and ensuring resilience in the face of evolving cybersecurity challenges. Let us explore the realm of Cyber Security Architects.
Who is a Cyber Security Architect?
A Cyber Security Architect is a professional responsible for designing and implementing security solutions for an organization's IT infrastructure. They use technical expertise with strategic vision to design and implement the security architecture for organizations' IT infrastructure. These professionals play a crucial role in analyzing, identifying, and mitigating cybersecurity risks in an organization.
What Does a Security Architect Do?
The primary role of a Security Architect is to analyze an organization's current security measures, identify vulnerabilities, and secure the organization's cloud infrastructure.
Consider a company transitioning its operations to the cloud. The Security Architect would perform the following work,
- The Security Architect's work begins by conducting a thorough risk assessment, identifying potential vulnerabilities in the cloud environment.
- They would then design and implement a robust security framework, incorporating encryption protocols, access controls, and continuous monitoring systems.
- Collaborating with the IT team, the Security Architect ensures the integration of security measures into the cloud migration process
Roles and Responsibilities
The various roles of Cyber Security Architects are:
- Development and design of comprehensive security frameworks aligned with organizational goals.
- Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities within the IT infrastructure, evaluating potential impact and devising mitigation strategies.
- Implement robust security policies and procedures to guide the organization's approach to safeguarding digital assets.
- Work closely with cross-functional teams, including IT, management, and other stakeholders, to ensure seamless integration of security measures within broader business objectives.
- Develop and manage incident response plans, enabling swift and effective action in the event of a cybersecurity incident.
- Conduct regular security audits to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Implement and oversee continuous monitoring systems to detect and respond to potential security threats in real time.
- Stay informed about the latest cyber threats and vulnerabilities, analyzing their potential impact on the organization and proactively implementing measures to address them.
Security Architect Skills
Becoming a proficient Security Architect requires a blend of technical and workplace skills.
Technical Skills
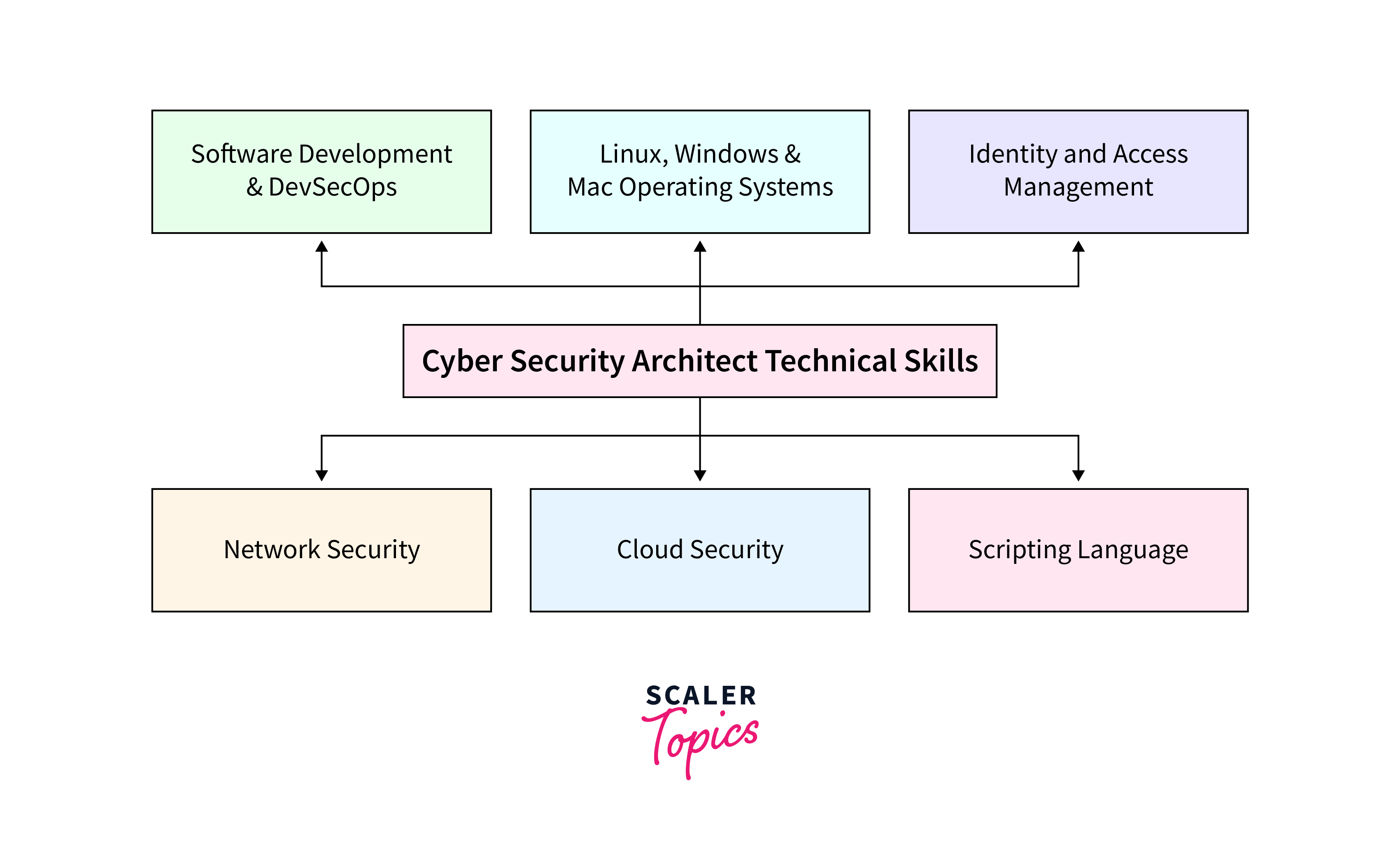
- Network Security: Proficient in configuring and managing network security protocols, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. Tools include Wireshark for network analysis and monitoring.
- Cloud Security: Expertise in securing cloud environments, utilizing tools like Amazon Web Services (AWS) Security Hub or Microsoft Azure Security Center for comprehensive cloud security management.
- Penetration Testing: Conducts ethical hacking to identify and rectify vulnerabilities. Tools such as Metasploit and Burp Suite are employed for penetration testing.
- Security Frameworks: Familiarity with industry standards like ISO 27001 and NIST, incorporating them to structure and fortify security measures.
- Encryption Technologies: Implements encryption algorithms and technologies to protect sensitive data, leveraging tools like OpenSSL or Microsoft BitLocker.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Utilizes IDPS tools like Snort or Suricata to detect and prevent unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
- Firewall Configuration: Configures and manages firewalls for network security, using tools such as Cisco Firepower or pfSense.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Uses SIEM tools like Splunk or ELK Stack to collect and analyze log data for proactive threat detection.
- Incident Response Tools: Leverages tools like IBM Resilient or Palo Alto Networks Cortex XSOAR for orchestrating and automating incident response processes.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Implements IAM solutions such as Microsoft Azure Active Directory or Okta to manage user access and permissions securely.
- Vulnerability Management: Utilizes tools like Nessus or Qualys to scan and assess system vulnerabilities, ensuring timely patching and mitigation.
- Application Security: Ensures the security of applications, employing tools like OWASP ZAP for application security testing.
Workplace Skills
- Communication: Effectively communicates complex security concepts to non-technical stakeholders, ensuring a shared understanding of risks and mitigation strategies across the organization.
- Problem-Solving: Rapidly addresses and resolves security issues, employing analytical and critical-thinking skills to identify root causes and implement effective solutions.
- Project Management: Coordinates security initiatives within larger organizational projects, ensuring that security measures align with overall business objectives and are delivered on time and within budget.
- Collaboration: Works seamlessly with cross-functional teams, including IT, management, and other stakeholders, fostering collaboration to implement and maintain robust security measures.
- Adaptability: Adapts to evolving cybersecurity trends and technologies, staying abreast of the latest threats to continually enhance security postures and respond effectively to emerging risks.
Security Architect Salary and Career Potential
As of 2023, the salary of security architect as per their experience is shown in the following table.
| Experience Level | Average Annual Salary (INR) |
|---|---|
| Entry Level | 6,00,000 - 8,00,000 |
| Mid-Level | 10,00,000 - 15,00,000 |
| Senior Level | 18,00,000 - 25,00,000 |
| Managerial Level | 25,00,000 and above |
The demand for skilled Security Architects is on the rise, reflecting the critical nature of their roles. Certifications significantly impact the salary trajectory of a Security Architect.
- Entry-level certifications like CompTIA Security+ can boost earning potential at the initial career stage.
- As professionals progress, advanced certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) or Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) play a crucial role in elevating salaries, showcasing specialized expertise, and contributing to career advancement.
How to Become a Cyber Security Architect?
- Obtain a bachelor's degree in a relevant field such as Computer Science, Information Technology, or Cybersecurity. This provides a solid foundation for understanding core concepts.
- Start with entry-level positions like Network Administrator or Systems Analyst to gain hands-on experience in managing and securing IT systems.
- Pursue certifications that are highly regarded in the cybersecurity field, such as CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH). These certifications validate your skills and knowledge.
- Consider pursuing a master's degree or relevant certifications for specialized knowledge in areas like cloud security, network security, or cryptography. While not mandatory, advanced education can enhance your expertise.
- Connect with cybersecurity professionals through networking events, conferences, and online forums. Building a strong professional network provides opportunities for learning, collaboration, and career advancement.
- Stay updated on the latest cybersecurity trends, technologies, and threats. Engage in continuous learning through webinars, workshops, and online courses to expand your knowledge base.
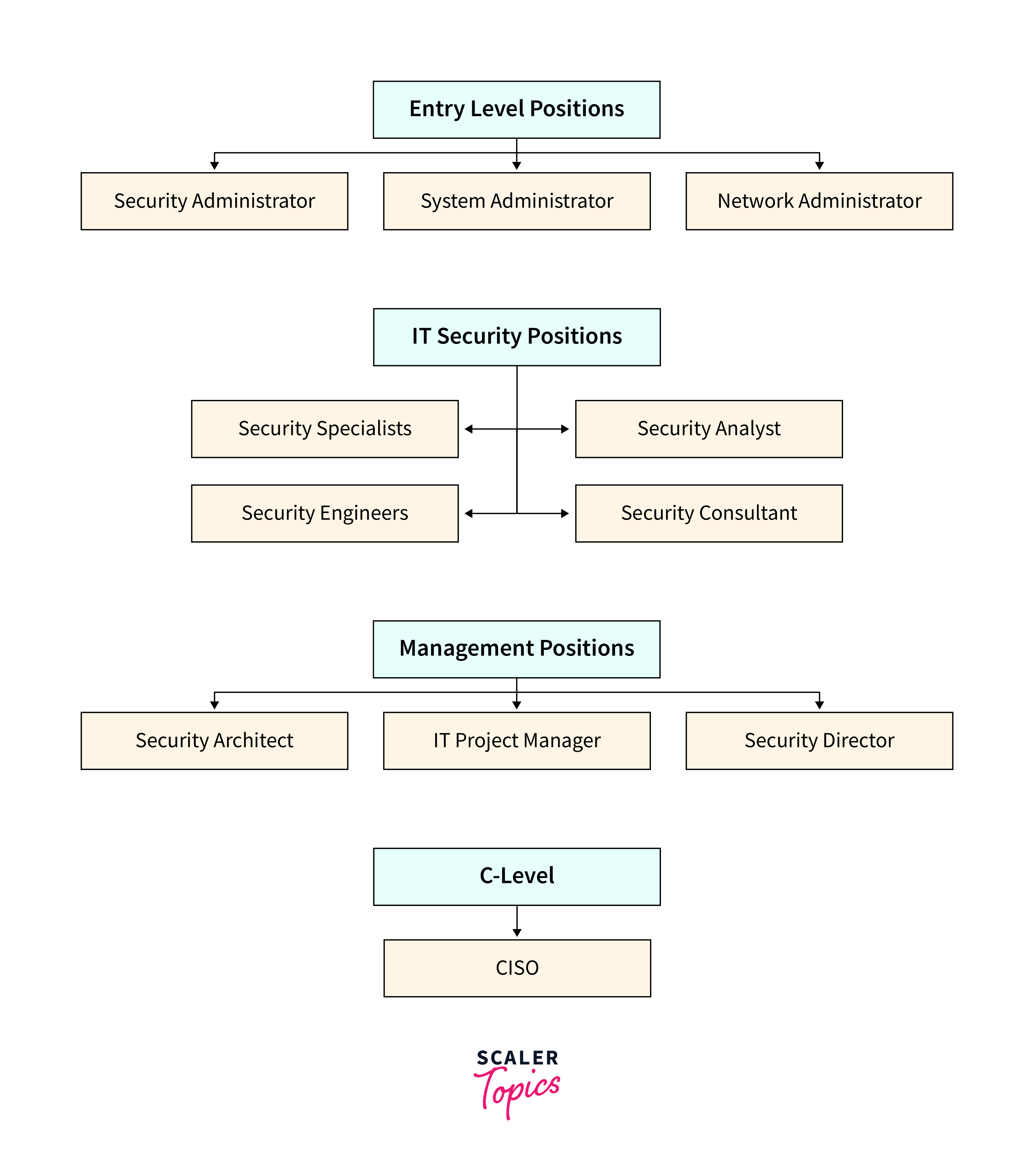
If you are already in the technology field and want to work as a Cyber Security Architect, consider doing the following:
- Develop proficiency in technical skills such as network security, cloud security, penetration testing, and secure coding. Stay versatile to adapt to evolving technologies and threats.
- Enhance communication, problem-solving, and project management skills. Cyber Security Architects often need to convey complex concepts to non-technical stakeholders and effectively manage security initiatives within larger projects.
- Gain familiarity with security frameworks and standards such as ISO 27001, NIST, and CIS Controls. Understanding these frameworks is essential for designing and implementing effective security measures.
- Join professional organizations related to cybersecurity, such as (ISC)² or ISACA. Being part of these communities provides access to resources, mentorship opportunities, and industry insights.
- Engage in hands-on projects or contribute to open-source cybersecurity initiatives. Practical experience is invaluable for honing your skills and showcasing your abilities to potential employers.
- Attend cybersecurity conferences and workshops to stay updated on industry trends, learn from experts, and network with professionals. These events offer valuable insights and opportunities for skill enhancement.
Get Started in Cyber Security
For those aspiring to become Cyber Security Architects, the journey begins with a solid educational foundation, hands-on experience, and a commitment to lifelong learning. By mastering the technical and interpersonal skills required, individuals can carve a path towards a rewarding career safeguarding digital landscapes against evolving cyber threats. Explore comprehensive learning resources at Scaler to further enhance your knowledge and skills.
Conclusion
- A Cyber Security Architect is a professional for designing and implementing security solutions for an organization's IT infrastructure. The major work of a security architect includes risk assessment and implementing a security framework.
- Their roles and responsibilities involve tasks such as assessing security frameworks, conducting risk assessments, collaborating with cross-functional teams, and ensuring the alignment of security measures with business objectives.
- Security Architects possess both technical expertise, utilizing various tools and techniques for network security, and crucial workplace skills such as effective communication, management, and adaptability for better collaboration.
- The salary for Security Architects varies based on experience, with opportunities for career growth and increased earning potential through certifications like CISSP, CISM, and CISA.
- The journey to becoming a security architect could start with a relevant bachelor's degree, gaining practical experience, earning certifications like CISSP, continuous learning, developing technical and soft skills, familiarizing with security frameworks, and building a professional network to understand the industry.
