The 7 Scrum Artifacts
Overview
Scrum artifacts list down all the major information about the project under development. These include the details of the process and product.
This information would outline how much task is done versus what is left out. Scrum artifacts have specific definitions, and will learn these terminologies in this article.
What are Scrum Artifacts?
There are multiple terminologies in the scrum framework called scrum artifacts.
Artifacts provide crucial information about the tasks under the development cycle. Below is listed one of the most crucial ones. Scrum is a framework for managing the product development cycle, and its special feature is the sprint. Scrum framework follows scrum ceremonies and tools to manage the project, like JIRA.
The 7 Scrum Artifacts
1. Product Vision
Product vision artifacts have documentation about the product's exact vision. This document would act as a reference for the entire to look up in case of any discrepancy. Product vision is a short note; around this, all the functionalities are built.
2. Product Backlog
Product backlog lists all the functionalities that need to be built. It consists of functional requirements, assets, non-functional requirements, features, and knowledge acquisition.
These features are then subdivided into smaller units. Product backlog keeps updating as new features get an add-on or when there is a requirement change.
3. Sprint Vision
Sprint Vision or Sprint Goal is the high-level objective a print project manager wants to achieve. So, a task list has already been created in the product backlog. Some are part of the club together to achieve in a sprint. For example, the product requires one year to develop. In the first month, the list of tasks that the project manager aspires to achieve is listed as a group as a sprint. And the objective of that sprint would become sprint vision.
4. Sprint Backlog
Sprint backlog lists all the activities to be delivered by the end of the sprint. For example, a product requires a login module, blog module, and payment gateway. By the end of the first two weeks- UI would be ready, and authentication would be done. So all tasks that have to be submitted by week 2 are part of the sprint backlog.
5. Definition of Done (DOD)
Definition of Done is a set of checklists that, when completed then, only would ensure the task is done. For instance, in the sprint, one authentication module must be done. DOD of it would be the test case of Gmail, Facebook, and basic authentication are passes then only sprint one is complete.
6. Product Increment
Product increment artifacts denote all the tasks of product backlog that are DOD plus the tasks of the previous sprint. Increment itself defines what all new features have been done among the product backlog task list.
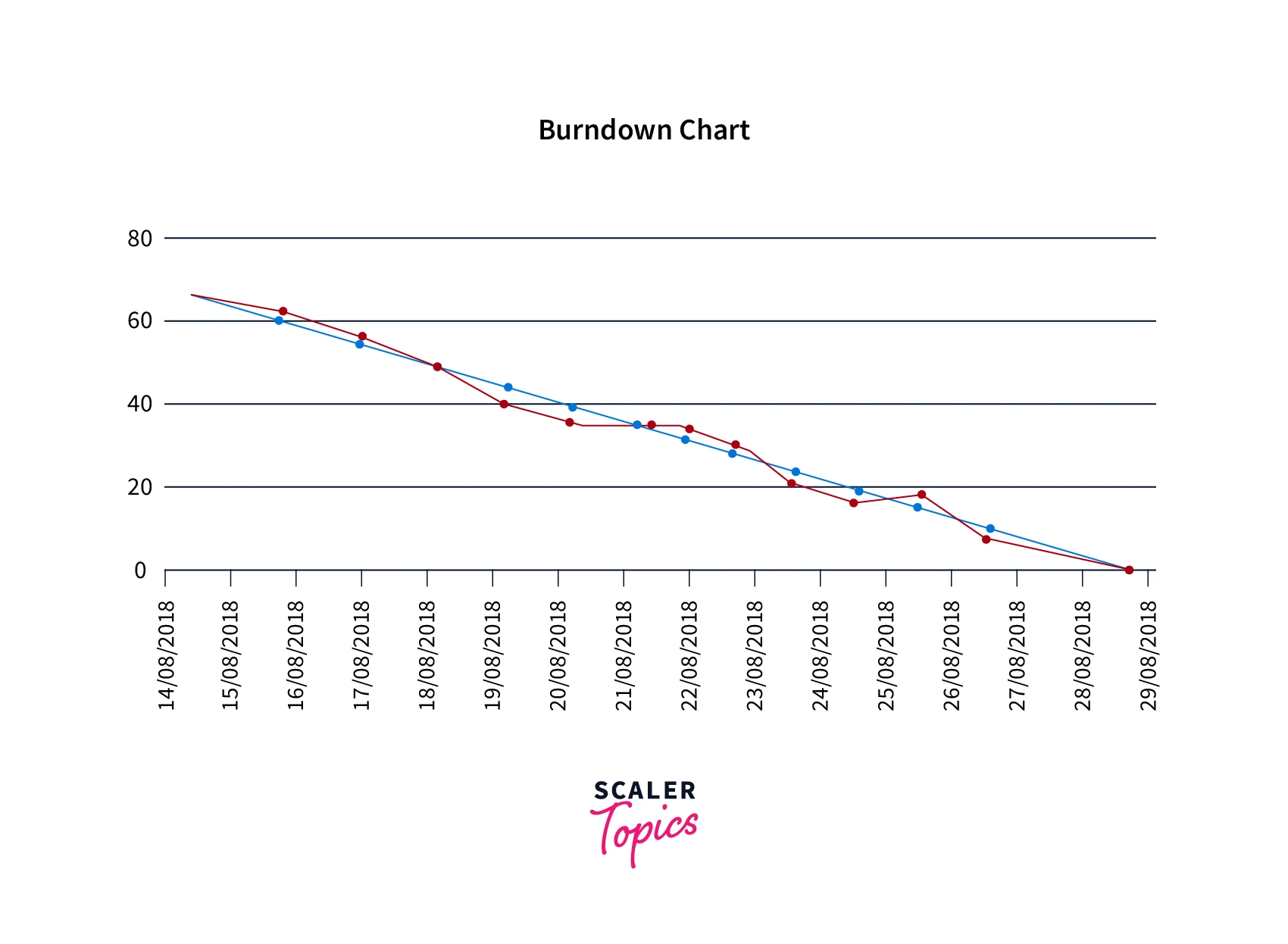
7. Burndown Chart
Burndown chart is a graphical chart depicting all the completed activities versus time. The chart burns down to zero when all the tasks are marked done. It is a progress task that would tell in how much duration % of tasks that are done.
Artifact Transparency
Scrum framework is a product handling mechanism. And this entire setup is made completely transparent. At every stage, the product owner assigns user stories to developers. Who has done it, in what duration, and why the development is falling back can be easily visible. The entire SDLC process has been made reliable that scrum is the truth. The scrum team must have visibility of all the artifacts at every stage of the development period.
Conclusion
- Scrum artifacts are the defined terminologies in the scrum framework, which serve a different role in the development cycle.
- Sprint is a defined event of limited duration where a set of tasks must be completed.
- Product Backlog lists all the activities that must be completed in the development cycle.
- Burndown chart reflects all the tasks that have been completed and left out at a given time.
