Static Class in Java

Overview
In Java, static is one of the most popular keywords associated with functions, variables, classes, and blocks. When any of these members are made static, we can access it without creating an instance of the class in which they are defined.
Static class in Java is a nested class and it doesn't need the reference of the outer class. Static class can access only the static members of its outer class.
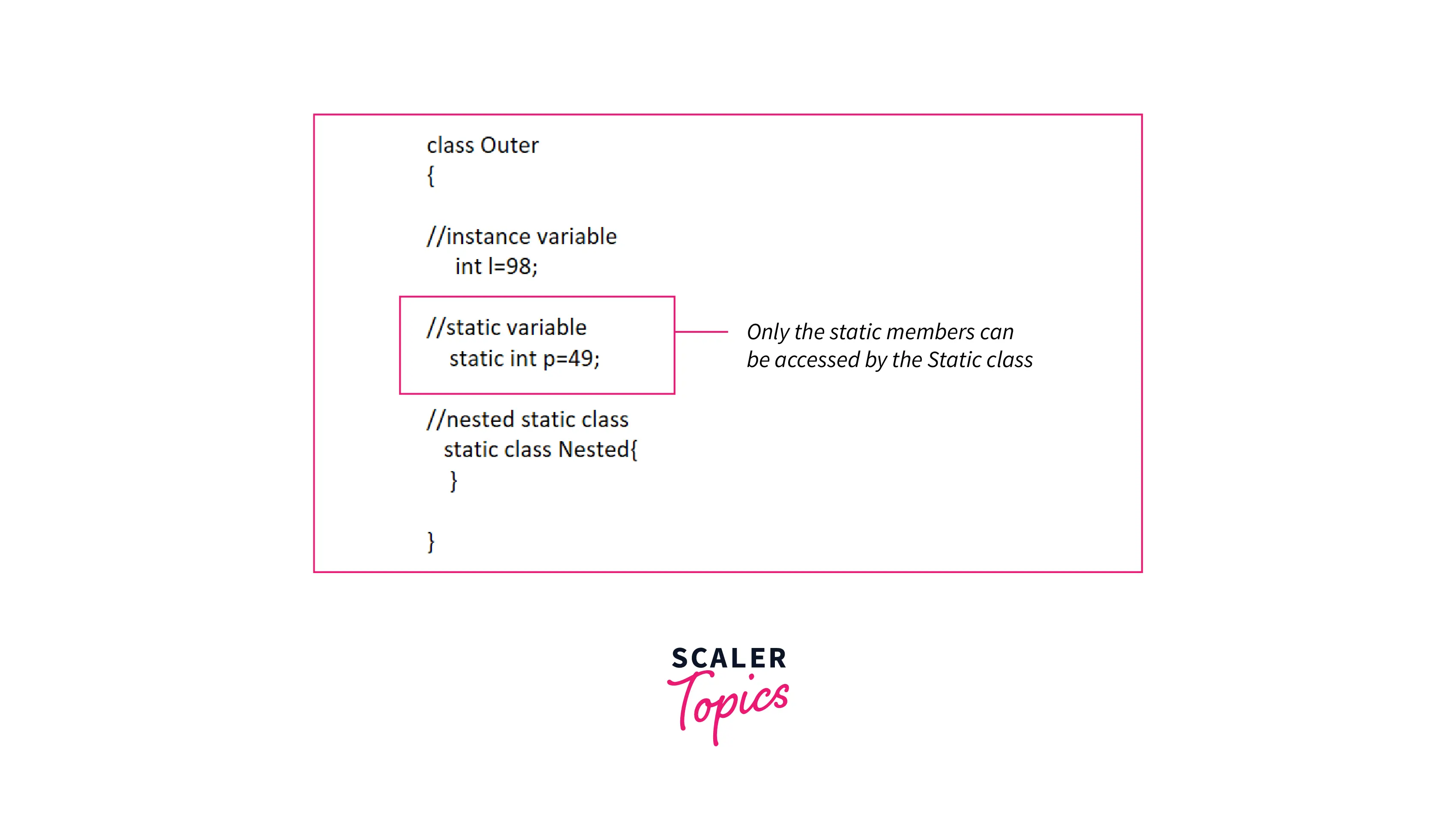
What is Static Class in Java?
We as Java programmers have come across the keyword static and it is majorly seen with the main() function in Java. But does it mean that only functions can be declared static? The answer is No. In Java, variables, blocks, methods, and classes can be declared as static.
In order to declare a member as static, we use the keyword static before the member. When we declare a certain member as static, we do not have to create an instance of the class to access it.
Syntax
Here we have declared an Outer class and then declared a nested class.
Static classes in Java can be created only as nested classes. Let us understand the concept of inner, outer, and nested classes first.
1. Inner Class
Inner classes are the classes that are non-static and nested. They are written inside an outer class. We are unable to create an instance of the inner class without creating an instance of its given outer class. This is needed when the user has to create a class but doesn't want other classes to access it. Here we can use an inner class for that reason.
2. Outer Class
Outer classes are the classes in which nested or inner classes are defined.
3. Nested Class
Nested class can be static or non-static. The non-static nested class is known as an inner class.
An instance of a static nested class can be created without the instance of the outer class. The static member of the outer class can be accessed only by the static nested class.
The following figure illustrates the inner, outer, and nested classes.
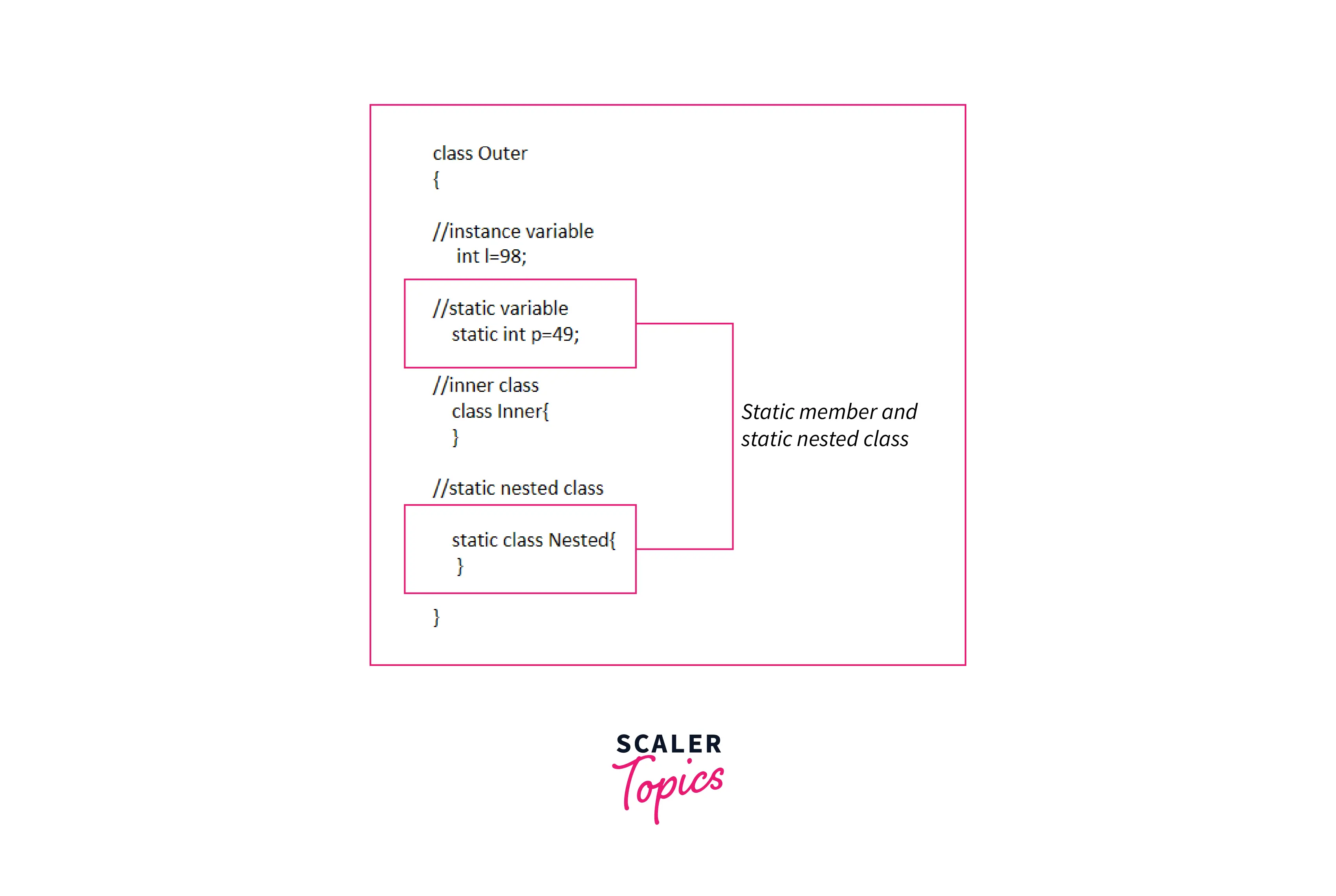
- The nested static class can access the static variables.
- Static nested classes do not have access to other members of the enclosing class which means it has no access to the instance variables (non-static variables) which are declared in the outer class.
Example
Output:
Explanation:
- We have declared Outer and Nested classes. In the outer class, we have created a static member which can be accessed by the static class.
- As we know, static members can be accessed by the static class only, so in the main() method, we have created an instance of the nested class without the instance of the outer class as our nested class is static.
Why We Use Static Class in Java?
In Java, the static keyword helps in efficient memory management. We can access the static members without creating an instance of a class. We can access them simply by using their class name. It is also a way of grouping classes together. Also, an instance of a static nested class can be created without the instance of the outer class.
Difference between Static and Non-static Nested Class
- Static nested class can access the static members of the outer class and not the non-static members, whereas non-static nested class, i.e., the inner class can access the static as well as the non-static members of the outer class.
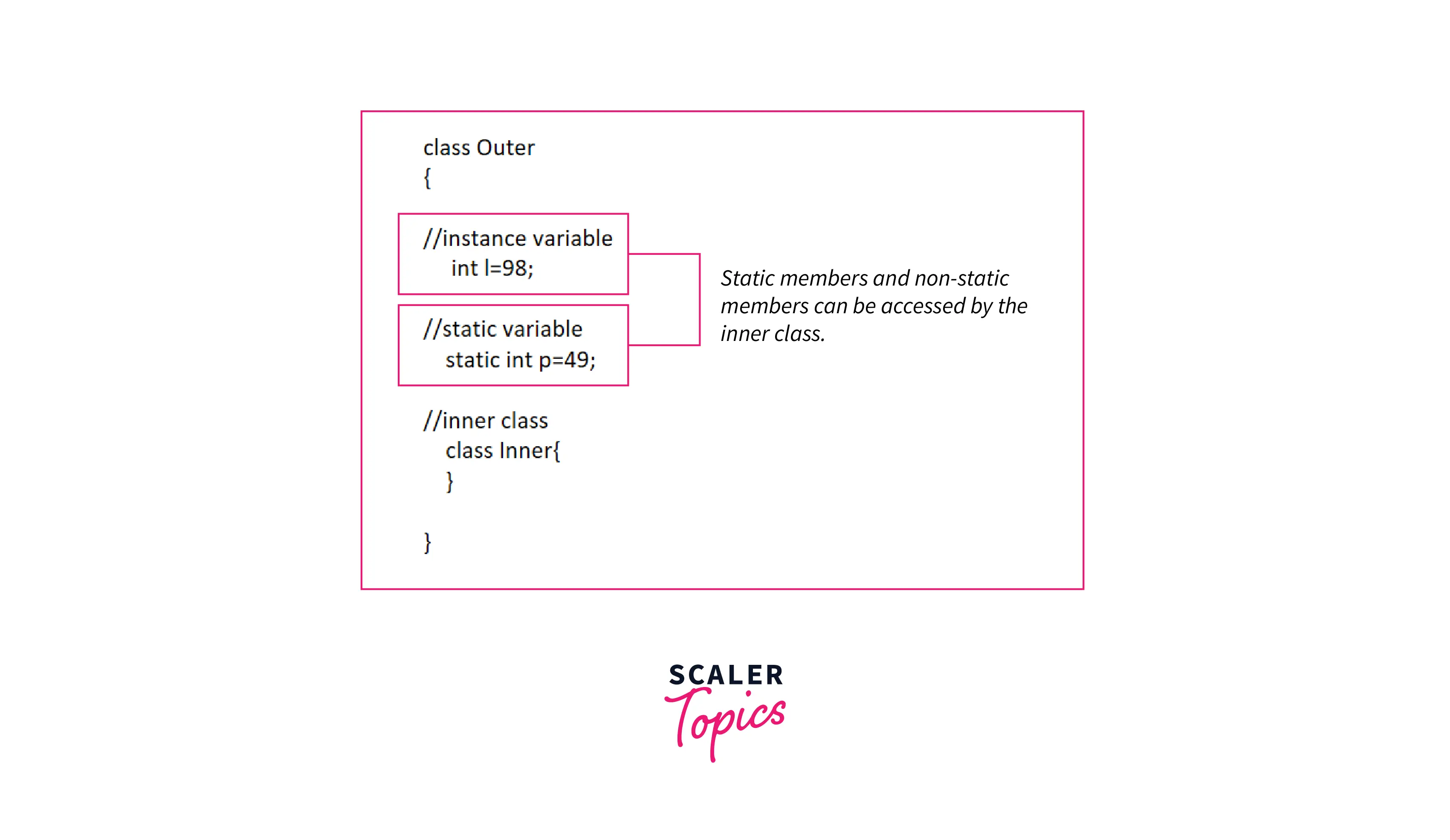
- We can create an instance of the static nested class without creating an instance of the outer class.
Conclusion
- Static class in Java is a nested class and it doesn't need the reference of the outer class.
- Static class can access only the static members of its outer class.
- Static class cannot access the non-static member of the outer classes.
- Inner classes can access the static and the non-static members of the outer class.
- We can create an instance of the static nested class without creating an instance of the outer class.
- The static keyword helps in memory management.
