Transpose of a Matrix in Java

Overview
Transpose of a matrix in Java is obtained by interchanging all rows to columns and columns to rows. This means that in the transpose of a matrix, rows in the normal matrix become the columns, and columns form the rows. If the dimension of the original matrix is , the dimension of the transpose matrix will be .
The transpose of a matrix can be computed by assigning element in the transpose matrix equal to the in the original matrix.
Introduction to Transpose of a Matrix in Java
Transpose of a matrix in Java is obtained by interchanging its rows into columns or columns into rows. This means that in the transpose of a matrix, rows in the normal matrix become the columns, and columns form the rows.
Let us look at an example. If the given matrix is:
Let us denote this matrix as M. Clearly this is a matrix, as it has three rows and four columns. If we try to write the transpose of this matrix in Java, it will be something like:
If you compare the two matrices, the rows of the previous matrix M have now become the columns in this transpose matrix, and the columns have become rows. Clearly, this matrix denoted as MT is a matrix, as it has four rows and three columns.
But how do find the transpose of a matrix in Java? Let us discuss the algorithm in the next section.
Algorithm to Find Transpose of a Matrix in Java
We already saw that if we have a matrix M having rows and columns, then its transpose, MT will have rows and columns.
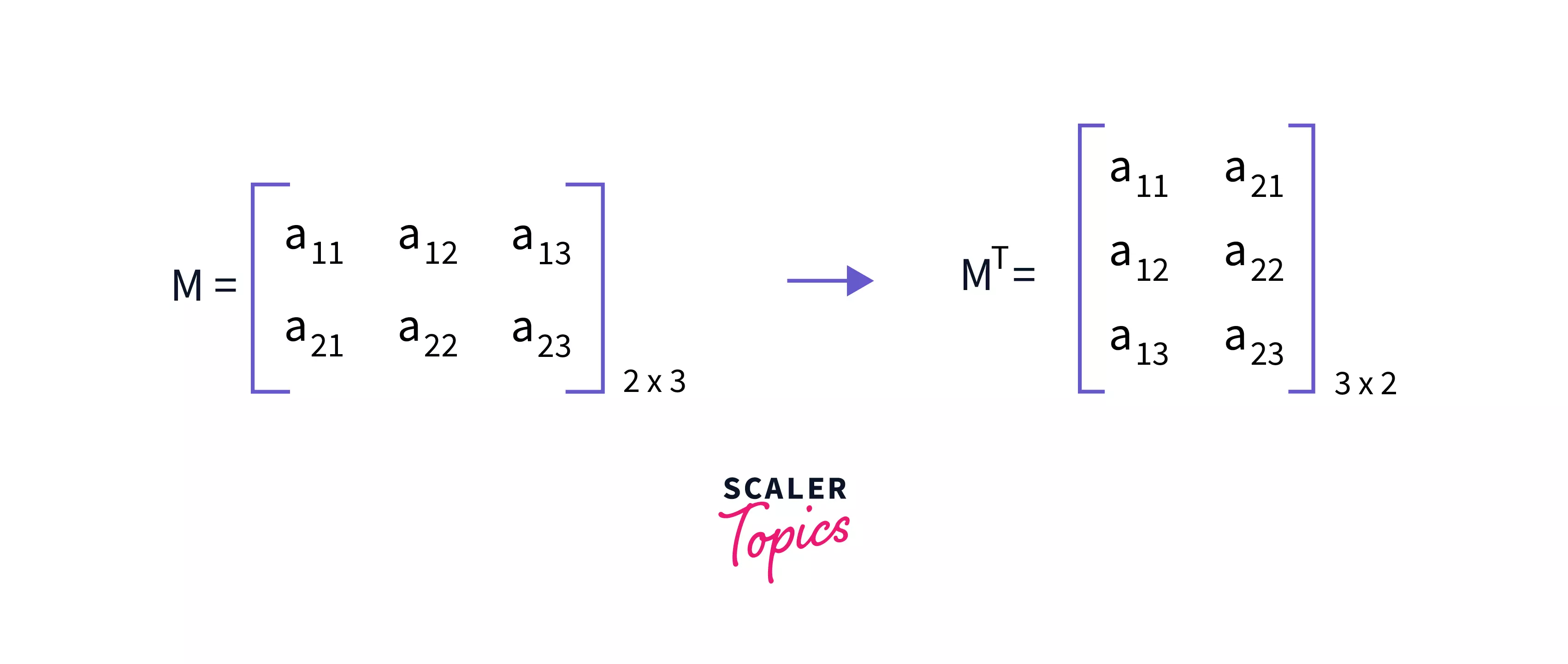
Let us look at how the elements change when a matrix is converted to its transpose using the following matrix M:
Here denotes the matrix element present at row and column. Now let us look at how the indices change in the transpose of this matrix. The transpose matrix MT is given as:
Looking at the example, it is clear we just need to replace the rows with the column values and the columns with the row values. That means if an element is at the index in the original matrix M, then in the transpose matrix MT it will be at the index .
Hence, in the code of converting a matrix to its transpose, we first need extra space for another 2-d matrix which will store the transpose of the matrix.
Then, in this new transpose matrix, we only need to assign the element at index in the original matrix to the element in the transpose matrix. This operation has to performed for every element of the original matrix. We can achieve this by iterating through every element of the matrix using two nested for loops.
Formally, the algorithm to find the transpose of a matrix will be:
- Create a two-dimensional integer array M_transpose[][] of size (m,n) where n is the number of rows and m the number of columns in the original matrix.
- Traverse the original matrix M[][] and for each element M[i][j], assign M_transpose[j][i] = M[i][j].
- M_transpose[][] is the required transpose matrix.
Let us look at the formal code to find the transpose of a matrix using a few examples in the next sections.
Example 1: Java Program to Find Transpose of a Matrix
Given a matrix, let us look at the code to find its transpose in Java.
Output
Following the above-defined algorithm, we can successfully find the transpose of a matrix in Java.
Time and Space Complexity
- The time complexity for this solution is where is the number of rows in the matrix, and is the number of columns.
- The space complexity is also , where is the number of rows in the matrix and is the number of columns, which is used to store the values in the transpose matrix.
Example 2: For Square Matrix
We saw the code for an arbitrary 2-d matrix, but what if the matrix we have is a square matrix. A square matrix is a matrix that has the same number of rows and columns. This means that if is the number of rows and is the number of columns in a matrix, then for a square matrix, .
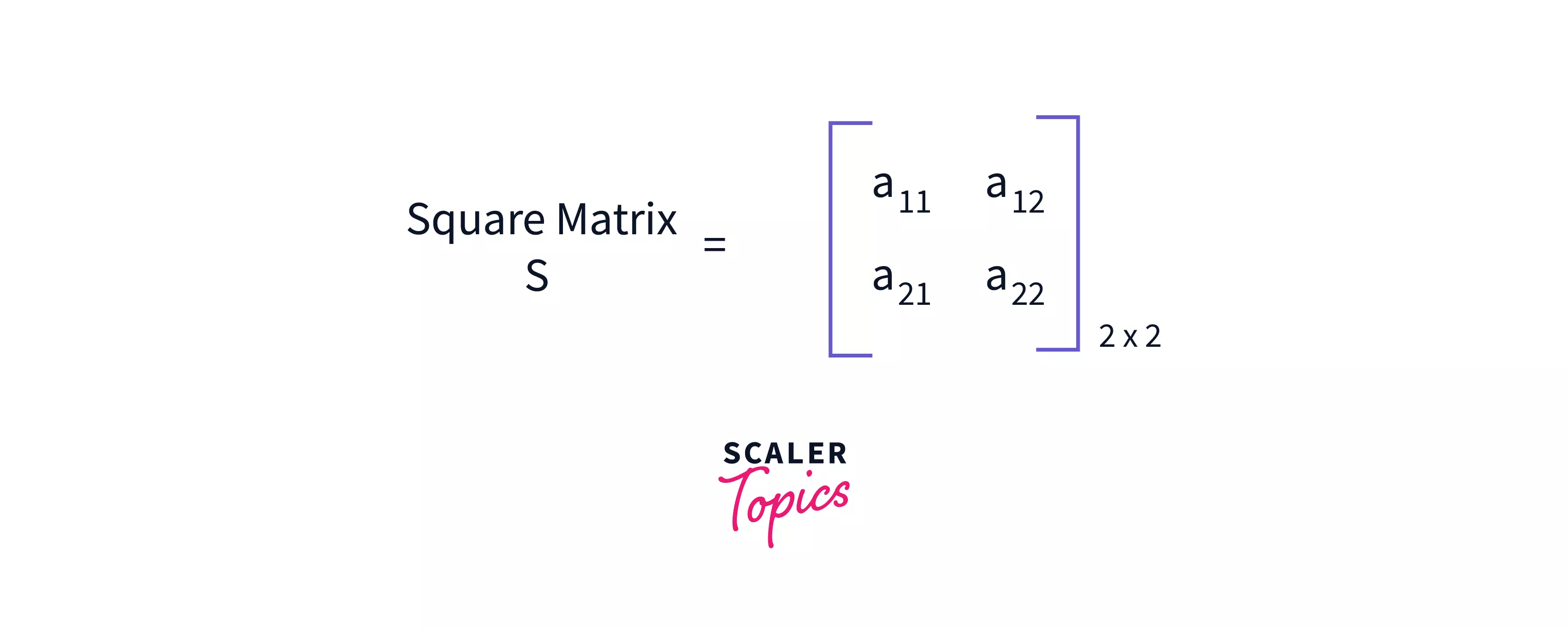
The only change this will bring in the original algorithm is that our transpose matrix will have the same size as the original matrix, i.e. of size (n, n). After that, the algorithm stays the same, we just have to iterate over all the elements of the original matrix and assign M_transpose[j][i] = M[i][j].
Let us look at the code to find the transpose of a square matrix in java.
Output
Time and Space Complexity
- The time complexity for this solution is where is the number of rows/columns in the square matrix.
- The space complexity is also where is the number of rows/columns in the matrix, which is used to store the values in the transpose matrix.
Example 3: For Rectangular Matrix
Let us see what the code will look like for a rectangular matrix, in which the number of rows is not equal to the number of columns. This means that if is the number of rows and is the number of columns in a matrix, then for a rectangular matrix, .

Output
Time and Space Complexity
- The time complexity for this solution is where is the number of rows in the matrix, and is the number of columns.
- The space complexity is also , where is the number of rows in the matrix and is the number of columns, which is used to store the values in the transpose matrix.
Example 4: In-Place for Square Matrix
For a square matrix, we can reduce the space complexity by not making a different matrix to store the transpose, but instead making changes in the original matrix itself.
Only possible for square matrices:
- We can do this in-place conversion for a square matrix only because the number of rows of a square matrix is equal to the number of columns, and because of this the size of the original and the transpose matrix is the same.
- But this is not the case with any other matrix which has different number of rows and columns.
Algorithm
- To obtain the transpose matrix in-place, we do not have to create any new matrix to store the transpose values.
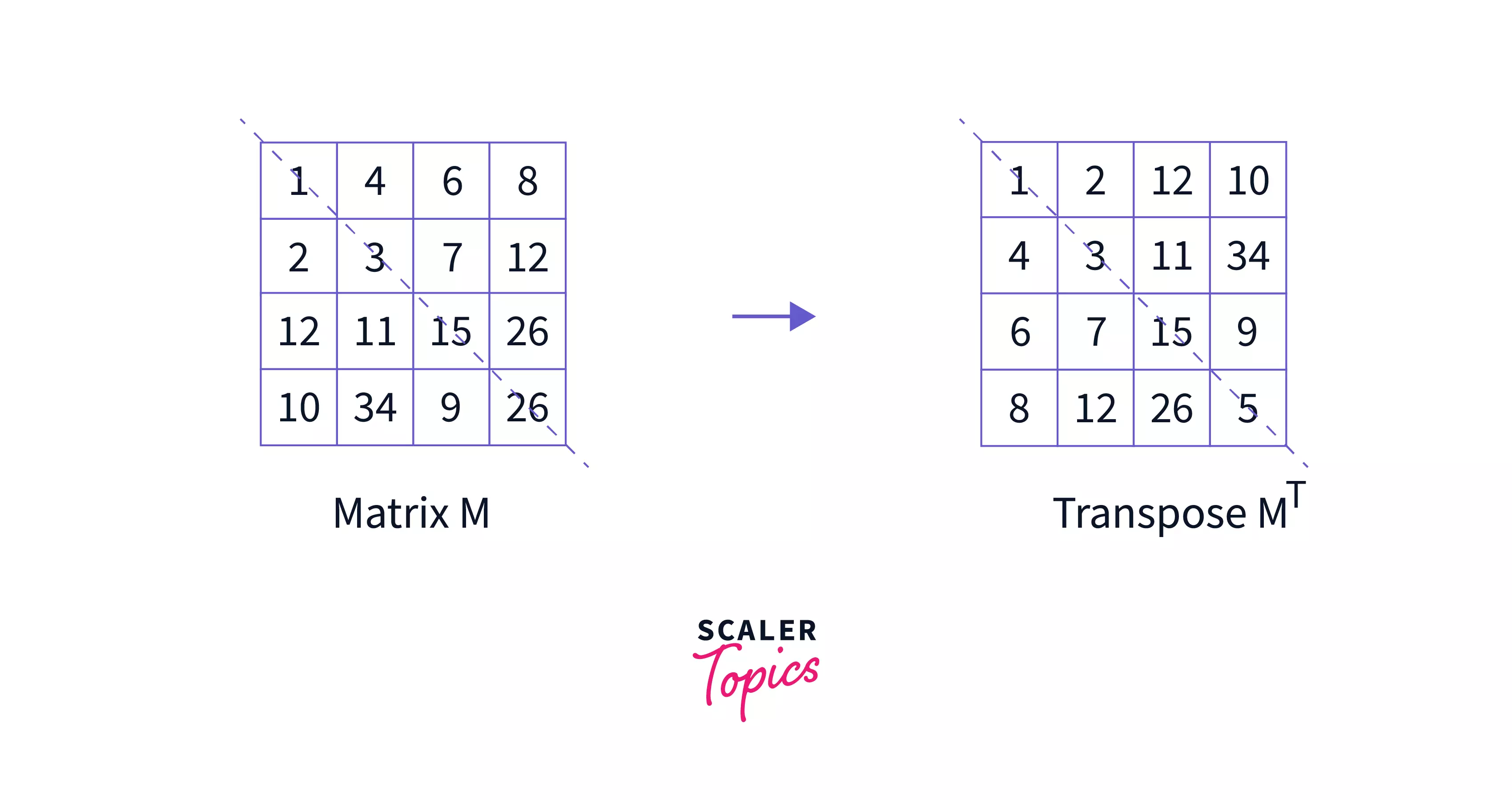
- What we have to do instead is just swap the values of with for all 0 <= i < N and i < j < N. Effectively only half of the matrix is traversed.
- This means, we are going to do the same thing that we used to do earlier, with the only exception being that this time we swap with instead of assigning = .
- Though we are traversing only half the matrix, but in each swap operation we are handling two positions in the matrix. Thus effectively it covers the whole matrix.
This is done because if we are transforming the original square matrix itself, then the values lying above the main diagonal need to be swapped with those lying below it, as shown in the diagram below.
Let us look at the code for finding the transpose of a square matrix in java in-place.
Output
Time and Space Complexity
- The time complexity for this solution is where is the number of rows/columns in the square matrix. This is because this time our matrix is a square matrix of size (n,n) and we iterate over it once.
- The space complexity is , as we perform the operations in-place.
Conclusion
- Transpose of any matrix in Java is obtained by interchanging all rows to columns and columns to rows.
- If we have a matrix M having rows and columns, then its transpose, MT will have rows and columns.
- To find the transpose of a matrix in Java, assign the element at index in the orinial matrix to the element in transpose matrix.
- The time and space complexity is where is the number of rows in the matrix, and is the number of columns.
- We can find the transpose of a square matrix in Java in place also, reducing the space complexity to .
- In-place algorithm to find transpose matrices is possible only in case of square matrices.
