Types of Data Analytics
In today's data-driven era, businesses and organizations harness the power of data analytics to derive meaningful insights and make informed decisions. Data analytics encompasses various approaches and techniques, each serving a specific purpose. In this article, we will delve into the diverse realms of data analytics, exploring its types, applications, and future possibilities.
What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics stands as the cornerstone of a transformative process that involves delving into raw data to extract meaningful insights, identify patterns, and uncover trends that might otherwise remain obscured. At its essence, data analytics is a comprehensive approach to deciphering the wealth of information contained within datasets, unlocking a trove of knowledge that holds immense value for businesses and decision-makers.
The process of data analytics spans a diverse array of methodologies and tools meticulously crafted to navigate the complexities of data interpretation. It is not merely about processing information but rather about extracting actionable intelligence that can guide strategic decision-making. The journey from raw data to insightful conclusions involves a strategic blend of statistical analysis, algorithmic processing, and visualization techniques.
Data analytics is not just a process; it is a transformative journey that empowers businesses to turn raw data into a valuable resource. By employing a combination of cutting-edge tools and analytical methodologies, data analytics enables decision-makers to make informed choices, unravel hidden patterns, and ultimately gain a competitive advantage in an increasingly data-driven world.
Types of Data Analytics
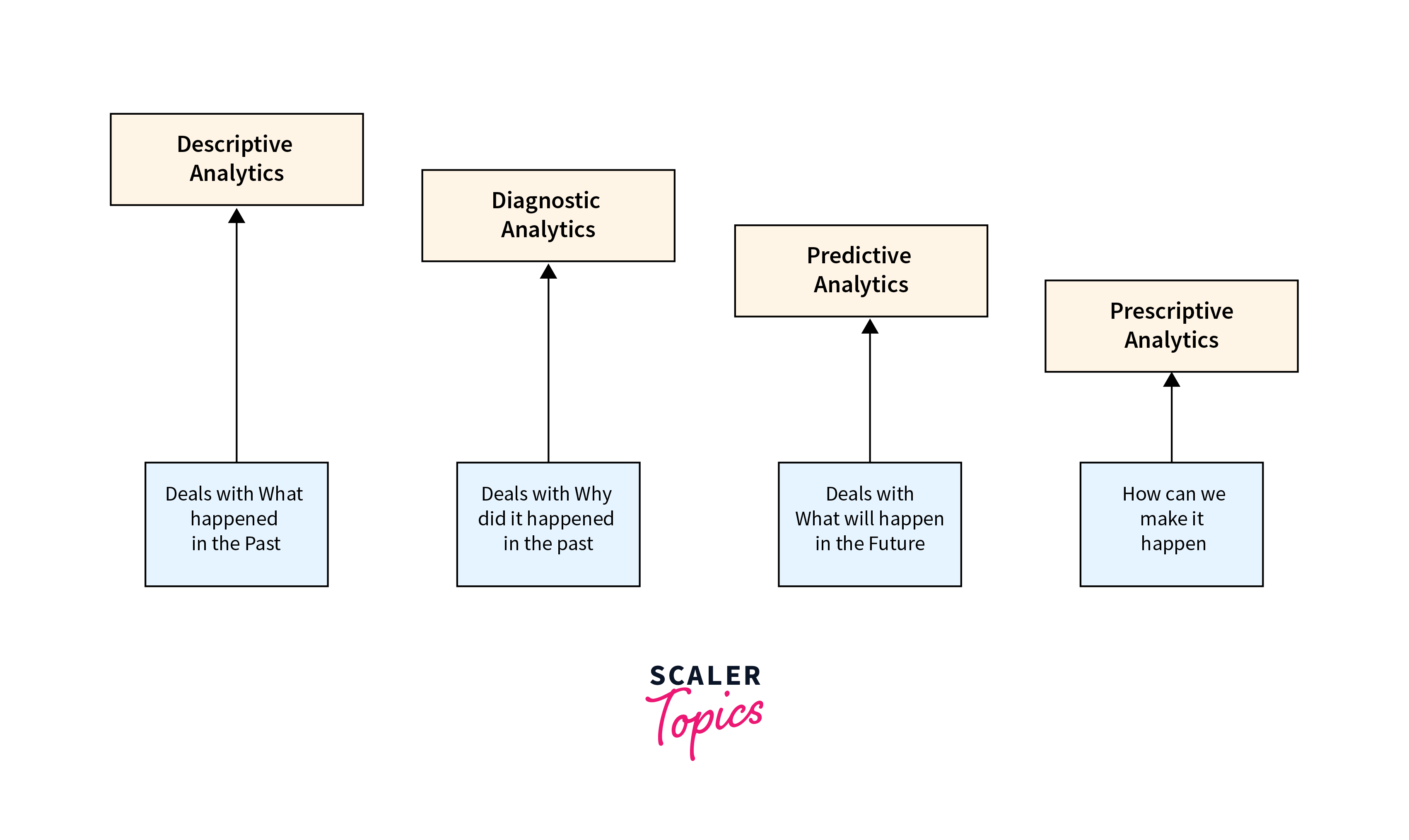
- Predictive Analytics (Forecasting)
Predictive analytics is a powerful tool that involves the use of historical data and advanced statistical algorithms to foresee future outcomes. Businesses employ this type of analytics to gain a competitive edge by anticipating trends, identifying potential risks, and making proactive decisions. Whether predicting consumer behavior or forecasting market trends, predictive analytics empowers organizations to stay ahead of the curve. By harnessing historical data, businesses can make informed strategic choices, minimizing uncertainties and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
- Descriptive Analytics (Business Intelligence and Data Mining)
Descriptive analytics serves as the cornerstone for business intelligence and data mining, focusing on summarizing and interpreting historical data to provide a comprehensive understanding of past events. This type of analytics enables businesses to uncover key performance indicators, recognize trends, and identify patterns within their data. By delving into historical data, organizations can draw valuable insights that inform decision-making based on lessons learned from previous experiences. Descriptive analytics forms the bedrock upon which businesses build their strategies, leveraging the wealth of information buried within their data repositories.
- Prescriptive Analytics (Optimization and Simulation)
Taking data analysis to a more sophisticated level, prescriptive analytics provides recommendations for optimal decision-making. It goes beyond predicting outcomes and suggests actions that maximize desired results, considering various constraints and scenarios. Optimization and simulation techniques play a crucial role in this process, allowing businesses to simulate different strategies and identify the most effective ones. By leveraging prescriptive analytics, organizations can enhance efficiency, optimize resource allocation, and make strategic decisions that align with their overarching goals.
- Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics is geared towards uncovering the root causes of problems or challenges by meticulously analyzing historical data. This type of analytics helps organizations understand why specific events occurred, providing insights into the factors contributing to particular outcomes. Diagnostic analytics is instrumental for troubleshooting and improving processes, enabling organizations to address issues at their source. By identifying and rectifying the underlying causes of challenges, businesses can enhance overall performance, refine operations, and foster continuous improvement.
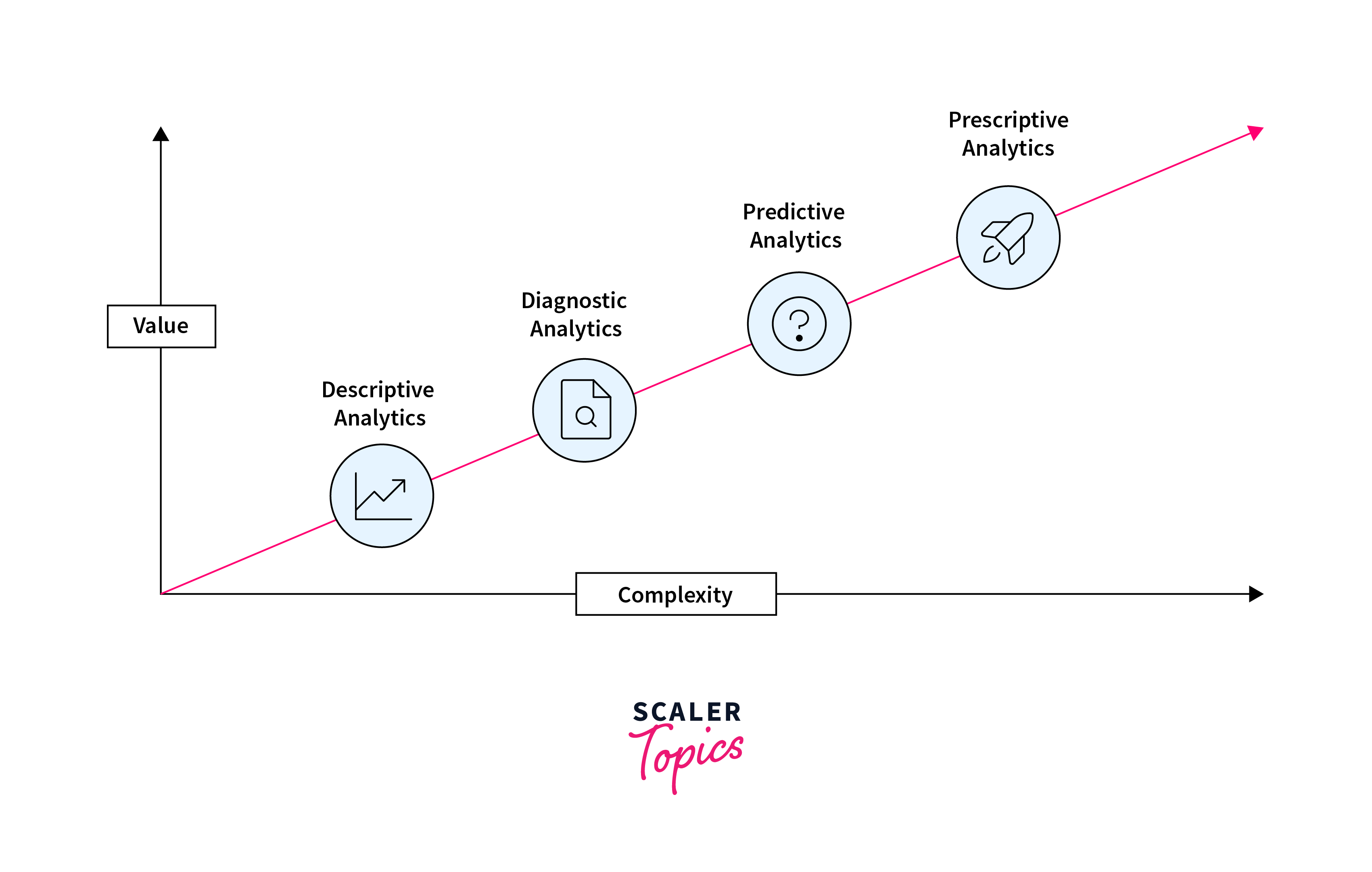
Usage of Data Analytics
- Improved Decision-Making
Data analytics serves as a beacon for improved decision-making within organizations. By harnessing the power of data, decision-makers can navigate complex landscapes with confidence. Analyzing relevant data provides valuable insights that act as a compass for strategic choices. This process not only minimizes risks but also maximizes opportunities by ensuring decisions are grounded in a thorough understanding of past trends, current dynamics, and future possibilities.
- Better Customer Service
In the competitive business landscape, understanding and meeting customer expectations are paramount. Data analytics plays a pivotal role in achieving this by providing insights into customer behavior, preferences, and feedback. Businesses can delve into the intricacies of customer interactions to personalize experiences, anticipate needs, and address concerns promptly. The result is an elevated level of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Efficient Operations
Efficiency lies at the core of operational success, and data analytics acts as a catalyst for optimizing internal processes. Through a meticulous analysis of operational data, organizations can identify bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and enhance overall operational efficiency. This not only improves resource utilization but also reduces unnecessary costs and enhances productivity.
- Effective Marketing
Marketing in the digital age demands precision, and data analytics emerges as a game-changer in this arena. It enables businesses to target the right audience with pinpoint accuracy, ensuring that marketing efforts resonate with potential customers. Through data analytics, marketers can delve into consumer behavior, preferences, and responses, allowing for the personalization of marketing campaigns. This personalized approach not only enhances customer engagement but also contributes to increased conversion rates. Additionally, data analytics provides the means to measure the effectiveness of advertising efforts, enabling marketers to allocate resources strategically and achieve a better return on investment (ROI).
Future Scope of Data Analytics
- Retail
In the retail sector, data analytics is poised to revolutionize various aspects of operations. Inventory management can be optimized through predictive analytics, helping retailers forecast demand accurately and prevent stockouts or overstock situations. Personalized customer experiences will be a key focus, as retailers can analyze consumer preferences and behavior to tailor promotions and recommendations. Pricing strategies can be fine-tuned based on real-time market dynamics, ensuring competitiveness and maximizing profits.
- Healthcare
Data analytics is set to transform the healthcare landscape by providing actionable insights from vast amounts of medical data. Predictive analytics can assist in early disease detection, enabling healthcare professionals to intervene proactively. Treatment optimization involves analyzing patient outcomes and adjusting medical approaches based on data-driven evidence. Electronic health records can be mined to identify patterns and trends, contributing to more effective and personalized patient care.
- Finance
In the financial sector, data analytics is a powerful tool for risk management and fraud detection. Real-time analysis of financial data allows institutions to identify and respond to potential risks promptly. Personalized financial services can be offered by understanding customer behavior and preferences, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Marketing
The future of marketing lies in data-driven insights that enable hyper-personalized campaigns and targeted communication. Marketers can use advanced analytics to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and purchase patterns, allowing for the creation of highly targeted and relevant marketing campaigns. Data-driven decision-making will maximize the impact of promotional efforts, leading to increased customer engagement and conversion rates.
- Manufacturing
In manufacturing, data analytics is a game-changer for optimizing production processes. Predictive maintenance helps anticipate equipment failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Supply chain optimization involves analyzing data to streamline logistics and inventory management, ensuring timely production and delivery. Quality control is enhanced through real-time monitoring and analysis, maintaining the highest standards in product manufacturing.
- Transportation
Data analytics in the transportation industry offers opportunities for optimizing routes, improving fuel efficiency, and enhancing overall logistics. Predictive analytics helps anticipate maintenance needs, reducing downtime and improving the reliability of transportation systems. Real-time data analysis facilitates dynamic route planning, minimizing delays and optimizing delivery schedules. By harnessing data, transportation companies can achieve cost savings, enhance customer satisfaction, and contribute to a more sustainable and efficient transportation ecosystem.
- Education
Data analytics has the potential to revolutionize the education sector by providing insights into student performance, learning trends, and teaching methodologies. Learning analytics can help educators understand how students engage with course material, identify areas where students may be struggling, and tailor instruction to individual learning styles. Predictive analytics can assist in early intervention for at-risk students, improving retention rates and academic outcomes. Additionally, data-driven decision-making can inform curriculum development and resource allocation, ensuring that educational institutions are meeting the evolving needs of students and society.
FAQs
Q. What is the role of data analytics?
A. Data analytics plays a crucial role in transforming raw data into actionable insights, guiding decision-making, improving efficiency, and driving innovation across various industries.
Q. What are the types of data analytics?
A. The types of data analytics include predictive analytics, descriptive analytics, prescriptive analytics, and diagnostic analytics, each serving a specific purpose in interpreting and utilizing data.
Q. What are the analytical tools used in data analytics?
A. Common analytical tools in data analytics include Python, R, SQL, Tableau, and Hadoop. These tools facilitate data processing, analysis, and visualization, allowing professionals to derive meaningful insights.
Q. What is the career growth in the data analytics field?
A. The field of data analytics offers promising career growth opportunities. As organizations increasingly rely on data for decision-making, the demand for skilled data analysts, data scientists, and business intelligence professionals continues to rise.
Q. How does data analytics contribute to business innovation?
A. Data analytics contributes to business innovation by providing insights that can lead to the development of new products or services, improved processes, and enhanced customer experiences. It helps businesses identify opportunities for growth and stay ahead of the competition.
Q. What skills are essential for a career in data analytics?
A. Essential skills for a career in data analytics include proficiency in programming languages like Python or R, statistical analysis, data visualization, database management (SQL), and a strong understanding of business concepts. Critical thinking and problem-solving skills are also highly valued.
Conclusion
- The diverse types of data analytics empower organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights.
- Data analytics is crucial in driving innovation within organizations by providing valuable insights for strategic decisions.
- From predictive analytics shaping future strategies to descriptive analytics offering a historical context, data analytics ensures that decisions are well-informed and grounded in data.
- data analytics applications are vast and impactful, ranging from predicting future trends to understanding historical patterns.
- As industries increasingly embrace data-driven approaches, there are boundless opportunities for professionals skilled in deciphering and interpreting data.
