Types of Linux Operating System
Overview
Linux is an open-source operating system kernel that serves as the foundation for numerous distributions, commonly referred to as Linux distributions or distros. These distributions are essentially different flavors or variations of Linux, each with its own set of features, package management systems, and target audience.
In this article, we will provide an overview of some popular Linux distributions, highlighting their key features, target audience, and use cases. By understanding the characteristics of these distributions, readers will gain insights into the diverse options available and be better equipped to choose a Linux distribution that aligns with their needs and preferences.
Understanding Linux OS Distribution
Linux operating system distributions, also known as Linux distros, are variations of the Linux operating system kernel packaged with additional software, libraries, and configurations. These distributions are created to provide users with different experiences, features, and tools while retaining the core Linux functionality.
One key aspect of understanding Linux OS distribution is recognizing the concept of modularity. Linux distributions are modular in nature, allowing users to choose from a wide array of options in terms of desktop environments, package managers, software repositories, and system configurations. This modular design empowers users to customize their Linux experience according to their specific needs and preferences. You can also check our article on Flavors of Linux.
Top Linux OS Distribution
Here we will discuss the top OS Linux Distribution. Lets's follow.
Ubuntu-based Linux Distributions
Ubuntu, being a widely used and popular Linux distribution, has inspired the creation of numerous Ubuntu-based distributions. These distributions are built upon the Ubuntu core, incorporating its package management system (APT) and software repositories.
Here are some notable Ubuntu-based Linux distributions:
Linux Mint:
Linux Mint is one of the most popular Ubuntu-based distributions. It provides a user-friendly and familiar desktop environment with a focus on simplicity and ease of use. Linux Mint offers multiple desktop flavors, including the Cinnamon, MATE, and Xfce environments.

Zorin OS:
Zorin OS is designed to provide a user-friendly transition for Windows users. It offers a customizable desktop environment with a familiar layout and appearance. Zorin OS includes various pre-installed software, including Wine for running Windows applications.
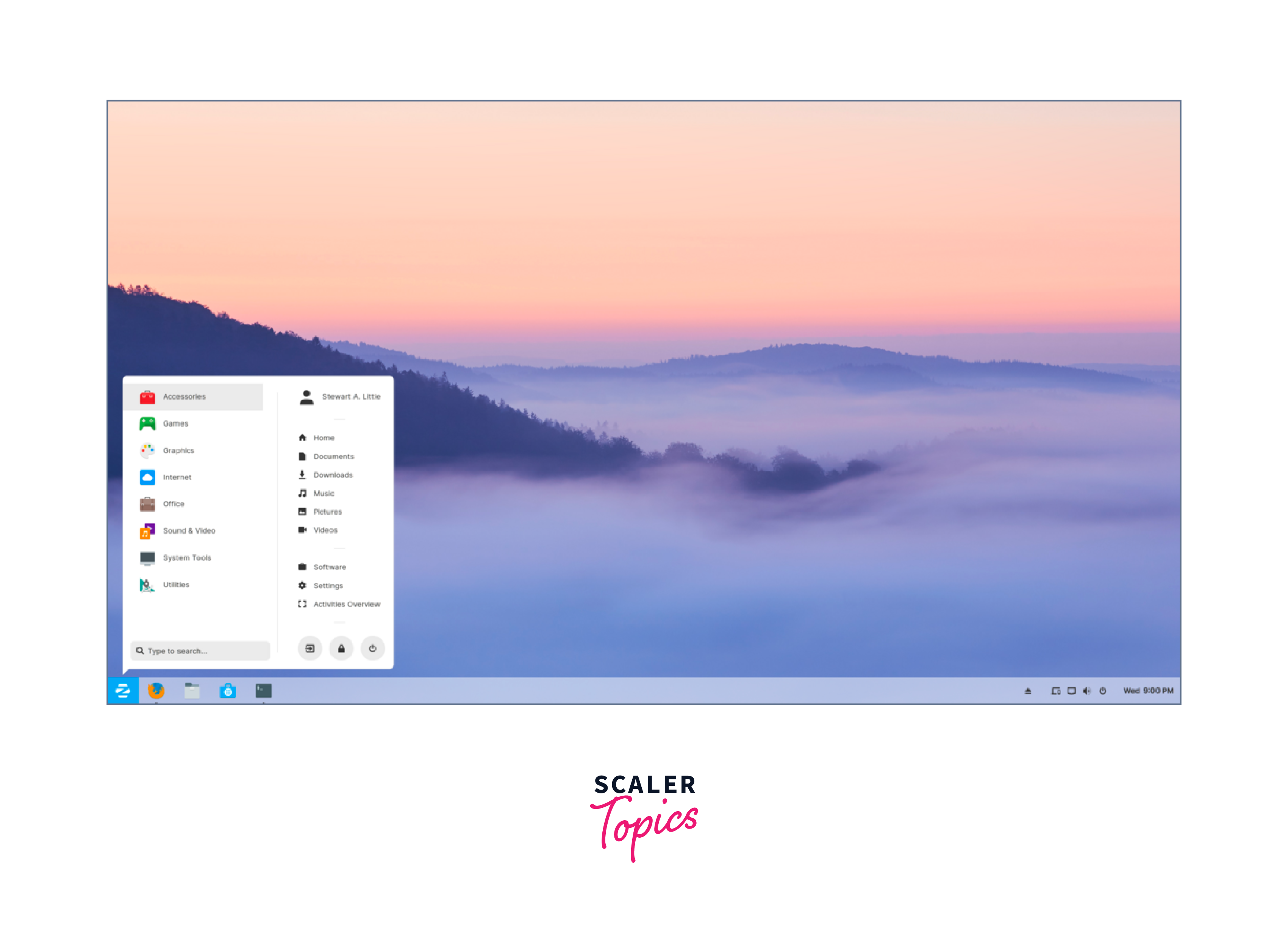
Kubuntu:
Kubuntu is an Ubuntu-based distribution that utilizes the KDE Plasma desktop environment. It provides a feature-rich and customizable desktop experience. Kubuntu combines the stability of Ubuntu with the flexibility and advanced features of KDE Plasma.

Xubuntu:
Xubuntu is a lightweight Ubuntu-based distribution that utilizes the Xfce desktop environment. It offers a balance between resource efficiency and a user-friendly interface. Xubuntu is well-suited for older or low-spec hardware.
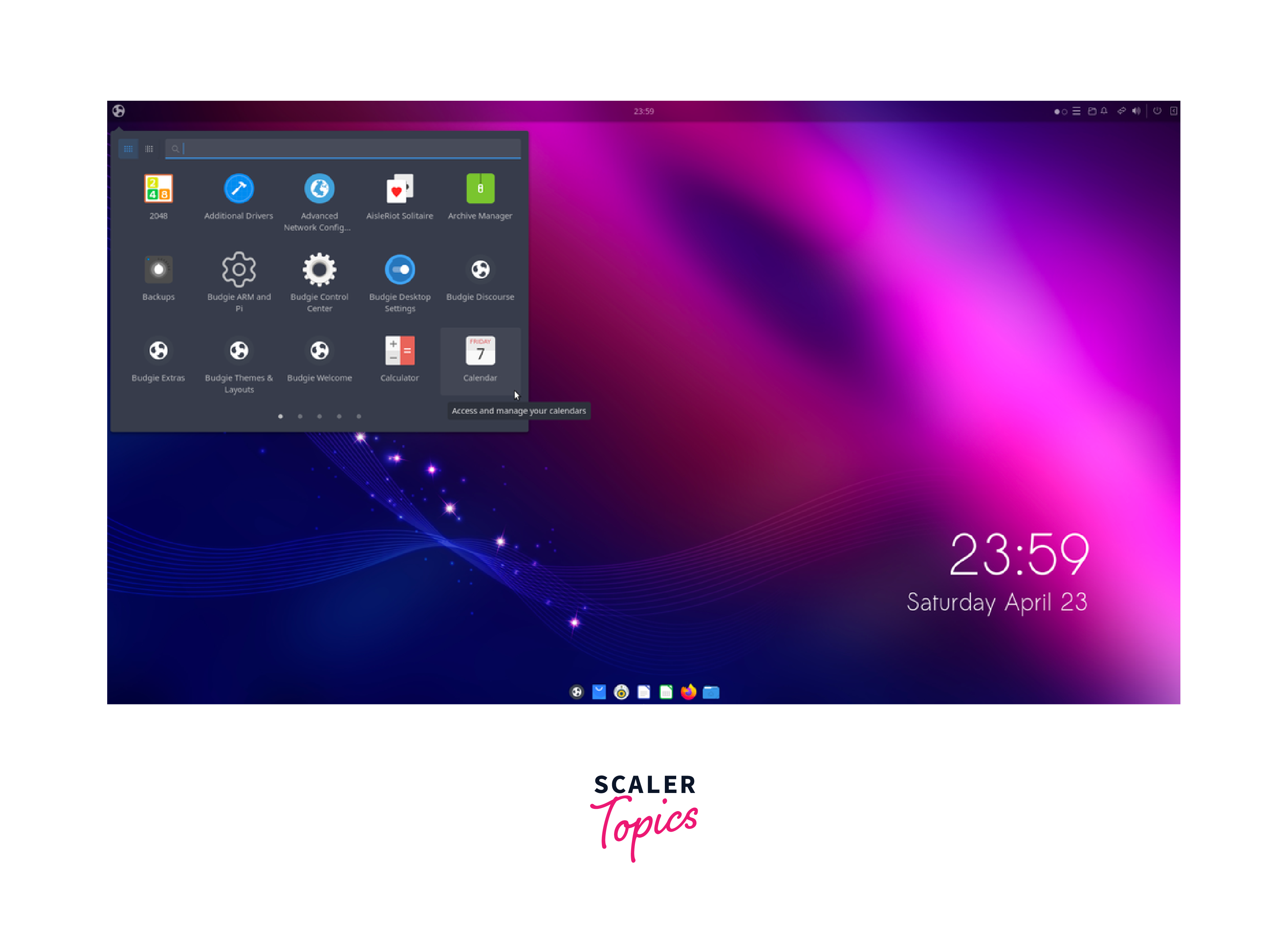
Ubuntu Budgie:
Ubuntu Budgie provides the Budgie desktop environment, known for its simplicity, elegance, and modern design. It offers a clean user interface and integrates well with the Ubuntu ecosystem. Ubuntu Budgie aims to create a productive and visually appealing user experience.
Debian-based Linux Distributions
Debian, known for its stability, adherence to free software principles, and strong community support, serves as the foundation for numerous Debian-based Linux distributions. These distributions inherit the core components of Debian while adding their own unique features and software packages. Here are some notable Debian-based Linux distributions:
Ubuntu:
Ubuntu, one of the most popular Linux distributions, is based on Debian. It builds upon Debian's stability and adds a user-friendly interface, extensive software repositories, and a focus on ease of use. Ubuntu is widely used both on desktops and servers.

MX Linux:
MX Linux focuses on providing a lightweight, efficient, and easy-to-use desktop environment. It incorporates the Xfce desktop environment and includes a wide range of tools and utilities to enhance the user experience. MX Linux prioritizes system performance and stability.

elementary OS:
elementary OS is designed to offer a polished and visually appealing user interface, resembling macOS. It builds upon Ubuntu and adds its own set of custom applications and design elements. elementary OS aims to provide a seamless and intuitive user experience.
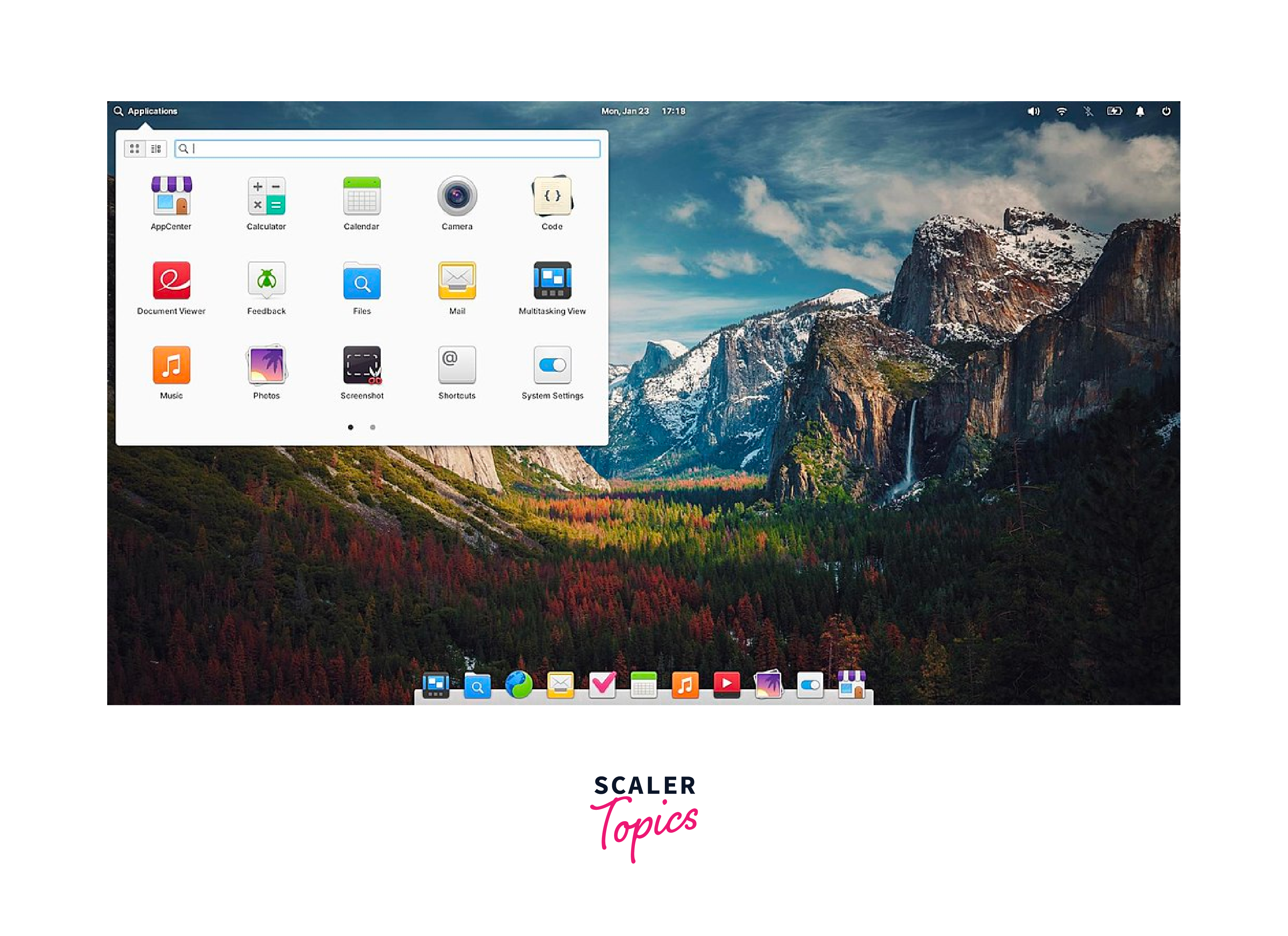
Kali Linux:
Kali Linux is a Debian-based distribution designed for penetration testing, ethical hacking, and cybersecurity. It includes a vast array of pre-installed tools and utilities for security testing and digital forensics. Kali Linux is widely used by security professionals and enthusiasts.
Raspbian:
Raspbian is a Debian-based operating system specifically tailored for the Raspberry Pi single-board computers. It provides an optimized environment for running on Raspberry Pi devices and offers a range of pre-installed software and tools.
Arch-based Linux Distributions
Arch Linux, known for its simplicity, flexibility, and user-centric approach, has inspired the development of several Arch-based Linux distributions. These distributions follow the principles of Arch Linux while providing their own unique features, pre-configured environments, and package management systems.
Here are some notable Arch-based Linux distributions:
Manjaro Linux:
Manjaro Linux is a user-friendly distribution that aims to provide an accessible Arch-based experience. It offers a user-friendly installer, pre-configured desktop environments (such as Xfce, KDE Plasma, and GNOME), and a curated selection of software. Manjaro focuses on providing stability, user-friendliness, and access to the Arch Linux package repositories.

EndeavourOS:
EndeavourOS aims to provide an easy-to-use Arch-based distribution while staying true to the principles of Arch Linux. It offers a lightweight and customizable Xfce desktop environment and a minimalistic installation process. EndeavourOS provides access to the Arch User Repository (AUR) and encourages users to explore and customize their systems.
ArcoLinux:
ArcoLinux is a distribution that aims to teach users about Linux while providing an Arch-based experience. It offers a range of desktop environments, including Xfce, GNOME, and KDE Plasma. ArcoLinux focuses on providing documentation, tutorials, and tools to help users learn and customize their Arch-based systems.
Artix Linux:
Artix Linux is an Arch-based distribution that focuses on providing a lightweight and minimalist environment. It offers multiple desktop environments and allows users to choose between OpenRC and Runit as their init systems instead of the traditional systemd. Artix Linux emphasizes simplicity, speed, and the avoidance of unnecessary dependencies.
ArchBang:
ArchBang is a lightweight Arch-based distribution that utilizes the Openbox window manager. It provides a minimalistic and fast environment, making it suitable for low-spec hardware or users who prefer a lightweight setup. ArchBang aims to provide a simple and efficient Arch Linux experience out of the box.

Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and CentOS
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and CentOS are two notable Linux distributions that share a close relationship. RHEL is a commercially supported distribution, while CentOS is a community-driven, free version of RHEL.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL):
RHEL is a leading enterprise-grade Linux distribution that focuses on stability, security, and long-term support. It offers a robust and reliable platform for mission-critical workloads. RHEL is backed by Red Hat, a renowned software company that provides commercial support, regular updates, and certifications. It is widely used in corporate environments, data centers, and cloud infrastructures.
CentOS:
CentOS (Community Enterprise Operating System) is a free, community-driven distribution that aims to provide a binary-compatible alternative to RHEL. CentOS is built from the same source code as RHEL and strives to maintain compatibility with RHEL packages. It offers the same stability and reliability as RHEL but without the commercial support or additional proprietary software.
Lightweight Linux Distributions
Lightweight Linux distributions are specifically designed to be resource-efficient, requiring minimal hardware specifications while still offering a functional and responsive computing environment. These distributions are ideal for older or low-spec hardware, as well as for users who prefer a lightweight and snappy system.
Here are some notable lightweight Linux distributions:
Lubuntu:
Lubuntu is an official Ubuntu variant that utilizes the lightweight LXQt desktop environment. It aims to provide a fast, energy-efficient, and resource-friendly system without compromising usability or functionality. Lubuntu is suitable for low-spec machines, netbooks, and older hardware.
Puppy Linux:
Puppy Linux is a lightweight distribution that can run entirely in RAM, allowing for fast boot times and responsiveness. It comes in various versions, such as Puppy Linux Slacko and Puppy Linux Bionic, each based on different core distributions. Puppy Linux is known for its small footprint, simplicity, and portability.
Bodhi Linux:
Bodhi Linux is based on Ubuntu and features the lightweight Enlightenment desktop environment. It focuses on minimalism, customization, and ease of use. Bodhi Linux provides a visually appealing interface and allows users to choose the level of system resources utilized.
AntiX:
AntiX is a lightweight distribution that aims to be fast, flexible, and energy-efficient. It utilizes the IceWM window manager and offers a range of customization options. AntiX is known for its low resource requirements and suitability for older hardware.
Peppermint OS:
Peppermint OS is designed to be lightweight, fast, and cloud-centric. It combines the LXQt desktop environment with web-based applications and cloud integration. Peppermint OS aims to provide a lightweight and efficient system for web-centric tasks.
Specialized Linux Distributions
Specialized Linux distributions are tailored to specific use cases, industries, or specialized fields. These distributions often come with pre-installed software, configurations, and tools specifically designed to meet the unique requirements of their intended purpose.
Here are some notable specialized Linux distributions:
Tails:
The Amnesic Incognito Live System, commonly known as Tails, is a privacy-focused Linux distribution. It is designed to preserve privacy and anonymity by routing internet connections through the Tor network. Tails includes built-in cryptographic tools, secure file deletion, and other privacy-enhancing features.
Scientific Linux:
Scientific Linux is an open-source distribution specifically developed for scientific and research purposes. It aims to provide a stable and well-maintained environment for scientific computing, data analysis, and research simulations. Scientific Linux includes various scientific libraries, tools, and applications.

SteamOS:
SteamOS is a Linux-based operating system developed by Valve Corporation for gaming. It is designed to run on living room gaming PCs and serves as a dedicated platform for the Steam gaming ecosystem. SteamOS comes with Steam Big Picture Mode and supports game streaming from other devices.
Ubuntu Studio:
Ubuntu Studio is an official Ubuntu variant focused on multimedia production, including audio, video, graphics, and publishing. It includes a range of software for audio editing, video editing, 3D modeling, graphic design, and more. Ubuntu Studio provides a dedicated environment for creative professionals.

Endless OS:
Endless OS is designed for users with limited internet connectivity, primarily targeting developing regions. It provides an offline-first approach with pre-installed educational content, apps, and tools for learning, entertainment, and productivity. Endless OS aims to bridge the digital divide and improve access to technology.
Check out our article on Desktop Environment in Linux.
Conclusion
- Linux distributions offer a wide range of choices:
The Linux ecosystem provides an extensive selection of distributions catering to various needs and preferences, ensuring users can find a distribution that aligns with their requirements. - Ubuntu-based distributions offer user-friendly experiences:
Ubuntu-based distributions, such as Linux Mint, Zorin OS, and Kubuntu, build upon the stability and usability of Ubuntu, providing user-friendly interfaces and a range of pre-installed software. - Debian-based distributions emphasize stability and free software:
Debian-based distributions, including Ubuntu itself, MX Linux, and Kali Linux, focus on stability, adherence to free software principles, and extensive software repositories. - Arch-based distributions provide flexibility and customization:
Arch-based distributions like Manjaro Linux and EndeavourOS prioritize user control, flexibility, and customization while staying true to the principles of Arch Linux. - Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and CentOS offer enterprise-grade solutions:
RHEL is a commercially supported distribution designed for enterprise environments, while CentOS provides a free, community-supported version of RHEL, both offering stability and reliability. - Lightweight distributions optimize resource usage:
Lightweight distributions like Lubuntu, Puppy Linux, and Xubuntu are specifically designed for low-spec hardware or users seeking fast and efficient systems. - Specialized distributions cater to specific needs:
Specialized distributions like Kali Linux, Tails, and Ubuntu Studio focus on cybersecurity, privacy, scientific research, multimedia production, gaming, and education, providing dedicated environments and pre-configured tools.
