Union and Union All in SQL

Overview
Union and Union All commands in SQL are used to combine two or more data sets. The Union command combines two or more data sets by removing all duplicate records. The Union All command combines two or more data sets by keeping duplicate records.
What is Union in SQL?
The Union in SQL combines two or more result sets by removing all the duplicate records. The Union operator first sorts the result set and removes all duplicate records before returning the combined result set. Each SELECT statement in UNION must have the same number of fields in the result sets with similar data types. The result of the SELECT statement can also be restricted with WHERE clause conditions.
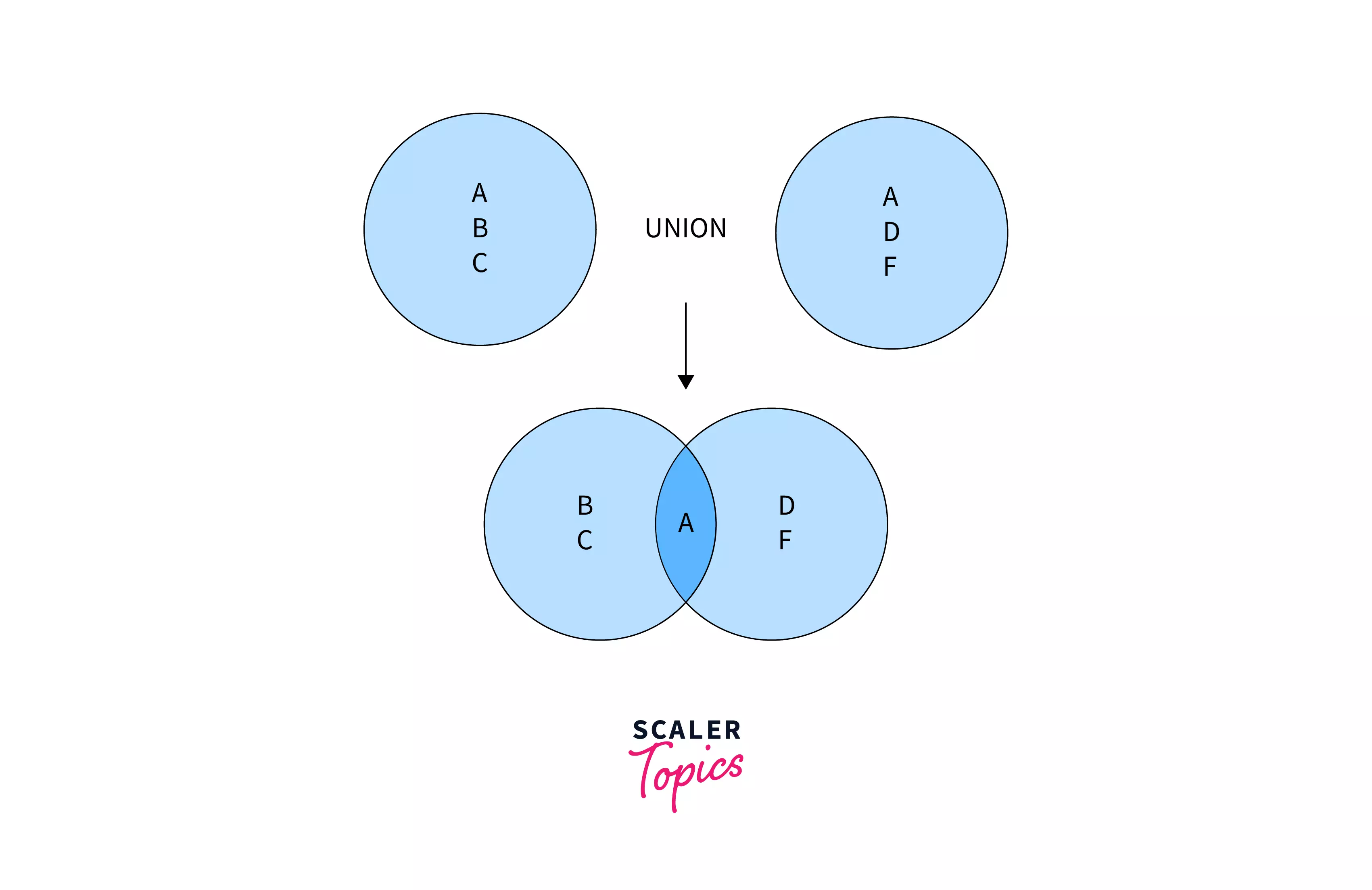
In the above diagram, A is present in both the result sets. The final result after the union of the above two sets is {A, B, C, D, F}. There are a total of two A in both the sets. But the final result has only one A as the Union operation removed the duplicate A from the result.
What is Union All in SQL?
The Union All in SQL combines two or more result sets, and it doesn't remove any duplicate records from the combined result set. The result of the union all operation contains all rows from both the result sets. Each SELECT statement in UNION ALL must have the same number of fields in the result sets with similar data types. The result of the SELECT statement can also be restricted with WHERE clause conditions.
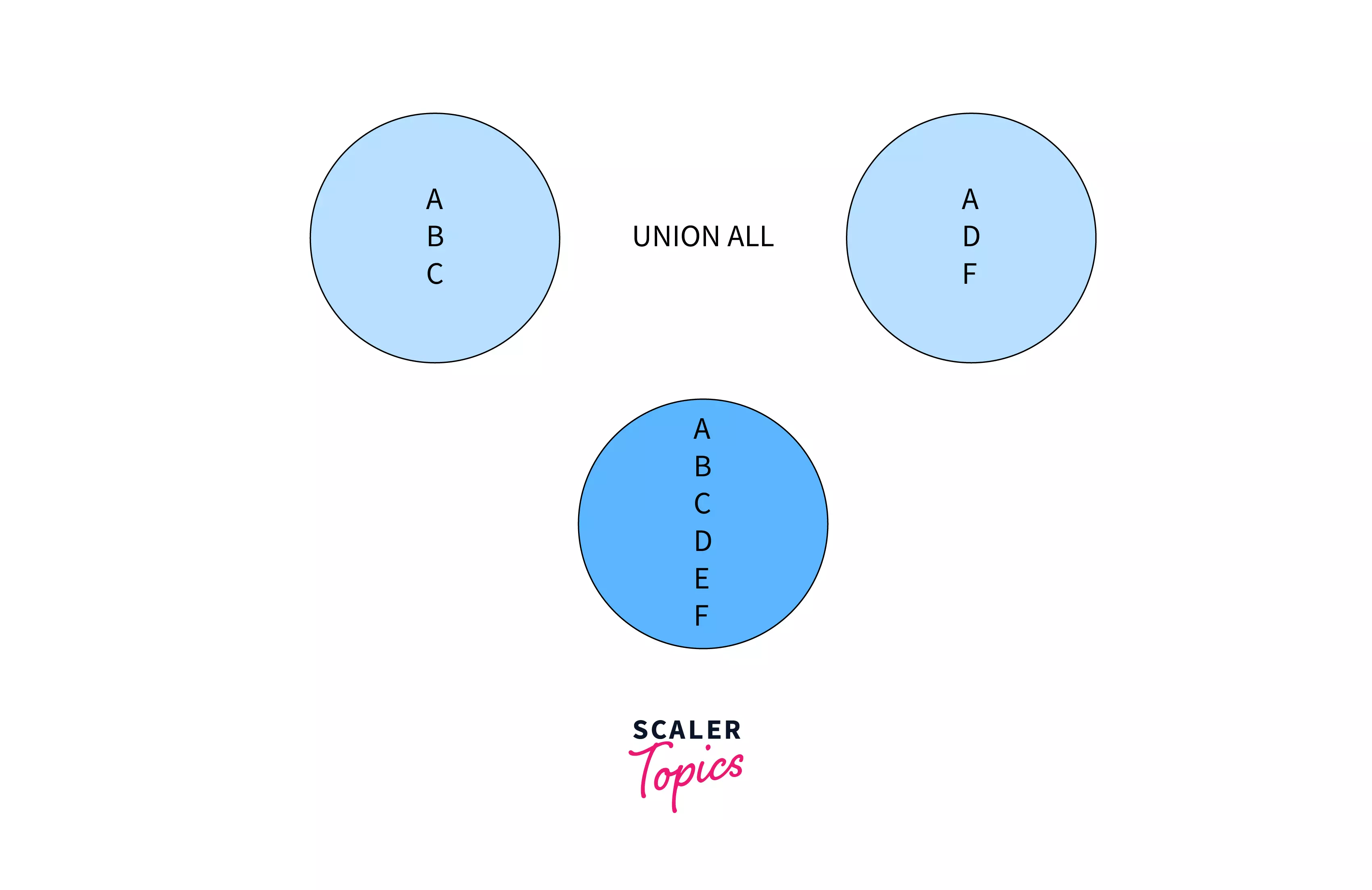
In the above diagram, A is present in both the result sets, and the final result set has two A's as the Union All operator doesn't remove duplicate values.
Syntax of Union in SQL
The UNION operator expects two or more result sets with the same number of fields with similar data types. The syntax of Union in SQL is
The UNION keyword is added between two select statements to combine their results. We can add an optional WHERE condition to filter the result of the SELECT statements.
Syntax of Union All in SQL
The UNION ALL operator expects two or more result sets with the same number of fields with similar data types. The syntax of Union All in SQL is
The UNION ALL keyword is added between two select statements to combine their results. We can add an optional WHERE condition to filter the result of the SELECT statements.
Example of Union in SQL
Let's understand Union in SQL by creating two tables, physics_coaching and maths_coaching, containing the list of students attending physics and maths coaching classes.
First, we create the tables physics_coaching and maths_coaching.
We insert records into the physics_coaching and maths_coaching tables.
The tables after inserting data are: PHYSICS_COACHING
| student_id | student_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Marleen Suggate |
| 2 | Vicki Nelm |
| 3 | Alexine McGregor |
| 4 | Sigvard Jeste |
| 5 | Ardelis Clatworthy |
MATHS_COACHING
| student_id | student_name |
|---|---|
| 5 | Ardelis Clatworthy |
| 6 | Wilton Dermott |
| 7 | Dorena Gravells |
| 8 | Morgen Furze |
| 9 | Alana Amey |
We will use the below Union query to find the list of students attending either physics or maths coaching classes.
Output
The output of the above Union query is
| student_id | student_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Marleen Suggate |
| 2 | Vicki Nelm |
| 3 | Alexine McGregor |
| 4 | Sigvard Jeste |
| 5 | Ardelis Clatworthy |
| 6 | Wilton Dermott |
| 7 | Dorena Gravells |
| 8 | Morgen Furze |
| 9 | Alana Amey |
Explanation
The Union query combines the results of the tables physics_coaching and maths_coaching. Even though the student Ardelis Clatworthy is part of both tables, the result of Union contains only one entry. This is because the Union operator removes the duplicate records.
Example of Union All in SQL
We use the same physics_coaching and maths_coaching tables to understand the Union All operator.
Output
The output of the above query is:
| student_id | student_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Marleen Suggate |
| 2 | Vicki Nelm |
| 3 | Alexine McGregor |
| 4 | Sigvard Jeste |
| 5 | Ardelis Clatworthy |
| 5 | Ardelis Clatworthy |
| 6 | Wilton Dermott |
| 7 | Dorena Gravells |
| 8 | Morgen Furze |
| 9 | Alana Amey |
Explanation:
We can see that the student Ardelis Clatworthy record is present twice in the result set. This is because the Union All operator doesn't remove duplicate records.
Union or Union All: Which Should You Choose?
The decision to use Union or Union All depends on the use case we want.
- If our goal is to combine two or more result sets and we want only distinct records, we can go with Union operator.
- On the other hand, if we don't have a problem with duplicate records, we can go with Union All.
- If we want to run the query faster, we can go with Union All as it is faster than Union because Union takes some extra time to remove duplicate records.
Difference between Union and Union All in SQL
| Union | Union All |
|---|---|
| The Union operator is used to combine two or more result sets by removing duplicate records | The Union All operator is used to combine two or more result sets by retaining duplicate records |
| The Union operator returns distinct records | The Union All operator returns all records |
| The syntax of Union is SELECT columns FROM table1 UNION SELECT columns from table2 | The syntax of Union All is SELECT columns FROM table1 UNION ALL SELECT columns from table2 |
| A query using the Union operator runs slowly because it takes some time to find and remove duplicate records | A query using Union All operator runs fast because it doesn't remove duplicate records |
Conclusion
- The Union and Union All operators in SQL are used to combine two or more result sets.
- The result set of the Union query doesn't have duplicate records, whereas the result set of the Union All query contains duplicate records.
- The Union All operator is faster than the Union operator as the Union operator takes some extra time to find and remove duplicate records.
- We can choose Union All over Union if we want the query to run fast, and the result set can contain duplicate records.
